Novel Insights into the Effects of Genetic Variants on Serum Urate Response to an Acute Fructose Challenge: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
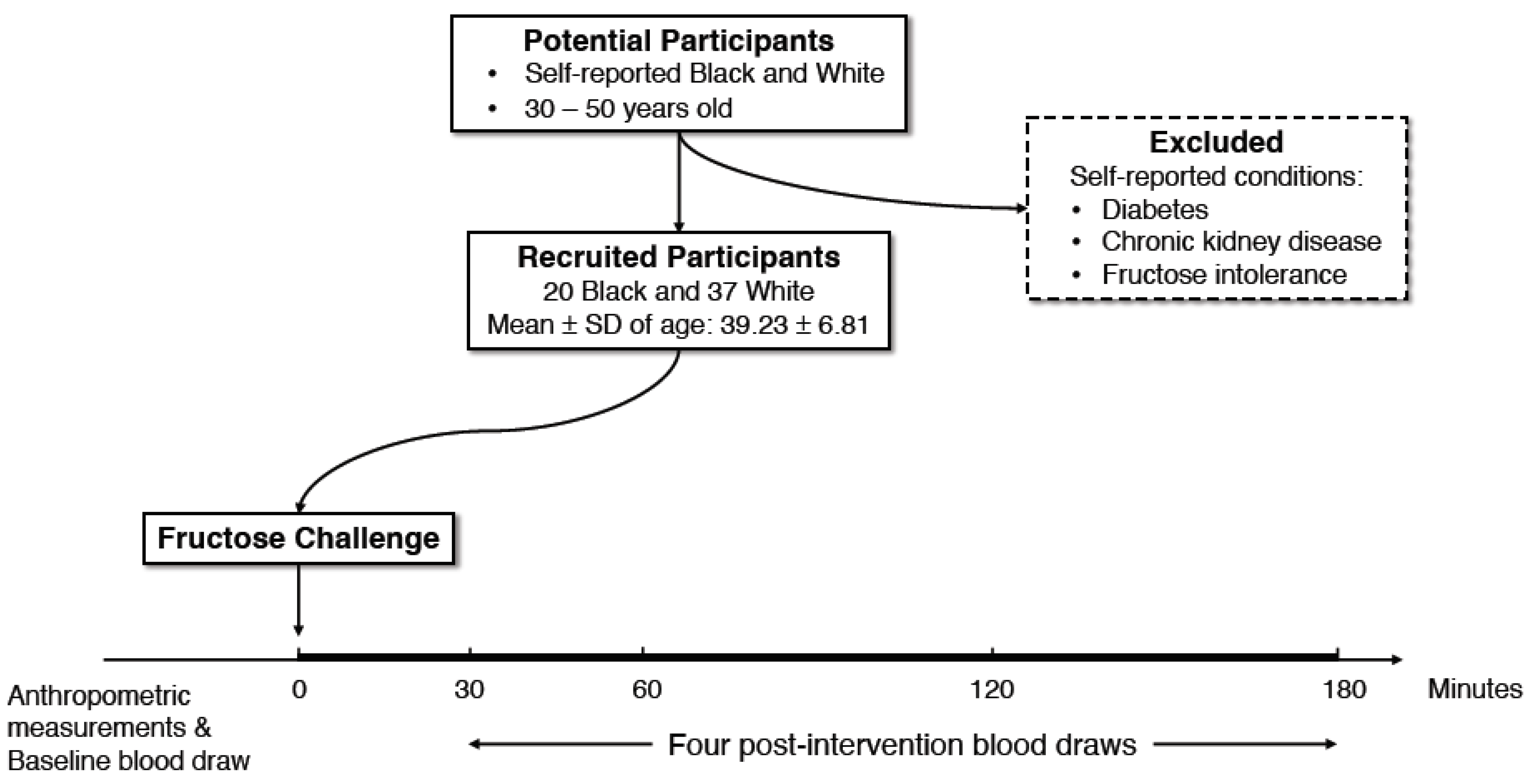
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Blood Processing
2.4. Measurements of Serum Urate
2.5. DNA Extraction, SNP Selection and Genotyping
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Associations between Baseline Serum Urate and SNPs
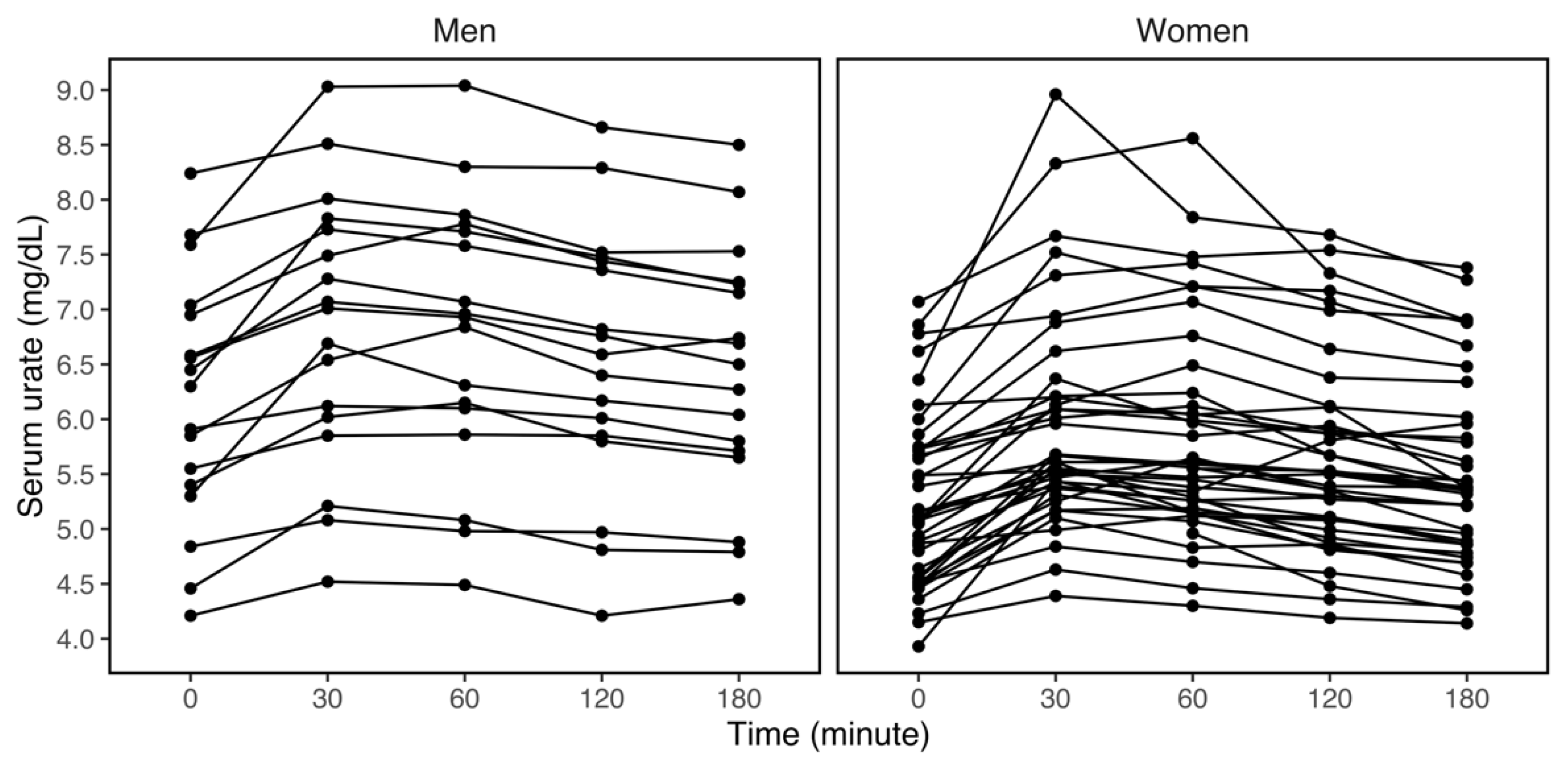
3.2. Variations in Serum Urate within Three Hours of the Fructose Challenge
3.3. Associations between Percent Changes in Serum Urate and SNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keenan, R.T. The Biology of Urate. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, S2–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, V.; Marchese, F.; Capuano, R.; Torre, S.; Iannone, A.G.; Capuano, E.; Lamaida, N.; Sonderegger, M.; Capuano, E. Hyperuricemia as an Independent Risk Factor for Major Cardiovascular Events: A 10-Year Cohort Study from Southern Italy. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 18, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen-Xu, M.; Yokose, C.; Rai, S.K.; Pillinger, M.H.; Choi, H.K. Contemporary Prevalence of Gout and Hyperuricemia in the United States and Decadal Trends: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2016. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.S.; Smith-Taillie, L.P.; Popkin, B.M. Added Sugars Intake Across the Distribution of US Children and Adult Consumers: 1977–2012. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1543–1550.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Tapia, E.; Soto, V.; Sautin, Y.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G. Uric Acid and Fructose: Potential Biological Mechanisms. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, T.; Anderson, G.H. Effects of Glucose-to-Fructose Ratios in Solutions on Subjective Satiety, Food Intake, and Satiety Hormones in Young Men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, C.L.; Stanhope, K.L.; Schwarz, J.M.; Graham, J.L.; Hatcher, B.; Griffen, S.C.; Bremer, A.A.; Berglund, L.; McGahan, J.P.; Keim, N.L.; et al. Consumption of Fructose- but Not Glucose-Sweetened Beverages for 10 Weeks Increases Circulating Concentrations of Uric Acid, Retinol Binding Protein-4, and Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase Activity in Overweight/Obese Humans. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; House, M.E.; Gamble, G.D.; Horne, A.; Pool, B.; Purvis, L.; Stewart, A.; Merriman, M.; Cadzow, M.; Phipps-Green, A.; et al. Population-Specific Influence of SLC2A9 Genotype on the Acute Hyperuricaemic Response to a Fructose Load. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; House, M.E.; Gamble, G.D.; Horne, A.; Purvis, L.; Stewart, A.; Merriman, M.; Cadzow, M.; Phipps-Green, A.; Merriman, T.R. Population-Specific Effects of SLC17A1 Genotype on Serum Urate Concentrations and Renal Excretion of Uric Acid during a Fructose Load. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; House, M.E.; Gamble, G.D.; Pool, B.; Horne, A.; Purvis, L.; Stewart, A.; Merriman, M.; Cadzow, M.; Phipps-Green, A.; et al. Influence of the ABCG2 Gout Risk 141 K Allele on Urate Metabolism during a Fructose Challenge. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanhope, K.L.; Medici, V.; Bremer, A.A.; Lee, V.; Lam, H.D.; Nunez, M.V.; Chen, G.X.; Keim, N.L.; Havel, P.J. A Dose-Response Study of Consuming High-Fructose Corn Syrup-Sweetened Beverages on Lipid/Lipoprotein Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Young Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, J.M.; Maersk, M.; Belza, A.; Astrup, A.; Richelsen, B. Consumption of Sucrose-Sweetened Soft Drinks Increases Plasma Levels of Uric Acid in Overweight and Obese Subjects: A 6-Month Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, C.; Anderstam, B.; Bragfors-Helin, A.-C.; Eriksson, M.; Qureshi, A.R.; Lindholm, B.; Hilding, A.; Wiczkowski, W.; Orsini, N.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Effects of Acute Fructose Loading on Levels of Serum Uric Acid-a Pilot Study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köttgen, A.; Albrecht, E.; Teumer, A.; Vitart, V.; Krumsiek, J.; Hundertmark, C.; Pistis, G.; Ruggiero, D.; O’Seaghdha, C.M.; Haller, T.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analyses Identify 18 New Loci Associated with Serum Urate Concentrations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, A.; Li, Y.; Brody, J.A.; Nutile, T.; Chu, A.Y.; Huffman, J.E.; Yang, Q.; Chen, M.-H.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Macé, A.; et al. Large-Scale Whole-Exome Sequencing Association Studies Identify Rare Functional Variants Influencing Serum Urate Levels. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravich, W.J.; Bayless, T.M.; Thomas, M. Fructose: Incomplete Intestinal Absorption in Humans. Gastroenterology 1983, 84, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.D.; Voruganti, V.S.; Arar, N.H.; Thameem, F.; Lopez-Alvarenga, J.C.; Bauer, R.; Blangero, J.; MacCluer, J.W.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Abboud, H.E. Genome Scan for Determinants of Serum Uric Acid Variability. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 3156–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voruganti, V.S.; Laston, S.; Haack, K.; Mehta, N.R.; Cole, S.A.; Butte, N.F.; Comuzzie, A.G. Serum Uric Acid Concentrations and SLC2A9 Genetic Variation in Hispanic Children: The Viva La Familia Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Abecasis, G.R. METAL: Fast and Efficient Meta-Analysis of Genomewide Association Scans. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2190–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.T.; Gogarten, S.M.; McHugh, C.P.; Stilp, A.M.; Sofer, T.; Bowers, M.L.; Wong, Q.; Cupples, L.A.; Hidalgo, B.; Johnson, A.D.; et al. Recommendations on the Use and Reporting of Race, Ethnicity, and Ancestry in Genetic Research: Experiences from the NHLBI TOPMed Program. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrell, L.N.; Elhawary, J.R.; Fuentes-Afflick, E.; Witonsky, J.; Bhakta, N.; Wu, A.H.B.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Rodríguez-Santana, J.R.; Lenoir, M.A.; Gavin, J.R., 3rd; et al. Race and Genetic Ancestry in Medicine—A Time for Reckoning with Racism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Caliceti, C.; Calabria, D.; Roda, A.; Cicero, A.F.G. Fructose Intake, Serum Uric Acid, and Cardiometabolic Disorders: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; de Souza, R.J.; Chiavaroli, L.; Ha, V.; Cozma, A.I.; Mirrahimi, A.; Yu, M.E.; Carleton, A.J.; Di Buono, M.; et al. The Effects of Fructose Intake on Serum Uric Acid Vary among Controlled Dietary Trials. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.W.; Dumke, K.A.; Goran, M.I. Fructose Content in Popular Beverages Made with and without High-Fructose Corn Syrup. Nutrition 2014, 30, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boocock, J.; Leask, M.; Okada, Y.; Matsuo, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Mount, D.B.; Mandal, A.K.; Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network (AGEN) Consortium; et al. Genomic Dissection of 43 Serum Urate-Associated Loci Provides Multiple Insights into Molecular Mechanisms of Urate Control. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatochi, M.; Kanai, M.; Nakayama, A.; Hishida, A.; Kawamura, Y.; Ichihara, S.; Akiyama, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Furusyo, N.; Shimizu, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Multiple Novel Loci Associated with Serum Uric Acid Levels in Japanese Individuals. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A Cross-Population Atlas of Genetic Associations for 220 Human Phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okegawa, T.; Ushio, K.; Imai, M.; Morimoto, M.; Hara, T. Orphan Nuclear Receptor HNF4G Promotes Bladder Cancer Growth and Invasion through the Regulation of the Hyaluronan Synthase 2 Gene. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ling, D.; Yang, Z. Expression of HNF4G and Its Potential Functions in Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18018–18028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestin, K.; Wolf, S.; Feldtmann, R.; Hussner, J.; Geissler, I.; Rimmbach, C.; Kroemer, H.K.; Zimmermann, U.; zu Schwabedissen, H.E.M. Transcriptional Regulation of Urate Transportosome Member SLC2A9 by Nuclear Receptor HNF4α. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F1041–F1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tin, A.; Marten, J.; Halperin Kuhns, V.L.; Li, Y.; Wuttke, M.; Kirsten, H.; Sieber, K.B.; Qiu, C.; Gorski, M.; Yu, Z.; et al. Target Genes, Variants, Tissues and Transcriptional Pathways Influencing Human Serum Urate Levels. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1459–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-D.; Chen, X.-C.; Pan, S.; Yang, Y.-N.; He, C.-H.; Liu, F.; Ma, X.; Gai, M.-T.; Ma, Y.-T. TT Genotype of Rs2941484 in the Human HNF4G Gene Is Associated with Hyperuricemia in Chinese Han Men. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26918–26926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dong, Z.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yang, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Ji, H.; et al. Effects of Multiple Genetic Loci on the Pathogenesis from Serum Urate to Gout. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.P.; Brennecke, S.P.; East, C.E.; Göring, H.H.H.; Kent, J.W., Jr.; Dyer, T.D.; Said, J.M.; Roten, L.T.; Iversen, A.-C.; Abraham, L.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan Identifies a Risk Locus for Preeclampsia on 2q14, near the Inhibin, Beta B Gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada-Niño, L.; Castillo-León, L.F.; Morel, A. Preeclampsia, Natural History, Genes, and MiRNAs Associated with the Syndrome. J. Pregnancy 2022, 2022, 3851225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps-Green, A.J.; Merriman, M.E.; Topless, R.; Altaf, S.; Montgomery, G.W.; Franklin, C.; Jones, G.T.; van Rij, A.M.; White, D.; Stamp, L.K.; et al. Twenty-Eight Loci That Influence Serum Urate Levels: Analysis of Association with Gout. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leask, M.; Dowdle, A.; Salvesen, H.; Topless, R.; Fadason, T.; Wei, W.; Schierding, W.; Marsman, J.; Antony, J.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; et al. Functional Urate-Associated Genetic Variants Influence Expression of LincRNAs LINC01229 and MAFTRR. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total | Men | Women | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 57 | 17 | 40 | |
| Age, years | 39.23 (6.81) | 38.71 (8.37) | 39.45 (6.14) | 0.74 |
| Weight, kg | 84.56 (21.66) | 90.77 (16.51) | 81.92 (23.19) | 0.11 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29.78 (7.50) | 28.97 (5.05) | 30.12 (8.36) | 0.53 |
| PBF, % | 34.65 (10.59) | 25.51 (8.22) | 38.53 (9.02) | <0.0001 |
| WC, cm | 97.02 (17.75) | 100.03 (13.27) | 95.74 (19.35) | 0.34 |
| WHtR | 0.58 (0.11) | 0.57 (0.08) | 0.58 (0.12) | 0.59 |
| SBP, mmHg | 115.91 (14.12) | 123.06 (11.01) | 112.88 (14.31) | 0.01 |
| DBP, mmHg | 74.57 (11.51) | 75.35 (12.93) | 74.24 (11.01) | 0.76 |
| Serum urate, mg/dL | 5.52 (0.99) | 6.17 (1.14) | 5.24 (0.79) | 0.01 |
| Groups | Subgroups | N | Time (minute) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | 120 | 180 | |||
| Race | Black | 20 | 5.37 (0.96) | 5.80 (1.06) | 5.69 (1.05) | 5.54 (1.04) | 5.42 (1.02) |
| White | 37 | 5.60 (1.01) | 6.44 (1.13) | 6.34 (1.11) | 6.12 (1.03) | 5.93 (1.02) | |
| Sex | Men | 17 | 6.17 (1.14) | 6.82 (1.25) | 6.77 (1.24) | 6.54 (1.21) | 6.42 (1.15) |
| Women | 40 | 5.24 (0.79) | 5.95 (0.99) | 5.84 (0.96) | 5.65 (0.88) | 5.47 (0.85) | |
| BMI | Normal | 18 | 5.34 (0.80) | 6.21 (1.05) | 6.12 (1.02) | 5.84 (0.86) | 5.65 (0.81) |
| Overweight | 14 | 5.42 (1.06) | 6.16 (1.30) | 6.08 (1.29) | 5.82 (1.24) | 5.69 (1.21) | |
| Obese | 25 | 5.69 (1.08) | 6.25 (1.16) | 6.12 (1.15) | 6.02 (1.12) | 5.88 (1.10) | |
| Nearest Gene | SNP | Allele | Black (N = 20) | White (N = 37) | Meta-Analysis | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Other | EAF | Beta | SE | p | EAF | Beta | SE | p | EAF | Beta | SE | p | ||||
| ABCG2 | rs2231142 | T | G | 0.00 | n.a | n.a | n.a | 8.11 | −0.01 | 0.36 | 0.98 | 5.36 | −0.01 | 0.36 | 0.98 | ||
| SLC2A9 | rs16890979 | T | C | 52.50 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 17.57 | −0.34 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 29.82 | −0.15 | 0.19 | 0.43 | ||
| SLC17A1 | rs1183201 | A | T | 7.50 | 0.31 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 41.89 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.56 | 29.82 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.47 | ||
| SLC2A9 | rs737267 | T | G | 52.63 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 20.27 | −0.40 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 31.25 | −0.15 | 0.19 | 0.42 | ||
| SLC2A9 | rs6449213 | C | T | 26.32 | −0.20 | 0.37 | 0.61 | 14.86 | −0.22 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 18.75 | −0.21 | 0.21 | 0.32 | ||
| SLC2A9 | rs3775948 | C | G | 39.47 | −0.32 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 18.92 | −0.32 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 25.89 | −0.32 | 0.18 | 0.08 | ||
| TRIM46 | rs11264341 | T | C | 23.68 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 48.65 | −0.08 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 40.18 | −0.06 | 0.17 | 0.74 | ||
| INHBB | rs17050272 | A | G | 10.53 | −0.52 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 51.35 | −0.10 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 37.50 | −0.19 | 0.19 | 0.32 | ||
| ORC4 | rs2307394 | G | A | 23.68 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.66 | 29.73 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.78 | 27.68 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.65 | ||
| LRRC16A | rs9358856 | A | G | 10.53 | −0.27 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 14.86 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.61 | 13.39 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.82 | ||
| SLC17A3 | rs2762353 | T | C | 5.26 | 0.53 | 0.72 | 0.48 | 40.54 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 28.57 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.40 | ||
| SLC17A1 | rs1165151 | A | C | 7.89 | 0.33 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 41.89 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.56 | 30.36 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.47 | ||
| SLC22A7 | rs4149178 | G | A | 31.58 | −0.12 | 0.30 | 0.69 | 14.86 | −0.02 | 0.26 | 0.93 | 20.54 | −0.07 | 0.20 | 0.74 | ||
| BAZ1B | rs1178977 | G | A | 21.05 | −0.38 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 6.76 | −0.29 | 0.39 | 0.46 | 11.61 | −0.34 | 0.27 | 0.21 | ||
| PRKAG2 | rs10480300 | T | C | 36.84 | −0.09 | 0.31 | 0.77 | 17.57 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 24.11 | −0.04 | 0.21 | 0.85 | ||
| MBOAT4 | rs7813902 | T | C | 21.05 | −0.29 | 0.37 | 0.46 | 2.70 | 0.32 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 8.93 | −0.11 | 0.32 | 0.73 | ||
| HNF4G | rs2941484 | C | T | 15.79 | −0.55 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 47.30 | −0.59 | 0.16 | 9.10 × 10−4 | 36.61 | −0.59 | 0.15 | 1.37 × 10−4 ** | ||
| A1CF | rs10821905 | A | G | 31.58 | 0.08 | 0.34 | 0.82 | 16.22 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 21.43 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.28 | ||
| SLC16A9 | rs12356193 | G | A | 7.89 | −0.10 | 0.62 | 0.88 | 20.27 | −0.10 | 0.22 | 0.67 | 16.07 | −0.10 | 0.21 | 0.65 | ||
| SLC16A9 | rs1171614 | A | G | 23.68 | −0.27 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 25.68 | −0.08 | 0.22 | 0.72 | 25.00 | −0.12 | 0.20 | 0.55 | ||
| NRXN2 | rs478607 | G | A | 55.26 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 20.27 | −0.18 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 32.14 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.66 | ||
| RERG | rs11056399 | T | C | 47.37 | −0.17 | 0.27 | 0.53 | 36.49 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 40.18 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.97 | ||
| ACVR1B/ACVRL1 | rs7976059 | T | G | 18.42 | −0.19 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 39.19 | −0.08 | 0.19 | 0.68 | 32.14 | −0.10 | 0.17 | 0.55 | ||
| INHBC | rs3741414 | A | G | 13.16 | −0.10 | 0.51 | 0.85 | 22.97 | −0.13 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 19.64 | −0.12 | 0.18 | 0.49 | ||
| B3GNT4 | rs7953704 | A | G | 36.84 | −0.03 | 0.51 | 0.95 | 48.65 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.47 | 44.64 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.51 | ||
| IGF1R | rs6598541 | A | G | 57.89 | −0.09 | 0.34 | 0.78 | 24.32 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.91 | 35.71 | −0.01 | 0.18 | 0.96 | ||
| UMOD | rs4293393 | C | T | 15.79 | 0.29 | 0.39 | 0.46 | 25.68 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.97 | 22.32 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.72 | ||
| HLF | rs7224610 | C | A | 0.00 | n.a | n.a | n.a | 32.43 | −0.07 | 0.20 | 0.74 | 21.43 | −0.07 | 0.20 | 0.74 | ||
| QRICH2 | rs164009 | G | A | 78.95 | −0.46 | 0.44 | 0.31 | 28.38 | −0.18 | 0.21 | 0.38 | 45.54 | −0.23 | 0.19 | 0.21 | ||
| INSR | rs1035942 | T | C | 34.21 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 32.43 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 33.04 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.38 | ||
| Nearest Gene | SNP | Allele | Time Period (minute) | Black (N = 20) | White (N = 37) | Meta-Analysis | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Other | EAF | Beta | SE | p | EAF | Beta | SE | p | EAF | Beta | SE | p | |||||
| SLC2A9 | rs3775948 | C | G | 0–30 | 39.47 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 18.92 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 25.89 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.89 | ||
| INHBB | rs17050272 | A | G | 10.53 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 51.35 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 37.50 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.83 | |||
| ORC4 | rs2307394 | G | A | 23.68 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.83 | 29.73 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 27.68 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.77 | |||
| BAZ1B | rs1178977 | G | A | 21.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 6.76 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 11.61 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.16 | |||
| PRKAG2 | rs10480300 | T | C | 36.84 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.74 | 17.57 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 24.11 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.76 | |||
| SLC16A9 | rs1171614 | A | G | 23.68 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 25.68 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 25.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.16 | |||
| ACVR1B/ACVRL1 | rs7976059 | T | G | 18.42 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 39.19 | −0.06 | 0.02 | 3.29 × 10−4 | 32.14 | −0.04 | 0.01 | 1.07 × 10−3 ** | |||
| INSR | rs1035942 | T | C | 34.21 | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 32.43 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 33.04 | −0.03 | 0.01 | 0.05 | |||
| SLC2A9 | rs3775948 | C | G | 30–60 | 39.47 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.76 | 18.92 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 25.89 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.84 | ||
| INHBB | rs17050272 | A | G | 10.53 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 51.35 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 37.50 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.89 | |||
| ORC4 | rs2307394 | G | A | 23.68 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 29.73 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 1.72 × 10−3 | 27.68 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 * | |||
| BAZ1B | rs1178977 | G | A | 21.05 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 6.76 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 11.61 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 * | |||
| PRKAG2 | rs10480300 | T | C | 36.84 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 17.57 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.38 | 24.11 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 * | |||
| SLC16A9 | rs1171614 | A | G | 23.68 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 25.68 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 25.00 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 * | |||
| ACVR1B/ACVRL1 | rs7976059 | T | G | 18.42 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 39.19 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 32.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.18 | |||
| INSR | rs1035942 | T | C | 34.21 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 32.43 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 33.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 * | |||
| SLC2A9 | rs3775948 | C | G | 60–120 | 39.47 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 18.92 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 25.89 | −0.01 | 0.00 | 1.73 × 10−3 * | ||
| INHBB | rs17050272 | A | G | 10.53 | −0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 51.35 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 37.50 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 5.92 × 10−5 ** | |||
| ORC4 | rs2307394 | G | A | 23.68 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 29.73 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 27.68 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.29 | |||
| BAZ1B | rs1178977 | G | A | 21.05 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.73 | 6.76 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 11.61 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.80 | |||
| PRKAG2 | rs10480300 | T | C | 36.84 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 17.57 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 24.11 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.64 | |||
| SLC16A9 | rs1171614 | A | G | 23.68 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 25.68 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.66 | 25.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.32 | |||
| ACVR1B/ACVRL1 | rs7976059 | T | G | 18.42 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.73 | 39.19 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.79 | 32.14 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.66 | |||
| INSR | rs1035942 | T | C | 34.21 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 32.43 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 33.04 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.48 | |||
| SLC2A9 | rs3775948 | C | G | 120–180 | 39.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 18.92 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 25.89 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.90 | ||
| INHBB | rs17050272 | A | G | 10.53 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 51.35 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.34 | 37.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.93 | |||
| ORC4 | rs2307394 | G | A | 23.68 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 29.73 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 27.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | |||
| BAZ1B | rs1178977 | G | A | 21.05 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 6.76 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.84 | 11.61 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.15 | |||
| PRKAG2 | rs10480300 | T | C | 36.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 17.57 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 24.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.95 | |||
| SLC16A9 | rs1171614 | A | G | 23.68 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 25.68 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 25.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | |||
| ACVR1B/ACVRL1 | rs7976059 | T | G | 18.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.96 | 39.19 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 32.14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.21 | |||
| INSR | rs1035942 | T | C | 34.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.81 | 32.43 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.34 | 33.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.62 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Mass, B.B.; Talevi, V.; Hou, R.; North, K.E.; Voruganti, V.S. Novel Insights into the Effects of Genetic Variants on Serum Urate Response to an Acute Fructose Challenge: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194030
Zhang X, Mass BB, Talevi V, Hou R, North KE, Voruganti VS. Novel Insights into the Effects of Genetic Variants on Serum Urate Response to an Acute Fructose Challenge: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194030
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinruo, Baba B. Mass, Valentina Talevi, Ruixue Hou, Kari E. North, and Venkata Saroja Voruganti. 2022. "Novel Insights into the Effects of Genetic Variants on Serum Urate Response to an Acute Fructose Challenge: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194030
APA StyleZhang, X., Mass, B. B., Talevi, V., Hou, R., North, K. E., & Voruganti, V. S. (2022). Novel Insights into the Effects of Genetic Variants on Serum Urate Response to an Acute Fructose Challenge: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 14(19), 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194030







