Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
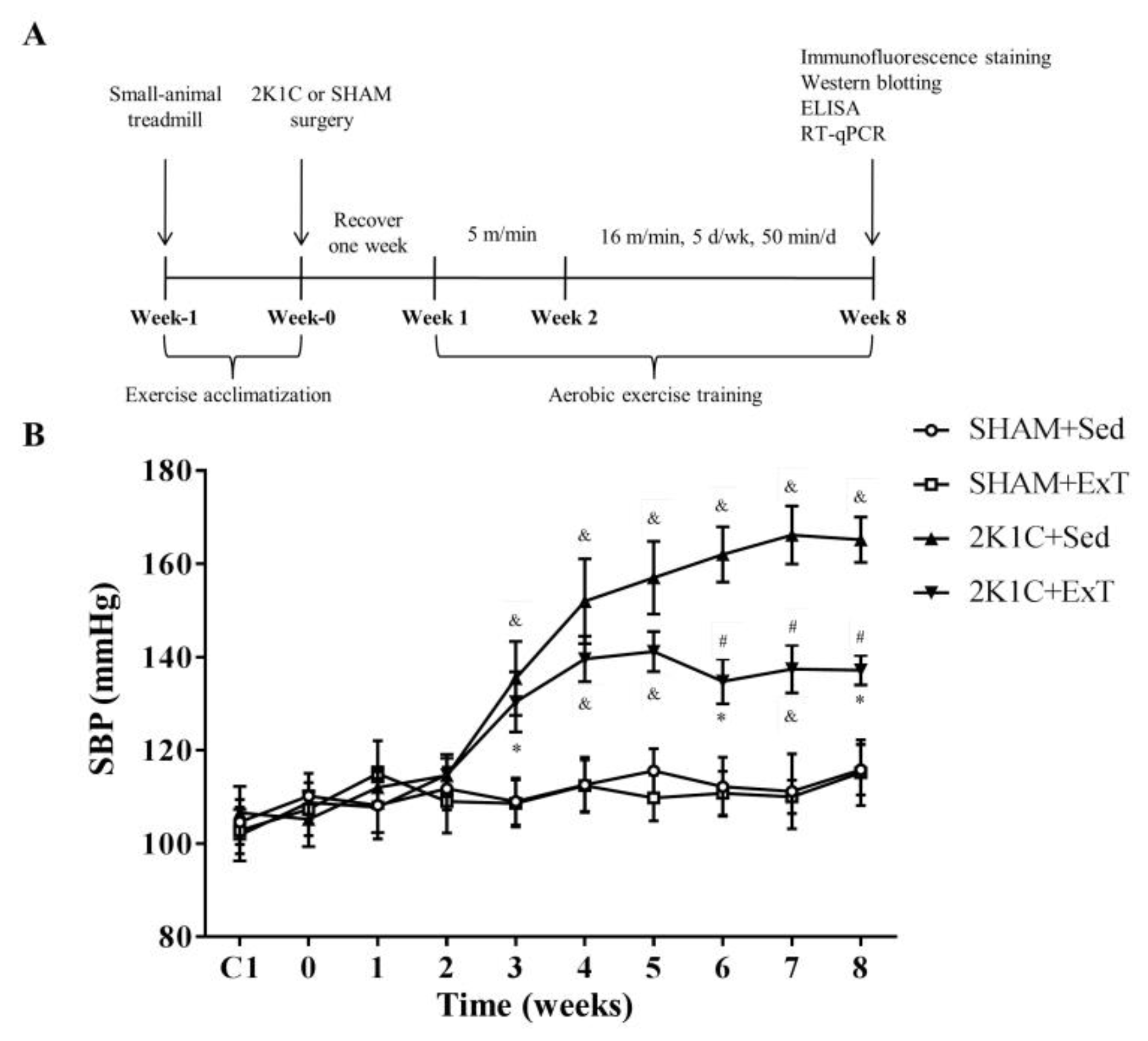
2.2. Exercise Training Protocols
2.3. Recording of Blood Pressure
2.4. Renal Sympathetic Nerve Recordings
2.5. Collection of Brain Tissue Samples and Blood
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. ELISA Studies
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Pressure
3.2. Renal Sympathetic Nerve Activity
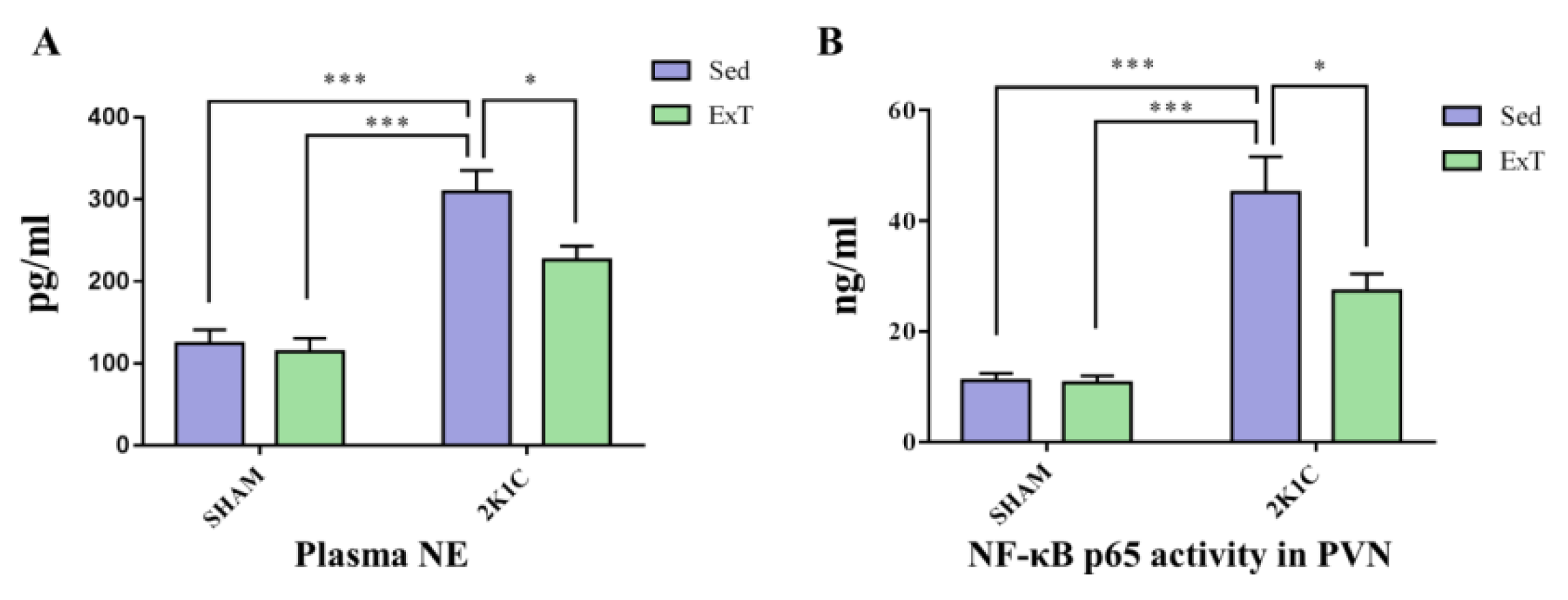
3.3. Plasma NE
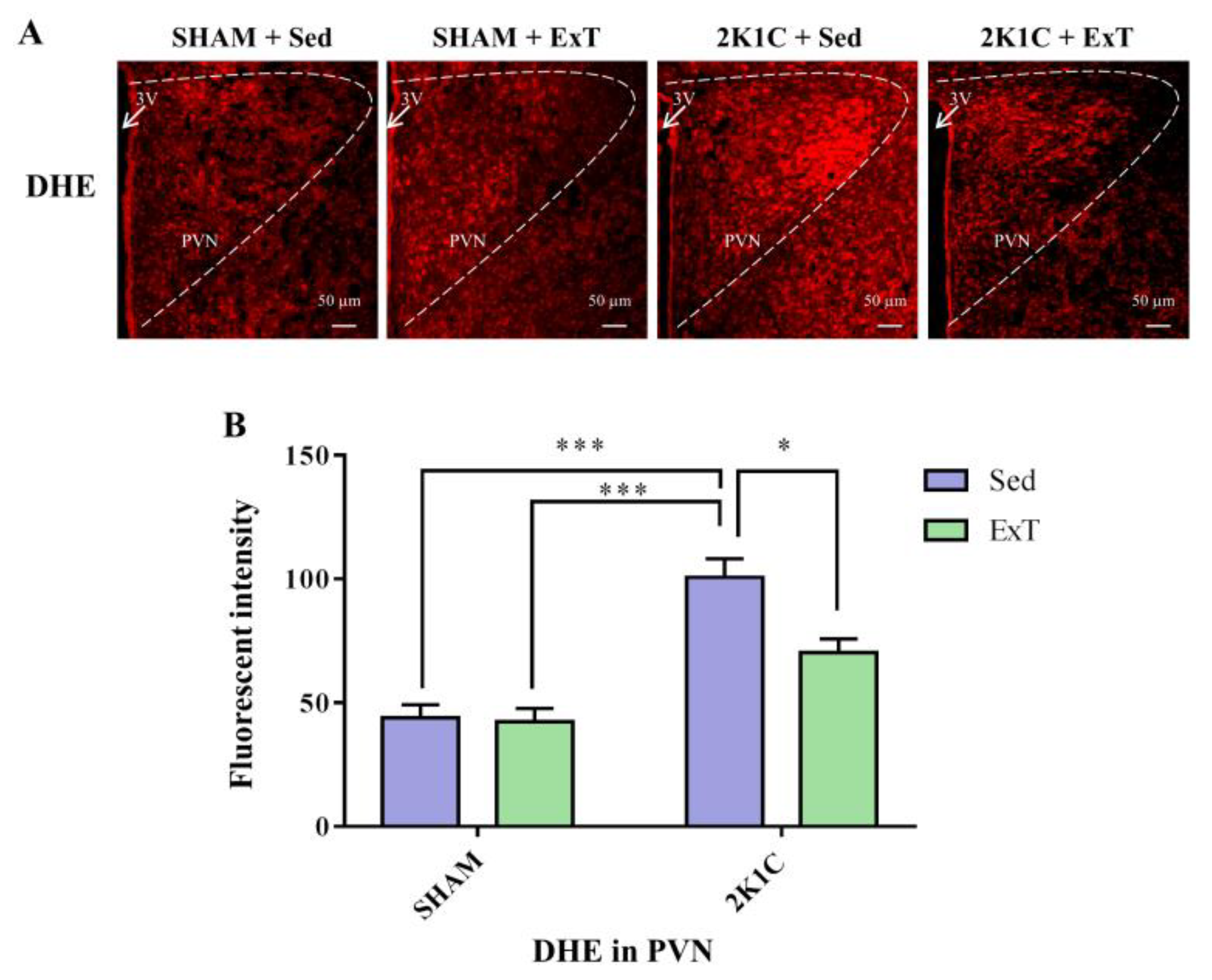
3.4. DHE Expression in the PVN
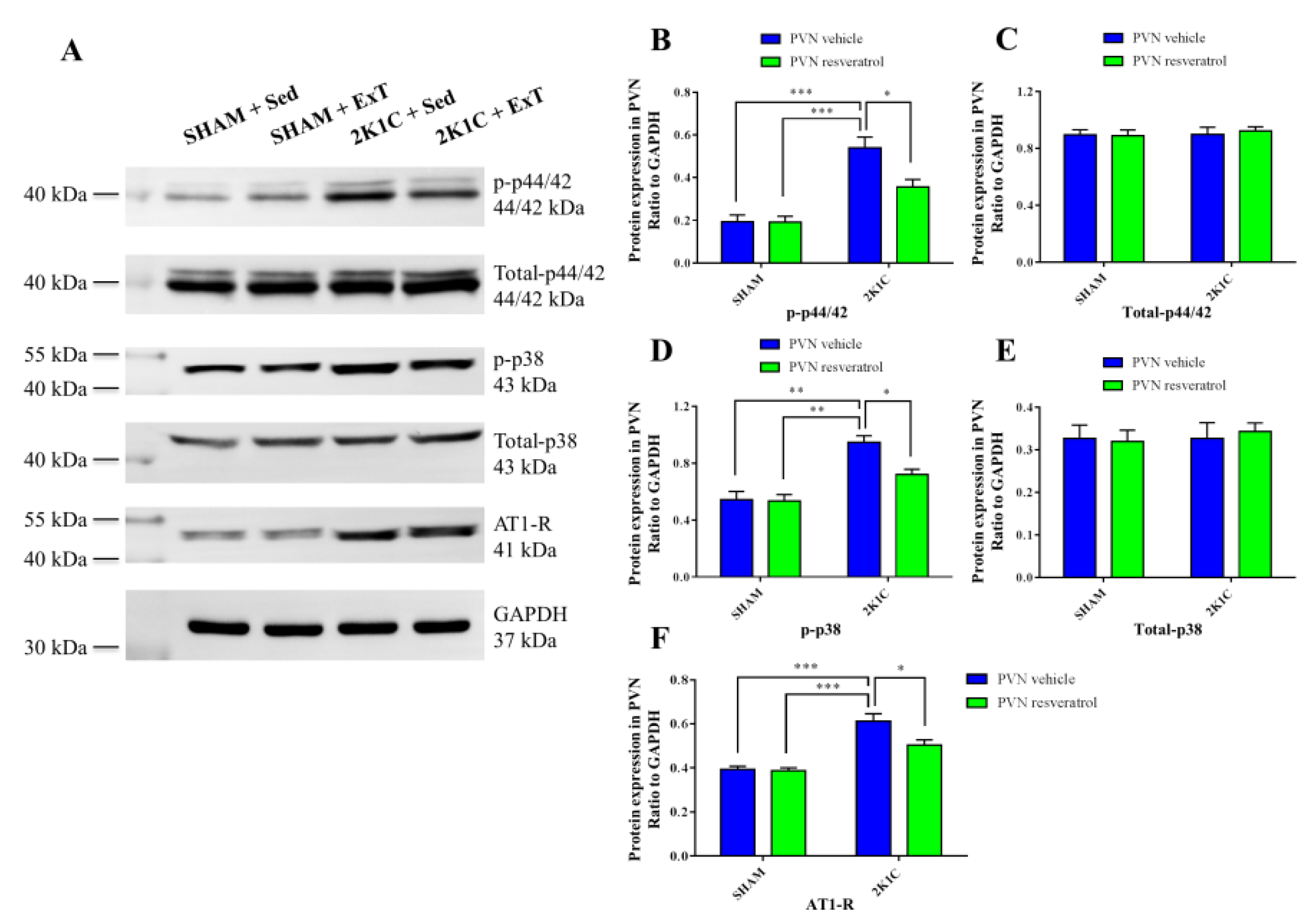
3.5. P-p44/42 MAPK Expression in the PVN
3.6. P-p38 MAPK Expression in the PVN
3.7. NF-κB Activity in the PVN
3.8. AT-1R Expression in the PVN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyenet, P.G.; Stornetta, R.L.; Souza, G.; Abbott, S.B.G.; Brooks, V.L. Neuronal Networks in Hypertension: Recent Advances. Hypertension 2020, 76, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsurada, K.; Ogoyama, Y.; Imai, Y.; Patel, K.P.; Kario, K. Renal denervation based on experimental rationale. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Schlaich, M.P.; Lobo, M.D. Device Therapy of Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1080–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, L.; Azizi, M.; Kirtane, A.J.; Bohm, M.; Mahfoud, F. Device-based therapies for arterial hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.Z.; Du, X.L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Zhu, G.Q.; et al. Impact of Selective Renal Afferent Denervation on Oxidative Stress and Vascular Remodeling in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyner, S. The heart is lost without the hypothalamus. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 182, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.R.; Bardgett, J.F.; Wolfgang, L.; Stocker, S.D. Sympathetic response to insulin is mediated by melanocortin 3/4 receptors in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Hypertension 2011, 57, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, A.D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. Chemical Stimulation of Renal Tissue Induces Sympathetic Activation and a Pressor Response via the Paraventricular Nucleus in Rats. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.L.; Barzel, B.; Jackson, K.L.; Gueguen, C.; Young, M.J.; Head, G.A. Role of Mineralocorticoid and Angiotensin Type 1 Receptors in the Paraventricular Nucleus in Angiotensin-Induced Hypertension. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 640373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghlam, D.; Jozwiak, M.; Nguyen, L.S. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Immunomodulation: A State-of-the-Art Review. Cells 2021, 10, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, Y.; Johnson, A.K. Interactions of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin-System (RAS) and Inflammation in the Sensitization of Hypertension. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi-Coelho, C.; Costa-Ferreira, W.; Reis-Silva, L.L.; Crestani, C.C. Angiotensinergic Neurotransmissions in the Medial Amygdala Nucleus Modulate Behavioral Changes in the Forced Swimming Test Evoked by Acute Restraint Stress in Rats. Cells 2021, 10, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minczuk, K.; Schlicker, E.; Malinowska, B. Cross-Talk between CB1, AT1, AT2 and Mas Receptors Responsible for Blood Pressure Control in the Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus in Conscious Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats and Their Normotensive Controls. Cells 2022, 11, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Yu, X.J.; Liu, K.L.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Fu, L.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhang, D.D.; Shi, X.L.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Chronic Infusion of Astaxanthin Into Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Modulates Cytokines and Attenuates the Renin-Angiotensin System in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.M.; Nandi, S.S.; Zheng, H.; Mishra, P.K.; Patel, K.P. A novel role for miR-133a in centrally mediated activation of the renin-angiotensin system in congestive heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H968–H979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, D.M.; Suo, Y.P.; Song, X.A.; Yu, X.J.; Elks, C.; Lin, Y.X.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zang, W.J.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system modulates neurotransmitters in the paraventricular nucleus and contributes to angiotensin II-induced hypertensive response. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2013, 13, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, A.; Leenen, F.H. Cardiovascular effects of angiotensin II and glutamate in the PVN of Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1447, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.J.; Chen, W.S.; Gao, H.L.; Liu, K.L.; Shi, X.L.; Fan, X.Y.; Jia, L.L.; Cui, W.; Zhu, G.Q.; et al. Exercise training attenuates renovascular hypertension partly via RAS- ROS- glutamate pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Xin, G.R.; Liu, K.L.; Liu, X.J.; Fu, L.Y.; Qi, J.; Kang, K.B.; Meng, T.T.; Yi, Q.Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Paraventricular Nucleus Infusion of Oligomeric Proantho Cyanidins Improves Renovascular Hypertension. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Kang, Y.; Dai, H.B.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Q.; Xiong, X.Q.; Zhang, F.; Song, T.R.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Adipose afferent reflex is enhanced by TNFalpha in paraventricular nucleus through NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation in obesity-related hypertensive rats. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Yu, X.J.; Wang, X.M.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.; Bai, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, N.; Liu, K.L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Bilateral Paraventricular Nucleus Upregulation of Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase Decreases Blood Pressure by Regulation of the NLRP3 and Neurotransmitters in Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 756671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Ding, L.; Dai, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, T.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendra, E.; Riabov, V.; Mossel, D.M.; Sevastyanova, T.; Harmsen, M.C.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophage activation and function in diabetes. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Weiss, R.M.; Felder, R.B. Angiotensin II-triggered p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates sympathetic excitation in heart failure rats. Hypertension 2008, 52, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.G.; Yu, Y.; Weiss, R.M.; Felder, R.B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress increases brain MAPK signaling, inflammation and renin-angiotensin system activity and sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, H871–H880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-kappaB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.X.; Shi, X.C.; Chen, T.; Tan, Z.N.; Lin, Q.Q.; Du, S.J.; Tian, Z.J. Exercise training activates neuregulin 1/ErbB signaling and promotes cardiac repair in a rat myocardial infarction model. Life Sci. 2016, 149, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Yu, X.J.; Fu, L.Y.; Liu, K.L.; Gao, T.T.; Tu, J.W.; Kang, K.B.; Shi, X.L.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.; et al. Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension Through TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB Signaling in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Barroso, M.; Moreno-Calderon, K.M.; Sanchez-Duarte, E.; Cortes-Rojo, C.; Saavedra-Molina, A.; Rodriguez-Orozco, A.R.; Montoya-Perez, R. Diazoxide and Exercise Enhance Muscle Contraction during Obesity by Decreasing ROS Levels, Lipid Peroxidation, and Improving Glutathione Redox Status. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.Y.; Qi, J.; Yu, X.J.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Q.; Shi, T.; Zhang, D.M.; Guo, J.; Feng, Z.P.; et al. Paraventricular Nucleus Infusion of Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate Improves Renovascular Hypertension. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.J.; Xu, M.L.; Yu, X.J.; Du, M.M.; Li, X.H.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Kang, K.B.; Su, Q.; et al. Antihypertensive effects of exercise involve reshaping of gut microbiota and improvement of gut-brain axis in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Qin, D.N.; Ma, L.; Miao, Y.W.; Zhang, D.M.; Lu, Y.; Song, X.A.; Zhu, G.Q.; Kang, Y.M. Chronic infusion of lisinopril into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus modulates cytokines and attenuates oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral medulla in hypertension. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 279, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, X.J.; Xiao, T.; Chi, H.L.; Zhu, G.Q.; Kang, Y.M. Nrf1 Knock-Down in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Alleviates Hypertension Through Intervention of Superoxide Production-Removal Balance and Mitochondrial Function. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2021, 21, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Miao, Y.W.; Li, H.B.; Su, Q.; Liu, K.L.; Fu, L.Y.; Hou, Y.K.; Shi, X.L.; Li, Y.; Mu, J.J.; et al. Blockade of Endogenous Angiotensin-(1-7) in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates High Salt-Induced Sympathoexcitation and Hypertension. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Salih Ibrahim, R.M.; Chi, H.L.; Xiao, T.; Xia, W.J.; Li, H.B.; Kang, Y.M. Altered Gut Microbiota is Involved in the Anti-Hypertensive Effects of Vitamin C in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Johnson, R.F.; Yu, Y.; Beltz, T.; Johnson, A.K.; Weiss, R.M.; Felder, R.B. Novel effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism to reduce proinflammatory cytokines and hypothalamic activation in rats with ischemia-induced heart failure. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, E.J. The neural regulation of the kidney in hypertension and renal failure. Exp. Physiol. 2014, 99, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Cui, J.L.; Guo, F.; Beltz, T.G.; Zhao, Z.G.; Zhang, G.S.; Johnson, A.K. Voluntary Exercise Prevents Hypertensive Response Sensitization Induced by Angiotensin II. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 848079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Junior, N.C.; Ruggeri, A.; Silva, S.D., Jr.; Zampieri, T.T.; Ceroni, A.; Michelini, L.C. Exercise training increases GAD65 expression, restores the depressed GABAA receptor function within the PVN and reduces sympathetic modulation in hypertension. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, L.; Kruger, K.; Conrad, K.; Weiss, A.; Alack, K. Effects of Different Types of Exercise Training on Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.M.; Haibara, A.S.; Katsurada, K.; Nandi, S.S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Patel, K.P. Central Ang II (Angiotensin II)-Mediated Sympathoexcitation: Role for HIF-1alpha (Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha) Facilitated Glutamatergic Tone in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Hypertension 2021, 77, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Beltz, T.G.; Johnson, R.F.; Guo, F.; Hay, M.; Johnson, A.K. PVN adenovirus-siRNA injections silencing either NOX2 or NOX4 attenuate aldosterone/NaCl-induced hypertension in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H733–H741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Huang, B.S.; Chen, A.; Ahmad, M.; White, R.A.; Leenen, F.H. Role of brain aldosterone and mineralocorticoid receptors in aldosterone-salt hypertension in rats. Neuroscience 2016, 314, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Yu, X.J.; Shi, X.L.; Gao, H.L.; Yi, Q.Y.; Tan, H.; Fan, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.A.; Cui, W.; et al. NF-kappaB Blockade in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Inhibits High-Salt-Induced Hypertension Through NLRP3 and Caspase-1. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Zhang, D.M.; Jia, L.L.; Qi, J.; Song, X.A.; Tan, H.; Cui, W.; Chen, W.; Zhu, G.Q.; Qin, D.N.; et al. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by modulating cytokines and attenuating oxidative stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 284, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Yu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.L.; Lei, Y.M.; Yu, J.Y.; Zong, D.M.; Liu, K.L.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, Y.; et al. Astaxanthin Ameliorates Blood Pressure in Salt-Induced Prehypertensive Rats Through ROS/MAPK/NF-kappaB Pathways in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2021, 21, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.; Kucheryavenko, O.; Wordsworth, J.; von Zglinicki, T. The senescent bystander effect is caused by ROS-activated NF-kappaB signalling. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 170, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.M.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, J.P.; Elks, C.; Sriramula, S.; Yang, Z.M.; Francis, J. Brain nuclear factor-kappa B activation contributes to neurohumoral excitation in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, J.P.; Sriramula, S.; Mariappan, N.; Agarwal, D.; Francis, J. Angiotensin II-induced hypertension is modulated by nuclear factor-kappaBin the paraventricular nucleus. Hypertension 2012, 59, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.M.; Gao, F.; Li, H.H.; Cardinale, J.P.; Elks, C.; Zang, W.J.; Yu, X.J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Qi, J.; Yang, Q.; et al. NF-kappaB in the paraventricular nucleus modulates neurotransmitters and contributes to sympathoexcitation in heart failure. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Suo, Y.P.; Qi, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, D.M.; Yi, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Interaction between AT1 receptor and NF-kappaB in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus contributes to oxidative stress and sympathoexcitation by modulating neurotransmitters in heart failure. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2013, 13, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundele, O.M.; Rosa, F.A.; Dharmakumar, R.; Lee, C.C.; Francis, J. Systemic Sympathoexcitation Was Associated with Paraventricular Hypothalamic Phosphorylation of Synaptic CaMKIIalpha and MAPK/ErK. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Felder, R.B. Angiotensin II upregulates hypothalamic AT1 receptor expression in rats via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 296, H1425–H1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Yu, Y.; Wei, S.G.; Felder, R.B. Aldosterone-induced brain MAPK signaling and sympathetic excitation are angiotensin II type-1 receptor dependent. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H742–H751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Genes | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| AT-1R | 5′-CAACCTCCAGCAATCCTTTC-3′ | 5′-CCCAAATCCATACAGCCACT-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGT-3′ | 5′-CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Li, R.-J.; Fu, L.-Y.; Liu, K.-L.; Qiao, J.-A.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.-J.; Yu, J.-Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, H.; et al. Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193968
Qi J, Li R-J, Fu L-Y, Liu K-L, Qiao J-A, Yang Y, Yu X-J, Yu J-Y, Li Y, Tan H, et al. Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193968
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Jie, Rui-Juan Li, Li-Yan Fu, Kai-Li Liu, Jin-An Qiao, Yu Yang, Xiao-Jing Yu, Jia-Yue Yu, Ying Li, Hong Tan, and et al. 2022. "Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193968
APA StyleQi, J., Li, R.-J., Fu, L.-Y., Liu, K.-L., Qiao, J.-A., Yang, Y., Yu, X.-J., Yu, J.-Y., Li, Y., Tan, H., & Kang, Y.-M. (2022). Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. Nutrients, 14(19), 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193968






