Abstract
Megalin is an endocytic receptor abundantly expressed in proximal tubular epithelial cells and other calciotropic extrarenal cells expressing vitamin D metabolizing enzymes, such as bone and parathyroid cells. The receptor functions in the uptake of the vitamin D-binding protein (DBP) complexed to 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3), facilitating the intracellular conversion of precursor 25(OH)D3 to the active 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3). The significance of renal megalin-mediated reabsorption of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 has been well established experimentally, and other studies have demonstrated relevant roles of extrarenal megalin in regulating vitamin D homeostasis in mammary cells, fat, muscle, bone, and mesenchymal stem cells. Parathyroid gland megalin may regulate calcium signaling, suggesting intriguing possibilities for megalin-mediated cross-talk between calcium and vitamin D regulation in the parathyroid; however, parathyroid megalin functionality has not been assessed in the context of vitamin D. Within various models of chronic kidney disease (CKD), megalin expression appears to be downregulated; however, contradictory results have been observed between human and rodent models. This review aims to provide an overview of the current knowledge of megalin function in the context of vitamin D metabolism, with an emphasis on extrarenal megalin, an area that clearly requires further investigation.
1. Introduction
Vitamin D is a steroid hormone that plays several critical roles in the body, including the regulation of systemic calcium and bone metabolism. It can be produced by the skin or ingested from the diet, after which it undergoes two consecutive hydroxylation steps. Firstly, in the liver, to 25(OH)D3 by mitochondrial or microsomal 25-hydroxylases cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2R1 or CYP27A1. Secondly, 25(OH)D3 is transported to the kidney, where it is hydroxylated to 1,25(OH)2D3 via the 1α-hydroxylase CYP27B1 [1]. The levels of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 in circulation appear to be primarily regulated by the 24-hydroxylase CYP24A1, which catabolizes them to 24,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (24,25(OH)2D3) or 1,24,25 trihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,24,25(OH)3D3) allowing for further catabolism into calcitroic acid and subsequent excretion in the urine [2,3] (Figure 1). Circulating vitamin D3 metabolites are transported by the 58 kDa vitamin D Binding Protein (DBP). DBP possesses the greatest affinity for 25(OH)D3, followed by 24,25(OH)2D3, 1,25(OH)2D3, and unhydroxylated vitamin D3 in order of greatest to least affinity [4,5,6]. As a result of DBP’s high circulating concentration and affinity for 25(OH)D3, virtually all circulating 25(OH)D3 molecules are DBP-bound [6]. Although the affinity of DBP for 1,25(OH)2D3 is lower than 25(OH)D3, the exceptionally high concentration of DBP in circulation also suggests that most circulating 1,25(OH)2D3 is DBP-bound. As such, the free concentrations of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 are 10 pM and 1 pM, respectively, representing <0.1% and ~1% of their total circulating concentrations [7,8].
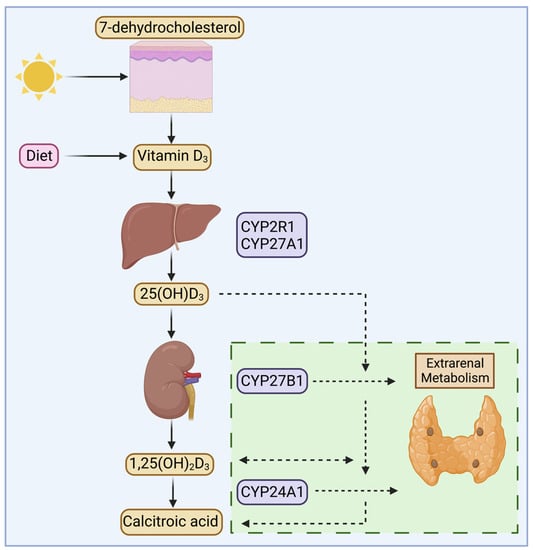
Figure 1.
General overview of vitamin D metabolism. Vitamin D3 can be obtained after ultraviolet-mediated conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol or from dietary sources. It then undergoes hydroxylation at the 25-position primarily through the enzymes cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2R1 or CYP27A1 to generate 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3). Maintenance of circulating levels of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) is primarily achieved after CYP27B1-mediated 1α-hydroxylation of 25(OH)D3 in the kidney, and CYP24A1 promotes catabolism of vitamin D compounds. Recent evidence shows that CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 are expressed in extrarenal calciotropic tissues, such as the parathyroid gland, raising possibilities for local, tissue-specific vitamin D activation, action, and inactivation.
Megalin, an endocytic receptor abundantly expressed in the proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTEC) of the kidney, functions in the uptake of DBP complexed to 25(OH)D3. This uptake facilitates the intracellular conversion of the 25(OH)D3 precursor to the active form, 1,25(OH)2D3. This role of megalin in the reabsorption of DBP-bound vitamin D metabolites from the renal proximal tubule in the kidney has been well established. 1,25(OH)2D3 or calcitriol, is the most biologically active form of vitamin D; however, other vitamin D metabolites have been implicated in conferring various biological functions [9].
The kidney was initially thought to be the sole organ responsible for producing active 1,25(OH)2D3, but it is now recognized that the expression of CYP27B1 is widespread, including in calciotropic tissues, such as the parathyroid gland [10]. Thus, although the kidney is the primary source for 1,25(OH)2D3 in the circulation, the presence of extrarenal CYP27B1 underscores the potential for local, tissue-specific 1,25(OH)2D3 production [11,12]. The actions of vitamin D can be broadly divided into two categories: (1) those that regulate calcium and phosphate homeostasis, termed the ‘classical’ actions, and (2) the ‘non-classical’ actions, which can affect inflammation, immune function, anti-oxidation, and anti-fibrosis, among many others [13,14,15,16]. Given its importance in nutrition, Vitamin D homeostasis has been studied in many diseases where low levels of serum DBP, 25(OH)D3, or 1,25(OH)2D3 have been implicated in various conditions including cancers, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases [17,18,19,20]. Vitamin D primarily exerts its actions through the nuclear vitamin D receptor (VDR), which is expressed in nearly all tissues, with genomic screens identifying thousands of vitamin D response elements (VDREs) throughout the genome controlling hundreds of genes [21]. CYP27B1 expression has been identified in numerous epithelia, the placenta, various bone cells, various cells of the immune system, and endocrine glands, such as the parathyroid and thyroid glands [22,23,24,25,26]. A complete list has been summarized by Bikle et al.; however, the physiological relevance of extrarenal tissues expressing CP27B1 has not been fully elucidated, and it is unclear if 1,25(OH)2D3 influences hormone release in the thyroid gland [12]. Megalin is also expressed in all of these tissues, suggesting an interconnected role between megalin-mediated uptake of vitamin D and the action of vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes in extrarenal tissues, such as the parathyroid gland [27]. The role of megalin in the metabolism of vitamin D in the kidney and extra-renal tissues is the focus of this review.
2. Megalin and Cubilin
2.1. Megalin Overview
Megalin is a large transmembrane glycoprotein of approximately 600 kDa (4665 amino acids) with homology to the human low-density lipoprotein receptor family [28,29,30]. The extracellular domain of human megalin has ligand-binding properties, due to the following three kinds of repeats: (1) four clusters of cysteine-rich complement-type repeats, representing the ligand-binding domains; (2) 16 growth factor repeats separated by eight spacer sequences containing the tetrapeptide YWTD (Tyr-Trp-Thr-Asp), functioning in the pH-dependent release of ligands; and (3) one epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeat [30]. Megalin possesses a single transmembrane domain of 23 amino acids and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of 209 amino acids [31]. Of interest are three NPXY (Asn-Pro-X-Tyr) motifs found in the cytoplasmic tail. Upon deletion of the second NPXY-like motif, megalin trafficking is impaired, and deletion of the first and third NPXY motifs diminishes effective megalin-mediated endocytosis [31]. Binding of the NPXY motifs to cytoplasmic adaptor proteins, such as ARH, AP-2, clathrin, Dab2, and GIPC, may promote the proper assembly of endocytic compartments, megalin trafficking and ligand-selectivity, and signal transduction, among other essential functional roles [32,33,34,35,36] (Figure 2).
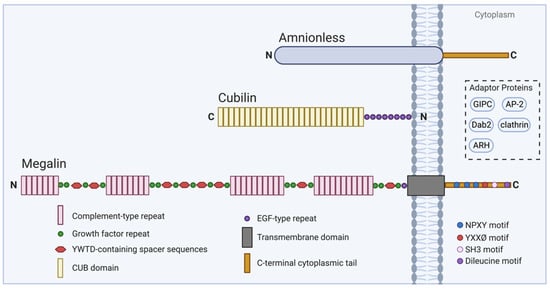
Figure 2.
Schematic of megalin and cubilin structure and associated molecules. The structure of megalin plays an essential role in its function, performing receptor-mediated endocytosis. The extracellular domain contains complement-type repeats with ligand-binding properties, YWTD-containing spacer sequences which function in the pH-dependent release of ligands, and other cooperating repeat sequences. The C-terminal cytoplasmic tail contains several motifs, such as NPXY, which are essential for proper megalin trafficking. Megalin trafficking may be enhanced through the interaction of intracellular adaptor proteins like GIPC, AP-2, Dab2, clathrin, and ARH with motifs in the cytoplasmic tail of megalin. Megalin function may also be enhanced through cooperative interaction with cubilin and amnionless (AMN).
In the kidney, megalin is abundantly expressed in the brush border of apical membranes of PTECs, endocytic vessels, microvilli, dense apical tubules, glomerular podocytes, and within lysosomes to a lesser extent [37,38,39,40,41]. However, megalin is also widely distributed and has been identified in several extrarenal absorptive epithelia, including the choroid plexus, the visceral yolk sac, the ciliary body and retinal pigment epithelium of the eye, gall bladder, placenta, ependymal cells, the epididymis, type II pneumocytes within the lung alveoli, the epithelium of the small intestine, and within the thyroid and parathyroid glands [38,42,43,44,45,46]. The widespread expression of megalin is consistent with its purported role as a multiligand scavenger receptor, as several physiologically relevant substrates have been identified as ligands for megalin, including albumin, hemoglobin, insulin, retinol-binding protein (RBP), and, of direct importance to this review, vitamin D-binding protein (DBP) [47,48,49,50,51]. A comprehensive list of megalin ligands has been summarized by Nielsen et al. [27]. This review focuses on the role of extrarenal megalin in the context of vitamin D metabolism, and how parathyroid megalin may have direct implications for disease.
2.2. Cubilin and Associated Molecules in Endocytosis
Cubilin, although not the primary focus of this review given the limited literature regarding its role in vitamin D metabolism, is a 460-kDa proximal tubular endocytic receptor that binds DBP and cooperates closely, and colocalizes with megalin [52]. Cubilin and megalin are co-expressed in apical epithelial cells and colocalize in the endocytic apparatus of absorptive epithelia in the intestine, kidney, yolk sac and gallbladder, among other tissues [44,46,53,54]. The structure of cubilin suggests an essential functional relationship to megalin, as cubilin has neither a transmembrane domain nor a cytoplasmic tail but is anchored to the membrane via a complex with the membrane protein amnionless (AMN) and megalin [55,56,57]. The binding of cubilin to megalin has been shown by in-vitro and in-vivo studies to be Ca2+-dependent, with binding significantly reduced in the presence of EDTA, a Ca2+-chelating agent. Functional cubilin was immunoprecipitated in complex with AMN and megalin from renal brush border membranes, and silencing of either megalin or AMN showed an 85–90% reduction in cubilin expression and a 2-fold decrease in its half-life, suggesting that the interaction of cubilin with both megalin and AMN is essential for its intracellular stability [57].
2.3. Megalin and Cubilin Interactions
Megalin-knockout mice demonstrate decreased cubilin expression and ligand uptake, and antibodies against megalin inhibit cubilin membrane association and increase degradation by 50–60%, reflecting a meaningful functional relationship between megalin and cubilin [58,59]. However, as indicated by a case study on a patient with a cubilin deficiency, cubilin dysfunction does not impair megalin-mediated endocytosis but exacerbates the loss of shared ligands, such as DBP [60]. Interestingly, thyroidectomized rats showed a 70% reduction in kidney levels of cubilin, and mucosal membrane cubilin associated with megalin was reduced by ~66% relative to controls, independent of megalin levels. These effects were reversed upon thyroxine treatment, where cubilin associated with megalin increased by 100% relative to controls, suggesting a thyroxine-mediated mechanism of regulation of megalin and cubilin association [45]. Cubilin has reduced function in the absence of megalin, as indicated by a kidney-specific knockout, where the cubilin-AMN complex promoted endocytosis of intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 and albumin, but megalin considerably increased this uptake by driving internalization of cubilin-ligand complexes [46,61]. As such, megalin and cubilin form a coreceptor complex in which cubilin likely sequesters specific ligands on the cell surface, enabling megalin-mediated internalization of the cubilin-bound ligand complex [62]. This has immediate relevance to vitamin D metabolism, as megalin, similarly to cubilin, demonstrates Ca2+-dependent binding to DBP, with Kd values of 110 ± 15 nM and 120 ± 27 nM for cubilin, and megalin, respectively [62]. As such, cubilin in dogs with impaired cubilin biosynthesis did not effectively colocalize with megalin and had reduced, but not abolished, endocytosis of DBP [62]. Conversely, megalin knockout mice showed no DBP endocytosis despite intact expression of cubilin. Nevertheless, circulating vitamin D metabolites (25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3) were reduced by approximately 50% in the cubilin-deficient dogs, highlighting a potentially important role of cubilin in vitamin D homeostasis [62]. Similar disruptions in DBP and circulating vitamin D handling were observed in human patients with cubilin mutations [62,63].
3. Megalin and Vitamin D Metabolism in the Kidney
In the kidney, 25(OH)D3 conversion to 1,25(OH)2D3 occurs primarily within the mitochondria of PTECs [64,65]. Megalin is abundantly expressed in the brush border of apical membranes of PTECs, endocytic vessels, microvilli, dense apical tubules, glomerular podocytes, and within lysosomes to a lesser extent [37,38,39,40,41]. For PTECs to sense and respond to systemic changes and demands for 1,25(OH)2D3 production, the precursor 25(OH)D3 must gain intracellular access. One theory, the free hormone hypothesis, states that the biological activity of vitamin D metabolites, including 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3, are mediated by their unbound (DBP-free) forms in circulation, which enter target cells through passive diffusion and not via an active transport mechanism [66]. Support for the free hormone hypothesis comes from a DBP knockout mouse model in which calcium homeostasis was not significantly altered despite there being severe circulating 1,25(OH)2D3 deficiency [67]. However, CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 activities were significantly upregulated and downregulated, respectively, in the kidneys of DBP-null mice, suggesting a compensatory mechanism for the lack of DBP to maintain 1,25(OH)2D3 levels [67].
While the free hormone hypothesis purports vitamin D metabolites enter PCT cells through passive diffusion, this was challenged by the findings of Nykjaer et al. (1999), who demonstrated that the 25(OH)D3-DBP complex is filtered through the glomerulus and reabsorbed in PTECs by megalin [51]. Endocytosis was required to preserve the systemic DBP concentration, as urinary DBP was exclusively observed in megalin-knockout animals but not controls [51]. The absence of renal megalin abolished any binding or uptake of endogenous DBP in the kidney, underscoring megalin as the primary renal DBP receptor [51]. Exposure to receptor-associated protein (RAP), a specific inhibitor of megalin-mediated endocytosis [68,69], decreased DBP uptake into the kidney to 8.2% of untreated controls, with the remainder excreted into the urine, suggesting that megalin has a functionally relevant role in the uptake of DBP and vitamin D-DBP complexes [51]. Further, endocytosis was required to preserve the systemic 25(OH)D3 concentration, as levels of plasma 25(OH)D3 were reduced by 80% and accompanied by severe bone disease [51]. These results suggest a significant and interconnected role for DBP-bound 25(OH)D3, megalin, and possibly RAP.
Additional knockout mouse models have further highlighted the importance of megalin as an endocytic receptor for vitamin D. The absence of megalin was associated with increased proteinuria, with increased urinary levels of albumin, major urinary protein 6, α1-microglobulin, RBP, and DBP compared to control mice, which corresponded to increased excretion of vitamin A (retinol) and 25(OH)D3 [50,70]. Further, the Ca2+-dependent binding mechanism of megalin appears to be essential, as EDTA treatment abolished ligand binding to megalin [70]. This has direct implications for diseases in which calcium homeostasis is disrupted, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT), which will be discussed below.
More specific insight towards the contribution of renal megalin was provided through a kidney-specific conditional knockout model. Consistent with global megalin-knockout models, these mice showed enhanced urinary loss of RBP and DBP, and a sixfold reduction in the uptake of 25(OH)D3-DBP complexes. This coincided with a 50% reduction in plasma 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 [71]. Due to reduced vitamin D levels, these mice developed hypocalcemia, dysregulated bone mineralization and severe bone abnormalities [71]. Interestingly, on a vitamin D-normal diet, the kidney-specific megalin knockout mice showed an increase in CYP27B1 and a twofold decrease in CYP24A1 mRNA levels. When placed on a low vitamin D diet, these numbers changed to a 10-fold increase and decrease, respectively [71]. These findings not only suggest that megalin is essential for the retrieval of glomerular filtered vitamin D-DBP complexes, but that compensatory changes in vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes occur to increase circulating and/or tissue levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 in the absence of functional vitamin D uptake.
Taken together, these results indicate that renal megalin primarily serves two purposes: (1) preventing urinary loss of vitamin D-DBP complexes and (2) supplying kidney cells with precursor 25(OH)D3 for production of the active 1,25(OH)2D3 (Figure 3). However, some evidence suggests that renal megalin may serve a third purpose related to vitamin D-related gene regulation [72]. Megalin binding protein (MegBP) is an intracellular protein that interacts with the megalin cytoplasmic tail and SKI-interacting protein (SKIP), a component of the VDR transcriptional regulatory complex [72]. As such, May et al. speculate that megalin-mediated endocytosis of vitamin D metabolites may modulate VDR-dependent gene transcription through MegBP and SKIP [73]. Megalin also participates in cell-signaling through regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) [74]. As a result of ligand binding to megalin, the megalin ectodomain is shed, generating a megalin C-terminal fragment (MCTF) that activates γ-secretase, releasing a free C-terminal intracellular megalin domain into the cytosol that is targeted to the nucleus [74]. As this RIP process can be activated by DBP binding to megalin, it is hypothesized that this pathway regulates genes involved in vitamin D metabolism [74]. A more nuanced investigation detailing the physiological relevance of this mechanism or the specific genes affected has yet to be completed.
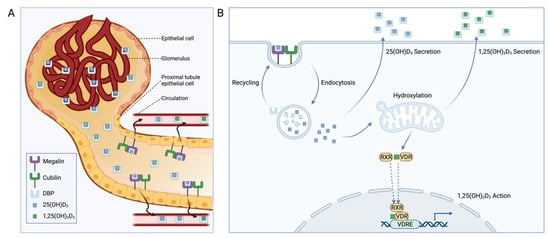
Figure 3.
Role of megalin and cubilin in renal vitamin D homeostasis. (A) Proximal tubular epithelial cells take up vitamin D-binding protein (DBP)-bound vitamin D metabolites from the glomerular ultrafiltrate through a megalin and cubilin-mediated mechanism [75]. (B) After endocytosis within megalin-expressing cells, DBP is degraded and recycled, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) can undergo 1α-hydroxylation to the active 1,25(OH)2D3 for subsequent vitamin D receptor (VDR) agonism through interactions with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) and VDR response elements (VDREs). Alternatively, endocytosed 25(OH)D3 or synthesized 1,25(OH)2D3 can be secreted to maintain circulating vitamin D homeostasis.
While the transcriptional impact of direct megalin-mediated intracellular signaling is somewhat unclear, it is well-established that megalin-mediated uptake of vitamin D can modulate vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes, as previously mentioned in DBP-null mice and kidney-specific megalin-null mice [67,71]. These results have been recapitulated in a human cell-derived micro-physiological system, whereby co-administration of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 resulted in a dose-dependent increase in 24,25(OH)2D3 levels, which was significantly impaired by RAP, suggesting that megalin-mediated uptake induces CYP24A1-mediated 24-hydroxylation [76]. Further, megalin may have a minor effect on the semi-selectivity of side-chain 19-nor analogs of 1,25(OH)2D3, as various forms of vitamin D differentially induced CYP24A1 expression in the absence of renal megalin [77].
The majority of studies regarding the role of megalin in vitamin D metabolism have either focused on global disruptions in megalin, which is problematic due to severe developmental defects allowing only 1–2% of receptor-deficient animals to be viable, or focused solely on renal megalin [51,78]. The contribution of extrarenal megalin towards vitamin D metabolism is discussed below, but it has received less attention, despite lines of evidence suggesting it may be as essential as renal megalin in the context of local, tissue-specific vitamin D action.
4. Extrarenal Megalin and Vitamin D Metabolism
The literature surrounding the role of extrarenal megalin in local vitamin D metabolism is limited. However, the studies that have been conducted demonstrate that megalin-mediated endocytosis is essential to functions unrelated to vitamin D in various epithelia, including the testes, vagina, thyroid gland, epididymis, uterus, oviduct, and gallbladder [44,79,80,81,82,83]. As the literature unfolds regarding the multiple functions of extrarenal megalin, many questions arise regarding the specific physiological contribution of these mechanisms and where vitamin D metabolism ranks among them. Functional studies underscore intriguing possibilities for megalin facilitating autocrine and paracrine actions of vitamin D at target tissues. We review all studies to date assessing the functional role of megalin in extrarenal vitamin D metabolism. The existing evidence is suggestive, although somewhat limited to date, in highlighting a clear need for megalin studies focusing on extrarenal target tissues of vitamin D, such as the parathyroid gland, and more physiologically relevant animal models.
4.1. Parathyroid Gland
Megalin is expressed in the parathyroid gland and demonstrates functionally important Ca2+-binding ability [84,85,86,87]. As megalin is specifically expressed on the surface of parathyroid hormone (PTH)-secreting cells of the parathyroid gland, it may serve as a potential calcium sensor in addition to the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) [88]. Whether a possible interaction exists between CaSR and megalin-mediated signaling has not been established, despite the fact that they share Ca2+ and vitamin D-related signaling properties [89,90]. A functional calcium-sensing role of megalin in the parathyroid gland may have been uncovered through the mouse monoclonal anti-parathyroid antibody G11, which targets megalin, since exposure to G11 led to the insensitivity of parathyroid cells to extracellular changes in Ca2+ for PTH release [91,92,93]. A phosphorylated form of megalin can be immunoprecipitated from cultures of primary human parathyroid cells, underscoring an additional, albeit speculative, role of megalin in phosphate sensing [29,84]. The expression of parathyroid megalin mRNA and protein is reduced in pathological parathyroid adenomas in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, and is associated with aberrant Ca2+ regulation, highlighting the immediate relevance of parathyroid megalin in pathologies, such as CKD and SHPT [42,94]. The role of parathyroid gland megalin in vitamin D metabolism has not yet been investigated. The parathyroid gland is significantly involved in the pathogenesis of CKD and SHPT, as well as a target of vitamin D receptor agonist (VDRA) therapy; thus, it is important that further studies focused on parathyroid megalin be undertaken.
4.2. Mammary Gland, Prostate, and Colon
Mammary epithelial cells express vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes such as CYP27B1 and CYP24A1, and have been shown to metabolize 25(OH)D3 to 1,25(OH)2D3 [22,95]. Rowling et al. sought to elucidate how 25(OH)D3-DBP complexes gain access to mammary cells. Using temperature-shift techniques, they observed the uptake of fluorophore-conjugated DBP into mammary cells at 37 °C, a temperature conducive to endocytosis, which was abolished at 4 °C, a microtubule-disrupting temperature. The essential role of megalin was confirmed using RAP, which significantly blunted DBP uptake into mammary cells at 37 °C. These data suggest that the internalization of DBP into mammary cells may occur via megalin-mediated endocytosis. Furthermore, endocytosed 25(OH)D3-DBP activated a CYP24A1 reporter gene, demonstrating that megalin-mediated endocytosis of vitamin D-DBP induces vitamin D-metabolizing enzyme activity in extrarenal tissues [96].
These findings have been recapitulated by Chlon et al., who showed physiologically-relevant megalin-mediated endocytosis in mammary cells, and modulation of megalin expression and action by retinoids [97]. Treatment of mammary cells with 10 μmol/L all-trans-retinoic acid (RA), or RA and 100 nmol/L 1,25(OH)2D3 in combination resulted in a 1.8-fold and 4.2-fold increase in megalin mRNA levels, respectively. Interestingly, RA did not significantly increase cubilin mRNA but elevated Dab2 mRNA, an essential intracellular protein for renal megalin function, by 6.2-fold [98]. The induction of megalin and Dab2 mRNA was consistent with significantly enhanced uptake of DBP in RA-supplemented media, supporting a meaningful role for both megalin-mediated uptake in the mammary gland alongside retinoid stimulation of megalin mRNA and function. This data also underscores a relationship between vitamin D and megalin, as 1,25(OH)2D3 alone enhanced megalin mRNA, which may correspond to stimulated uptake of vitamin D into target tissues [97]. Similar findings have been observed in prostate and colon epithelial cells. Following treatment with 10 μmol/L RA, megalin and Dab2 mRNA expression increased by approximately 3-fold in the tested prostate and colon cell lines [99]. RA-mediated increases in megalin and Dab2 expression coincided with enhanced megalin-mediated uptake, which again was inhibited at 4 °C. Immunofluorescence assays demonstrated punctate colocalization of DBP and megalin around the perimeter of prostate cells, suggesting the subcellular localization of megalin is physiologically relevant to its function. These results provide evidence that prostate and colon megalin are functional in internalizing vitamin D-DBP complexes and that its activity is inducible by RA [99].
4.3. Muscle and Fat
Megalin and cubilin expression were identified in differentiated muscle cells but not in undifferentiated myoblasts [100]. Interestingly, the time-dependent uptake of isotopically-labelled 25(OH)D3 was 2- to 3-fold higher in differentiated myotubes than in myoblasts, suggesting that megalin promotes the uptake of vitamin D into differentiated muscle cells, and that differentiation itself may moderate megalin function [100]. The function of megalin in myotubes was confirmed via RAP inhibition of megalin, which reduced the uptake of 25(OH)D3 into myotubes by 66% over a 16-h incubation [100]. These results were recapitulated by the same group, who again observed a significantly higher uptake of 25(OH)D3 in myotubes than undifferentiated myoblasts at 4 or 16 h, consistent with their high and low megalin expression, respectively [101]. In their analysis of fat cells, pre-adipocytes demonstrated significant uptake of 25(OH)D3 at 4 and 16 h, and differentiated adipocytes did not, which paralleled their strong and negligible megalin expression, respectively [101]. As skeletal muscle consists primarily of differentiated muscle cells and adipose tissue primarily of differentiated fat cells, these results suggest that megalin-mediated endocytosis of vitamin D-DBP complexes is a predominant mechanism of vitamin D uptake in muscle, but not in fat tissue.
4.4. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
As both muscle and fat cells are derived from mesenchymal stem cells, it is of interest to uncover the role of megalin within them. Gao et al. demonstrated that megalin is essential for the biosynthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3 and stimulation of VDR and osteoblastogenesis target genes in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) [102]. In comparing hMSCs with high or low constitutive megalin expression, the biosynthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3 in hMSCs with low megalin was shown to be 46% of hMSCs with high megalin [102]. This corresponded to osteoblastogenesis induction, whereby incubating hMSCs with 25(OH)D3 induced expression of osteoblast signature genes Runx2 and ALP in hMSCs with high megalin, but not with low megalin, suggesting that megalin is required for both intracellular synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3 from substrate 25(OH)D3, and 25(OH)D3-mediated induction of osteoblastogenesis [102]. These results were further supported by siRNA-mediated knockdown of megalin, whereby 1,25(OH)2D3 synthesis from 25(OH)D3 was reduced by 77% in siRNA-exposed hMSCs [102]. Correspondingly, 25(OH)D3 stimulated Runx2, ALP, and BSP expression in control hMSCs, but not in hMSCs exposed to megalin siRNA [102]. Similar results were observed for CYP24A1 after exposure to 25(OH)D3, suggesting that megalin is required to induce VDR target genes by the 25(OH)D3-DBP complex. It is of interest that exposure of hMSCs to 1,25(OH)2D3 in either the low megalin or siRNA-mediated knockdown experiments did not lead to differential effects on osteoblastogenesis or induction of VDR target genes, suggesting that the actions of 1,25(OH)2D3 in hMSCs are independent of megalin-mediated endocytosis. The differences in megalin handling of 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 were also observed in mammary epithelial cells [96]. Thus, the expression of megalin in hMSCs and mammary epithelial cells appears necessary for the uptake and conversion of 25(OH)D3 to 1,25(OH)2D3.
4.5. Bone
Primary human osteoblast cells have been found to express CYP27B1 mRNA and secrete detectable levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 in response to 25(OH)D3 exposure [103]. Exposure of these cells to physiological levels of 25(OH)D3 (20–100 nM) coincided with stimulation of CYP24A1 mRNA and VDR target genes related to osteogenesis, such as osteocalcin, osteopontin and RANKL [103]. Further, siRNA-mediated knockdown of CYP27B1 almost wholly abolished the response of osteoblasts to 25(OH)D3, supporting local 25(OH)D3 conversion and activation to 1,25(OH)2D3. While this study did not assess the functional role of megalin in facilitating these actions, megalin mRNA was detected in the human osteoblast cells [103]. These results not only parallel those discussed earlier in terms of the stimulatory capacity of 25(OH)D3 in extrarenal tissues but also suggest that megalin-mediated endocytosis of 25(OH)D3 promotes the autocrine synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3 at target tissues, which has functional regulatory consequences for these tissues. A receptor-mediated mechanism for DBP uptake has also been observed for human B-lymphoid cells; however, whether megalin is the receptor involved remains unclear [104].
5. Megalin in Chronic Kidney Disease
Many diseases have been associated with maladaptive alterations in megalin expression or function, or the opposite, where megalin dysfunction leads to various pathological states, summarized by Nielsen et al. [27]. The scope of this section will henceforth be focused on the vitamin D-related implications of altered megalin expression in kidney diseases.
5.1. Chronic Kidney Disease Overview
CKD is a disease of great interest, given its enormous costs to patient well-being and health care systems; consequently, its intimate relationship with abnormal vitamin D metabolism has been extensively explored. CKD is clinically defined by a chronic reduction in kidney function and is associated with the pathogenesis of SHPT, the pathological rise in PTH. CKD is associated with decreased levels of the active form of vitamin D, 1,25(OH)2D3, leading to reduced VDR-mediated suppression of PTH secreted by the parathyroid gland and contributing to SHPT development [105]. Treatment of SHPT commonly involves the administration of VDRAs, such as 1,25(OH)2D3. However, these treatments can become problematic in patients, either indirectly mediating off-target effects, such as left ventricular hypertrophy or, most notably, the emergence of VDRA resistance [106]. Approximately 20–30% of SHPT patients become resistant to treatment with VDRAs, as serum PTH does not decrease despite increasing doses of VDRAs, representing a state of ‘active vitamin D failure,’ that may exacerbate cardiovascular toxicity [107]. The mechanisms of treatment-acquired vitamin D resistance are incompletely understood, with contributions potentially arising from impaired function or expression of VDR, retinoid X receptor (RXR), increased uremic toxins, elevated parathyroid calreticulin, alterations in vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes (CYP2R1, CYP27A1, CYP27B1) or DBP [108,109]. The contribution of megalin towards vitamin D resistance as a receptor for vitamin D substrate supply for the parathyroid gland has, to date, received little attention in the literature.
5.2. Megalin in Chronic Kidney Disease
A partial nephrectomy rat model of CKD demonstrated a gradual decrease of megalin mRNA in the remnant kidney as early as week 2, which continued to decline throughout the study [110]. This was accompanied by an increase and decrease in CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 mRNA, respectively. By week 8, the levels of CYP27B1 mRNA were significantly elevated, VDR mRNA was reduced, and the ratio of CYP27B1 to CYP24A1 and megalin mRNA was more pronounced [110]. As indicated above, the up and downregulation of vitamin D activating and deactivating enzymes suggest a compensatory mechanism to enhance 1,25(OH)2D3 biosynthesis and preservation in the absence of megalin-mediated endocytosis. Interestingly, the plasma levels of calcium, phosphate, and 1,25(OH)2D3 were not significantly different from controls in the study duration, while PTH was elevated considerably [110]. Thus, it is unclear whether this was due to compensatory up and downregulation of CYP27B1 and CYP24A1, a non-megalin-mediated mechanism of 1,25(OH)2D3 synthesis, or an early state of SHPT attempting to compensate for impaired mineral and vitamin D handling [111,112]. In a transgenic mouse model overexpressing renin to recapitulate CKD, megalin protein expression in proximal tubules was significantly decreased but returned to normal levels following angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonism [113]. These results were concordant with angiotensin II-mediated suppression of megalin mRNA and protein in another CKD model, followed by impaired megalin-mediated uptake [114]. As angiotensin II levels are elevated in CKD, this data suggests a potential mechanism by which megalin expression and function are inhibited in kidney diseases, potentially leading to detrimental effects on vitamin D metabolism [115]. In a 5/6 nephrectomy rat model of CKD, megalin expression was significantly reduced in the renal cortex after 8 weeks, but the expression of cubilin remained unchanged [116]. The physiological relevance of a differential renal expression of megalin and cubilin is unclear, however, as uptake functionality was not assessed. Human kidney biopsies from patients with CKD and Fabry nephropathy also show reduced megalin and cubilin expression compared to healthy controls [117]. However, reports of decreased renal megalin expression in CKD are not consistent. In another nephrectomy rat model of CKD, the megalin and cubilin protein levels were increased relative to controls [118]. As these findings were based on a qualitative assessment of an immunohistochemical characterization of kidney tissue, they should be interpreted cautiously. Nonetheless, they suggest that further studies must be conducted to elucidate the pathophysiologic role of decreased megalin expression in a CKD setting.
A recent study suggests that megalin dysfunction may, in itself, contribute to CKD progression; in a kidney-specific knockout model of megalin, the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreased, and plasma creatinine increased, both being clinical indicators of CKD [119,120]. Similar findings were observed in a clinical cohort of patients with pathogenic megalin mutations, where, in addition to classical signs of renal decline, enhanced proteinuria of DBP and other megalin ligands, and glomerular and tubulointerstitial pathohistological lesions, were observed [119,121].
5.3. Vitamin D Regulation
As CKD seems to induce alterations in megalin expression, vitamin D-mediated regulation of megalin becomes relevant, given the relationship between CKD and reduced 1,25(OH)2D3 levels. Megalin mRNA and protein were stimulated after exposing rat PTECs to 1,25(OH)2D3 and RA [97,122], suggesting a “vicious cycle” hypothesis in the context of CKD. Assuming 1,25(OH)2D3 can stimulate renal megalin expression, this would ensure maintenance of systemic vitamin D levels via megalin-mediated endocytosis. In CKD, where levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 levels are reduced, this would lead to decreased megalin expression, reducing the capacity of renal 25(OH)D3 uptake and further reducing 1,25(OH)2D3 production, propagating the cycle and exacerbating vitamin D deficiency (Figure 4) [123]. This may, partially, explain the phenotype of abnormalities in CKD-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD), in which reduced levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 promotes hypocalcemia, stimulating excessive PTH production and, in turn, accelerated bone turnover [124]. Other reviews by Dusso, Kim and Kim, and Bosworth and de Boer have discussed this concept [125,126,127,128]. This hypothesis has been challenged by a more recent study using a human cell-derived micro-physiological system, in which exposure to 1,25(OH)2D3 did not induce upregulation of megalin but instead demonstrated a significant downward trend of megalin mRNA expression [76]. While these results are interesting, statistically significant suppression of megalin mRNA was only achieved at a supraphysiological dose of 1,25(OH)2D3 at 500 nM. This dose is well above the upper limit of circulating levels and at a level consistent with 1,25(OH)2D3 toxicity, where pro-apoptotic effects, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis are observed [129,130,131,132]. Precluding the possibility that it was high-dose exposure of 1,25(OH)2D3 mediating toxic effects on megalin mRNA, these results highlight potential interspecies variability involving megalin regulation within humans and rodents and challenge the relationship of 1,25(OH)2D3 regulation of megalin expression. The concept of interspecies variability in vitamin D handling is not foreign, as differences between humans and rodent models have also been demonstrated with urinary DBP excretion. For example, urinary DBP excretion was not found to be increased in cubilin-deficient mice; however, it was raised in both megalin-deficient and cubilin-deficient patients [60,61,121]. Although limited, these data suggest that reabsorption of DBP in mice can occur without cubilin, whereas it may play a more significant role in humans.
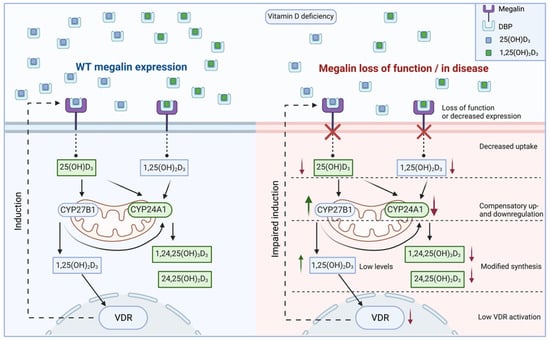
Figure 4.
Involvement of megalin in vitamin D metabolism and proposed effect of kidney disease or loss of function. After megalin-mediated endocytosis, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) may be sent to the mitochondria for cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated inactivation or CYP27B1-mediated activation. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3), either endocytosed or intracellularly generated, may be inactivated via CYP24A1, or interact with the vitamin D-receptor (VDR) to exert intracrine genomic effects such as upregulating megalin gene expression. Alternatively, vitamin D metabolites may re-enter the circulation to exert endocrine effects. Evidence from knockout models and models of kidney disease suggests megalin function or expression is decreased, leading to a reduced capacity for endocytosis. In a setting of vitamin D deficiency, this leads to the compensatory up and downregulation of CYP27B1 and CYP24A1, respectively, modifying the synthesis of vitamin D metabolites. Low levels of 1,25(OH)2D3, due to decreased uptake, may cause lower VDR activation and reduced megalin expression. For visual clarity, only the VDR genomic effect on megalin expression has been displayed, but it is conceivable that many other expression profiles would be altered due to impaired megalin endocytosis.
5.4. Diabetic Nephropathy
A major cause of CKD in patients is diabetic nephropathy, which develops in approximately 40% of patients with diabetes [133]. Diabetic nephropathy induces a similar inhibition of megalin and Dab2 mRNA to CKD, with approximately 50 and 80% reductions in mRNA, respectively, whereas cubilin mRNA remains unchanged [134]. Reductions in megalin and Dab2 mRNA correspond to increased DBP, 25(OH)D3, and 1,25(OH)2D3 urinary excretion in diabetic fatty rats, concomitant with reduced serum levels of both 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 [134]. Dysregulation of intrarenal vitamin D metabolism has been similarly reported in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy, consistent with increased excretion of DBP, 25(OH)D3, megalin itself, and elevated CYP27B1 mRNA [135]. Other animal studies have also reported decreased proximal tubule megalin protein expression in rat models of diabetic nephropathy [136,137]. In patients with type 1 diabetes, a significant elevation in the urinary excretion of low molecular weight proteins, DBP and megalin was observed that paralleled the magnitude of vitamin D deficiency in these patients, linking megalin dysfunction to impaired vitamin D homeostasis [138,139]. The findings of increased urinary megalin excretion raise meaningful implications for kidney disease, as full-length urinary megalin (C-megalin) excretion is related to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy [140,141]. The significance of urinary C-megalin excretion in vitamin D metabolism was assessed in pre-dialysis CKD patients, where it was negatively associated with serum levels of 25(OH)D3, 1,25(OH)2D3, and 24,25(OH)2D3 [142]. These results suggest that impaired megalin-mediated endocytosis of 25(OH)D3-DBP complexes contributes to dysregulated systemic vitamin D homeostasis. Both diabetic nephropathy and CKD likely impair the reabsorption of 25(OH)D3-DBP complexes via decreased megalin protein and mRNA expression, or increased urinary excretion, ultimately comprising hypovitaminosis D.
6. Summary and Outlook
The role of the endocytic receptor megalin in reabsorbing DBP-bound vitamin D metabolites from the renal proximal tubule has been well established, confirming its significance in the metabolism and homeostasis of circulating vitamin D. It is well known that vitamin D-metabolizing machinery is widely expressed in the body and can take up 25(OH)D3 for local conversion into 1,25(OH)2D3 via CYP27B1. However, little attention has been given to the mechanisms of extrarenal 25(OH)D3 uptake and how these mechanisms are modified in diseases. In addition to the kidney, megalin is widely expressed in several cell types, including mammary cells, osteoblasts, muscle, fat, mesenchymal stem cells, thyroid, and parathyroid cells, among many others. Not only does this expression coincide with the expression of vitamin D-metabolizing enzymes, but functional studies have demonstrated through knockout models, or RAP-mediated inhibition, that megalin-mediated endocytosis is essential for the uptake of vitamin D into cells, and its impairment leads to maladaptive alterations in vitamin D metabolism. However, the understanding of extrarenal megalin is quite incomplete, with essential calciotropic tissues expressing megalin, such as the parathyroid gland, not having been investigated sufficiently, thereby leaving gaps in knowledge regarding the contribution of megalin to tissue-specific 1,25(OH)2D3 production. More studies about the role of megalin in these tissues are needed, as megalin dysfunction has been associated with vitamin D deficiency, and evidence suggests that megalin is critical to the progression of dysregulated vitamin D metabolism in CKD and other kidney diseases. The specific contribution of megalin in the pathogenesis of CKD remains elusive, however, as not all findings of megalin expression and regulation by 1,25(OH)2D3 are consistent. As analogs of vitamin D are given as treatments for conditions like SHPT in CKD, the complications arising from the free hormone hypothesis, inconsistent 1,25(OH)2D3 regulation of megalin and the incompletely understood mechanisms of megalin regulation in disease and extrarenal tissues all suggest the need for additional research assessing the role of megalin in vitamin D homeostasis. Megalin is very likely an important player in local networks of vitamin D metabolism within extrarenal tissues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.K., M.A.A., R.M.H. and M.P.; investigation, S.S.K.; writing–original draft preparation, S.S.K.; writing–review and editing, S.S.K., M.A.A., R.M.H. and M.P.; visualization, S.S.K.; supervision, M.A.A., R.M.H. and M.P.; project administration, M.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
All figures made in BioRender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 1,25(OH)2D3 | 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 |
| 25(OH)D3 | 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 |
| 24,25(OH)2D3 | 24,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 |
| 1,24,25(OH)3D3 | 1,24,25 trihydroxyvitamin D3 |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| AMN | Amnionless |
| AP-2 | Adaptor protein-2 |
| ARH | Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia |
| AT1 | Angiotensin II type 1 |
| CaSR | Calcium-sensing receptor |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CYP24A1 | Cytochrome P450 24A1 |
| CYP27B1 | Cytochrome P450 27B1 |
| Dab-2 | Disabled-2 |
| DBP | Vitamin D-binding protein |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| GIPC | GAIP interacting protein |
| GAIP | G alpha interacting protein |
| hMSC | Human mesenchymal stem cell |
| MegBP | Megalin binding protein |
| PTEC | Proximal tubular epithelial cells |
| PTH | Parathyroid hormone |
| RA | All-trans-retinoic acid |
| RAP | Receptor-associated protein |
| RBP | Retinol-binding protein |
| RIP | Regulated intramembrane proteolysis |
| RXR | Retinoid X receptor |
| SHPT | Secondary hyperparathyroidism |
| SKIP | SKI-interacting protein |
| VDR | Vitamin D receptor |
| VDRA | Vitamin D receptor agonist |
| VDRE | VDR response element |
References
- Wierzbicka, J.; Piotrowska, A.; Żmijewski, M.A. The Renaissance of Vitamin D. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 61, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusso, A.S.; Brown, A.J.; Slatopolsky, E. Vitamin D. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2005, 289, F8–F28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, N.E.; Haddad, J.G. Vitamin D Binding Protein (Gc-Globulin)*. Endocr. Rev. 1989, 10, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Van Baelen, H.; Rombauts, W.; De Moor, P. The Purification and Characterisation of the Human-Serum Binding Protein for the 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol (Transcalciferin) Identity with Group-Specific Component. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 66, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HADDAD, J.G.; HILLMAN, L.; ROJANASATHIT, S. Human Serum Binding Capacity and Affinity for 25-Hydroxyergocalciferol and 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1976, 43, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D.; Gee, E.; Halloran, B.; Kowalski, M.A.; Ryzen, E.; Haddad, J.G. Assessment of the Free Fraction of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Serum and Its Regulation by Albumin and the Vitamin D-Binding Protein. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 63, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R.; Van Assche, F.A.; Van Baelen, H.; Heyns, W.; De Moor, P. Influence of the Vitamin D-Binding Protein on the Serum Concentration of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 67, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R.; Schuit, F.; Antonio, L.; Rastinejad, F. Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.S.; Tserng, K.Y. Calcitroic Acid, End Product of Renal Metabolism of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 through C-24 Oxidation Pathway. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Extra Renal Synthesis of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D and Its Health Implications. Clin. Rev. Bone Min. Metab. 2009, 7, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.R.; Kodicek, E. Unique Biosynthesis by Kidney of a Biological Active Vitamin D Metabolite. Nature 1970, 228, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D.; Patzek, S.; Wang, Y. Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Roles of Extra Renal CYP27b1: Case Report and Review. Bone Rep. 2018, 8, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiosano, D.; Wildbaum, G.; Gepstein, V.; Verbitsky, O.; Weisman, Y.; Karin, N.; Eztioni, A. The Role of Vitamin D Receptor in Innate and Adaptive Immunity: A Study in Hereditary Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, M.; Andreesen, R.; Krause, S.W.; Szabo, A.; Ritz, E.; Reichel, H. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Production and Vitamin D3 Receptor Expression Are Developmentally Regulated during Differentiation of Human Monocytes into Macrophages. Blood 1993, 82, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, H. Vitamin D Is a Membrane Antioxidant. Ability to Inhibit Iron-Dependent Lipid Peroxidation in Liposomes Compared to Cholesterol, Ergosterol and Tamoxifen and Relevance to Anticancer Action. FEBS Lett. 1993, 326, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzilas, V.; Bouros, E.; Barbayianni, I.; Karampitsakos, T.; Kourtidou, S.; Ntassiou, M.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Bouros, D.; Tzouvelekis, A. Vitamin D Prevents Experimental Lung Fibrosis and Predicts Survival in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Pulm. Pharm. 2019, 55, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorham, E.D.; Garland, C.F.; Garland, F.C.; Grant, W.B.; Mohr, S.B.; Lipkin, M.; Newmark, H.L.; Giovannucci, E.; Wei, M.; Holick, M.F. Vitamin D and Prevention of Colorectal Cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 97, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, C.J.; Dinicolantonio, J.J.; Milani, R.V.; O’Keefe, J.H. Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Health. Circulation 2013, 128, 2404–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinarayan, C.V. Vitamin D and Diabetes Mellitus. Hormones 2014, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, L.E.; Qureshi, O.S.; Gardner, D.; Hou, T.Z.; Briggs, Z.; Soskic, B.; Baker, J.; Raza, K.; Sansom, D.M. Vitamin D Antagonises the Suppressive Effect of Inflammatory Cytokines on CTLA-4 Expression and Regulatory Function. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D Metabolism, Mechanism of Action, and Clinical Applications. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmis, C.M.; Salvador, S.M.; Smith, K.M.; Welsh, J. Human Mammary Epithelial Cells Express CYP27B1 and Are Growth Inhibited by 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-3, the Major Circulating Form of Vitamin D-3. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.O.; Li, S.; Cao, C.; Kent, T.; Young, B.V.; Queenan, R.A.; Pressman, E.K.; Cooper, E.M. Placental CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 Expression in Human Placental Tissue and Their Association with Maternal and Neonatal Calcitropic Hormones. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anderson, P.H.; Iida, S.; Tyson, J.H.T.; Turner, A.G.; Morris, H.A. Bone CYP27B1 Gene Expression Is Increased with High Dietary Calcium and in Mineralising Osteoblasts. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.H. Vitamin D Metabolism and Signaling in the Immune System. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2012, 13, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanakul, A.; Zhang, M.Y.H.; Louw, A.; Armbrecht, H.J.; Miller, W.L.; Portale, A.A.; Perwad, F. FGF-23 Regulates CYP27B1 Transcription in the Kidney and in Extra-Renal Tissues. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Christensen, E.I.; Birn, H. Megalin and Cubilin in Proximal Tubule Protein Reabsorption: From Experimental Models to Human Disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychowdhury, R.; Niles, J.L.; McCluskey, R.T.; Smith, J.A. Autoimmune Target in Heymann Nephritis Is a Glycoprotein with Homology to the LDL Receptor. Science 1989, 244, 1163–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjälm, G.; Murray, E.; Crumley, G.; Harazim, W.; Lundgren, S.; Onyango, I.; Ek, B.; Larsson, M.; Juhlin, C.; Hellman, P.; et al. Cloning and Sequencing of Human Gp330, a Ca(2+)-Binding Receptor with Potential Intracellular Signaling Properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 239, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Pietromonaco, S.; Loo, A.K.; Farquhar, M.G. Complete Cloning and Sequencing of Rat Gp330/"megalin," a Distinctive Member of the Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene Family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9725–9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Farquhar, M.G. Identification of an Apical Sorting Determinant in the Cytoplasmic Tail of Megalin. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 284, C1105–C1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Meerloo, T.; Takeda, T.; Farquhar, M.G. The Adaptor Protein ARH Escorts Megalin to and through Endosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4984–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Gupta, S.; Yi, M.; Michaely, P.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. ARH Is a Modular Adaptor Protein That Interacts with the LDL Receptor, Clathrin, and AP-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44044–44049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyel, P.A.; Thieman, J.R.; Roth, R.; Erkan, E.; Everett, E.T.; Watkins, S.C.; Heuser, J.E.; Traub, L.M. The AP-2 Adaptor Β2 Appendage Scaffolds Alternate Cargo Endocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 5309–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleinikov, A.V.; Zhao, J.; Makker, S.P. Cytosolic Adaptor Protein Dab2 Is an Intracellular Ligand of Endocytic Receptor Gp600/Megalin. Biochem. J. 2000, 347, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; McQuistan, T.; Orlando, R.A.; Farquhar, M.G. GAIP, GIPC and Galphai3 Are Concentrated in Endocytic Compartments of Proximal Tubule Cells: Putative Role in Regulating Megalin’s Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerjaschki, D.; Farquhar, M.G. The Pathogenic Antigen of Heymann Nephritis Is a Membrane Glycoprotein of the Renal Proximal Tubule Brush Border. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 5557–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatelet, F.; Brianti, E.; Ronco, P.; Roland, J.; Verroust, P. Ultrastructural Localization by Monoclonal Antibodies of Brush Border Antigens Expressed by Glomeruli. I. Renal Distribution. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 122, 500–511. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, E.I.; Nielsen, S.; Moestrup, S.K.; Borre, C.; Maunsbach, A.B.; de Heer, E.; Ronco, P.; Hammond, T.G.; Verroust, P. Segmental Distribution of the Endocytosis Receptor Gp330 in Renal Proximal Tubules. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 66, 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki, D.; Farquhar, M.G. Immunocytochemical Localization of the Heymann Nephritis Antigen (GP330) in Glomerular Epithelial Cells of Normal Lewis Rats. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 157, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wen, Y.; Tang, T.-T.; Lv, L.-L.; Tang, R.-N.; Liu, H.; Ma, K.-L.; Crowley, S.D.; Liu, B.-C. Megalin/Cubulin-Lysosome-Mediated Albumin Reabsorption Is Involved in the Tubular Cell Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome and Tubulointerstitial Inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18018–18028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, S.; Carling, T.; Hjälm, G.; Juhlin, C.; Rastad, J.; Pihlgren, U.; Rask, L.; Akerström, G.; Hellman, P. Tissue Distribution of Human Gp330/Megalin, a Putative Ca(2+)-Sensing Protein. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1997, 45, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storm, T.; Heegaard, S.; Christensen, E.I.; Nielsen, R. Megalin–Deficiency Causes High Myopia, Retinal Pigment Epithelium-Macromelanosomes and Abnormal Development of the Ciliary Body in Mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erranz, B.; Miquel, J.F.; Argraves, W.S.; Barth, J.L.; Pimentel, F.; Marzolo, M.-P. Megalin and Cubilin Expression in Gallbladder Epithelium and Regulation by Bile Acids. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 2185–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yammani, R.R.; Seetharam, S.; Seetharam, B. Cubilin and Megalin Expression and Their Interaction in the Rat Intestine: Effect of Thyroidectomy. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E900–E907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birn, H.; Verroust, P.J.; Nexo, E.; Hager, H.; Jacobsen, C.; Christensen, E.I.; Moestrup, S.K. Characterization of an Epithelial Approximately 460-KDa Protein That Facilitates Endocytosis of Intrinsic Factor-Vitamin B12 and Binds Receptor-Associated Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26497–26504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Verroust, P.J.; Moestrup, S.K.; Christensen, E.I. Megalin/Gp330 Mediates Uptake of Albumin in Renal Proximal Tubule. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, F900–F907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gburek, J.; Verroust, P.J.; Willnow, T.E.; Fyfe, J.C.; Nowacki, W.; Jacobsen, C.; Moestrup, S.K.; Christensen, E.I. Megalin and Cubilin Are Endocytic Receptors Involved in Renal Clearance of Hemoglobin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, R.A.; Rader, K.; Authier, F.; Yamazaki, H.; Posner, B.I.; Bergeron, J.J.; Farquhar, M.G. Megalin Is an Endocytic Receptor for Insulin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.I.; Moskaug, J.O.; Vorum, H.; Jacobsen, C.; Gundersen, T.E.; Nykjaer, A.; Blomhoff, R.; Willnow, T.E.; Moestrup, S.K. Evidence for an Essential Role of Megalin in Transepithelial Transport of Retinol. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykjaer, A.; Dragun, D.; Walther, D.; Vorum, H.; Jacobsen, C.; Herz, J.; Melsen, F.; Christensen, E.I.; Willnow, T.E. An Endocytic Pathway Essential for Renal Uptake and Activation of the Steroid 25-(OH) Vitamin D3. Cell 1999, 96, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.Y.; Nielsen, R.; Birn, H.; Drumm, K.; Mildenberger, S.; Freudinger, R.; Moestrup, S.K.; Verroust, P.J.; Christensen, E.I.; Gekle, M. Cubilin- and Megalin-Mediated Uptake of Albumin in Cultured Proximal Tubule Cells of Opossum Kidney. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahali, D.; Mulliez, N.; Chatelet, F.; Dupuis, R.; Ronco, P.; Verroust, P. Characterization of a 280-KD Protein Restricted to the Coated Pits of the Renal Brush Border and the Epithelial Cells of the Yolk Sac. Teratogenic Effect of the Specific Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahali, D.; Mulliez, N.; Chatelet, F.; Laurent-Winter, C.; Citadelle, D.; Sabourin, J.C.; Roux, C.; Ronco, P.; Verroust, P. Comparative Immunochemistry and Ontogeny of Two Closely Related Coated Pit Proteins. The 280-Kd Target of Teratogenic Antibodies and the 330-Kd Target of Nephritogenic Antibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 142, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fyfe, J.C.; Madsen, M.; Højrup, P.; Christensen, E.I.; Tanner, S.M.; de la Chapelle, A.; He, Q.; Moestrup, S.K. The Functional Cobalamin (Vitamin B12)-Intrinsic Factor Receptor Is a Novel Complex of Cubilin and Amnionless. Blood 2004, 103, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudroy, G.; Gburek, J.; Kozyraki, R.; Madsen, M.; Trugnan, G.; Moestrup, S.K.; Verroust, P.J.; Maurice, M. Contribution of Cubilin and Amnionless to Processing and Membrane Targeting of Cubilin–Amnionless Complex. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2330–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, R.; Yammani, R.; Bauer, J.A.; Kalra, S.; Seetharam, S.; Seetharam, B. Interactions of Cubilin with Megalin and the Product of the Amnionless Gene (AMN): Effect on Its Stability. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauris, J.; Christensen, E.I.; Nykjaer, A.; Jacobsen, C.; Petersen, C.M.; Ovesen, T. Cubilin and Megalin Co-Localize in the Neonatal Inner Ear. Audiol. Neurootol. 2009, 14, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyraki, R.; Fyfe, J.; Kristiansen, M.; Gerdes, C.; Jacobsen, C.; Cui, S.; Christensen, E.I.; Aminoff, M.; de la Chapelle, A.; Krahe, R.; et al. The Intrinsic Factor–Vitamin B12 Receptor, Cubilin, Is a High-Affinity Apolipoprotein A-I Receptor Facilitating Endocytosis of High-Density Lipoprotein. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storm, T.; Emma, F.; Verroust, P.J.; Hertz, J.M.; Nielsen, R.; Christensen, E.I. A Patient with Cubilin Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsellem, S.; Gburek, J.; Hamard, G.; Nielsen, R.; Willnow, T.E.; Devuyst, O.; Nexo, E.; Verroust, P.J.; Christensen, E.I.; Kozyraki, R. Cubilin Is Essential for Albumin Reabsorption in the Renal Proximal Tubule. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykjaer, A.; Fyfe, J.C.; Kozyraki, R.; Leheste, J.-R.; Jacobsen, C.; Nielsen, M.S.; Verroust, P.J.; Aminoff, M.; de la Chapelle, A.; Moestrup, S.K.; et al. Cubilin Dysfunction Causes Abnormal Metabolism of the Steroid Hormone 25(OH) Vitamin D3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13895–13900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, E.; Lange, B.; Penna-Martinez, M.; Brück, P.; Swiech, K.; Mauf, S.; Kahles, H.; Badenhoop, K. The Role of Cubilin Gene Polymorphisms and Their Influence on 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 Plasma Levels in Type 1 Diabetes Patients. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbrecht, H.J.; Zenser, T.V.; Davis, B.B. Conversion of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 to 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 in Renal Slices from the Rat. Endocrinology 1981, 109, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyama, K.; Kitanaka, S.; Sato, T.; Kobori, M.; Yanagisawa, J.; Kato, S. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-Hydroxylase and Vitamin D Synthesis. Science 1997, 277, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, C.M. The Free Hormone Hypothesis: A Physiologically Based Mathematical Model. Endocr. Rev. 1989, 10, 232–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zella, L.A.; Shevde, N.K.; Hollis, B.W.; Cooke, N.E.; Pike, J.W. Vitamin D-Binding Protein Influences Total Circulating Levels of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 but Does Not Directly Modulate the Bioactive Levels of the Hormone in Vivo. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3656–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moestrup, S.K.; Cui, S.; Vorum, H.; Bregengård, C.; Bjørn, S.E.; Norris, K.; Gliemann, J.; Christensen, E.I. Evidence That Epithelial Glycoprotein 330/Megalin Mediates Uptake of Polybasic Drugs. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moestrup, S.K.; Birn, H.; Fischer, P.B.; Petersen, C.M.; Verroust, P.J.; Sim, R.B.; Christensen, E.I.; Nexø, E. Megalin-Mediated Endocytosis of Transcobalamin-Vitamin-B12 Complexes Suggests a Role of the Receptor in Vitamin-B12 Homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8612–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leheste, J.R.; Rolinski, B.; Vorum, H.; Hilpert, J.; Nykjaer, A.; Jacobsen, C.; Aucouturier, P.; Moskaug, J.O.; Otto, A.; Christensen, E.I.; et al. Megalin Knockout Mice as an Animal Model of Low Molecular Weight Proteinuria. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leheste, J.R.; Melsen, F.; Wellner, M.; Jansen, P.; Schlichting, U.; Renner-Müller, I.; Andreassen, T.T.; Wolf, E.; Bachmann, S.; Nykjaer, A.; et al. Hypocalcemia and Osteopathy in Mice with Kidney-Specific Megalin Gene Defect. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, H.H.; Hilpert, J.; Militz, D.; Zandler, V.; Jacobsen, C.; Roebroek, A.J.M.; Willnow, T.E. Functional Interaction of Megalin with the Megalinbinding Protein (MegBP), a Novel Tetratrico Peptide Repeat-Containing Adaptor Molecule. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, P.; Bock, H.H.; Herz, J. Integration of Endocytosis and Signal Transduction by Lipoprotein Receptors. Sci. STKE 2003, 2003, PE12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemesderfer, D. Regulated Intramembrane Proteolysis of Megalin: Linking Urinary Protein and Gene Regulation in Proximal Tubule? Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, L.E.; Wagner, M.C.; Sandoval, R.M.; Molitoris, B.A. The Proximal Tubule and Albuminuria: Really! J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapron, B.D.; Chapron, A.; Phillips, B.; Okoli, M.C.; Shen, D.D.; Kelly, E.J.; Himmelfarb, J.; Thummel, K.E. Reevaluating the Role of Megalin in Renal Vitamin D Homeostasis Using a Human Cell-Derived Microphysiological System. ALTEX 2018, 35, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowska, K.; Corcoran, A.; Grudzień, M.; Jakuszak, A.; Chodyński, M.; Kutner, A.; Marcinkowska, E. Investigating the Role of VDR and Megalin in Semi-Selectivity of Side-Chain Modified 19-nor Analogs of Vitamin D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willnow, T.E.; Hilpert, J.; Armstrong, S.A.; Rohlmann, A.; Hammer, R.E.; Burns, D.K.; Herz, J. Defective Forebrain Development in Mice Lacking Gp330/Megalin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8460–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, A.; Andreassen, T.K.; Spoelgen, R.; Raila, J.; Hubner, N.; Schulz, H.; Metzger, J.; Schweigert, F.J.; Luppa, P.B.; Nykjaer, A.; et al. Role of Endocytosis in Cellular Uptake of Sex Steroids. Cell 2005, 122, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinò, M.; Zheng, G.; Chiovato, L.; Pinchera, A.; Brown, D.; Andrews, D.; McCluskey, R.T. Role of Megalin (Gp330) in Transcytosis of Thyroglobulin by Thyroid Cells: A novel function in the control of thyroid hormone release. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7125–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinò, M.; Zheng, G.; McCluskey, R.T. Megalin (Gp330) Is an Endocytic Receptor for Thyroglobulin on Cultured Fisher Rat Thyroid Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12898–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermo, L.; Lustig, M.; Lefrancois, S.; Argraves, W.S.; Morales, C.R. Expression and Regulation of LRP-2/Megalin in Epithelial Cells Lining the Efferent Ducts and Epididymis during Postnatal Development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1999, 53, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argraves, W.S.; Morales, C.R. Immunolocalization of Cubilin, Megalin, Apolipoprotein J, and Apolipoprotein A-I in the Uterus and Oviduct. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2004, 69, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, S.; Hjälm, G.; Hellman, P.; Ek, B.; Junlin, C.; Rastad, J.; Klareskog, L.; Åkerström, G.; Rask, L. A Protein Involved in Calcium Sensing of the Human Parathyroid and Placental Cytotrophoblast Cells Belongs to the LDL-Receptor Protein Superfamily. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 212, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herz, J.; Hamann, U.; Rogne, S.; Myklebost, O.; Gausepohl, H.; Stanley, K.K. Surface Location and High Affinity for Calcium of a 500-Kd Liver Membrane Protein Closely Related to the LDL-Receptor Suggest a Physiological Role as Lipoprotein Receptor. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 4119–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, E.I.; Gliemann, J.; Moestrup, S.K. Renal Tubule Gp330 Is a Calcium Binding Receptor for Endocytic Uptake of Protein. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1992, 40, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. A Receptor-Mediated Pathway for Cholesterol Homeostasis. Science 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.M. Role of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor in Extracellular Calcium Homeostasis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.-L.; Crumrine, D.A.; Man, M.-Q.; Chang, W.; Elalieh, H.; You, M.; Elias, P.M.; Bikle, D.D. Ablation of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor in Keratinocytes Impairs Epidermal Differentiation and Barrier Function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, A.; Kállay, E. Cross Talk between the Calcium-Sensing Receptor and the Vitamin D System in Prevention of Cancer. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhlin, C.; Johansson, H.; Holmdahl, R.; Gylfe, E.; Larsson, R.; Rastad, J.; Akerström, G.; Klareskog, L. Monoclonal Anti-Parathyroid Antibodies Interfering with a Ca2+-Sensor of Human Parathyroid Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 143, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhlin, C.; Holmdahl, R.; Johansson, H.; Rastad, J.; Akerström, G.; Klareskog, L. Monoclonal Antibodies with Exclusive Reactivity against Parathyroid Cells and Tubule Cells of the Kidney. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 2990–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, P.; Ridefelt, P.; Juhlin, C.; Akerström, G.; Rastad, J.; Gylfe, E. Parathyroid-like Regulation of Parathyroid-Hormone-Related Protein Release and Cytoplasmic Calcium in Cytotrophoblast Cells of Human Placenta. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 293, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhlin, C.; Klareskog, L.; Nygren, P.; Ljunghall, S.; Gylfe, E.; Rastad, J.; Akerström, G. Hyperparathyroidism Is Associated with Reduced Expression of a Parathyroid Calcium Receptor Mechanism Defined by Monoclonal Antiparathyroid Antibodies. Endocrinology 1988, 122, 2999–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.; Wietzke, J.A.; Zinser, G.M.; Byrne, B.; Smith, K.; Narvaez, C.J. Vitamin D-3 Receptor as a Target for Breast Cancer Prevention. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2425S–2433S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowling, M.J.; Kemmis, C.M.; Taffany, D.A.; Welsh, J. Megalin-Mediated Endocytosis of Vitamin D Binding Protein Correlates with 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol Actions in Human Mammary Cells. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2754–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlon, T.M.; Taffany, D.A.; Welsh, J.; Rowling, M.J. Retinoids Modulate Expression of the Endocytic Partners Megalin, Cubilin, and Disabled-2 and Uptake of Vitamin D-Binding Protein in Human Mammary Cells. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.M.; Tallquist, M.D.; Rock, C.O.; Cooper, J.A. Dual Roles for the Dab2 Adaptor Protein in Embryonic Development and Kidney Transport. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, S.B.; Rowling, M.J. Vitamin D Transport Proteins Megalin and Disabled-2 Are Expressed in Prostate and Colon Epithelial Cells and Are Induced and Activated by All-Trans-Retinoic Acid. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, M.; Puglisi, D.A.; Davies, B.N.; Rybchyn, M.; Whitehead, N.P.; Brock, K.E.; Cole, L.; Gordon-Thomson, C.; Fraser, D.R.; Mason, R.S. Evidence for a Specific Uptake and Retention Mechanism for 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3022–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, M.; Gordon-Thomson, C.; Hoy, A.J.; Balaban, S.; Rybchyn, M.S.; Cole, L.; Su, Y.; Brennan-Speranza, T.C.; Fraser, D.R.; Mason, R.S. Uptake of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D by Muscle and Fat Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Luu, S.; Glowacki, J. Megalin Mediates 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Actions in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7684–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, G.J.; Anderson, P.H.; Findlay, D.M.; Welldon, K.J.; Vincent, C.; Zannettino, A.C.W.; O’Loughlin, P.D.; Morris, H.A. Metabolism of Vitamin D3 in Human Osteoblasts: Evidence for Autocrine and Paracrine Activities of 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. Bone 2007, 40, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, C.; Geuskens, M.; Ena, J.M.; Mishal, Z.; Macho, A.; Torres, J.M.; Uriel, J. Receptor-Mediated Uptake and Processing of Vitamin D-Binding Protein in Human B-Lymphoid Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10177–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolasco, P. Treatment Options of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 and 4: An Historic Review. Clin. Cases Min. Bone Metab. 2009, 6, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Grabner, A.; Schramm, K.; Silswal, N.; Hendrix, M.; Yanucil, C.; Czaya, B.; Singh, S.; Wolf, M.; Hermann, S.; Stypmann, J.; et al. FGF23/FGFR4-Mediated Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Is Reversible. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.L.; Brandenburg, V.M.; Brandemburg, V.M. Calcitriol Resistance in Hemodialysis Patients with Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusso, A.S. Vitamin D Receptor: Mechanisms for Vitamin D Resistance in Renal Failure. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2003, 63, S6–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, D.; Klement, R.J.; Schweiger, F.; Schweiger, B.; Spitz, J. Vitamin D Resistance as a Possible Cause of Autoimmune Diseases: A Hypothesis Confirmed by a Therapeutic High-Dose Vitamin D Protocol. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, F.; Shinki, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Inokami, T.; Hara, S.; Yamada, A.; Kurokawa, K.; Uchida, S. Gene Expression of Vitamin D Hydroxylase and Megalin in the Remnant Kidney of Nephrectomized Rats. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehnder, D.; Bland, R.; Walker, E.A.; Bradwell, A.R.; Howie, A.J.; Hewison, M.; Stewart, P.M. Expression of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-Hydroxylase in the Human Kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, N.H. Renal and Nonrenal 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-1alpha-Hydroxylases and Their Clinical Significance. J. Bone Min. Res. 1998, 13, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huby, A.-C.; Rastaldi, M.-P.; Caron, K.; Smithies, O.; Dussaule, J.-C.; Chatziantoniou, C. Restoration of Podocyte Structure and Improvement of Chronic Renal Disease in Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Renin. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosojima, M.; Sato, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Kaseda, R.; Soma, T.; Kobayashi, A.; Suzuki, A.; Kabasawa, H.; Takeyama, A.; Ikuyama, K.; et al. Regulation of Megalin Expression in Cultured Proximal Tubule Cells by Angiotensin II Type 1A Receptor- and Insulin-Mediated Signaling Cross Talk. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Han, J.; Zou, C.; Huang, W.; Yu, W.; Shan, X.; Lum, H.; Li, X.; Liang, G. Angiotensin II Induces Kidney Inflammatory Injury and Fibrosis through Binding to Myeloid Differentiation Protein-2 (MD2). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, A.; Martins, F.L.; Sene, L.B.; Shimizu, M.H.M.; Seguro, A.C.; Luchi, W.M.; Girardi, A.C.C. Urinary DPP4 Correlates with Renal Dysfunction, and DPP4 Inhibition Protects against the Reduction in Megalin and Podocin Expression in Experimental CKD. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2021, 320, F285–F296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimarchi, H.; Ceol, M.; Gianesello, L.; Priante, G.; Iotti, A.; Del Prete, D. Downregulation of Megalin, Cubilin, ClC-5 and Podocin in Fabry Nephropathy: Potential Implications in the Decreased Effectiveness of Enzyme Replacement Therapy. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Moradi, H.; Yuan, J.; Norris, K.; Vaziri, N.D. Renal Mass Reduction Results in Accumulation of Lipids and Dysregulation of Lipid Regulatory Proteins in the Remnant Kidney. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F1297–F1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, J.R.; Tan, W.; Daouk, G.; Teot, L.; Rosen, S.; Bennett, K.M.; Cwiek, A.; Nam, S.; Emma, F.; Jouret, F.; et al. Beyond the Tubule: Pathological Variants of LRP2, Encoding the Megalin Receptor, Result in Glomerular Loss and Early Progressive Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 319, F988–F999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgarten, M.; Gehr, T. Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection and Evaluation. AFP 2011, 84, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Storm, T.; Tranebjærg, L.; Frykholm, C.; Birn, H.; Verroust, P.J.; Nevéus, T.; Sundelin, B.; Hertz, J.M.; Holmström, G.; Ericson, K.; et al. Renal Phenotypic Investigations of Megalin-Deficient Patients: Novel Insights into Tubular Proteinuria and Albumin Filtration. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yu, W.R.; Carling, T.; Juhlin, C.; Rastad, J.; Ridefelt, P.; Akerström, G.; Hellman, P. Regulation of Gp330/Megalin Expression by Vitamins A and D. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 28, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusso, A.S.; Tokumoto, M. Defective Renal Maintenance of the Vitamin D Endocrine System Impairs Vitamin D Renoprotection: A Downward Spiral in Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Lu, K.-C. Mineral Bone Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrology 2018, 23, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusso, A.; González, E.A.; Martin, K.J. Vitamin D in Chronic Kidney Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusso, A.S. Kidney Disease and Vitamin D Levels: 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D, and VDR Activation. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2011, 1, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Kim, S.W. Vitamin D and Chronic Kidney Disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosworth, C.; de Boer, I.H. Impaired Vitamin D Metabolism in CKD. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Katayama, M.L.H.; de Lyra, E.C.; Welsh, J.; Campos, L.T.; Brentani, M.M.; Maciel, M.D.S.; Roela, R.A.; del Valle, P.R.; Góes, J.C.G.S.; et al. Transcriptional Effects of 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Physiological and Supra-Physiological Concentrations in Breast Cancer Organotypic Culture. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bemd, G.J.; Pols, H.A.; van Leeuwen, J.P. Anti-Tumor Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and Vitamin D Analogs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Kato, S.; Kubodera, N.; Okano, T. 22-Oxa-1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Inhibits Metastasis and Angiogenesis in Lung Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, S.; Raghavachari, N.; Muller, U.R.; Bao, Y.P.; Feldman, D. Vitamin D Growth Inhibition of Breast Cancer Cells: Gene Expression Patterns Assessed by CDNA Microarray. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 80, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.L.; de Azevedo, M.J.; Silveiro, S.P.; Canani, L.H.; Caramori, M.L.; Zelmanovitz, T. Diabetic Nephropathy: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.L.; Ternes, S.B.; Strand, K.A.; Rowling, M.J. Vitamin D Homeostasis Is Compromised Due to Increased Urinary Excretion of the 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol-Vitamin D-Binding Protein Complex in the Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rat. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E959–E967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowlkes, J.L.; Bunn, R.C.; Cockrell, G.E.; Clark, L.M.; Wahl, E.C.; Lumpkin, C.K.; Thrailkill, K.M. Dysregulation of the Intrarenal Vitamin D Endocytic Pathway in a Nephropathy-Prone Mouse Model of Type 1 Diabetes. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011, 2011, 269378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.M.; del Re, E.; Brown, D.; Lin, H.Y. Evidence for a Role of Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-Beta1 in the Induction of Postglomerular Albuminuria in Diabetic Nephropathy: Amelioration by Soluble TGF-Beta Type II Receptor. Diabetes 2007, 56, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, A.; Onozato, M.L.; Ha, H.; Kurihara, H.; Sakai, T.; Goto, A.; Fujita, T.; Endou, H. Reduced Albumin Reabsorption in the Proximal Tubule of Early-Stage Diabetic Rats. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 116, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Jo, C.-H.; Cockrell, G.E.; Moreau, C.S.; Fowlkes, J.L. Enhanced Excretion of Vitamin D Binding Protein in Type 1 Diabetes: A Role in Vitamin D Deficiency? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Nimmo, T.; Bunn, R.C.; Cockrell, G.E.; Moreau, C.S.; Mackintosh, S.; Edmondson, R.D.; Fowlkes, J.L. Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes Is Associated with Enhanced Excretion of the Endocytic Multiligand Receptors Megalin and Cubilin. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1266–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, S.; Hosojima, M.; Kaseda, R.; Kabasawa, H.; Yamamoto-Kabasawa, K.; Kurosawa, H.; Sato, H.; Iino, N.; Takeda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Significance of Urinary Full-Length and Ectodomain Forms of Megalin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Kuwahara, S.; Hosojima, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Kaseda, R.; Sarkar, P.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kabasawa, H.; Iida, T.; Goto, S.; et al. Exocytosis-Mediated Urinary Full-Length Megalin Excretion Is Linked With the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, N.; Inaba, M.; Ishimura, E.; Tsugawa, N.; Imanishi, Y.; Emoto, M.; Hirayama, Y.; Nakatani, S.; Saito, A.; Yamada, S. Significance of Urinary C-Megalin Excretion in Vitamin D Metabolism in Pre-Dialysis CKD Patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).