Effects of Carbohydrate and Protein Administration by Food Items on Strength Response after Training in Stable COPD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
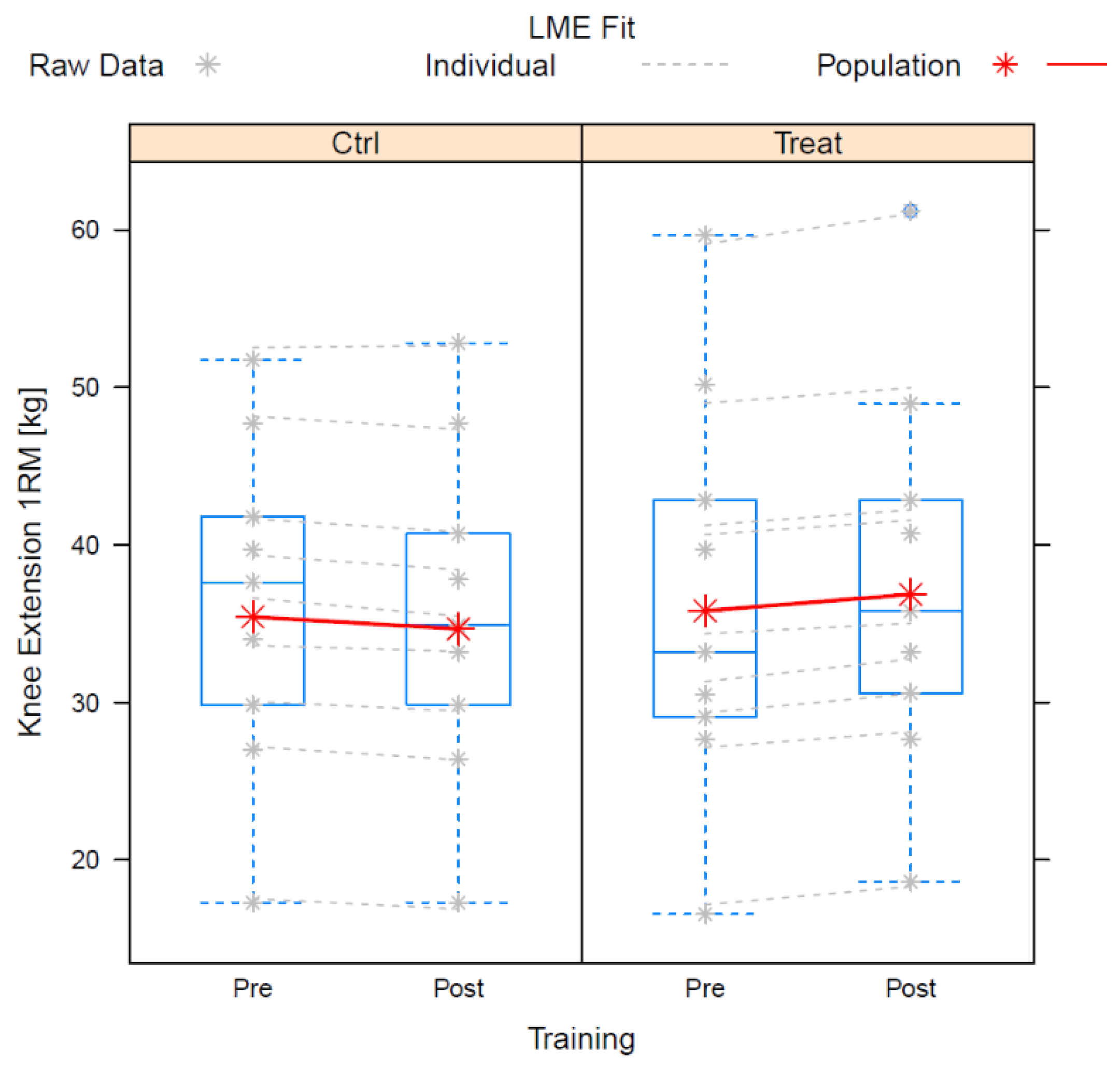
3.1. Quadriceps Strength
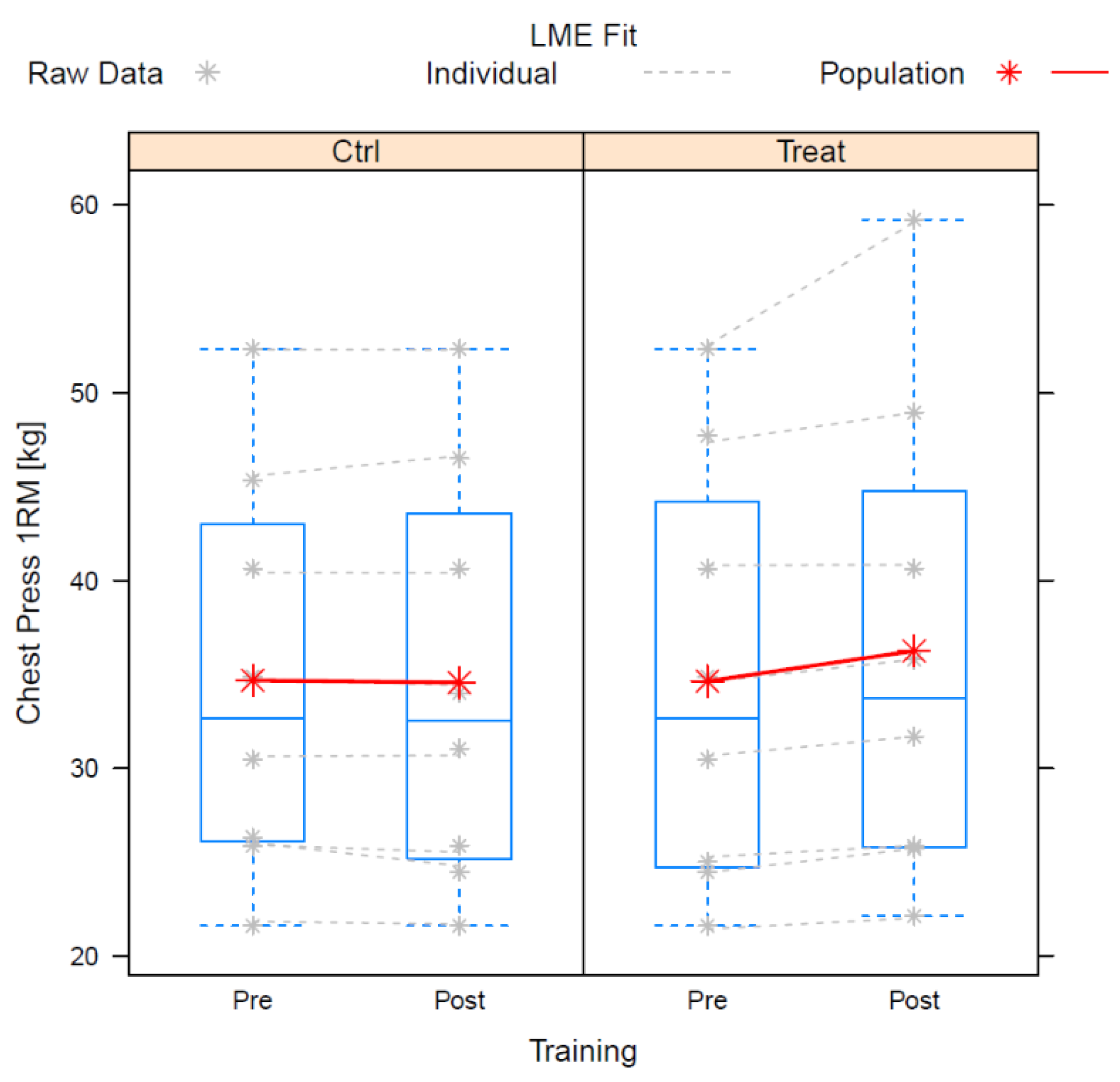
3.2. Chest Press
3.3. Other Measurements
3.4. Responsiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibson, G.J.; Loddenkemper, R.; Lundbäck, B.; Sibille, Y. Respiratory health and disease in Europe: The new European Lung White Book. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization, Active Ageing: A Policy Framework; Bundesministerium für soziale Sicherheit, Generationen und Konsumentenschutz, Kompetenzzentrum für Senioren- und Bevölkerungspolitik: Madrid, Spain, 2002.
- Maltais, F.; Decramer, M.; Casaburi, R.; Barreiro, E.; Burelle, Y.; Debigaré, R.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.R.; Franssen, F.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; Gea, J.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update on limb muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, e15–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gea, J.; Agustí, A.; Roca, J. Pathophysiology of muscle dysfunction in COPD. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillet, C.; Boirie, Y. Insulin resistance: A contributing factor to age-related muscle mass loss? Diabetes Metab. 2005, 31, 5S20–5S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weineck, J. Sportbiologie, 10th ed.; Auflage; Spitta: Balingen, Germany, 2010; ISBN 9783938509258. [Google Scholar]
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Gold Report: Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2019. Available online: www.goldcopd.org (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Gosselink, R.; Langer, D.; Burtin, C. KNGF-guideline for physical therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. R. Dutch Soc. Phys. Ther. 2008, 118, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Spruit, M.A.; Singh, S.J.; Garvey, C.; ZuWallack, R.; Nici, L.; Rochester, C.; Hill, K.; Holland, A.E.; Lareau, S.C.; Man, W.D.-C.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Key concepts and advances in pulmonary rehabilitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, e13–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundesärztekammer (BÄK); Kassenärztliche Bundesvereinigung (KBV); Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Medizinischen Fachgesellschaften (AWMF). Nationale Versorgungs Leitlinie COPD–Teilpublikation der Langfassung, 2. Auflage. Version 1. 2021 [Cited: 2022-05-22]. Available online: https://www.kbv.de/media/sp/copd-2aufl-vers1.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bui, K.-L.; Nyberg, A.; Rabinovich, R.; Saey, D.; Maltais, F. The Relevance of Limb Muscle Dysfunction in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review for Clinicians. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iepsen, U.W.; Jørgensen, K.J.; Ringbæk, T.; Hansen, H.; Skrubbeltrang, C.; Lange, P. A combination of resistance and endurance training increases leg muscle strength in COPD: An evidence-based recommendation based on systematic review with meta-analyses. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2015, 12, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Thériault, M.-E.; Debigaré, R.; Maltais, F. Should all patients with COPD be exercise trained? J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.; Deakin, V. Clinical Sports Nutrition, 5th ed.; McGraw Hill Education: North Ryde, NSW, Australia, 2015; ISBN 9781743073681. [Google Scholar]
- Kerksick, C.; Harvey, T.; Stout, J.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; Kreider, R.; Kalman, D.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Lopez, H.; Landis, J.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Nutrient timing. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2008, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isenmann, E.; Blume, F.; Bizjak, D.A.; Hundsdörfer, V.; Pagano, S.; Schibrowski, S.; Simon, W.; Schmandra, L.; Diel, P. Comparison of Pro-Regenerative Effects of Carbohydrates and Protein Administrated by Shake and Non-Macro-Nutrient Matched Food Items on the Skeletal Muscle after Acute Endurance Exercise. Nutrients 2019, 11, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.F.; Stratton, R.J.; Elia, M. Nutritional support in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Brooks, D.; Lacasse, Y.; Goldstein, R.S.; White, J. Nutritional supplementation for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002, 12, CD000998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhahir, A.M.; Rajeh, A.M.A.; Aldabayan, Y.S.; Drammeh, S.; Subbu, V.; Alqahtani, J.S.; Hurst, J.R.; Mandal, S. Nutritional supplementation during pulmonary rehabilitation in COPD: A systematic review. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2020, 17, 1479973120904953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.F.; Yang, I.A.; Chang, Y.-C.; Vaughan, A. Nutritional support in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): An evidence update. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S2230–S2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camillo, C.A.; Osadnik, C.R.; van Remoortel, H.; Burtin, C.; Janssens, W.; Troosters, T. Effect of “add-on” interventions on exercise training in individuals with COPD: A systematic review. ERJ Open Res. 2016, 2, 00078-2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-J.; Yang, T.-M.; Tsai, Y.-H. Nutritional supplementation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Horton, S.; Weir, P. (Eds.) The Masters Athlete: Understanding the Role of Sport and Exercise in Optimizing Aging; Routledge: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 9780203885512. [Google Scholar]
- Constantin, D.; Menon, M.K.; Houchen-Wolloff, L.; Morgan, M.D.; Singh, S.J.; Greenhaff, P.; Steiner, M.C. Skeletal muscle molecular responses to resistance training and dietary supplementation in COPD. Thorax 2013, 68, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.P.; Wouters, E.F.; Deutz, N.E.; Does, J.D.; Schols, A.M. Effects of exercise on amino acid metabolism in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trommelen, J.; Betz, M.W.; van Loon, L.J.C. The Muscle Protein Synthetic Response to Meal Ingestion Following Resistance-Type Exercise. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cote, C.G.; Casanova, C.; Marín, J.M.; Lopez, M.V.; Pinto-Plata, V.; de Oca, M.M.; Dordelly, L.J.; Nekach, H.; Celli, B.R. Validation and comparison of reference equations for the 6-min walk distance test. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westra, B.; de Wolf, S.; Legemaat, M.; Nyberg, A.; de Vaate, E.b.; van Etten-Jamaludin, F.; Klijn, P. Quality of resistance training description in COPD trials: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, OA2922. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin, M.E.; Swank, A.M.; Adams, K.J.; Barnard, K.L.; Berning, J.M.; Green, A. Cardiopulmonary responses, muscle soreness, and injury during the one repetition maximum assessment in pulmonary rehabilitation patients. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. 1999, 19, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinger, I.; Goodman, C.; Hare, D.L.; Jerums, G.; Toia, D.; Selig, S. The reliability of the 1RM strength test for untrained middle-aged individuals. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2009, 12, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, P.G.; Mathur, S.; Janaudis-Fereira, T.; Dolmage, T.E.; Goldstein, R.S.; Brooks, D. Measurement of peripheral muscle strength in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 31, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmler, W.K.; Lauber, D.; Wassermann, A.; Mayhew, J.L. Predicting maximal strength in trained postmenopausal woman. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Available online: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 3.1-159. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Swallow, E.B.; Reyes, D.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Man, W.D.-C.; Porcher, R.; Cetti, E.J.; Moore, A.J.; Moxham, J.; Polkey, M.I. Quadriceps strength predicts mortality in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 2007, 62, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelen, M.P.K.J.; Rutten, E.P.A.; de Castro, C.L.N.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Deutz, N.E.P. Supplementation of soy protein with branched-chain amino acids alters protein metabolism in healthy elderly and even more in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.P.K.J.; Rutten, E.P.A.; de Castro, C.L.N.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Deutz, N.E.P. Casein protein results in higher prandial and exercise induced whole body protein anabolism than whey protein in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2012, 61, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, J. Muskelregenerative Effekte von Protein-Kohlenhydrat-Shakes im Vergleich zu Nahrungsmitteln nach einer Einmaligen Kraftbelastung. Bachelor’s Thesis, German Sport University Cologne, Cologne, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Amarante do Nascimento, M.; Januário, R.S.B.; Gerage, A.M.; Mayhew, J.L.; Cheche Pina, F.L.; Cyrino, E.S. Familiarization and reliability of one repetition maximum strength testing in older women. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Avelar, A.; Salvador, E.P.; Cyrino, E.S. Influence of previous experience on resistance training on reliability of one-repetition maximum test. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, G.; Harre, D.; Krug, J.; Kaeubler, W.-D. (Eds.) Trainingslehre-Trainingswissenschaft: Leistung-Training-Wettkampf; Meyer & Meyer: Aachen, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783898993326. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Atherton, P.; Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J. Human muscle protein synthesis and breakdown during and after exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Hector, A.J.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Josse, A.R.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance exercise enhances myofibrillar protein synthesis with graded intakes of whey protein in older men. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Selby, A.; Rankin, D.; Patel, R.; Atherton, P.; Hildebrandt, W.; Williams, J.; Smith, K.; Seynnes, O.; Hiscock, N.; et al. Age-related differences in the dose-response relationship of muscle protein synthesis to resistance exercise in young and old men. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Blasio, F.; Di Gregorio, A.; de Blasio, F.; Bianco, A.; Bellofiore, B.; Scalfi, L. Malnutrition and sarcopenia assessment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease according to international diagnostic criteria, and evaluation of raw BIA variables. Respir. Med. 2018, 134, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, M.; Beck, A.M.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Lange, P. Insufficient intake of energy and protein is related to physical functional capacity among COPD patients referred to municipality based pulmonary rehabilitation. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 30, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, W. Optimale Sporternährung: Grundlagen für Leistung und Fitness im Sport, 4th ed.; Überarbeitete und Erweiterte Auflage; Spitta Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Balingen, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783943996739. [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson, D.; Smith, K.; Babraj, J.; Leese, G.; Waddell, T.; Atherton, P.; Wackerhage, H.; Taylor, P.M.; Rennie, M.J. Anabolic signaling deficits underlie amino acid resistance of wasting, aging muscle. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.P.; Wilson, J.M.; Austin, K.G.; Greer, B.K.; St John, N.; Panton, L.B. Effect of carbohydrate-protein supplement timing on acute exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2008, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Steele, J.; Bruce-Low, S.; Smith, D. Evidence-Based Resistance Training Recommendations. Med. Sport. 2011, 15, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, A.L.; Bauldoff, G.S.; Carlin, B.W.; Casaburi, R.; Emery, C.F.; Mahler, D.A.; Make, B.; Rochester, C.L.; ZuWallack, R.; Herrerias, C. Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Joint ACCP/AACVPR Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2007, 131, 4S–42S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brandt, J.; Spruit, M.A.; Hansen, D.; Franssen, F.M.; Derave, W.; Sillen, M.J.; Burtin, C. Changes in lower limb muscle function and muscle mass following exercise-based interventions in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A review of the English-language literature. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2018, 15, 182–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, S.D.; Taylor, N.F.; Paratz, J.D. Progressive resistance exercise improves muscle strength and may improve elements of performance of daily activities for people with COPD: A systematic review. Chest 2009, 136, 1269–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brandt, J.; Spruit, M.A.; Derave, W.; Hansen, D.; Vanfleteren, L.E.G.W.; Burtin, C. Changes in structural and metabolic muscle characteristics following exercise-based interventions in patients with COPD: A systematic review. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 521–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Training Variable | Realization in Training Intervention |
|---|---|
| Muscle actions | Dynamic with 30% increased eccentric weight |
| Intensity (loading) | momentary muscle failure after 1 min |
| Volume | 2 sets of machine circle with 8 machines 1 min of each exercise |
| Velocity of muscle action | Breathing frequency |
| Exercise selection (in order) | Electronic resistance machines (circle training): rowing, leg press, back extensor, abdominal flexor, knee flexor, knee extensor, bench press, lat pull-down |
| Rest period between sets | 1–5 Min |
| Rest periods between exercises | 1 Min |
| Nutrient | Sour-Milk Cheese (100 g) | White Bun (60 g) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | <0.1 g | 31.8 g | 31.8 g |
| Protein | 30 g | 4.74 g | 34.74 g |
| Fat | 0.5 g | 1.26 g | 1.76 g |
| Est. | Std. Err. | DF | t-Value | p-Value | Cohen’s d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 35.43 | 3.755 | 24 | 9.434 | 0.000 | - |
| Training Post | −0.765 | 0.484 | 24 | −1.58 | 0.127 | −0.645 |
| (Food) | 0.384 | 0.983 | 24 | 0.391 | 0.699 | 0.16 |
| Training Post × Food | 1.804 | 0.681 | 24 | 2.65 | 0.014 | 1.082 |
| Est. | Std. Err. | DF | t-Value | p-Value | Cohen’s d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 34.69 | 3.773 | 21 | 9.194 | 0.000 | - |
| Training Post | −0.125 | 0.319 | 21 | −0.391 | 0.699 | −0.171 |
| (Food) | −0.044 | 0.417 | 21 | −0.105 | 0.917 | −0.046 |
| Training Post × Food | 1.731 | 0.82 | 21 | 2.112 | 0.047 | 0.922 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huhn, A.; Flenker, U.; Diel, P. Effects of Carbohydrate and Protein Administration by Food Items on Strength Response after Training in Stable COPD. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173565
Huhn A, Flenker U, Diel P. Effects of Carbohydrate and Protein Administration by Food Items on Strength Response after Training in Stable COPD. Nutrients. 2022; 14(17):3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173565
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuhn, Andrea, Ulrich Flenker, and Patrick Diel. 2022. "Effects of Carbohydrate and Protein Administration by Food Items on Strength Response after Training in Stable COPD" Nutrients 14, no. 17: 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173565
APA StyleHuhn, A., Flenker, U., & Diel, P. (2022). Effects of Carbohydrate and Protein Administration by Food Items on Strength Response after Training in Stable COPD. Nutrients, 14(17), 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173565






