Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Chinese Community-Dwelling Adults with and without Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
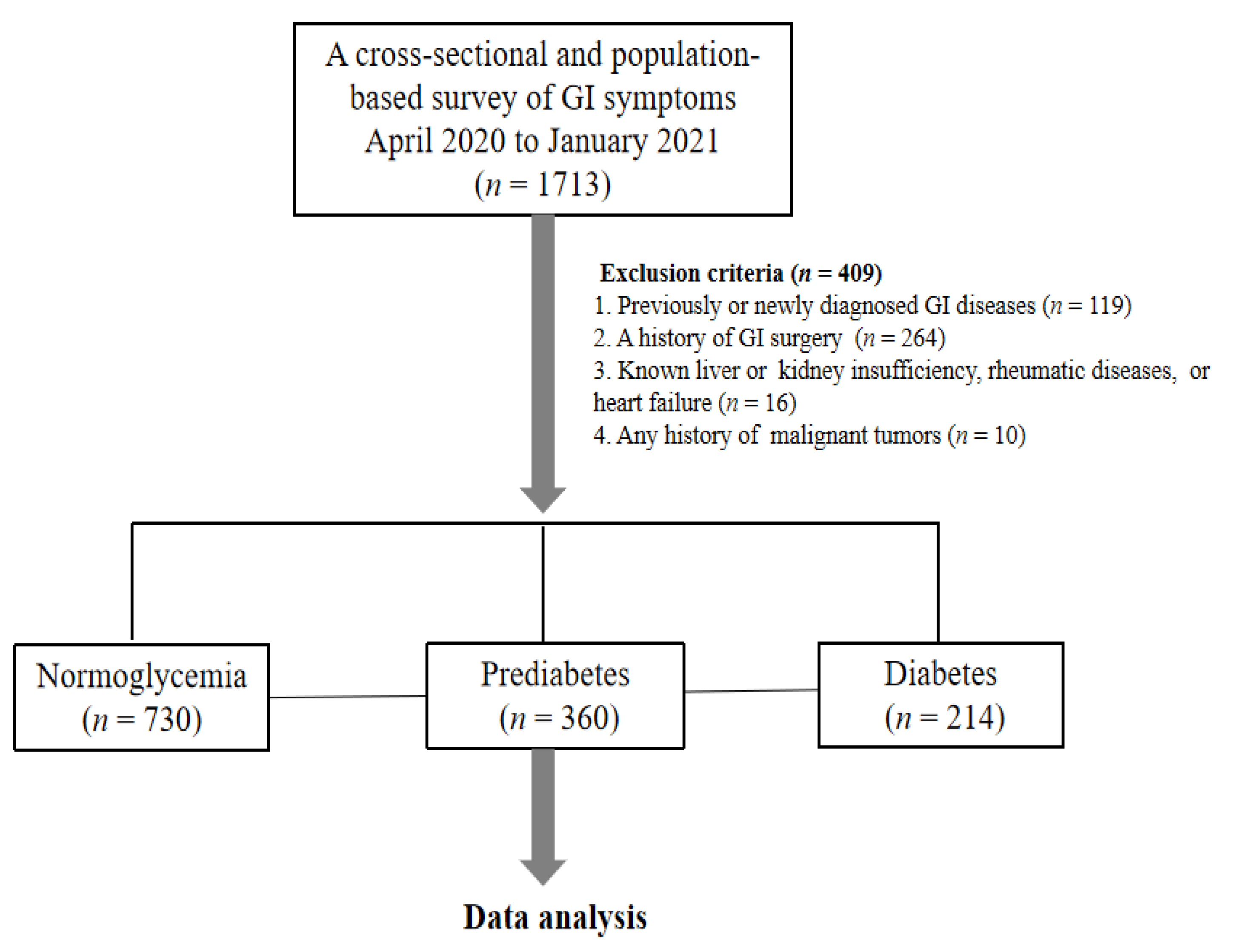
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Definitions of Glycemic Status and Diabetic Complications
2.4. Assessment of GI Symptoms
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. GI Symptoms in Participants with Normoglycemia, Prediabetes and Diabetes
3.3. Potential Factors Associated with GI Symptoms
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Drossman, D.A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Simren, M.; Tack, J.; Whitehead, W.E.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Fang, X.; Fukudo, S.; et al. Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 99–114.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Hasler, W.L. Rome IV-Functional GI Disorders: Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.T.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Talley, N.J.; Horowitz, M. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Diabetes: Prevalence, Assessment, Pathogenesis, and Management. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Aros, S.; Locke, G.R.; Camilleri, M., 3rd; Talley, N.J.; Fett, S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Melton, L.J., 3rd. Obesity is associated with increased risk of gastrointestinal symptoms: A population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Leemon, M.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: A population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Hammer, J.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. GI symptoms in diabetes mellitus are associated with both poor glycemic control and diabetic complications. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Ko, S.Y.; Hong, S.N.; Sung, I.K.; Shim, C.S.; Song, K.H.; Kim, D.L.; Kim, S.K.; Oh, J. Diabetic factors associated with gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbaten, M.; Madad, L.; Baladast, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aliasgarzadeh, A. Gastrointestinal signs and symptoms among persons with diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2011, 4, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Florez, H.; Luo, J.; Castillo-Florez, S.; Mitsi, G.; Hanna, J.; Tamariz, L.; Palacio, A.; Nagendran, S.; Hagan, M. Impact of metformin-induced gastrointestinal symptoms on quality of life and adherence in patients with type 2 diabetes. Postgrad. Med. 2010, 122, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.; Schiller, L.R. Disorders of gastrointestinal motility associated with diabetes mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, D.; Locke, G.R.; Camilleri, M.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Yawn, B.P.; Leibson, C.; Melton, L.J. Gastrointestinal tract symptoms among persons with diabetes mellitus in the community. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2808–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Talley, N.J.; Cross, S.; Jones, M.; Hammer, J.; Giles, N.; Horowitz, M. Development and validation of the Diabetes Bowel Symptom Questionnaire. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2003, 17, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.; Harding, P.E.; Chatterton, B.E.; Collins, P.J.; Shearman, D.J. Acute and chronic effects of domperidone on gastric emptying in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1985, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, G.T.; Chan, W.B.; Chan, J.C.; Tsang, L.W.; Cockram, C.S. Gastrointestinal symptoms in Chinese patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 1999, 16, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xie, B.; Qiu, S.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tu, P. Non-lab and semi-lab algorithms for screening undiagnosed diabetes: A cross-sectional study. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Du, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Cai, M.; Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Sun, Z. Exploration and Validation of the Performance of Hemoglobin A1c in Detecting Diabetes in Community-Dwellers With Hypertension. Ann. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, H.; Wen, L.; Wang, F.; Guo, H.; Wang, B.; et al. Novel clusters of newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes and their association with diabetic retinopathy: A 3-year follow-up study. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs—An extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Ophthalmology 1991, 98 (Suppl. 5), 786–806.
- Talley, N.J.; Stanghellini, V.; Heading, R.C.; Koch, K.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Tytgat, G.N. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gut 1999, 45 (Suppl 2), II37–II42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummond, N.R.; Locke, G.R., 3rd; Choung, R.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Talley, N.J. Effects of Birth Cohorts on the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Support Early-Life Risk Factors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Lee, O.Y.; Shim, S.G.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, K.N.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S. The Differences in Prevalence and Sociodemographic Characteristics of Irritable Bowel Syndrome According to Rome II and Rome III. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 16, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yang, Y.S.; Cui, L.H.; Zhao, K.B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Peng, L.H.; Guo, X.; Sun, G.; Shang, J.; Wang, W.F. Subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome on Rome III criteria: A multicenter study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.Y.; Fang, X.C.; Li, X.Q.; Fei, G.J. Ethnic differences in genetic polymorphism associated with irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, J. The Association Between Fasting C-peptide and Gastrointestinal Symptoms of Gastroparesis in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spångéus, A.; El-Salhy, M.; Suhr, O.; Eriksson, J.; Lithner, F. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in young and middle-aged diabetic patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 34, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Rizvi, A.; Jahan, F.; Rabbani, F.; Islam, N.; Khan, M.H.; Masood, R. Poor glycaemic control is the major factor associated with increased frequency of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with diabetes mellitus. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2007, 57, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, P.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Chiu, H.M.; Chen, C.C.; Liao, W.C.; Tu, C.H.; Yang, W.S.; Wu, M.S. Association of diabetes and HbA1c levels with gastrointestinal manifestations. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Hong, X.; Jiang, X.; Su, Q.; Zhao, D.; Wu, X.; Ji, L. Effects of body mass index or dosage on gastrointestinal disorders associated with extended-release metformin in type 2 diabetes: Sub-analysis of a Phase IV open-label trial in Chinese patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2016, 10, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Oral hypoglycaemic drugs and gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2001, 15, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderquist, F.; Syk, M.; Just, D.; Kurbalija Novicic, Z.; Rasmusson, A.J.; Hellström, P.M.; Ramklint, M.; Cunningham, J.L. A cross-sectional study of gastrointestinal symptoms, depressive symptoms and trait anxiety in young adults. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Normoglycemia (n = 730) | Prediabetes (n = 360) | Diabetes (n = 214) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 460 (63.0%) | 225 (62.5%) | 121 (56.5%) | 0.22 |
| Age (y) | 52.1 ± 9.9 | 55.7 ± 8.4 ** | 56.9 ± 8.8 ** | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.0 ± 11.1 | 26.2 ± 10.4 | 26.2 ± 3.7 | 0.09 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 83.9 ± 9.8 | 87.3 ± 9.3 ** | 89.1 ± 9.4 ** | 0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 130.7 ± 18.4 | 137.7 ± 17.9 ** | 141.8 ± 20.3 ** | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 82.7 ± 12.3 | 86.4 ± 11.4 ** | 85.3 ± 14.1 * | <0.001 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 71.4 ± 11.0 | 72.5 ± 10.9 | 74.7 ± 11.4 ** | 0.001 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 5.6 ± 0.5 ** | 7.3 ± 1.8 ** | <0.001 |
| 2hPG (mmol/L) a | 6.2 ± 1.0 | 8.8 ± 1.2 ** | 12.8 ± 2.5 ** | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 5.7 ± 0.5 ** | 6.8 ± 1.3 ** | <0.001 |
| Cr (umol/L) | 56.6 ± 12.9 | 55.8 ± 13.7 | 57.2 ± 16.1 | 0.49 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.6 ± 0.8 | 4.7 ± 0.9 * | 4.8 ± 0.9 ** | 0.002 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.2 (0.9, 1.7) | 1.6 (1.1, 2.1) ** | 1.5 (1.1, 2.1) ** | <0.001 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 0.46 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 0.07 |
| Current Smoking, n (%) | 128 (17.5%) | 51 (14.2%) | 35 (16.4%) | 0.37 |
| Alcohol intake | 0.48 | |||
| None, n (%) | 537 (73.6%) | 247 (68.6%) | 149 (69.6%) | |
| Less than 10 g per week, n (%) | 66 (9.0%) | 36 (10.0%) | 17 (7.9%) | |
| 10–100 g per week, n (%) | 77 (10.5%) | 46 (12.8%) | 31 (14.5%) | |
| 100–300 g per week, n (%) | 16 (2.2%) | 15 (4.2%) | 8 (3.7%) | |
| More than 300 g per week, n (%) | 34 (4.7%) | 16 (4.4%) | 9 (4.2%) | |
| Newly diagnosed diabetes | NA | NA | 123 (57.5%) | |
| Previously diagnosed diabetes | NA | NA | 91 (42.5%) | |
| Duration of known diabetes (years) b | NA | NA | 6.5 ± 5.4 | |
| Glucose-lowering therapies c | NA | NA | ||
| Oral hypoglycemic agents only, n (%) | NA | NA | 46 (50.5%) | |
| Insulin ± oral hypoglycemic agents, n (%) | NA | NA | 12 (13.2%) | |
| Lifestyle measures only, n (%) | NA | NA | 18 (19.8%) | |
| Unclassified, n (%) | NA | NA | 15 (16.5%) | |
| Diabetic complications | ||||
| Albuminuria d | NA | NA | 71 (34.9%) | |
| Diabetic retinopathy e | NA | NA | 22 (10.8%) |
| Total (n = 1304) | Normoglycemia (n = 730) | Prediabetes (n = 360) | Diabetes (n = 214) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At least one GI symptom, n (%) | 243 (18.6%) | 129 (17.7%) | 71 (19.7%) | 43 (20.1%) | 0.59 |
| Abdominal pain, n (%) | 15 (1.2%) | 9 (1.2%) | 4 (1.1%) | 2 (0.9%) | 1.00 |
| Irritable bowel syndrome, n (%) | 28 (2.1%) | 10 (1.4%) | 14 (3.9%) * | 4 (1.9%) | 0.025 |
| Ulcer-like dyspepsia, n (%) | 15 (1.2%) | 9 (1.2%) | 4 (1.1%) | 2 (0.9%) | 1.00 |
| Early satiety, n (%) | 29 (2.2%) | 14 (1.9%) | 10 (2.8%) | 5 (2.3%) | 0.66 |
| Postprandial fullness, n (%) | 23 (1.8%) | 13 (1.8%) | 5 (1.4%) | 5 (2.3%) | 0.71 |
| Nausea, n (%) | 7 (0.5%) | 4 (0.5%) | 3 (0.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.44 |
| Retching, n (%) | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.69 |
| Vomiting, n (%) | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.69 |
| Loss of appetite, n (%) | 12 (0.9%) | 8 (1.1%) | 2 (0.6%) | 2 (0.9%) | 0.72 |
| Abdominal fullness or bloating, n (%) | 37 (2.8%) | 21 (2.9%) | 11 (3.1%) | 5 (2.3%) | 0.89 |
| Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, n (%) | 38 (2.9%) | 22 (3.0%) | 8 (2.2%) | 8 (3.7%) | 0.56 |
| Dysphagia, n (%) | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.69 |
| Diarrhea, n (%) | 79 (6.1%) | 43 (5.9%) | 23 (6.4%) | 13 (6.1%) | 0.95 |
| Constipation, n (%) | 72 (5.5%) | 38 (5.2%) | 22 (6.1%) | 12 (5.6%) | 0.83 |
| Fecal incontinence, n (%) | 9 (0.7%) | 7 (1.0%) | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (0.5%) | 0.53 |
| Symptom complex | |||||
| Upper GI symptoms €, n (%) | 102 (7.8%) | 56 (7.7%) | 28 (7.8%) | 18 (8.4%) | 0.94 |
| Lower GI symptoms ∳, n (%) | 153 (11.7%) | 83 (11.4%) | 44 (12.2%) | 26 (12.1%) | 0.89 |
| Groups | Total Male n = 498 Female n = 806 | Normoglycemia Male n = 270 Female n = 460 | Prediabetes Male n = 135 Female n = 225 | Diabetes Male n = 93 Female n = 121 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | |||||||
| At least one GI symptom, n (%) | Male | 80 (16.1%) | 38 (14.1%) | 20 (14.8%) | 22 (23.7%) | 0.09 | |
| Female | 163 (20.2%) | 91 (19.8%) | 51 (22.7%) | 21 (17.4%) | 0.47 | ||
| Abdominal pain, n (%) | Male | 3 (0.6%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.2%) | 0.15 | |
| Female | 12 (1.5%) | 8 (1.7%) | 4 (1.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.39 | ||
| Irritable bowel syndrome, n (%) | Male | 6 (1.2%) | 2 (0.7%) | 3 (2.2%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.41 | |
| Female | 22 (2.7%) | 8 (1.7%) | 11 (4.9%) | 3 (2.5%) | 0.06 | ||
| Ulcer-like dyspepsia, n (%) | Male | 3 (0.6%) | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (0.7%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.76 | |
| Female | 12 (1.5%) | 8 (1.7%) | 3 (1.3%) | 1 (0.8%) | 0.92 | ||
| Early satiety, n (%) | Male | 5 (1.0%) | 2 (0.7%) | 2 (1.5%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.84 | |
| Female | 24 (3.0%)¶ | 12 (2.6%) | 8 (3.6%) | 4 (3.3%) | 0.77 | ||
| Postprandial fullness, n (%) | Male | 6 (1.2%) | 4 (1.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.2%) | 0.22 | |
| Female | 17 (2.1%) | 9 (2.0%) | 5 (2.2%) | 3 (2.5%) | 0.84 | ||
| Nausea, n (%) | Male | 3 (0.6%) | 2 (0.7%) | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 | |
| Female | 4 (0.5%) | 2 (0.4%) | 2 (0.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.63 | ||
| Retching, n (%) | Male | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 | |
| Female | 1 (0.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.43 | ||
| Vomiting, n (%) | Male | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | / | |
| Female | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.68 | ||
| Loss of appetite, n (%) | Male | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 | |
| Female | 11 (1.4%)¶ | 7 (1.5%) | 2 (0.9%) | 2 (1.7%) | 0.76 | ||
| Abdominal fullness or bloating, n (%) | Male | 9 (1.8%) | 2 (0.7%) | 4 (3.0%) | 3 (3.2%) | 0.09 | |
| Female | 28 (3.5%) | 19 (4.1%) # | 7 (3.1%) | 2 (1.7%) | 0.39 | ||
| Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, n (%) | Male | 16 (3.2%) | 10 (3.7%) | 3 (2.2%) | 3 (3.2%) | 0.79 | |
| Female | 22 (2.7%) | 12 (2.6%) | 5 (2.2%) | 5 (4.1%) | 0.57 | ||
| Dysphagia, n (%) | Male | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | / | |
| Female | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.68 | ||
| Diarrhea, n (%) | Male | 32 (6.4%) | 16 (5.9%) | 8 (5.9%) | 8 (8.6%) | 0.64 | |
| Female | 47 (5.8%) | 27 (5.9%) | 15 (6.7%) | 5 (4.1%) | 0.63 | ||
| Constipation, n (%) | Male | 16 (3.2%) | 6 (2.2%) | 5 (3.7%) | 5 (5.4%) | 0.27 | |
| Female | 56 (6.9%) # | 32 (7.0%) # | 17 (7.6%) | 7 (5.8%) | 0.83 | ||
| Fecal incontinence, n (%) | Male | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 | |
| Female | 8 (1.0%) | 6 (1.3%) | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (0.8%) | 0.78 | ||
| Symptom complex | |||||||
| Upper GI symptoms €, n (%) | Male | 35 (7.0%) | 17 (6.3%) | 10 (7.4) | 8(8.6%) | 0.74 | |
| Female | 67 (8.3%) | 39 (8.5%) | 18 (8.0%) | 10 (8.3%) | 0.98 | ||
| Lower GI symptoms ∳, n (%) | Male | 48 (9.6%) | 23 (8.5%) | 12 (8.9%) | 13 (14.0%) | 0.29 | |
| Female | 105 (13.0%) | 60 (13.0%) | 32 (14.2%) | 13 (10.7%) | 0.66 | ||
| Groups | Total Age < 65 n = 1126 Age ≥ 65 n = 178 | Normoglycemia Age < 65 n = 657 Age ≥ 65 n = 73 | Prediabetes Age < 65 n = 301 Age ≥ 65 n = 59 | Diabetes Age < 65 n = 168 Age ≥ 65 n = 46 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | |||||||
| At least one GI symptom, n (%) | Age < 65 | 204 (18.1%) | 119 (18.1%) | 58 (19.3%) | 27 (16.1%) | 0.69 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 39 (21.9%) | 10 (13.7%) | 13 (22.0%) | 16 (34.8%) *,⟂ | 0.03 | ||
| Abdominal pain, n (%) | Age < 65 | 14 (1.2%) | 9 (1.4%) | 3 (1.0%) | 2 (1.2%) | 0.93 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 1 (0.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.59 | ||
| Irritable bowel syndrome, n (%) | Age < 65 | 23 (2.0%) | 10 (1.5%) | 11 (3.7%) | 2 (1.2%) | 0.07 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 5 (2.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3(5.1%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.11 | ||
| Ulcer-like dyspepsia, n (%) | Age < 65 | 12 (1.1%) | 9 (1.4%) | 2 (0.7%) | 1 (0.6%) | 0.65 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 3 (1.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (3.4%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.35 | ||
| Early satiety, n (%) | Age < 65 | 25 (2.2%) | 13 (2.0%) | 8 (2.7%) | 4 (2.4%) | 0.79 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 4 (2.2%) | 1 (1.4%) | 2 (3.4%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.82 | ||
| Postprandial fullness, n (%) | Age < 65 | 21 (1.9%) | 13 (2.0%) | 4 (1.3%) | 4 (2.4%) | 0.68 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 2 (1.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.7%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.51 | ||
| Nausea, n (%) | Age < 65 | 6 (0.5%) | 3 (0.5%) | 3 (1.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.50 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 1 (0.6%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 | ||
| Retching, n (%) | Age < 65 | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.66 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | / | ||
| Vomiting, n (%) | Age < 65 | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.66 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | / | ||
| Loss of appetite, n (%) | Age < 65 | 10 (0.9%) | 7 (1.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | 2 (1.2%) | 0.55 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 2 (1.1%) | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 | ||
| Abdominal fullness or bloating, n (%) | Age < 65 | 32 (2.8%) | 20 (3.0%) | 8 (2.7%) | 4 (2.4%) | 0.88 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 5 (2.8%) | 1 (1.4%) | 3 (5.1%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.53 | ||
| Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, n (%) | Age < 65 | 31 (2.8%) | 18 (2.7%) | 8 (2.7%) | 5 (3.0%) | 0.98 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 7 (3.9%) | 4 (5.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (6.5%) | 0.11 | ||
| Dysphagia, n (%) | Age < 65 | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.66 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | / | ||
| Diarrhea, n (%) | Age < 65 | 70 (6.2%) | 41 (6.2%) | 18 (6.0%) | 11 (6.5%) | 0.97 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 9 (5.1%) | 2 (2.7%) | 5 (8.5%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.35 | ||
| Constipation, n (%) | Age < 65 | 58 (5.2%) | 36 (5.5%) | 18 (6.0%) | 4 (2.4%) | 0.20 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 14 (7.9%) | 2 (2.7%) | 4 (6.8%) | 8 (17.4%) *,⟂ | 0.019 | ||
| Fecal incontinence, n (%) | Age < 65 | 7 (0.6%) | 5 (0.8%) | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (0.6%) | 0.87 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 2 (1.1%) | 2 (2.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.34 | ||
| Symptom complex | |||||||
| Upper GI symptoms €, n (%) | Age < 65 | 86 (7.6%) | 49 (7.5%) | 24 (8.0%) | 13 (7.7%) | 0.96 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 16 (9.0%) | 7 (9.6%) | 4 (6.8%) | 5 (10.9%) | 0.75 | ||
| Lower GI symptoms ∳, n (%) | Age < 65 | 129 (11.5%) | 77 (11.7%) | 36 (12.0%) | 16 (9.5%) | 0.69 | |
| Age ≥ 65 | 24 (13.5%) | 6 (8.2%) | 8 (13.6%) | 10 (21.7%)∓ | 0.11 | ||
| At least one GI Symptom | Abdominal Pain | Irritable Bowel Syndrome | Ulcer-like Dyspepsia | Upper GI Symptoms | Lower GI Symptoms | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Male | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||||
| Female | 1.36 (1.01, 1.84) | 0.04 | 2.51 (0.69, 9.07) | 0.16 | 2.39 (0.95, 5.99) | 0.06 | 2.63 (0.72, 9.69) | 0.15 | 1.21 (0.79, 1.87) | 0.38 | 1.44 (1.003, 2.08) | 0.048 |
| Age (years) | 1.04 (1.02, 1.05) | <0.001 | 1.05 (0.99, 1.12) | 0.11 | 1.03 (0.99, 1.08) | 0.14 | 1.05 (0.98, 1.11) | 0.15 | 1.04 (1.01, 1.06) | 0.004 | 1.03 (1.01, 1.05) | 0.005 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.99 (0.97, 1.02) | 0.49 | 1.00 (0.95, 1.05) | 0.97 | 1.01 (0.98, 1.03) | 0.62 | 0.99 (0.87, 1.13) | 0.87 | 0.97 (0.91, 1.03) | 0.35 | 0.99 (0.97, 1.02) | 0.73 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 1.04 (0.87, 1.24) | 0.74 | 0.51 (0.20, 1.26) | 0.14 | 0.65 (0.37, 1.14) | 0.13 | 0.52 (0.23, 1.16) | 0.11 | 1.12 (0.89, 1.42) | 0.33 | 1.04 (0.85, 1.28) | 0.69 |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.87 (0.67, 1.13) | 0.33 | 1.46 (0.59, 3.58) | 0.41 | 1.48 (0.81, 2.71) | 0.20 | 1.73 (0.84, 3.59) | 0.14 | 0.78 (0.54, 1.14) | 0.20 | 0.92 (0.68, 1.25) | 0.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, M.; Wu, T.; Zhou, X.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L.; Qiu, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, D.; Rayner, C.K.; et al. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Chinese Community-Dwelling Adults with and without Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173506
Sang M, Wu T, Zhou X, Horowitz M, Jones KL, Qiu S, Guo H, Wang B, Wang D, Rayner CK, et al. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Chinese Community-Dwelling Adults with and without Diabetes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(17):3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173506
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Miaomiao, Tongzhi Wu, Xiaoying Zhou, Michael Horowitz, Karen L. Jones, Shanhu Qiu, Haijian Guo, Bei Wang, Donglei Wang, Christopher K. Rayner, and et al. 2022. "Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Chinese Community-Dwelling Adults with and without Diabetes" Nutrients 14, no. 17: 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173506
APA StyleSang, M., Wu, T., Zhou, X., Horowitz, M., Jones, K. L., Qiu, S., Guo, H., Wang, B., Wang, D., Rayner, C. K., & Sun, Z. (2022). Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Chinese Community-Dwelling Adults with and without Diabetes. Nutrients, 14(17), 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173506








