Astaxanthin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and H. pylori Infection
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.5. Invasion Assay
2.6. Wound-Healing Assay
2.7. Measurement of Cell Viability
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
2.10. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
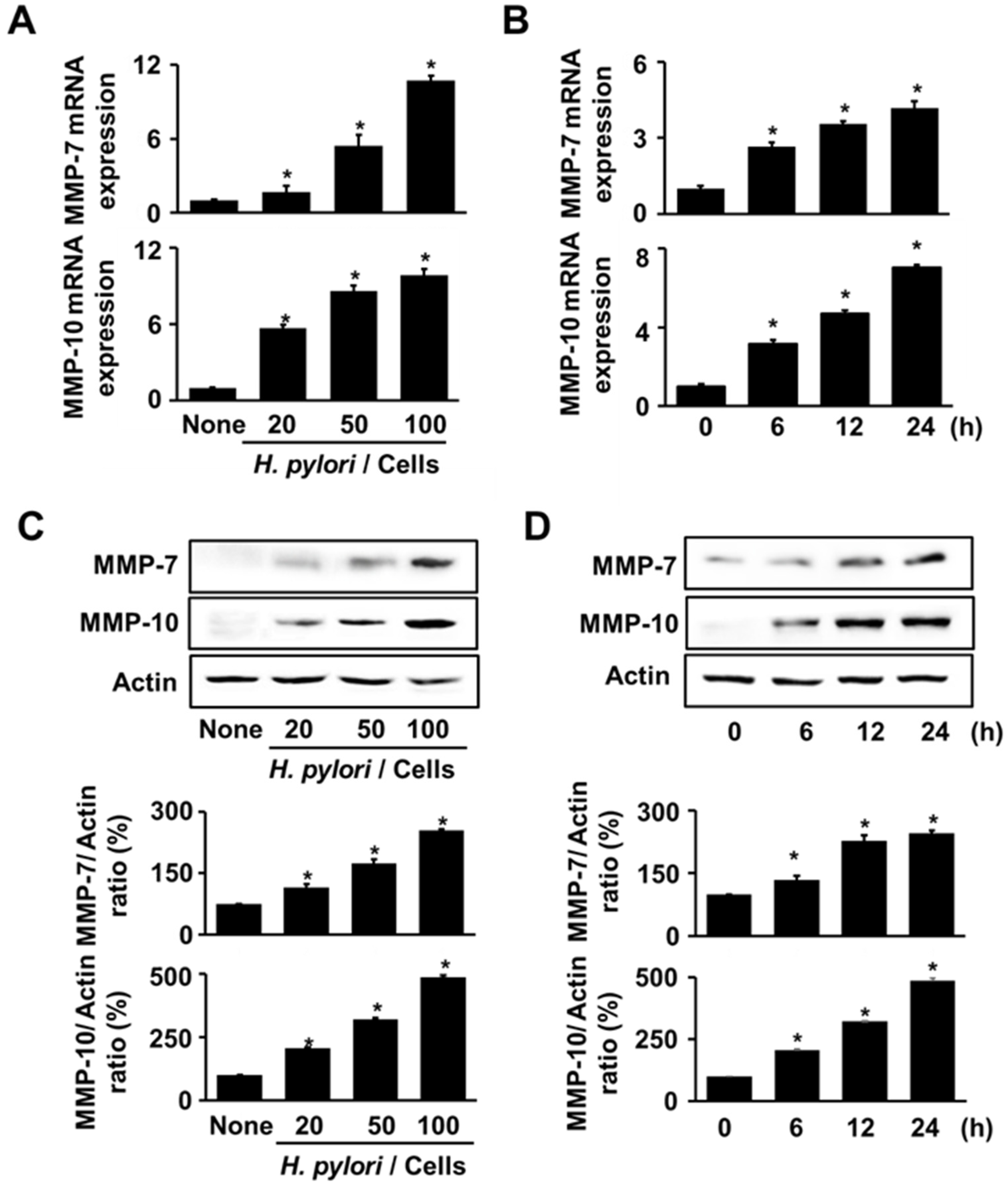
3.1. H. pylori Increases the Expression of MMP-7 and MMP-10 in AGS Cells
3.2. H. pylori Activates PI3K, AKT, mTOR, and NF-kB in AGS Cells
3.3. Astaxanthin Suppresses Expression of MMP-7 and MMP-10 in H. pylori-Infected Cells
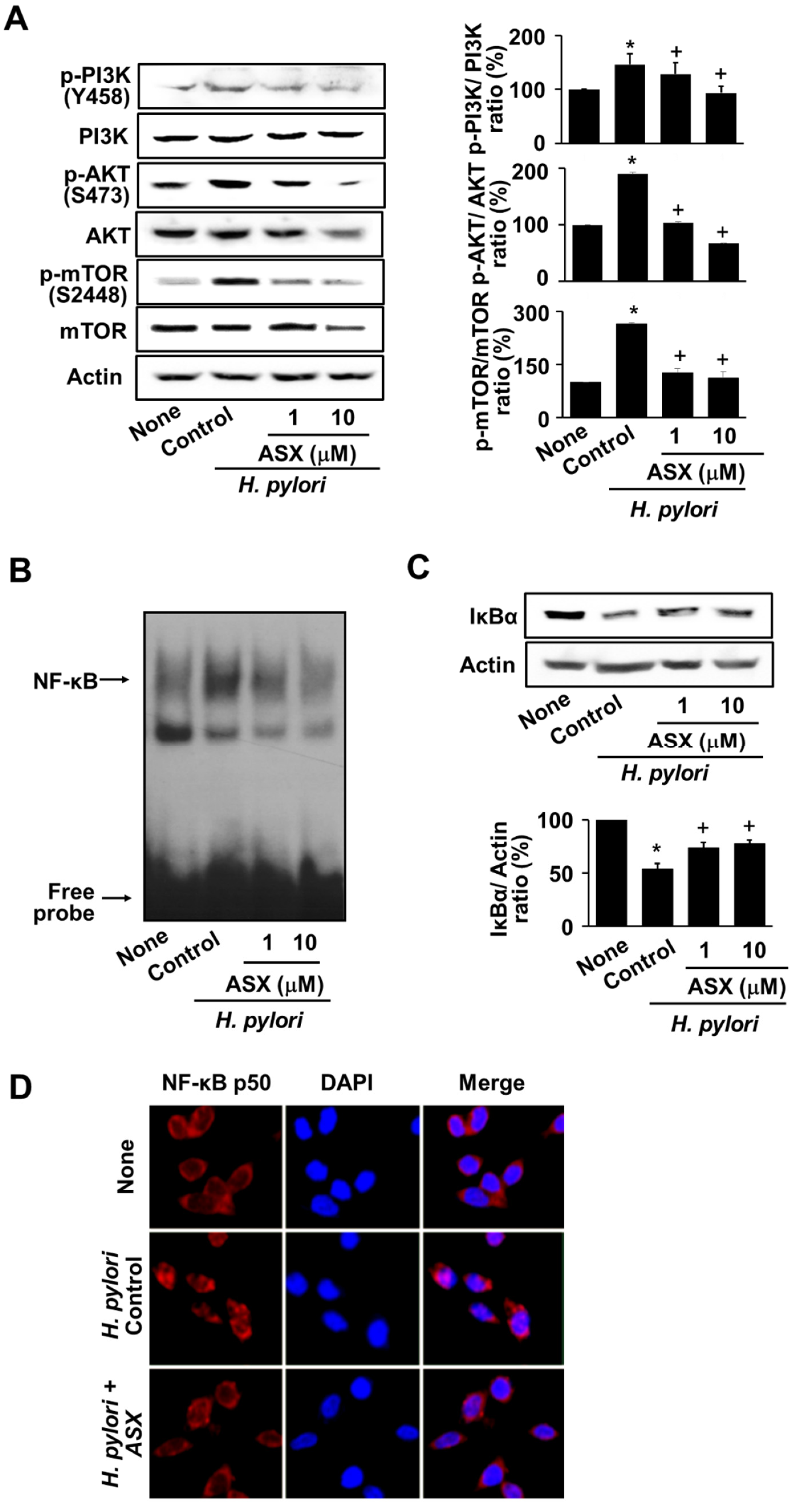
3.4. Astaxanthin Suppresses the Activation of PI3K, AKT, mTOR, and NF-kB in H. pylori-Stimulated AGS Cells
3.5. Astaxanthin Inhibits H. pylori-Induced Invasion in AGS Cells
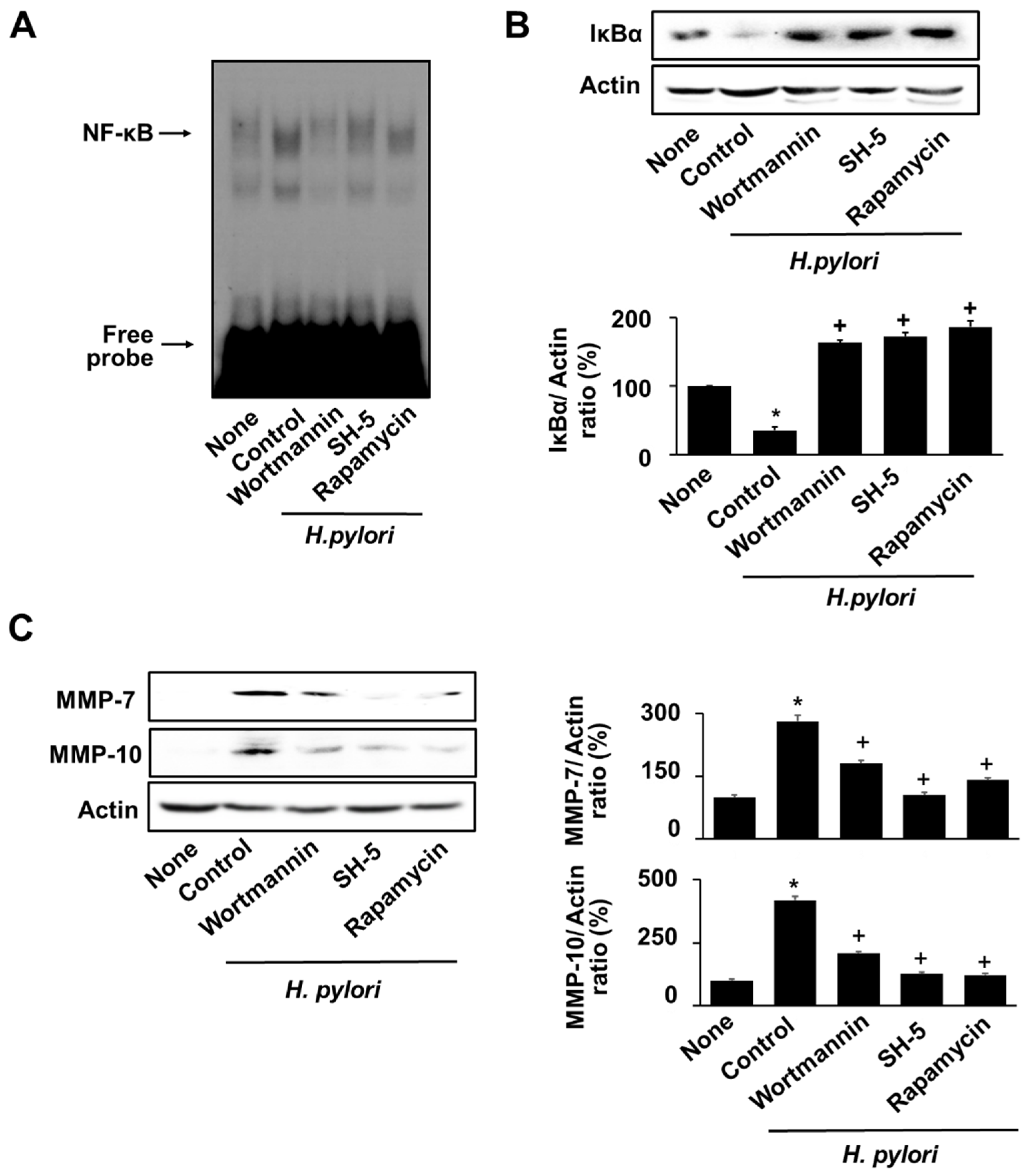
3.6. Specific Inhibitors for PI3K, AKT, and mTOR Reversed the H. pylori-Induced NF-κB Activation, IκBα Degradation, and MMPs Expression in AGS Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M.; Wilson, K.T. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: Factors that modulate disease risk. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, P.; Valenzuela Valderrama, M.; Bravo, J.; Quest, A.F.G. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: Adaptive cellular mechanisms involved in disease progression. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. β-carotene inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-10 and invasion in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffek, S.; Schilling, O.; Franzke, C. Biological role of matrix metalloproteinases: A critical balance. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 38, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, S.; Dundas, S.R.; Buxton, J.; Leeman, M.F.; Ramsay, R.; Murray, G.I. Matrix metalloproteinase/tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase phenotype identifies poor prognosis colorectal cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 10, 8229–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhrmann, A.; Kammerer, U.; Kapp, M.; Dietl, J.; Anacker, J. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialeli, C.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 2010, 278, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.A.O.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Q.; Ouyang, H. Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer through increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-10. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillinger, M.H.; Marjanovic, N.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Scher, J.U.; Roper, J.; Abeles, A.M.; Izmirly, P.I.; Axelrod, M.; Pillinger, M.Y.; et al. Helicobacter pylori stimulates gastric epithelial cell MMP-1 Secretion via CagA-dependent and -independent Erk Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18722–18731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, S.; Hundertmark, T.; Kalinski, T.; Peitz, U.; Wex, T.; Malfertheiner, P.; Naumann, M.; Roessnr, A. Helicobacter pylori encoding the pathogenicity island activates matrix metalloproteinase 1 in gastric epithelial cells via JNK and Erk. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.; Sheu, B.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. Elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -7 in H. pylori-related gastric cancer can be biomarkers correlating with a poor survival. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göõz, M.; Göõz, P.; Smolka, A.J. Epithelial and bacterial metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in H. pylori infection of human gastric cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G823–G832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebb, J.R.; Letley, D.P.; Thomas, R.J.; Aviles, F.; Collins, H.M.; Watson, S.A.; Hand, N.M.; Zaitoun, A.; Atherton, J.C. Helicobacter pylori upregulates matrilysin (MMP-7) in epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro in a CAG dependent manner. Gut 2003, 52, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, H.C.; Krishna, U.S.; Israel, D.A.; Matrisian, L.M.; Washington, M.; Peek, R.M. Helicobacter pylori strain-selective induction of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in vitro and within gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Sato, H.; Hayashibara, T.; Senba, M.; Geleziunas, R.; Wada, A.; Hirayama, T.; Yamamoto, N. Helicobacter pylori induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 through activation of nuclear factor κB. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.; Ferreira, R.M.; Pinto-Ribeiro, I.; Sougleri, I.S.; Oliveira, M.; Carreto, L.; Santos, M.A.; Sgouras, D.N.; Carneiro, F.; Leite, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori activates matrix metalloproteinase 10 in gastric epithelial cells via EGFR and ERK-mediated pathways. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleyman-Jahi, S.; Nedjat, S.; Abdirad, A.; Hoorshad, N.; Heidari, R.; Zendehdel, K. Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in gastric cancer survival: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varro, A.; Kenny, S.; Hemers, E.; McCaig, C.; Przemeck, S.; Wang, T.C.; Bodger, K.; Pritchard, M. Increased gastric expression of MMP-7 in hypergastrinemia and significance for epithelial-mesenchymal signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1133–G1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Noble, P.M.; Pagliocca, A.; Pritchard, D.M.; Hart, C.A.; Campbell, F.; Varro, A. Stimulation of MMP-7 (matrilysin) by Helicobacter pylori in human gastric epithelial cells: Role in epithelial cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senota, A.; Itoh, F.; Yamamoto, H.; Adachi, Y.; Hinoda, Y.; Imai, K. Relation of matrilysin messenger RNA expression with invasive activity in human gastric cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1998, 16, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; Azumano, I.; Mai, M.; Okada, Y. Expression and tissue localization of matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin) in human gastric carcinomas. Implications for vessel invasion and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 79, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Fujii, Y.; Ohuchi, E.; Yamamoto, E.; Okada, Y. Activation of the precursor of human stromelysin 2 and its interactions with other matrix metalloproteinases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 253, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Costache, R.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9423907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, E.; Bagwell, K.; Wagner, J.; Mysona, D.; Sandirasegarane, S.; Smith, N.; Bai, S.; Sharma, A.; Schleifer, R.; She, J. A pan-cancer perspective of matrix metalloproteases (MMP) gene expression profile and their diagnostic/prognostic potential. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, O.; Naumann, M. Matrix metalloproteinases in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis and gastric cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J.; Mao, F.; Teng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kong, H.; Wu, X.; Hao, C.; Han, B.; et al. Helicobacter pylori—Induced matrix metallopeptidase-10 promotes gastric bacterial colonization and gastritis. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Na, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Retracted article: Roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathways in neurodegenerative diseases and tumours. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, S.; Kind, M.; Arcaro, A. The role of the PI3K/AKT/mtor pathway in brain tumor metastasis. J. Cancer Metastatis Treat. 2016, 2, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Fu, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; Chen, L.; Tan, H.; Li, W.; Bi, J.; et al. Involvement of PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in invasion and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma: Association with MMP-9. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.J.; Lin, S.H.; Din, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Liu, C.I. Sinulariolide inhibits gastric cancer cell migration and invasion through downregulation of the EMT process and suppression of FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPKS signaling pathways. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Biersack, B.; Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Bao, B.; Schobert, R.; Padhye, S.; Sarkar, F. Targeted regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/NF-κB signaling by indole compounds and their derivatives: Mechanistic details and biological implications for cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneum, A.; Said, N. PI3K-AKT-mTOR and NFκB pathways in ovarian cancer: Implications for targeted therapeutics. Cancers 2019, 11, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, H.C.; Cooper, M.J.; Cogswell, P.C.; Duncan, J.A.; Ting, J.P.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt-dependent regulation of NF-κB is controlled by mTOR and Raptor in association with IKK. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Oxidative stress in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cell injury. Inflammopharmacology 2005, 13, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, O.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Helicobacter pylori: A ROS-inducing bacterial species in the stomach. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.H. Transcriptional regulation by thiol compounds in Helicobacter pylori induced IL-8 production in human gastric epithelial cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 973, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.H. Helicobacter pylori in a Korean isolate activates mitogen-activated protein kinases, AP-1, and NF-κB and induces chemokine expression in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundouros, N.; Poulogiannis, G. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling and Redox Metabolism in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; John, S.; Sapra, L.; Sharma, S.C.; Das, S.N. Targeted disruption of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, via PI3K inhibitors, promotes growth inhibitory effects in oral cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019, 83, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Multiple mechanisms of anti-cancer effects exerted by astaxanthin. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4310–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, S.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Dargahi, L.; Jorjani, M. Astaxanthin: A mechanistic review on its biological activities and health benefits. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D. Astaxanthin, cell membrane nutrient with diverse clinical benefits and anti-aging potential. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction and interleukin-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, L.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Duan, W.; Lei, J.; Xu, Q.; et al. Lipoxin A4 Attenuates Cell Invasion by Inhibiting ROS/ERK/MMP Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 6815727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Lin, H.; Fan, Z.; Cai, T.Q.; Kaplan, R.A.; Ma, C.; Bower, K.A.; Shi, X.; Luo, J. MMP-2 mediates ethanol-induced invasion of mammary epithelial cells over-expressing ErbB2. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Q. Chloride intracellular channel 1 regulates migration and invasion in gastric cancer by triggering the ROS-mediated p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, Y.M. Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Pérez-Moreno, M.A.; Rodrigo, I.; Locascio, A.; Blanco, M.J.; del Barrio, M.G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chai, K.; Ying, X.; Zhou, B.P. The Role of Snail in EMT and Tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva, L.M.; González, T.D.J.M.; Jiménez, F.N.P.; Besada, A.P.; Pascual, M.G.C.; Morejón, D.D. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Rev. Cuba. Med. Mil. 2020, 49, e0200616. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.; Gírio, A.; Cebola, I.; Santos, C.I.; Antunes, F.; Barata, J.T. Intracellular reactive oxygen species are essential for PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent IL-7-mediated viability of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2011, 25, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, T.G.; Park, S.; Yun, H.R.; Nguyen, N.N.Y.; Jo, Y.H.; Jang, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, I.; et al. Mitochondrial ROS-derived PTEN oxidation activates PI3K pathway for mTOR-induced myogenic autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1921–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, S.R.; Yang, K.S.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Stadtman, E.R.; Rhee, S.G. Reversible oxidation and inactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN in cells stimulated with peptide growth factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16419–16424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, H.G.; Meng, P.; Kuma, H.P.; Ghosh, R. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis disrupts oxidative stress-mediated survival of melanoma cells. Ontarget 2015, 6, 7195–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, D.; Gubler, H.U.; Haefliger, W.; Hauser, D. Antiinflammatory activity of the new mould metabolite 11-desacetoxy-wortmannin and of some of its derivatives. Experientia 1974, 30, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, B.H.; Shih, C.; Toth, J.E.; Ray, J.E.; Dodge, J.A.; Johnson, D.W.; Rutherford, P.G.; Schultz, R.M.; Worzalla, J.F.; Vlahos, C.J. Studies on the mechanism of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition by wortmannin and related analogs. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliocca, A.; Wroblewski, L.E.; Ashcroft, F.J.; Noble, P.J.; Dockray, G.J.; Varro, A. Stimulation of the gastrin-cholecystokinin b receptor promotes branching morphogenesis in gastric AGS Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G292–G299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kozikowski, A.P.; Sun, H.; Brognard, J.; Dennis, P.A. Novel PI analogues selectively block activation of the pro-survival serine/threonine kinase Akt. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1144–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Sung, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. SH-5, an AKT inhibitor potentiates apoptosis and inhibits invasion through the suppression of anti-apoptotic, proliferative and metastatic gene products regulated by IκBα kinase activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sarbassov, D.D.; Ali, S.M.; King, J.E.; Latek, R.R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 2002, 110, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, J.; Valenzuela, M.; Bravo, J.; Cerda-Opazo, P.; Jorquera, C.; Toledo, H.; Bravo, D.; Quest, A.F.G. Helicobacter pylori induced phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/mTOR activation increases hypoxia inducible factor-1α to promote loss of cyclin D1 and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in human gastric cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.; Shang, J.; Hao, M. Actin-Like Protein 8 Promotes the Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via Activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. Onco. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Xu, C.; Xia, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H. Downregulation of P300/CBP-Associated Factor Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Via Inhibiting Autophagy. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.J.; Kim, A.; Sohn, D.S.; Lee, C.S. Apocynin inhibits Toll-like receptor-4-mediated activation of NF-κB by suppressing the Akt and mTOR pathways. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Duan, L.; Zou, Z.; Li, H.; Yuan, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Zha, H.; et al. Activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K Pathway is Involved in S100A4-induced Viability and Migration in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchenwitz, M.; Stahnke, S.; Prettin, S.; Borowiak, M.; Menke, L.; Sieben, C.; Birchmeier, C.; Rottner, K.; Stradal, T.E.B.; Steffen, A. SMER28 attenuates PI3K/mTOR signaling by direct inhibition of PI3K p110 delta. Cells 2022, 11, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, J. Dihydroartemisinin Induces Endothelial Cell Autophagy through Suppression of the Akt/mTOR Pathway. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6057–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, J.H.; Lee, Y.; Hassan, M.M.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, E.Y.; Hong, S.T.; Park, B.H.; Park, J.H. mTOR- and SGK-mediated Connexin 43 expression participates in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage migration through the iNOS/Src/FAK axis. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2986–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, J.C.; Cao, P.; Peek, R.M.; Tummuru, M.K.R.; Blaser, M.J.; Cover, T.L. Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17771–17777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censini, S.; Lange, C.; Xiang, Z.; Crabtree, J.E.; Ghiara, P.; Borodovsky, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. Cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, W.; Lambert, J.R.; Dwyer, B. Cytotoxin production by Helicobacter pylori from patients with upper gastrointestinal tract diseases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.T.; Johnston, E.; Krishna, U.; Yamaoka, Y.; Israel, D.A.; Nagy, T.A.; Wroblewski, L.E.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Correa, P.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Regulation of gastric carcinogenesis by Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khattaf, A.S. Helicobacter pylori virulence markers in gastroduodenal disorders. Detection of cytotoxin-associated gene A and vacuolating cytotoxin-associated gene A genes in Saudi patients. Saudi Med. J. 2012, 33, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gwack, J.; Shin, A.; Kim, C.-S.; Ko, K.-P.; Kim, Y.; Jun, J.K.; Bae, J.; Park, S.K.; Hong, Y.-C.; Kang, D.; et al. CagA-producing Helicobacter pylori and increased risk of gastric cancer: A nested case–control study in Korea. Br. J Cancer 2006, 95, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, R.M.; Thompson, S.A.; Donahue, J.P.; Tham, K.T.; Atherton, J.C.; Blaser, M.J.; Miller, G.G. Adherence to gastric epithelial cells induces expression of a Helicobacter pylori gene, iceA, that is associated with clinical outcome. Proc. Assoc. Am. Phys. 1998, 110, 531–544. [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn, L.-J.; Figueiredo, C.; Sanna, R.; Plaisier, A.; Schneeberger, P.; Boer, W.D.; Quint, W. Clinical relevance of the cagA, vacA, and iceA status of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Azuma, T.; Ito, S.; Suto, H.; Miyaji, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kato, T.; Kohli, Y.; Keida, Y.; Kuriyama, M. Sequence analysis and clinical significance of the iceA gene from Helicobacter pylori strains in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlosama-Roseroa, Y.H.; Bolaños-Bravob, H.; Sierra-Tórresc, C.H.; Roserod, E.A. Association of the Helicobacter pylori cagA, vacA, and iceA genotypes with chronic follicular gastritis in a Colombian population at high risk for gastric cancer. Rev. De Gastroenteroligia De Mex. 2019, 84, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Azuma, T.; Ito, S.; Suto, H.; Miyaji, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kohli, Y.; Kuriyama, M. Full-length sequence analysis of the vacA gene from cytotoxic and noncytotoxic Helicobacter pylori. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltermann, A.; Koetzer, S.; Eigenmann, F.; Komminoth, P. Correlation of Helicobacter pylori virulence genotypes vacA and cagA with histological parameters of gastritis and patient’s age. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.J.; Berg, D.E.; van der Hulst, R.W.M.; Su, W.-W.; Raudonikiene, A.; Xiao, S.-D.; Dankert, J.; Tytgat, G.N.J.; van der Ende, A. Prevalence of vacuolating cytotoxin production and distribution of distinct vacA alleles in Helicobacter pylori from China. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Effect of astaxanthin on activation of autophagy and inhibition of apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cell line AGS. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, B.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Jak1/Stat3 is an upstream signaling of NF-κB activation in Helicobacter pylori-induced IL-8 production in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. β-Carotene inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric epithelial AGS cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, B.; McPartland, C.K.; Moore, R.; Frank-Kamenetskii, A.; Booth, B.W. Effects of astaxanthin on the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells in vitro. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Xiong, Y.; Shi, Y.X.; Hu, P.F.; Bao, J.P.; Wu, L.D. Astaxanthin reduces matrix metalloproteinase expression in human chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J.; Vreeburg, R.A.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Wichers, H.J. Transcriptional profiling of the LPS induced NF-κB response in macrophages. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Song, G.; Pagliari, L.J.; Birrer, M.J.; Stein, B.; Anrather, J.; Pope, R.M. TNF-α Gene Expression in Macrophages: Regulation by NF-κB Is Independent of c-Jun or C/EBPβ. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Montes, A.; Ruiz-Corro, L.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Lopez-Reyes, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Increased DNA binding activity of NF-kB.; STAT-3.; SMAD3 and AP-1 in acutely damaged liver. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5995–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.K.; Lee, H.G.; Piao, J.Y.; Zhong, X.; Lee, H.N.; Han, H.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.H.; Cha, Y.N.; Na, H.K.; et al. Helicobacter pylori induces Snail expression through ROS-mediated activation of Erk and inactivation of GSK-3β in human gastric cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 2236–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.G.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Cha, S.Y.; Ota, I.; Kim, N.H.; Cha, Y.H.; Yang, D.H.; Lee, Y.; et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA promotes Snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition by reducing GSK-3 activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163427
Lee J, Lim JW, Kim H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163427
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jimin, Joo Weon Lim, and Hyeyoung Kim. 2022. "Astaxanthin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163427
APA StyleLee, J., Lim, J. W., & Kim, H. (2022). Astaxanthin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients, 14(16), 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163427






