Abstract
There are many different probiotic products on the market. Are they all equally effective? What criteria should a probiotic formulation meet to provide the most benefit to the patient? The current research aims to evaluate the parameters that influence the effectiveness of market probiotic products. These properties are critical for restoring eubiosis in patients with drug-induced dysbiosis or other pathological conditions, which could be caused by stress, wrong eating. Methods: The disintegration time of probiotic capsules in hydrochloric acid was investigated using a disintegration testing device. The survival rate of probiotic preparations in hydrochloric acid at pH 2 and in a 0.4% bile solution was then evaluated. For this purpose, the number of bacteria before and after incubation in the respective solutions was determined using the plate method. Inhibition of gastrointestinal pathogens by the probiotic products was determined using the Strus bar graph method. The highest survival rate of probiotic bacteria at low pH is shown by preparations produced in the form of acid-resistant capsules. Conclusions: The most important factor determining the good survival of bacterial strains under conditions simulating the gastrointestinal tract is the type of capsule used for their production and storage. The best antimicrobial activity against most common human gastrointestinal pathogens such as Eschericha coli, Shigella, Salmonella spp., Clostridioides difficile (the largest inhibition zones) are shown by probiotic products with the greatest diversity of bacterial strains.
1. Introduction
According to the FAO/WHO definition, probiotics are live microorganisms that, when incorporated into the body in adequate amounts, result in health benefits to the host [1,2]. Unfortunately, there are still disturbing reports that some probiotic preparations placed on the market are not fully characterized or tested [3]. Despite the growing knowledge of probiotics, studies do not always pay enough attention to quality aspects. In addition, the choice of probiotics is very large. Few studies have been motivated in their search for probiotics by analyzing the function and action of a particular strain of bacteria, the number of bacterial strains in a capsule or the pharmaceutical technology used by the manufacturer. Additionally, these are the essential factors determining the optimal performance of a given probiotic market product [4]. The environmental conditions in the various parts of the gastrointestinal tract limit the number of live bacteria reaching their destination [5]. The second important factor determining the optimal survival of probiotic bacteria is the method of their production, which determines the number of live bacteria reaching the intestine, resulting in its colonization [6,7]. The bacteria’s passage through the acidic environment of the stomach, which is extremely negative for living bacteria, is crucial for the proper colonization of the intestine by probiotics. After the oral intake of a probiotic product, it reaches the stomach, where it is exposed to hydrochloric acid contained in gastric juice. In the case of probiotics, the effect of hydrochloric acid on the microorganisms present is unfavorable, decreasing their survival [8,9]. In order to protect the bacterial strains in probiotic preparations, various technologies have been introduced. These technologies basically work to protect the bacterial strains from the destructive effects of hydrochloric acid and other digestive factors. Probiotic forms encapsulated in oil or acid-resistant capsules that are supposed to protect Lactobacilli [10] or Bifidobacterium from the negative effects of enzymes and low pH, are appearing with increasing frequency [9,11].
An important property of the intestinal microbiota, especially for administered probiotic microorganisms, is their resistance to further gastrointestinal conditions, especially their tolerance and growth in the presence of bile salts. Bacteria can utilize several mechanisms of defense against bile, including special transport mechanisms, the synthesis of various surface proteins and fatty acids, or the production of exopolysaccharides [12]. The ability to enzymatically hydrolyze bile salts is found in many bacteria. Cholylglycine hydrolase hydrolyzes bile salts and is a constitutive intracellular enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of the amide bond between glycine or taurine and the steroid nucleus of bile acids [13]. Its presence has been demonstrated in specific microorganisms from several bacterial types (Lactobacillus spp., Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium spp., and Bacteroides spp.).
Bile salt hydrolase activity may facilitate bile detoxification, provide opportunities for bacteria to utilize released amino acids as a carbon and nitrogen source, or promote cholesterol incorporation into the cell wall. The deconjugation of bile salts may be directly related to the reduction of serum cholesterol, from which conjugated bile salts are synthesized de novo [14]. The ability of microorganisms to assimilate or bind ingested cholesterol to the cell wall or to eliminate it by co-precipitation with released cholic acid has also been documented. Some gut microbiota produce cholesterol reductase, which catalyzes the conversion of cholesterol to insoluble coprostanol that is then excreted in the feces, also reducing exogenous cholesterol [15,16]. As we can see, there is a wide spectrum of defense mechanisms in probiotic microorganisms against bile. It seems obvious that probiotic preparations on the market should be tested for resistance to hydrochloric acid (in an imitation of gastric conditions) and bile, because only after passage through the stomach and duodenum do they reach their proper site of action.
Another very important factor in choosing the right probiotic is the inhibitory effect on pathological bacteria. One simple test to determine the predicted action is to examine the inhibition zones of probiotics against pathological bacteria [17,18]. At the same time, it should be noted that we can also be faced with dysbiosis when using drugs such as metformin, proton pump inhibitors (PPI), or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics. The medicines mentioned above may increase the risk of developing intestinal pathogens. For example, treatment with PPI could induce Salmonella and C. dificille infections, while metformin may cause excessive growth of Escherichia and Shigella spp. Another widely used class of medicines – NSAIDs, can induce dysbiosis and damage the intestinal mucosa by activating inappropriate mechanisms of the non-specific immune response. It should be emphasized that NSAIDs are often used with PPIs, and such a combination may potentiate dysbiosis and increase the risk of C. dificille infection [19,20].
The human digestive tract under physiological conditions is colonized by more than 400 different species of bacteria. Their total mass reaches up to 2 kg. It is therefore no surprise that the intestinal microbiota has a huge impact on our health and its disorders can have serious health consequences. Bacterial flora disturbances may occur as a result of infection with pathological bacteria such as Salmonella, Shigella, or Escherichia coli [21,22]. Moreover, both quantitative and qualitative disorders of the intestinal microbiota may occur during antibiotic therapy [23]. This particularly concerns patients receiving chronic high doses of antibiotics. In such cases, we usually deal with Clostridium superinfection [24]. Considering the above data, the model of our study seems to be the most reasonable.
2. The Aim of the Study
The objectives of our study are as follows:
1. To evaluate the bacterial survival of several commercially available probiotic preparations as dietary supplements under conditions simulating the stomach environment (low pH) and the initial intestinal segment (bile).
2. To evaluate the inhibitory capacity of four gastrointestinal pathogens by the probiotic formulations tested.
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Capsule Disintegration Study
The disintegration test of probiotic capsules was performed using disintegration apparatus: DisiTest 50, Dr. Schleuniger Pharmatron (Sotax), Swiss/USA. Experiments were carried out at a temperature of 37.0 °C ± 2 °C. The test was performed in a buffer of pH 2. The pH 2.0 buffer solution was prepared by dissolving 6.57 g of potassium chloride in water and adding 119.0 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, with water added to a volume of 1000 mL (Figure 1). The integrity of the capsules was observed at intervals of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, and 120 min.
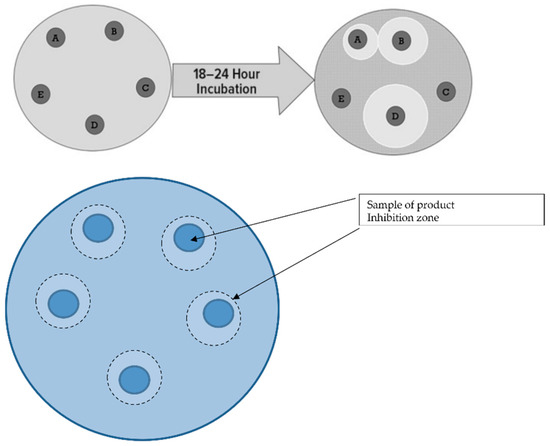
Figure 1.
Schematic of the culture medium for pathological bacteria and probiotic market products. Explanation: product A (Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactococcus lactis, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Strepto-coccus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum), product B (Lactobacillus plantarum), product C (4 Lactobacillis, 2 Bifidobacterium, Lactococcus lactis), product D (Lactobacillus rhamnosus), product E (4 Lactobacillis3 Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus thermophilus).
3.2. Microbial Survival Study
Survival studies of probiotic microorganisms were conducted in three stages (Table 1). In this study, an experimental model was created to simulate “in vitro” acidic conditions in the stomach and in the presence of bile acid salts corresponding to their concentration in duodenal juice. Under these conditions (a solution of pH 2 equal to the acidity of the gastric juice of an adult), the first stage of the study determined the time after which disintegration of capsules containing different marketed probiotic products occurs. For this purpose, the capsules of market products were placed in a hydrochloric acid solution of pH 2. Additionally, the time after which the disintegration of the capsule wall and the release of its contents occurred was recorded.

Table 1.
Probiotic products used in the study.
In the second stage of the study, capsules with a known concentration of probiotic microorganisms were placed in hydrochloric acid pH 2 and incubated for 90 min. After this time, the number of live microorganisms present in the solution was determined.
In the third stage of the study, the microorganisms contained in one capsule of market preparation were incubated for 180 min in 0.4% bile solution and the number of microorganisms after incubation was determined.
The study was conducted according to the methodology described in “Enumeration of probiotic microorganisms exposed to acid conditions” [25].
3.3. Examination of the Amount of LAB Bacteria before and after Exposure to Hydrochloric Acid
In the conducted experiments it was assumed that the tested capsules contained the concentration of probiotic microorganisms as declared by the manufacturer. The number of bacteria after incubation with hydrochloric acid and bile was measured using the plate method [26]. The results are presented as the arithmetic mean from three consecutive determinations.
3.4. Investigation of the Inhibition Zones of Marketed Probiotic against Pathological Bacteria
The four most common human gastrointestinal pathogens were used for this study.
- Eschericha coli;
- Shigella;
- Salmonella spp.;
- Clostridioides difficile [27].
The gastrointestinal-pathogen-inhibitory abilities of microorganisms contained in five commercially available probiotic products were evaluated. To investigate the inhibitory effect of probiotics against pathological bacteria, experiments were performed by measuring the growth inhibition of these bacteria. Antagonism between microbiota was determined using the bar graph method according to Strus [28]. The quantitative results of inhibition of each probiotic product are presented as the arithmetic mean ± SD of three measurements obtained by inoculating pathological bacteria and determining the zone of inhibition (Table 1).
For in vitro growth inhibition studies with C. difficile, the pathogen was cultured under anaerobic conditions at 35–37 °C for 24–48 h on Schaedler agar (CM0437, Fisher Scientific GmbH, Schwerte, Germany). Suspensions, each containing 106 CFU of each of the five products evaluated, were seeded onto MRS agar and incubated for 48 h in the presence of 5% CO2. Probiotic samples were transferred to Mueller–Hinton agar supplemented with 5% horse blood and 20 mg/L NAD (PP0972, E&O Laboratories Ltd., Bonnybridge, UK) and incubated under anaerobic conditions for 24 h. The zones of inhibition were measured as in the previous case.
4. Results
The longest time (60 min) after which the complete disintegration of the capsule, with the release of the probiotic into an environment imitating that of the stomach, occurred was observed for product A (Table 2, Figure 1). This product has an acid-resistant capsule with the highest resistance to hydrochloric acid. The time of the disintegration of regular capsules was from 10 min, products B and C, to 20 min for product D, and was 25 min for product E (Figure 2).

Table 2.
Capsule disintegration time in hydrochloric acid at pH 2 in minutes.
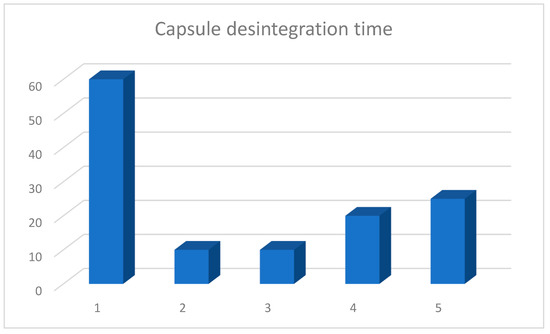
Figure 2.
Average disintegration time of capsules containing market products of probiotics. Arithmetic means of three independent experiments.
The greatest reduction in the number of live microorganisms after 90 min of incubation in hydrochloric acid at pH 2 was observed in the case of product C, in a capsule produced by traditional technology (Figure 3). This reduction was 3.12 on a logarithmic scale. The survival of microorganisms contained in product A, produced with acid-resistant capsule technology was the highest, and the reduction in the number of viable bacteria was the lowest, amounting to 1.08 on a logarithmic scale. The values of the reduction in the number of live microorganisms were comparable for all probiotic products produced with traditional technologies.
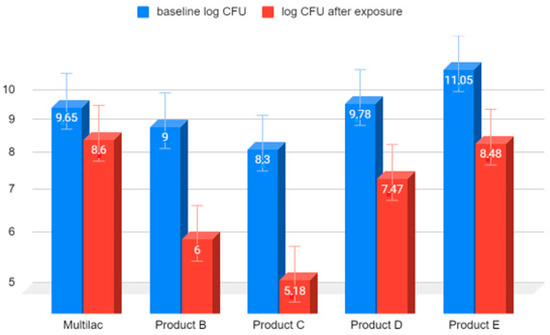
Figure 3.
Comparison on a logarithmic scale of the decrease in the number of live LAB bacteria in market preparations of probiotics after 90 min of exposure to HCl solution at pH 2. Arithmetic means of three independent experiments.
The reduction in the number of live microorganisms after 180 min exposure to 0.4% bile solution was similar in all tested probiotic products (Figure 4).
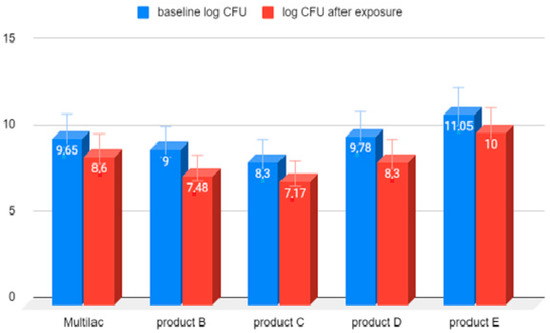
Figure 4.
LAB bacterial counts before and after 180 min of exposure to 0.4% bile solution. Arithmetic means of three independent experiments.
The reduction in live microorganisms after 180-minute exposure to 0.4% bile solution was similar in all tested probiotic products.
The largest zone of inhibition against pathological bacteria was found in cultures containing product A, produced by technology containing nine different bacterial strains (Figure 1 and Figure 5). The largest zones of inhibition were encountered with all four tested pathological bacteria (Salmonella spp. E. coli, C. difficile, and Shigella spp.). The smallest zones of inhibition were encountered in the case of probiotic products containing only one strain of probiotic bacteria. In this case, this was also observed for all four types of pathological bacteria. Intermediate sizes of inhibition zones occurred for the remaining probiotic products.

Figure 5.
Zones of inhibition of tested probiotics against pathological gastrointestinal bacteria. Arithmetic mean of 3 independent experiments.
5. Discussion
It is well known that orally ingested food travels through the esophagus to the stomach. The enzymes and hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach are components of the gastric juice.
Under physiological conditions, food in the stomach is exposed to digestive juices and gastric motility for approximately 60 to 120 min [29,30]. These extreme environmental conditions are a requirement for proper digestion and provide a barrier to pathological microorganisms. The low pH of gastric juice disinfects the food and activates proenzymes [31]. In certain situations, this stage of digestion becomes unbeneficial for the human body. In cases where we want to intentionally introduce health-promoting substances, the gastric digestion process may reduce the expected effects of the administered preparations. An attempt to populate the gastrointestinal mucosa with microbiota administered in probiotics may serve as a typical example of these adverse interactions [9]. In order to populate further sections of the intestine, the process of “passage” through the stomach and duodenum should be taken into account and the preparations should be designed in such a way that the microorganisms survive and can reach the intestine alive.
There are 1012 bacteria in 1 g of colonic contents, making it the most colonized section of the gastrointestinal tract [32,33,34]. Bacteria colonizing the intestine create a complex ecosystem and having a great influence on the human body. The life processes of microorganisms produce metabolites that exert various effects on the host [35,36]. The extreme conditions in the stomach are an important barrier, the overcoming of which is a necessary condition for the proper development of bacterial colonies after the administration of probiotics from the outside [37]. The results of “in vitro” studies clearly suggest that the exposure of bacterial strains to concentrated acidic pH significantly affects their ability to survive in these adverse conditions. Based on the results of our study, it is clear that the most significant factor determining the high survival of microorganisms in conditions imitating the gastric environment is the type of capsule used during production and its susceptibility to concentrated hydrochloric acid. First of all, it is obvious that the time of disintegration and release of living microorganisms determine the later biological effect of a probiotic. A short time for disintegration of the probiotic capsule exposes the microorganisms contained within it due to the lack of a protective element, which in turn makes the microorganisms more susceptible to a low pH and affects their ability to survive these conditions.
Interestingly, even in the case of products with the highest content of live microorganisms, as declared by the producer, after their incubation for 90 min in hydrochloric acid, the amount of remaining live bacteria was lower than in preparations with a lower initial content. Obviously, this phenomenon was caused by the better protection of capsules made with a different technology. In our study, we showed that the exposure of microorganisms contained in probiotic preparations to bile acids contained in duodenal juice had less effect on their survival.
These results are consistent with those obtained in the works of other authors [7]. Based on the results obtained, we can conclude that the most negative conditions for the survival of microorganisms take place in the gastric environment. The second important criterion for choosing the right probiotic preparation is undoubtedly the ability of the bacterial strains contained within to inhibit the development of pathological bacteria [17].
It should be noted that the formulations tested have different qualitative compositions of similar bacterial strains. This is important due to the fact that even bacteria from the same species may have different effects that are characteristic and specific to a given strain. The effectiveness of probiotics to inhibit the growth of pathological bacteria is shown by the size of the zone of inhibition measured on an agar plate. So far, the mechanisms responsible for these properties of probiotics have not been precisely determined in scientific studies. There is no doubt that we are dealing with an antagonistic effect of beneficial bacteria in relation to pathological bacteria. Currently, research is being conducted to explain this phenomenon. Probiotic microorganisms compete with pathological bacteria for space and nutrients. Bacteria in probiotics produce bacteriocins, substances that inhibit the colonization of potential pathogens [36,37]. This commensalism of probiotic microorganisms in the human body maintains a specific homeostasis, the disruption of which leads to gastrointestinal dysfunction. Based on the results obtained in our experiments, we can conclude that the most significant factor affecting the ability to inhibit the growth of pathological gastrointestinal bacteria is the diversity of bacterial strains contained in a given market product.
Enteropathogenic E. coli, EPEC, is a major cause of diarrhea in infants [38]. As long as there is no evidence of systemic infection, antibiotic therapy is rarely indicated and should be delayed until culture results are available. For this reason, and because of the emerging antibiotic resistance of E. coli [39], probiotics are being considered as additional treatment options for E. coli infections [40]. In previous in vitro pathogen growth inhibition experiments, no clear inhibition of E. coli growth by S. Boulardii yeast has been reported [41]. In contrast, the in vitro growth inhibition of E. coli has been described for many single-strain bacterial probiotics, among them L. rhamnosus GG [42] and L. reuteri DSM 17938, and multi-strain probiotics [43,44]. Intestinal microbiota disorders also affect the oral cavity, which is a challenge in dentistry [45]. The situation is similar for other intestinal pathogens (Shigella, Salmonella spp, and C. difficile), and probiotics may also be beneficial in these cases. Questions related to bacterial flora disorders dependent on antibiotic therapy have been asked for a very long time. In recent years, studies have found that dysbiosis can also occur in cases of therapy with drugs such as metformin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or proton pump inhibitors [46,47,48]. It is worth emphasizing that the use of these drugs may be associated with the development of intestinal pathogens such as E. coli, Shigella, Salmonella spp, and C. difficile. This is important because these drugs are used in the population in very large amounts.
These facts show the importance of choosing the right probiotic formulation to obtain the best clinical effect. Further studies of both single-bacterial-strain probiotics and combinations of probiotics are needed to obtain the optimal formulation in a given clinical situation.
6. Conclusions
The survival of microorganisms contained in market products of probiotics depends mainly on the type of capsule used in the production and the time of its disintegration. The fast disintegration of the capsule and the low survival rate of the microorganisms contained within it contribute to the weaker colonization of the intestine and the lower effectiveness of their action. It can be clearly stated that the greater the diversity of bacterial strains in a given probiotic preparation, the greater the ability of this population to inhibit pathological bacteria under “in vitro” conditions. This relates to all four gastrointestinal pathological bacteria we tested (Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, Clostridioides difficile, and Shigella spp.) Of the market products tested, Multilac® showed the best survival rate and the best antimicrobial properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B. and J.P.; methodology, M.B., J.P., S.L.-W. and W.Ż.-S.; formal analysis, J.P.; investigation, M.B. and J.P.; resources, M.B. and J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B. and J.P.; writing—review and editing, J.P. and S.L.-W.; visualization, J.P. and S.L.-W.; supervision, J.P. and S.L.-W.; project administration, M.B. and J.P.; funding acquisition, J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study has been financially supported by UNILAB LP.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Supported by the Foundation for Polish Science (FNP), and by the scholarship for young scientists of the Ministry of Education and Science (MEIN) for Sabina Lachowicz-Wiśniewska.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO/WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, B.R.; Flint, J.H.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungh, A.; Wadström, T. Lactic acid bacteria as probiotics. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2006, 7, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heczko, P.B.; Strus, M.; Kochan, P. Projektowanie probiotyków do zastosowań medycznych. Post. Mikrobiol. 2008, 47, 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Klewicka, E.; Śleżewska, K.; Nowak, A. Ocena przeżywalności bakterii Lactobacillus zawartych w preparacie probiotycznym podczas pasażu w stymulowanym przewodzie pokarmowym. Żywność. Nauka. Technologia. Jakość. 2014, 6, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Del Piano, M.; Carmagnola, S.; Andorno, S.; Pagliarulo, M.; Tari, R.; Mogna, L.; Strozzi, G.P.; Sforza, F.; Capurso, L. Evaluation of the intestinal colonization by microencapsulated probiotic bacteria in comparison with the same uncoated strains. J. Clinic. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, S42–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Piano, M.; Carmagnola, S.; Ballarè, M.; Sartori, M.; Orsello, M.; Balzarini, M.; Pagliarulo, M.; Tari, R.; Anderloni, A.; Strozzi, G.P.; et al. Is microencapsulation the future of probiotic preparations? The increased efficacy of gastro-protected probiotics. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillie, A.; Johansen, A.K. Disintegration and in vitro acid stability testes on nine lactic acid bacteria preparations. In Proceedings of the XXIII, Nordic Gastroenterology Meeting, Reykjavik, Iceland, 14–16 June 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Corneliussen, L.; Skov, R.; Espersen, F. Effect of low pH on survival of lactic producing bacteria in oral formulation. In Proceedings of the 9th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and infectious Diseases, Berlin, Germany, 21–24 May 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.; Harris, H.M.; Mattarelli, P.; Lebeer, S. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Piano, M.; Strozzi, P.; Barba, M.; Allesina, S.; Deidda, F.; Lorenzini, P.; Lorenzo, M.; Stefania, C.; Pagliarulo, M.; Balzarini, M.; et al. In vitro sensitivity of probiotics to human pancreatic juice. J. Clinic. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, S170–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbubani, K.T.; Slater, N.K.; Edwards, A.D. Protection of dried probiotic bacteria from bile using bile adsorbent resins. N. Biotechnol. 2014, 31, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustos, A.; de Valdez, G.F.; Fadda, S.; Taranto, M.P. New insights into bacterial bile resistance mechanisms: The role of bile salt hydrolase and its impact on human health. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horáčková, Š.; Plocková, M.; Demnerová, K. Importance of microbial defence systems to bile salts and mechanisms of serum cholesterol reduction. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Gómez, J.G.; López-Bonilla, A.; Trejo-Tapia, G.; Ávila-Reyes, S.V.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Hernández-Sánchez, H. In Vitro Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) Activity Screening of Different Probiotic Microorganisms. Foods 2021, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatek, J.; Krauss, H.; Ciechelska-Rybarczyk, A.; Bernatek, M.; Wojtyla-Buciora, P.; Sommermeyer, H. In-Vitro Growth Inhibition of Bacterial Pathogens by Probiotics and a Synbiotic: Product Composition Matters. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Korte, F.; Dörfer, C.E.; Kneist, S.; Fawzy, K.; Paris, S. Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Growth and Biofilm Formation by Probiotics in vitro. Caries Res. 2017, 51, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlicz, W.; Igor Łoniewski, I. NSAIDs and PPI induced enteropathy— Important and neglected clinical problem. Gastroenterologia Kliniczna. 2014, 6, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bryrup, T.; Thomsen, C.W.; Kern, T.; Allin, K.H.; Brandslun, I.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Vestergaard, H.; Hansen, T.; Hansen, T.H.; Pedersen, O.; et al. Metformin-induced changes of the gut microbiota in healthy young men: Results of a non-blinded, one-armed intervention study. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, B.; Frassl, G.A.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella, the host and disease: A brief review. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2006, 85, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatek, J.; Sommermeyer, H.; Bernatek, M.; Ciechelska-Rybarczyk, A.; Oleskow, B.; Sommer Mikkelsen, L.; Barken, K.B. Persistent infection by Salmonella enterica servovar Typhimurium: Are synbiotics a therapeutic option?–A case report. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strus, M.; Pakosz, K.; Gościniak, H.; Przondo-Mordarska, A.; Rozynek, E.; Pituch, H.; Meisel-Mikołajczyk, F.; Heczko, P.B. Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus bacteria strains against anaerobic gastrointestinal tract pathogens (Helicobacter pylori, Campylobacter coli, Campylobacter jejuni, Clostridium difficile). Med. Doswiad. Mikrob. 2001, 53, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, K. Enumeration of probiotics microorganisms exposed to acidic condition. Report 2010.
- PN-ISO 15214:2002; Mikrobiologia żywności I pasz. Horyzontalna metoda oznaczania liczby mezofilnych bakterii fermentacji mlekowej. Metoda płytkowa w temperaturze 30 °C. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2002; ISBN 832368331X.
- Lancet Infectious Diseases. C difficile—A rose by any other name. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 19, 449.
- Strus, M. A new mthod for evaluation of the antagonistic action of bacterial lactic acid (LAB) on selected pathogenic indicator bacteria. Med. Doswiad. Mikrobiol. 1998, 50, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Rostas, J.W.; Mai, T.T.; Richards, W.O. Gastric motility physiology and surgical intervention. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2011, 91, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, R.H.; Camilleri, M.; Crowe, S.E.; El-Omar, E.M.; Fox, J.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; Malfertheiner, P.; McColl, K.E.; Pritchard, D.M.; Rugge, M.; et al. The stomach in health and disease. Gut 2015, 64, 1650–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, J.J.; Kelly, K.A. Gastric motor physiology and pathophysiology. Surg. Clin. North Am. 1993, 73, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegold, S.M.; Sutter, V.L.; Mathisen, G.E. Normal indigenous intestinal flora. In Human Intestinal Microflora in Health and Disease; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sartor, R.B. Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: Antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Guevarra, R.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.H. Role of Probiotics in Human Gut Microbiome-Associated Diseases. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, M.J. Probiotics, gut microbiota and health. Med. Mal. Infect. 2014, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, A.R.; Pereira, C.I.; Truszkowska, K.; Gomesa, A.M.; Pintadoa, M.E.; Malcataa, F.X. Sur-vival of probiotic bacteria in a whey cheese vector submitted to environmental conditions prevailing in the gastrointestinal tract. Int. Dairy. J. 2005, 15, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilbronner, S.; Krismer, B.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H.; Peschel, A. The microbiome-shaping roles of bacteriocins. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumariya, R.; Garsa, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sood, S.K.; Akhtar, N.; Patel, S. Bacteriocins: Classification, synthesis, mechanism of action and resistance development in food spoilage causing bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, T.J.; Contreras, C.A. Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) infection in children. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.K.; Kieer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, S.; Sulc, D.; Steyer, A. Study of the In Vitro Antagonistic Activity of Various Mono-Strain and Multi-Strain Probiotics against Escherichia coli. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, K.; Kunicka-Styczynska, A.; Rygala, A. Probiotic Activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii Against Human Pathogens. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 50, 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hütt, P.; Shchepetova, J.; Lõivukene, K.; Kullisaar, T.; Mikelsaar, M. Antagonistic activity of probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against entero- and uropathogens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Sieo, C.C.; Kalavathy, R.; Liang, J.B.; Alitheen, N.B.; Jahromi, M.F.; Ho, Y.W. Probiotic Potential of Lactobacillus Strains with Antimicrobial Activity against Some Human Pathogenic Strains. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 927268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, C.N.; Rosenfeldt Nielsen, V.; Hayford, A.E.; Møller, L.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Pærregaard, A.; Sandström, B.; Tvede, M.; Jakobsen, M. Screening of Probiotic Activities of Forty-Seven Strains of Lactobacillus spp. by In Vitro Techniques and Evaluation of the Colonization Ability of Five Selected Strains in Humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4949–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatek, M.; Sommermeyer, H.; Pituch, H.; Wultańska, D.; Kopczyński, Z.; Piątek, J.; Wojtyła-Buciora, P. Clindamycin-resistant Clostridioides difficile: A challenge in dentistry. J. Health Inequal. 2022, 8, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersma, R.K.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J. Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut 2020, 69, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.B.; Chae, S.U.; Jo, S.J.; Jerng, U.M.; Bae, S.K. The relationship between the gut microbiome and metformin as a key for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbere, I.; Kalnina, I.; Silamikelis, I.; Konrade, I.; Zaharenko, L.; Sekace, K.; Radovica-Spalvina, I.; Fridmanis, D.; Gudra, D.; Pirags, V.; et al. Association of metformin administration with gut microbiome dysbiosis in healthy volunteers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).