Chinese Food Image Database for Eating and Appetite Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Establishment and Studies of Existing Food Image Databases
1.2. Research Significance
1.3. Research Purpose and Hypothesis
2. Methods
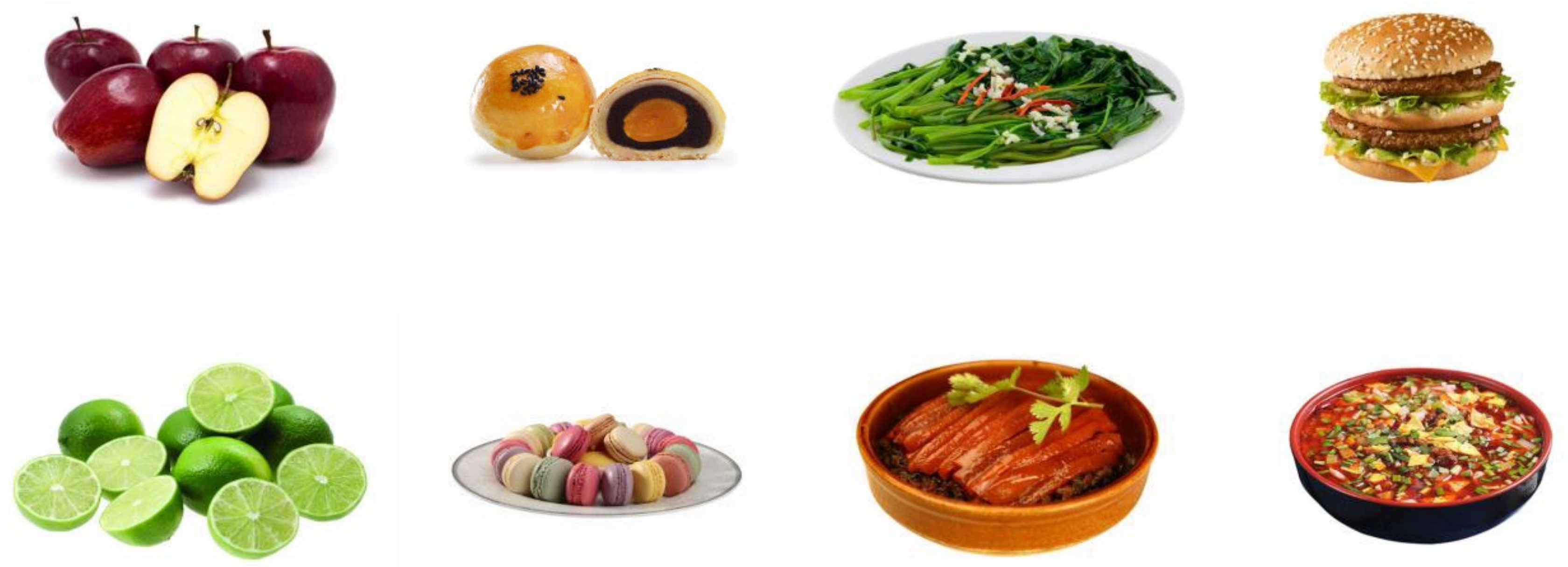
2.1. The Collection and Processing of Food Images
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Image Physical Characteristics
2.1.3. Macronutrients
2.1.4. Category
2.2. Participants
2.3. Demographics and Scales
2.4. Image Rating Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Food Image Classification
3.2. Identifiability and Familiarity Ratings
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Agricultural Data; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Trends in Adult Body-Mass Index in 200 Countries from 1975 to 2014: A Pooled Analysis of 1698 Population-Based Measurement Studies with 19·2 Million Participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J. Obesity and Cancer. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6365–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppan, C.M.; Bailey, S.T.; Bhat, S.; Brown, E.J.; Banerjee, R.R.; Wright, C.M.; Patel, H.R.; Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The Hormone Resistin Links Obesity to Diabetes. Nature 2001, 409, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolan, K.J.; Breslin, G.; Hanna, D.; Murphy, K.; Gallagher, A.M. Visual Attention to Food Cues in Obesity: An Eye-Tracking Study: Attentional Bias to Food Cues in Obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poli, V.F.S.; Sanches, R.B.; dos Santos Moraes, A.; Fidalgo, J.P.N.; Nascimento, M.A.; Bresciani, P.; Andrade-Silva, S.G.; Cipullo, M.A.T.; Clemente, J.C.; Caranti, D.A. The Excessive Caloric Intake and Micronutrient Deficiencies Related to Obesity after a Long-Term Interdisciplinary Therapy. Nutrition 2017, 38, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, N.L.; Brownell, K.D. Obesity: A Public Health Approach. Psychiatr. Clin. 2011, 34, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friel, S.; Hattersley, L.; Ford, L. Addressing Inequities in Healthy Eating. Health Promot. Int. 2015, 30, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ensaff, H. A Nudge in the Right Direction: The Role of Food Choice Architecture in Changing Populations’ Diets. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornier, M.A. Behavior Is Your Brain to Blame for Weight Regain? Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.H.; Charboneau, E.; Dietrich, M.S.; Park, S.; Bradley, B.P.; Mogg, K.; Cowan, R.L. Obese Adults Have Visual Attention Bias for Food Cue Images: Evidence for Altered Reward System Function. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagher, A. Functional Brain Imaging of Appetite. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokum, S.; Ng, J.; Stice, E. Attentional Bias to Food Images Associated with Elevated Weight and Future Weight Gain: An FMRI Study. Obesity 2011, 19, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havermans, R.C.; Giesen, J.C.; Houben, K.; Jansen, A. Weight, Gender, and Snack Appeal. Eat. Behav. 2011, 12, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, I.M.T.; Franken, I.H.A. Attentional Processing of Food Cues in Overweight and Obese Individuals. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Killgore, W.D.S.; Young, A.D.; Femia, L.A.; Bogorodzki, P.; Rogowska, J.; Yurgelun-Todd, D.A. Cortical and Limbic Activation during Viewing of High-versus Low-Calorie Foods. Neurogimage 2003, 19, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, Y.; Preuschhof, C.; Bohner, G.; Bauknecht, H.C.; Klingebiel, R.; Flor, H.; Klapp, B.F. Differential Activation of the Dorsal Striatum by High-Calorie Visual Food Stimuli in Obese Individuals. Neurogimage 2007, 37, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankort, A.; Roefs, A.; Siep, N.; Roebroeck, A.; Havermans, R.; Jansen, A. Reward Activity in Satiated Overweight Women Is Decreased during Unbiased Viewing but Increased When Imagining Taste: An Event-Related FMRI Study. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoeckel, L.E.; Weller, R.E.; Cook, E.W.; Twieg, D.B.; Knowlton, R.C.; Cox, J.E. Widespread Reward-System Activation in Obese Women in Response to Pictures of High-Calorie Foods. Neurogimage 2008, 41, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechert, J.; Meule, A.; Busch, N.A.; Ohla, K. Food-Pics: An Image Database for Experimental Research on Eating and Appetite. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechert, J.; Lender, A.; Polk, S.; Busch, N.A.; Ohla, K. Food-Pics_Extended—An Image Database for Experimental Research on Eating and Appetite: Additional Images, Normative Ratings and an Updated Review. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geliebter, A.; Benson, L.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Hirsch, J.; Carnell, S. Greater Anterior Cingulate Activation and Connectivity in Response to Visual and Auditory High-Calorie Food Cues in Binge Eating: Preliminary Findings. Apetite 2016, 96, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meule, A.; Platte, P. Attentional Bias toward High-Calorie Food-Cues and Trait Motor Impulsivity Interactively Predict Weight Gain. Health Psychol. Open 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charbonnier, L.; Meer, F.V.; Laan, L.N.V.D.; Viergever, M.A.; Smeets, P.A.M. Standardized Food Images: A Photographing Protocol and Image Database. Apetite 2016, 96, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccoli, L.; Delgado, R.; Rodríguezruiz, S.; Guerra, P.; Garcíamármol, E.; Fernándezsantaella, M.C. Meet OLAF, a Good Friend of the IAPS! The Open Library of Affective Foods: A Tool to Investigate the Emotional Impact of Food in Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; He, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X. Increased BOLD Signals in DlPFC Is Associated With Stronger Self-Control in Food-Related Decision-Making. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, X.; Small, D.M.; Chen, H. Extreme Spicy Food Cravers Displayed Increased Brain Activity in Response to Pictures of Foods Containing Chili Peppers: An FMRI Study. Appetite 2019, 142, 104379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wethington, E.; Johnson-Askew, W.L. Contributions of the Life Course Perspective to Research on Food Decision Making. Ann. Behav. Med. 2009, 38, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.E.R.; Bergers, G.; Defares, P.B. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for Assessment of Restrained, Emotional, and External Eating Behavior. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cai, T.; Luo, X. Validation of the Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) in a Sample of Chinese Adolescents. Psychol. Health Med. 2017, 22, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F. The Neural Mechanisms in Attentional Bias on Food Cues for Restraint Eaters. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring Emotion: The Self-Assessment Manikin and the Semantic Differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, L.; Miguet, M.; Bournez, M.; Nicklaus, S.; Chambaron, S.; Monnery-Patris, S. Do Hedonic- versus Nutrition-Based Attitudes toward Food Predict Food Choices? A Cross-Sectional Study of 6- to 11-Year-Olds. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marty, L.; Nicklaus, S.; Miguet, M.; Chambaron, S.; Monnery-Patris, S. When Do Healthiness and Liking Drive Children’s Food Choices? The Influence of Social Context and Weight Status. Apetite 2018, 125, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, L.; Green, E.; Murphy, C. Males and Females Show Differential Brain Activation to Taste When Hungry and Sated in Gustatory and Reward Areas. Appetite 2011, 57, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoeckel, L.E.; Cox, J.E.; Cook, E.W.; Weller, R.E. Motivational State Modulates the Hedonic Value of Food Images Differently in Men and Women. Appetite 2007, 48, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werthmann, J.; Roefs, A.; Nederkoorn, C.; Mogg, K.; Bradley, B.P.; Jansen, A. Can (Not) Take My Eyes off It: Attention Bias for Food in Overweight Participants. Health Psychol. 2011, 30, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serdula, M.K.; Ivery, D.; Coates, R.J.; Freedman, D.S.; Williamson, D.F.; Byers, T. Do Obese Children Become Obese Adults? A Review of the Literature. Prev. Med. 1993, 22, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kegler, M.C.; Alcantara, I.; Haardörfer, R.; Gazmararian, J.A.; Ballard, D.; Sabbs, D. The Influence of Home Food Environments on Eating Behaviors of Overweight and Obese Women. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2014, 46, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermstad, A.K.; Swan, D.W.; Kegler, M.C.; Barnette, J.K.; Glanz, K. Individual and Environmental Correlates of Dietary Fat Intake in Rural Communities: A Structural Equation Model Analysis. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.; Laska, M.N.; Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Predictors of Fruit and Vegetable Intake in Young Adulthood. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Strien, T.; Herman, C.P.; Verheijden, M.W. Eating Style, Overeating, and Overweight in a Representative Dutch Sample. Does External Eating Play a Role? Appetite 2009, 52, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Participants’ Characteristics | n(%) | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | 989 | |
| Female | 666 (67.34%) | - |
| Male | 323 (32.66%) | - |
| Age Group | 989 | |
| Junior high school | 263 (26.59%) | 12.84 (0.79) |
| Senior high school | 307 (31.04%) | 15.89 (0.80) |
| University | 419 (42.37%) | 19.95 (0.94) |
| Body Mass Index | 952 | |
| BMI ≤ 18 | 283 (29.73%) | 17.17 (1.01) |
| 18 < BMI ≤ 24 | 586 (61.55%) | 20.73 (1.44) |
| BMI > 24 | 83 (8.72%) | 25.99 (1.78) |
| DEBQ-RS | 793 | 22.40 (8.13) |
| DEBQ-Em | 792 | 28.84 (12.50) |
| DEBQ-Ex | 811 | 30.74 (8.58) |
| Healthiness | Palatability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| Total | 0.2508 | 0.2620 | 0.6277 | 0.2698 |
| Male | 0.2373 | 0.2383 | 0.5958 ** | 0.2622 |
| Female | 0.2574 | 0.2727 | 0.6431 ** | 0.2723 |
| High school | 0.1996 *** | 0.2380 | 0.6114 ** | 0.2679 |
| University | 0.3203 *** | 0.2771 | 0.6498 ** | 0.2713 |
| BMI ≤ 18 | 0.2264 | 0.2495 | 0.6346 | 0.2592 |
| 18 < BMI ≤ 24 | 0.2615 | 0.2636 | 0.6239 | 0.2755 |
| BMI > 24 | 0.2655 | 0.2764 | 0.6306 | 0.2697 |
| Healthiness (β) | Palatability (β) | DEBQ-RS | DEBQ-Em | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthiness (β) | 1.000 | |||
| Palatability (β) | −0.684 ** | 1.000 | ||
| DEBQ-RS | 0.150 ** | −0.053 | 1.000 | |
| DEBQ-Em | 0.034 | 0.029 | 0.267 ** | 1.000 |
| DEBQ-Ex | −0.015 | 0.150 ** | 0.249 ** | 0.440 ** |
| Healthiness (β) | Palatability (β) | Family Income | Father’s BMI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthiness (β) | 1.000 | |||
| Palatability (β) | −0.684 ** | 1.000 | ||
| Family income | 0.073 * | 0.050 | 1.000 | |
| Father’s BMI | −0.069 * | 0.014 | −0.001 | 1.000 |
| Mother’s BMI | −0.080 * | −0.004 | −0.014 | 0.813 ** |
| Standard Beta | t | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Palatability | 0.851 | 79.868 | <0.001 | |
| Healthiness | 0.247 | 23.215 | <0.001 | ||
| Low-calorie food | Palatability | 0.860 | 52.835 | <0.001 | |
| Healthiness | 0.196 | 12.062 | <0.001 | ||
| High-calorie food | Palatability | 0.837 | 52.9410 | <0.001 | |
| Healthiness | 0.233 | 14.7720 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Han, Y.; Liang, Q.; Yang, X.; Meng, X.; Gao, X. Chinese Food Image Database for Eating and Appetite Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142916
Li X, Pan Y, Han Y, Liang Q, Yang X, Meng X, Gao X. Chinese Food Image Database for Eating and Appetite Studies. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142916
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinhang, Yue Pan, Yan Han, Qianlin Liang, Xinmeng Yang, Xia Meng, and Xiao Gao. 2022. "Chinese Food Image Database for Eating and Appetite Studies" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142916
APA StyleLi, X., Pan, Y., Han, Y., Liang, Q., Yang, X., Meng, X., & Gao, X. (2022). Chinese Food Image Database for Eating and Appetite Studies. Nutrients, 14(14), 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142916




