Interdisciplinary Educational Interventions Improve Knowledge of Eating, Nutrition, and Physical Activity of Elementary Students
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Population
2.3. Assessment of Nutritional Status
2.4. Pre-Intervention Stage
2.4.1. Eating and Nutrition Knowledge
2.4.2. Physical Activity Knowledge
2.5. Intervention Stage
2.5.1. Eating and Nutrition Actions
2.5.2. Physical Activity Actions
2.6. Post-Intervention Stage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethical Issues
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutritional Status Assessment
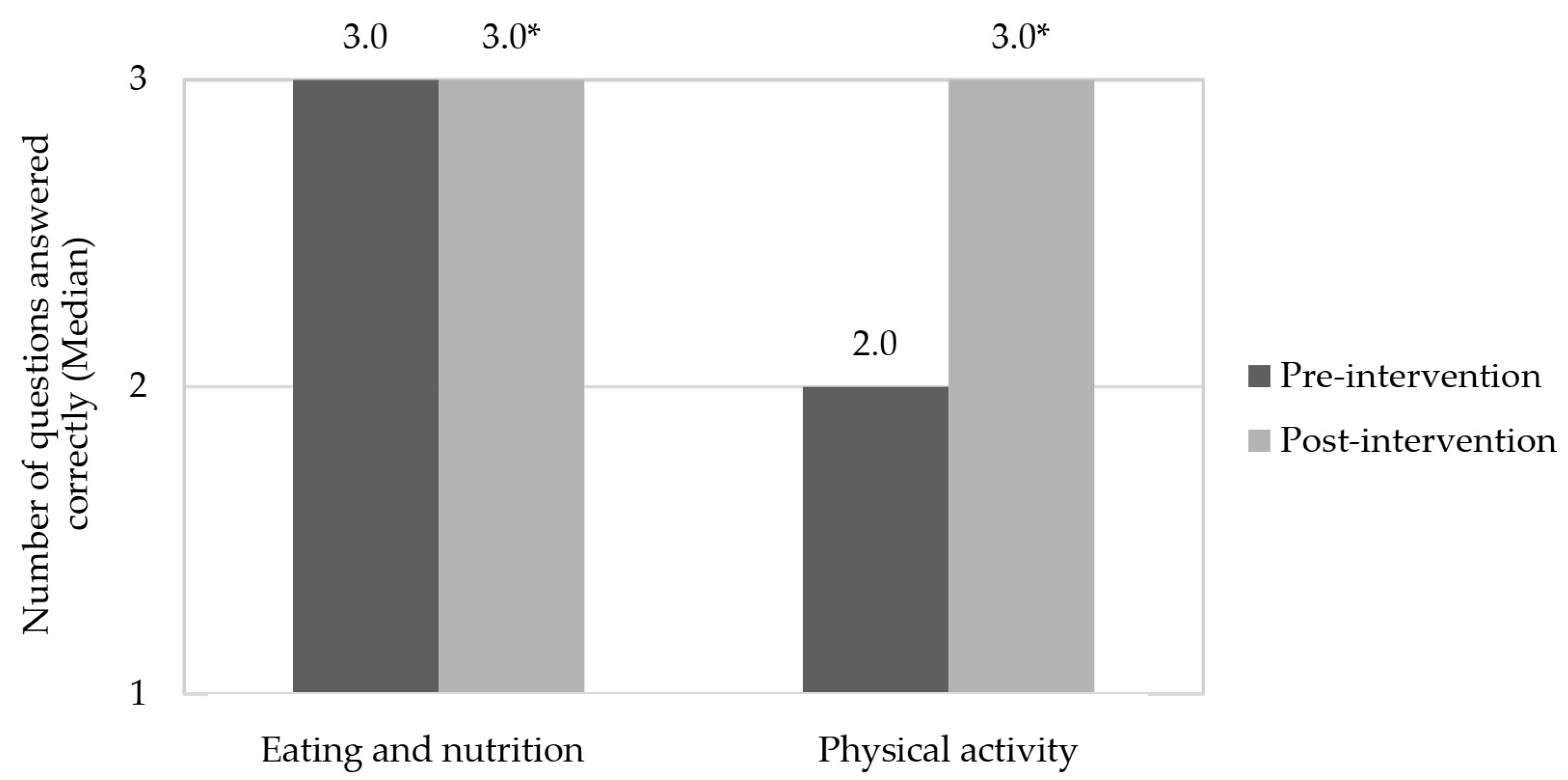
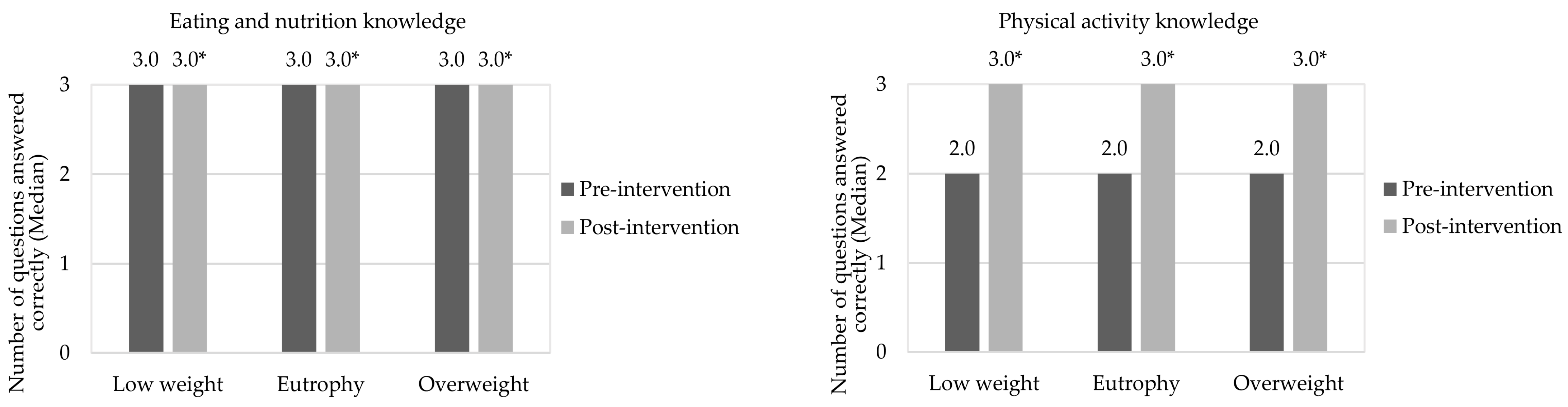
3.2. Evaluation of Pre- and Post-Intervention Stages
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Associação Brasileira para Estudo da Obesidade e da Síndrome Metabólica (ABESO): Mapa da Obesidade. Available online: http://www.abeso.org.br/noticia/quase-60-dos-brasileirosestao-acima-do-peso-revela-pesquisa-do-ibge (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Popkin, B. Nutrition Transition, Diet Change, and Its Implications; Elsevier: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, G.F.; Turner, K.M.; Jago, R. Mothers’ views of their preschool child’s screen-viewing behaviour: A qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birken, C.S.; Lichtblau, B.; Lenton-Brym, T.; Tucker, P.; Maguire, J.L.; Parkin, P.C.; Mahant, S. Parents’ perception of stroller use in young children: A qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Biggers, J.; Spaccarotella, K.; Hongu, N.; Alleman, G.; Worobey, J.; Bredbenner, C.B. Translating it into real life: A qualitative study of the cognitions, barriers and supports for key obesogenic behaviors of parents of preschoolers. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guevara, R.M.; Urchaga, J.D.; Cabaco, A.S.; Moral-García, J.E. The quality of breakfast and healthy diet in school-aged adolescents and their association with bmi, weight loss diets and the practice of physical activity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, J.F.K.; Slonczewski, T.; Clisnei, I.M.M. Estratégias interdisciplinares na abordagem do risco cardiovascular para combate à obesidade infantil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Clin. Med. 2017, 15, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Muftuoglu, S.; Bayram, S. Determination of the relationship between nutrition habits, social physique anxiety, and physical activity levels of adolescent students. World Nutr. 2020, 11, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reloba-Martínez, S.; Reigal-Garrido, E.R.; Hernández Mendo, A.; Martínez-López, E.J.; Martín-Tamayo, I.; Chirosa Ríos, L.J. Effects of vigorous extracurricular physical exercise on the attention of schoolchildren. J. Psychol. Del. Deporte 2017, 26, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- López, L.M.J. Condición física y rendimiento académico. J. Sport Health Res. 2018, 10, 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- National Cancer Institute (NIH). Division of Cancer Control & Population Sciences. Usual Dietary Intakes: Food Intakes, U.S. Population, 2007–2010. Available online: http://epi.grants.cancer.gov/diet/usualintakes/pop/2007-10/ (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Increasing Fruit and Vegetable Consumption To Reduce the Risk of Noncommunicable Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Sistema de Vigilância Alimentar Nutricional (SISVAN). Consumo Alimentar. Available online: http://dabsistemas.saude.gov.br/sistemas/sisvanV2/relatoriopublico/index (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Gomes, T.N.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Hedeker, D.; Fogelholm, M.; Standage, M.; Onywera, V.; Lambert, E.; Tremblay, M.S.; Chaput, J.-P.; Tudor-Locke, C.; et al. Correlates of compliance with recommended levels of physical activity in children. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Physical Activity. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Matsudo, V.K.R.; Ferrari, G.L.M.; Araújo, T.L.; Oliveira, L.C.; Mire, E.; Barreira, T.V.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Katzmarzyk, P. Indicadores de nível socioeconômico, atividade física e sobrepeso/obesidade em crianças brasileiras. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2016, 34, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, F.R.; Molena-Fernandes, C.A.; Guilherme, V.R.; Fávero, M.T.M.; Reis, E.J.B.; Rinaldi, W. Physical inactivity and anthropometric measures in schoolchildren from Paranavaí, Paraná, Brasil. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2015, 33, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kilanowski, J.F. Influences on healthy-eating decision making in latino adolescent children of migrant and seasonal agricultural workers. J. Pediatr. Health Care. 2016, 30, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, J.; Haycraft, E.; Lytle, L.; Nicklaus, S.; Kok, F.J.; Merdji, M.; Fisberg, M.; Moreno, L.A.; Goulet, O.; Hughes, S.O. Nurturing children’s healthy eating: Position statement. Appetite 2019, 137, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmett, P.M.; Jones, L.R. Diet, growth, and obesity development throughout childhood in the avon longitudinal study of parents and children. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 175–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matin, N.; Kelishadi, R.; Heshmat, R.; Motamed-Gorji, N.; Djalalinia, S.; Motlagh, M.E. Joint association of screen time and physical activity on self-rated health and life satisfaction in children and adolescents: The CASPIAN-IV study. Int. Health 2017, 9, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Stolk, R.P.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Sijtsma, A.; Wiersma, R.; Huang, G.; Corpeleijn, E. Factors of physical activity among Chinese children and adolescents: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, S.; Morawska, A.; Mitchell, A. Promoting children’s healthy habits through self-regulation via parenting. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2019, 22, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, J. Nutrition education impact on nutrition knowledge, attitude and practice of schoolchildren: A pilot study in Ghana. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morano, M.; Robazza, C.; Bortoli, L.; Rutigliano, I.; Ruiz, M.C.; Campanozzi, A. Physical activity and physical competence in overweight and obese children: An intervention study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatoug, J.; Msakni, Z.; Zammit, N.; Bhiri, S.; Harrabi, I.; Boughammoura, L.; Slama, S.; Larbi, C.; Ghannem, H. School-based intervention as a component of a comprehensive community program for overweight and obesity prevention, Sousse, Tunisia, 2009–2014. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2015, 12, E160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib-Mourad, C.; Ghandour, L.A.; Maliha, C.; Dagher, M.; Kharroubi, S.; Hwalla, N. Impact of a three-year obesity prevention study on healthy behaviors and BMI among Lebanese schoolchildren: Findings from ajyal salima program. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde Departamento de Atenção Básica Coordenação-Geral da Política de Alimentação e Nutrição. Orientações Para a Coleta e Análise de Dados Antropométricos em Serviços de Saúde: Norma Técnica do Sistema de Vigilância Alimentar e Nutricional—SISVAN/Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde, Departamento de Atenção Básica; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2011.
- Philippi, S.T. Pirâmide dos Alimentos: Fundamentos Básicos da Nutrição, 3rd ed.; Manole: São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bertin, R.L.; Malkowski, J.; Zutter, L.C.I.; Ulbrich, A.Z. Estado nutricional, hábitos alimentares e conhecimentos de nutrição em escolares. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2010, 28, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R.F. Scale Development: Theory and Applications; Sage Publications: Sauzen Oaks, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Domingues, M.R.; Araújo, C.L.P.; Gigante, D.P. Conhecimento e percepção sobre exercício físico em uma população adulta urbana do sul do Brasil. Cad. Saúde Pública 2004, 20, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silveira, E.F.; Silva, M.C. Conhecimento sobre atividade física dos estudantes de uma cidade do sul do Brasil. Mot. Rev. Educ. Fis. 2011, 17, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde; Secretaria de Atenção Primária à Saúde; Departamento de Promoção da Saúde. Guia de Atividade Física para a População Brasileira; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2021.
- Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans; Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria (SBP). Atividade Física na Infância e na Adolescência: Guia Prático para o Pediatra; SBP: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, I.M.G. Promoção de Hábitos Alimentares Saudáveis no Ambiente Escolar: Fortalecimento das Ações de Educação Alimentar e Nutricional e do Programa de Alimentação Escola. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Vitória de Santo Antão, Brazil, 2018; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Radaeli, P.; Irala, C.; Duarte, D.; Coutinho, J.; Fernadez, P. Educação Nutricional para Alunos do Ensino Fundamental; Universidade de Brasília: Brasília, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, B.G.; Fortes, E.N.S.; Lopes, M.A.L.; Guimarães, L.V. Ações de educação alimentar e nutricional para escolares: Um relato de experiência. Demetra Aliment. Nutr. Saúde 2016, 11, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klassmann, L.M.G. O lúdico no Processo de Aprendizagem de Crianças da Educação Infantil; Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso (Especialização)—Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná: Medianeira, Brazil, 2013; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Coraça, F.F. Resgate dos Jogos e Brincadeiras nas Aulas de Educação Física; Universidade Estadual do Oeste do Paraná: Cascavel, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years. 2007. Available online: https://www.who.int/growthref/en/ (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hu, P.; Dong, B.; Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wen, B.; et al. Ethnicity, socioeconomic status and the nutritional status of Chinese children and adolescents: Findings from three consecutive national surveys between 2005 and 2014. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, H.; Goudie, A.; Rettiganti, M.; Leath, K.; Riser, Q.; Thompson, J. Prevalence, patterns, and predictors: A statewide longitudinal study of childhood obesity. J. Sch. Health 2019, 89, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, R.C.; Di Renzo, L.; Cupertino, V.; Romano, L.; De Lorenzo, A.; Salimei, C.; De Lorenzo, A. Secular trend of childhood nutritional status in Calabria (Italy) and the United States: The spread of obesity. Nutr. Res. 2019, 62, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.M.; Rodrigues, M.S. Estado nutricional de crianças e adolescentes residentes na região nordeste do Brasil. Rev. Med. 2020, 99, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.A.S.; Mondini, L.; Jaime, P.C. Ações do Programa Saúde na Escola e da alimentação escolar na prevenção do excesso de peso infantil: Experiência no município de Itapevi, São Paulo, Brasil, 2014. Epidemiol. Serv. 2017, 26, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglioni, S.; De Cosmi, V.; Ciappolino, V.; Parazzini, F.; Brambilla, P.; Agostoni, C. Factors influencing children’s eating behaviours. Nutrients 2018, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Au, L.E.; Rosen, N.J.; Fenton, K.; Hecht, K.; Ritchie, L.D. Eating school lunch is associated with higher diet quality among elementary school students. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchetto, F.H.; Pena, D.B.; Pellanda, L.C. Playful interventions increase knowledge about healthy habits and cardiovascular risk factors in children: The CARDIOKIDS randomized study. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2017, 109, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotich-Mukigi, D.; Bovell-Benjamin, A.C. A Nutrition and Physical Activity Education Model for Cancer Risk Reduction Improves Knowledge and Dietary Behaviors among Students in the Alabama Black Belt. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2017, 4, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciscato, S.J.; Janson, G.; Machado, R.; Lauris, J.R.P.; Andrade, S.M.J.; Fisberg, M. Impacto do Programa de educação nutricional “Nutriamigos®” nos níveis de conhecimento sobre alimentação saudável em crianças escolares. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 2019, 29, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drapeau, V.; Savard, M.; Gallant, A.; Nadeau, L.; Gagnon, J. The effectiveness of a school-based nutrition intervention on children’s fruit, vegetables, and dairy product intake. J. Sch. Health 2016, 86, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrmpas, I.; Goudas, M. Elementary Students’ Knowledge Development during the Implementation of “After School Exercise” Program. Children 2021, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziose, M.M.; Koch, P.A.; Wang, Y.C.; Gray, H.L.; Contento, I.R. Costeffectiveness of a nutrition education curriculum intervention in elementary schools. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, L.R.; Dudley, D.A.; Cotton, W.G. Teaching healthy eating to elementary school students: A scoping review of nutrition education resources. J. Sch. Health 2016, 86, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kigaru, D.M.D.; Loechl, C.; Moleah, T.; Macharia-Mutie, C.W.; Ndungu, Z.W. Nutrition knowledge, attitude and practices among urban primary school children in Nairobi City, Kenya: A KAP study. BMC Nutr. 2015, 1, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandeweghe, L.; Moens, E.; Braet, C.; Van Lippevelde, W.; Vervoort, L.; Verbeken, S. Perceived effective and feasible strategies to promote healthy eating in young children: Focus groups with parents, family child care providers and daycare assistants. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battram, D.S.; Piché, L.; Beynon, C.; Kurtz, J.; He, M. Sugar-sweetened beverages: Children’s perceptions, factors of influence, and suggestions for reducing intake. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2016, 48, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, C.W.; Ørntoft, C.; Larsen, M.N.; Elbe, A.M.; Ottesen, L.; Junge, A.; Krustrup, P. ‘FIFA 11 for Health’for Europe. 1: Effect on health knowledge and well-being of 10-to 12-year-old Danish school children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalkanen, H.; Lindi, V.; Schwab, U.; Kiiskinen, S.; Venäläinen, T.; Karhunen, L.; Lakka, T.; Eloranta, A. Eating behaviour is associated with eating frequency and food consumption in 6–8 year-old children: The physical activity and nutrition in children (PANIC) study. Appetite 2017, 114, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, P.H.; Gerson, D.; Porter, K.; Petrillo, J. A study of school lunch food choice and consumption among elementary school students. Int. J. Child Health Nutr. 2015, 4, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Shariff, Z.M.; Mukhtar, F.; Lye, M.S. Effect of family-based REDUCE intervention program on children eating behavior and dietary intake: Randomized controlled field trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, E.; Eck, K.M.; Delaney, C.; Famodu, O.A.; Olfert, M.D.; Shelnutt, K.P.; Byrd-Bredbenner, C. “It’s Good, It’s Delicious, It’s Great”: Cognitions, barriers, and supports for fruit and vegetable intake of parents and school-aged children. Top. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 34, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Executive Board EB138 th Session 6.3 Noncommunicable Diseases, Geneva. 2016. Available online: https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB138/B138_1(annotated)-en.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Brasil. Ministério da Educação. Fundo Nacional de Desenvolvimento da Educação. Sobre o PNAE. 2020. Available online: http://www.fnde.gov.br/programas/alimentacao-escolar (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Brasil. Ministério da Educação. Programa Saúde na Escola. 2020. Available online: http://portal.mec.gov.br/programa-saude-da-escola/194-secretarias-112877938/secad-educacao-continuada-223369541/14578-programa-saude-nas-escolas (accessed on 5 April 2022).




| Month | Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Practice | |
| Eating and nutrition | ||
| 1 | Cereal group | Food traffic light [38] |
| 2 | Fruit and vegetables group | Seasonality [39] |
| 3 | Dairy, meat and derivatives group | Healthy bowling play [40] |
| 4 | Beans and oilseeds group | Hangman play and beans word search [39] |
| 5 | Oils and fats and sugars and sweets groups | Amount of sugars and fats in foods [39] |
| Physical education | ||
| 1 | Disease prevention through daily physical activity | Undead play [41] |
| 2 | Consequences of physical activity lack | Hopscotch play [41] |
| 3 | Daily physical activity benefits | Mirror play [41] |
| 4 | Physical exercises that help promote health | Musical chairs play [42] |
| 5 | Review of previously discussed topics | Capture the flag play [42] |
| Knowledge Level | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Low | Good | Great | p-Value | |||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Pre-intervention | |||||||
| Eating and nutrition knowledge | 22 | 6.0 c | 131 | 35.6 b | 215 | 58.4 a | <0.001 |
| Physical activity knowledge | 51 | 13.9 c | 162 | 44.0 a | 155 | 42.1 b | <0.001 |
| Post-intervention | |||||||
| Eating and nutrition knowledge | 1 | 0.3 c | 2 | 0.5 b | 365 | 99.2 a | <0.001 |
| Physical activity knowledge | * | * | 1 | 0.3 b | 367 | 99.7 a | <0.001 |
| Knowledge Level | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Low | Good | Great | p-Value | ||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Eating and nutrition knowledge | ||||||||
| Pre-intervention | Gender | |||||||
| Female (n = 201) | 13 | 6.5 c | 65 | 32.3 b | 123 | 61.2 a | <0.001 | |
| Male (n = 167) | 9 | 5.4 c | 66 | 39.5 b | 92 | 55.1 a | <0.001 | |
| Nutritional status | ||||||||
| Low weight (n = 14) | - | - | 6 | 42.9 a | 8 | 57.1 a | =0.593 | |
| Eutrophy (n = 214) | 15 | 7.0 c | 79 | 36.9 b | 120 | 56.1 a | <0.001 | |
| Overweight (n = 140) | 7 | 5.0 c | 46 | 32.9 b | 87 | 62.1 a | <0.001 | |
| Physical activity knowledge | ||||||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female (n = 201) | 21 | 10.4 c | 83 | 41.3 b | 97 | 48.3 a | <0.001 | |
| Male (n = 167) | 30 | 18.0 c | 79 | 47.3 a | 58 | 34.7 b | <0.001 | |
| Nutritional status | ||||||||
| Low weight (n = 14) | 1 | 7.1 c | 9 | 64.3 a | 4 | 28.6 b | =0.030 | |
| Eutrophy (n = 214) | 29 | 13.6 c | 100 | 46.7 a | 85 | 39.7 b | <0.001 | |
| Overweight (n = 140) | 21 | 15.0 c | 53 | 37.9 b | 66 | 47.1 a | <0.001 | |
| Eating and nutrition knowledge | ||||||||
| Post-intervention | Gender | |||||||
| Female (n = 201) | 1 | 0.5 b | 1 | 0.5 b | 199 | 99.0 a | <0.001 | |
| Male (n = 167) | * | * | 1 | 0.6 b | 166 | 99.4 a | <0.001 | |
| Nutritional status | ||||||||
| Low weight (n = 14) | * | * | * | * | 14 | 100.0 | - | |
| Eutrophy (n = 214) | 1 | 0.5 b | 1 | 0.5 b | 212 | 99.1 a | <0.001 | |
| Overweight (n = 140) | * | * | 1 | 0.7 b | 139 | 99.3 a | <0.001 | |
| Physical activity knowledge | ||||||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female (n = 201) | * | * | 1 | 0.5 b | 200 | 99.5 a | <0.001 | |
| Male (n = 167) | * | * | * | * | 167 | 100.0 | - | |
| Nutritional status | ||||||||
| Low weight (n = 14) | * | * | 1 | 7.1 b | 13 | 92.9 a | <0.001 | |
| Eutrophy (n = 214) | * | * | * | * | 214 | 100.0 | - | |
| Overweight (n = 140) | * | * | * | * | 140 | 100.0 | - | |
| Question | Pre-Intervention | Post-Intervention | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Correct Answers (Average ± SD) | Number of Correct Answers (Average ± SD) | ||
| Eating and nutrition knowledge | |||
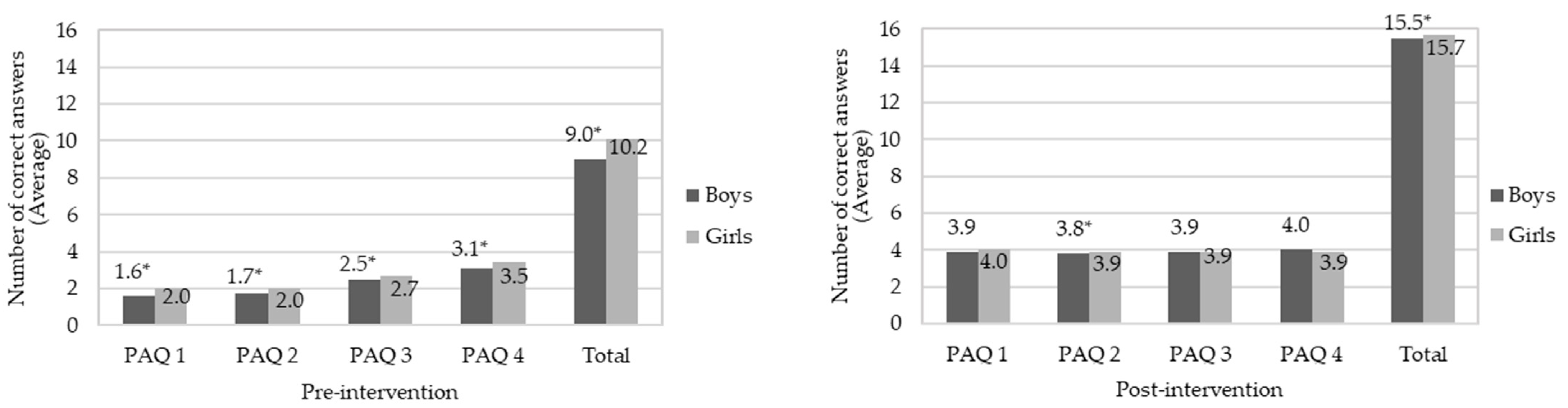
| ENQ 1 | 1.67 ± 1.1 c | 3.86 ± 0.5 b, c | <0.01 |
| ENQ 2 | 3.28 ± 1.1 a | 3.93 ± 0.3 a, b | <0.01 |
| ENQ 3 | 2.11 ± 1.0 b | 3.79 ± 0.6 c | <0.01 |
| ENQ 4 | 3.45 ± 0.9 a | 3.94 ± 0.3 a | <0.01 |
| Total hits | 10.50 ± 2.8 | 15.49 ± 1.3 | <0.01 |
| Physical activity knowledge | |||
| PAQ 1 | 1.80 ± 1.3 c | 3.94 ± 0.3 a, b | <0.01 |
| PAQ 2 | 1.89 ± 1.2 c | 3.87 ± 0.4 c | <0.01 |
| PAQ 3 | 2.61 ± 1.1 b | 3.88 ± 0.3 b, c | <0.01 |
| PAQ 4 | 3.30 ± 1.1 a | 3.95 ± 0.3 a | <0.01 |
| Total hits | 9.63 ± 3.6 | 15.63 ± 0.9 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, M.L.d.; Castagnoli, J.d.L.; Machado, K.M.C.; Soares, J.M.; Teixeira, F.; Schiessel, D.L.; Santos, E.F.d.; Novello, D. Interdisciplinary Educational Interventions Improve Knowledge of Eating, Nutrition, and Physical Activity of Elementary Students. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142827
Oliveira MLd, Castagnoli JdL, Machado KMC, Soares JM, Teixeira F, Schiessel DL, Santos EFd, Novello D. Interdisciplinary Educational Interventions Improve Knowledge of Eating, Nutrition, and Physical Activity of Elementary Students. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142827
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Mayra Lopes de, Juliana de Lara Castagnoli, Kerulyn Maria Chanivski Machado, Jaqueline Machado Soares, Flávia Teixeira, Dalton Luiz Schiessel, Elisvânia Freitas dos Santos, and Daiana Novello. 2022. "Interdisciplinary Educational Interventions Improve Knowledge of Eating, Nutrition, and Physical Activity of Elementary Students" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142827
APA StyleOliveira, M. L. d., Castagnoli, J. d. L., Machado, K. M. C., Soares, J. M., Teixeira, F., Schiessel, D. L., Santos, E. F. d., & Novello, D. (2022). Interdisciplinary Educational Interventions Improve Knowledge of Eating, Nutrition, and Physical Activity of Elementary Students. Nutrients, 14(14), 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142827









