Pollen Food Allergy Syndrome in Allergic March
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
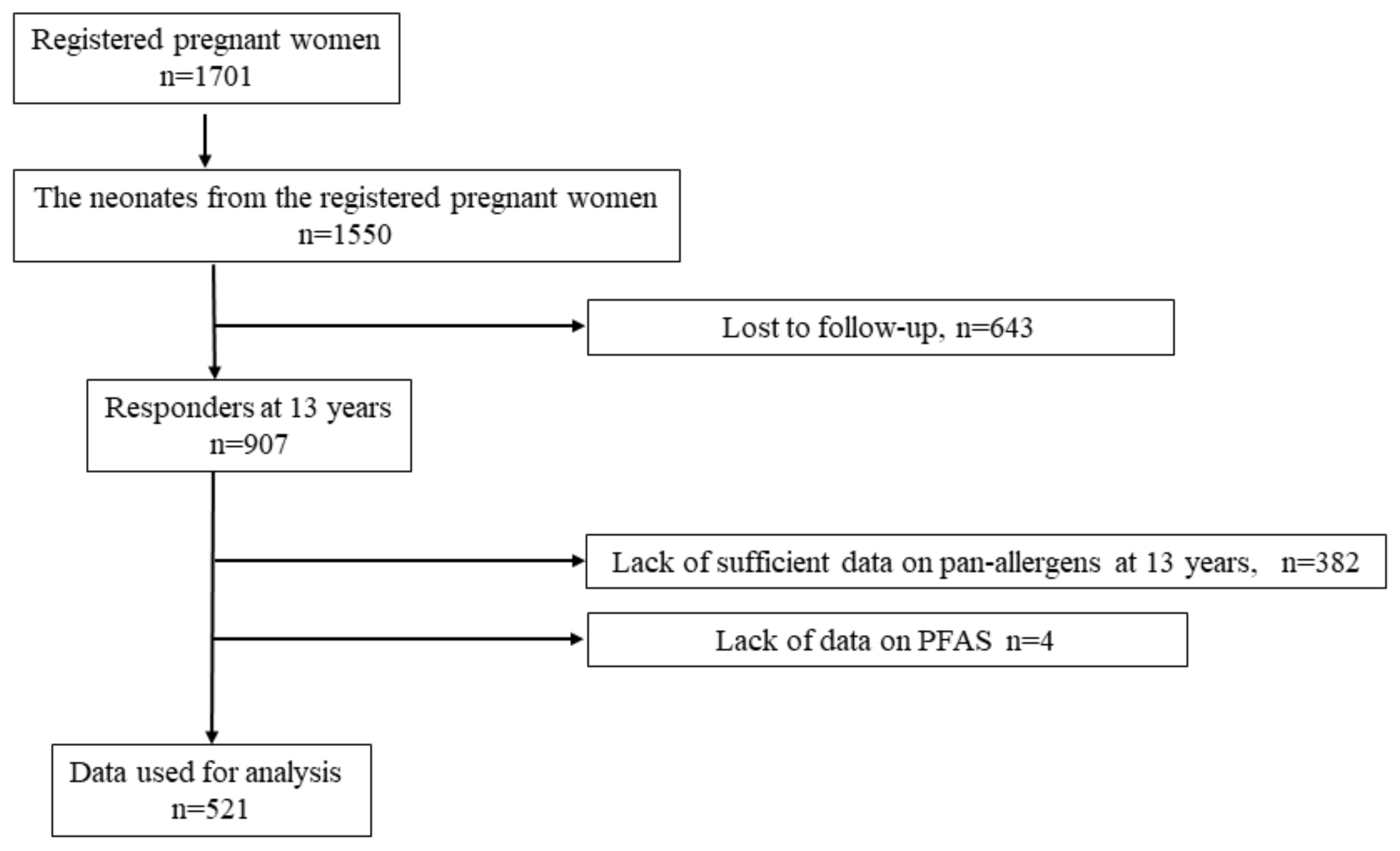
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Participants
2.2. Exposure Variables
2.3. Outcome Variables
2.4. Questionnaire Survey
2.5. Blood Sampling and IgE Component Measurement
2.6. Bias and Study Size
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Association of Allergen Sensitization at 5 or 9 Years of Age with PFAS Outcomes at 13 Years of Age
3.3. Association between Symptoms Suggestive of Allergic Diseases at 5 Years of Age and PFAS Outcomes at 13 Years of Age
3.4. Association between Symptoms Suggestive of Allergic Diseases at 9 Years of Age and PFAS Outcomes at 13 Years of Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amlot, P.L.; Kemeny, D.M.; Zachary, C.; Parkes, P.; Lessof, M.H. Oral allergy syndrome (OAS): Symptoms of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to foods. Clin. Allergy 1987, 17, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessof, M.H. Pollen-food allergy syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, G.; Coop, C. Pollen food allergy syndrome (PFAS): A review of current available literature. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matricardi, P.M.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Hoffmann, H.J.; Valenta, R.; Hilger, C.; Hofmaier, S.; Aalberse, R.C.; Agache, I.; Asero, R.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; et al. EAACI molecular allergology User’s guide. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. S23), 1–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geroldinger-Simic, M.; Zelniker, T.; Aberer, W.; Ebner, C.; Egger, C.; Greiderer, A.; Prem, N.; Lidholm, J.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Vieths, S.; et al. Birch pollen-related food allergy: Clinical aspects and role of allergen-specific IgE and IgG4 antibodies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 616–622.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciprandi, G.; Comite, P.; Ferrero, F.; Bignardi, D.; Minale, P.; Voltolini, S.; Troisse, C.; Mussap, M. Birch allergy and oral allergy syndrome: The practical relevance of serum immunoglobulin E to Bet v 1. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016, 37, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, Y.; Ito, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Sugimoto, C.; Kohno, Y.; Mori, S.; Morikawa, T.; Kato, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Kanno, M.; et al. Epidemiological study of oral allergy syndrome in birch pollen dispersal-free regions. Allergol Int. 2020, 69, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguchi, T.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Saito-Abe, M.; Sato, M.; Irahara, M.; Ogita, H.; Miyagi, Y.; Inuzuka, Y.; Toyokuni, K.; Nishimura, K.; et al. Pollen-food allergy syndrome and component sensitization in adolescents: A Japanese population-based study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.A.; Spergel, J.M. The atopic march: Critical evidence and clinical relevance. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, D.Y.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Deciphering the complexities of atopic dermatitis: Shifting paradigms in treatment approaches. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paller, A.S.; Spergel, J.M.; Mina-Osorio, P.; Irvine, A.D. The atopic march and atopic multimorbidity: Many trajectories, many pathways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, M.M.; Lefebvre, D.L.; Dharma, C.; Dai, D.; Lou, W.Y.W.; Subbarao, P.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Sears, M.R.; et al. Predicting the atopic march: Results from the Canadian Healthy Infant Longitudinal Development study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 601–607.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belgrave, D.C.; Granell, R.; Simpson, A.; Guiver, J.; Bishop, C.; Buchan, I.; Henderson, A.J.; Custovic, A. Developmental profiles of eczema, wheeze, and rhinitis: Two population-based birth cohort studies. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Borres, M.P.; Åberg, M.K.; Yang, L.; Fukuie, T.; Narita, M.; Saito, H.; Ohya, Y. IgE responses to multiple allergen components among school-aged children in a general population birth cohort in Tokyo. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Yang, L.; Narita, M.; Saito, H.; Ohya, Y. Influence of antibiotic use in early childhood on asthma and allergic diseases at age 5. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Narita, M.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Saito, H.; Ohya, Y. Phenotypes of childhood wheeze in Japanese children: A group-based trajectory analysis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koseki, R.; Morii, W.; Noguchi, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Yang, L.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Narita, M.; Saito, H.; Ohya, Y. Effect of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations on atopic dermatitis in young age: A longitudinal birth cohort study. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irahara, M.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Yang, L.; Saito-Abe, M.; Sato, M.; Inuzuka, Y.; Toyokuni, K.; Nishimura, K.; Ishikawa, F.; Miyaji, Y.; et al. Impact of swimming school attendance in 3-year-old children with wheeze and rhinitis at age 5 years: A prospective birth cohort study in Tokyo. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.G.; Hemmer, W.; Nopp, A.; Kleine-Tebbe, J. Advances in IgE testing for diagnosis of allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Aranguren, R.; Lizaso, M.T.; Goikoetxea, M.J.; García, B.E.; Cabrera-Freitag, P.; Trellez, O.; Sanz, M.L. Is the determination of specific IgE against components using ISAC 112 a reproducible technique? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, M.; Roulias, A.; Ferreira, F.; Egger, M. Panallergens and their impact on the allergic patient. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asher, M.I.; Keil, U.; Anderson, H.R.; Beasley, R.; Crane, J.; Martinez, F.; Mitchell, E.A.; Pearce, N.; Sibbald, B.; Stewart, A.W.; et al. International study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC): Rationale and methods. Eur. Respir. J. 1995, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiland, S.K.; Björkstén, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Cookson, W.O.; Von Mutius, E.; Strachan, D.P.; International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood Phase II Study Group. Phase II of the international study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC II): Rationale and methods. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwood, P.; Asher, M.I.; Beasley, R.; Clayton, T.O.; Stewart, A.W.; ISAAC Steering Committee. The international study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC): Phase three rationale and methods. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2005, 9, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marrs, T.; Logan, K.; Craven, J.; Radulovic, S.; McLean, W.H.A.I.; Lack, G.; Lack, G.; Flohr, C.; Perkin, M.R.; EAT Study Team. Dog ownership at three months of age is associated with protection against food allergy. Allergy 2019, 74, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yin, M.; Yang, P.; Li, X.; Di, L.; Wang, W.; Cui, H.; Yan, X.; Liu, J. Effect of exposure to cats and dogs on the risk of asthma and allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2020, 34, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawankar, R.; Holgate, S.T.; Canonica, W.; Lockey, R.F.; Blaiss, M.S. White Book on Allergy 2013 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pawankar, R. Allergic diseases and asthma: A global public health concern and a call to action. World Allergy Organ. J. 2014, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, D.A.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Ram, G.; Spergel, J.M. The epidemiologic characteristics of healthcare provider-diagnosed eczema, asthma, allergic rhinitis, and food allergy in children: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| OR | 95% CI | p | aOR † | 95% CI | p | aOR ‡ | 95% CI | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| At 5 years | ||||||||||||
| Pan-allergen sensitization (278) | 3.52 | 1.72 | 7.17 | <0.001 | 3.23 | 1.58 | 6.62 | 0.0014 | 3.06 | 1.42 | 6.62 | 0.0044 |
| Bet v 1 sensitization (9) | 17.4 | 4.22 | 71.9 | <0.001 | 10.6 | 2.64 | 42.5 | 0.0010 | 11.1 | 1.67 | 73.8 | 0.013 |
| Cry j 1 sensitization (150) | 2.88 | 1.62 | 5.11 | <0.001 | 2.74 | 1.53 | 4.91 | <0.001 | 2.59 | 1.34 | 5.01 | 0.0048 |
| Der p 1 sensitization (181) | 1.59 | 0.90 | 2.82 | 0.11 | 1.66 | 0.92 | 2.99 | 0.096 | 1.47 | 0.75 | 2.90 | 0.26 |
| Der f 1 sensitization (194) | 1.65 | 0.94 | 2.92 | 0.083 | 1.71 | 0.94 | 3.09 | 0.078 | 1.65 | 0.84 | 3.23 | 0.14 |
| Can f 1 sensitization (28) | 1.32 | 0.44 | 3.97 | 0.62 | 1.49 | 0.48 | 4.60 | 0.49 | 2.11 | 0.65 | 6.89 | 0.21 |
| Fel d 1 sensitization (59) | 2.92 | 1.48 | 5.79 | 0.0021 | 2.61 | 1.31 | 5.19 | 0.0066 | 2.83 | 1.28 | 6.25 | 0.010 |
| At 9 years | ||||||||||||
| Pan-allergen sensitization (291) | 12.8 | 3.9 | 41.7 | <0.001 | 8.17 | 2.80 | 23.9 | <0.001 | 11.7 | 3.50 | 39.0 | <0.001 |
| Bet v 1 sensitization (63) | 9.64 | 5.13 | 18.1 | <0.001 | 9.10 | 4.71 | 17.6 | <0.001 | 8.65 | 4.05 | 18.5 | <0.001 |
| Cry j 1 sensitization (268) | 5.15 | 2.38 | 11.2 | <0.001 | 4.28 | 1.98 | 9.25 | <0.001 | 5.35 | 2.27 | 12.6 | <0.001 |
| Der p 1 sensitization (236) | 1.84 | 1.03 | 3.31 | 0.040 | 1.82 | 0.99 | 3.35 | 0.055 | 1.79 | 0.92 | 3.48 | 0.085 |
| Der f 1 sensitization (250) | 1.94 | 1.07 | 3.52 | 0.030 | 1.83 | 0.98 | 3.39 | 0.058 | 1.72 | 0.88 | 3.38 | 0.11 |
| Can f 1 sensitization (43) | 1.59 | 0.67 | 3.78 | 0.29 | 1.40 | 0.58 | 3.41 | 0.46 | 1.93 | 0.73 | 5.13 | 0.18 |
| Fel d 1 sensitization (118) | 2.78 | 1.55 | 4.99 | <0.001 | 2.40 | 1.33 | 4.32 | 0.0037 | 2.47 | 1.27 | 4.81 | 0.0076 |
| OR | 95% CI | p | aOR † | 95% CI | p | aOR ‡ | 95% CI | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| At 5 years | ||||||||||||
| Wheeze current (98) | 2.10 | 1.15 | 3.86 | 0.016 | 2.03 | 1.09 | 3.80 | 0.027 | 1.98 | 0.99 | 3.94 | 0.052 |
| Eczema current (128) | 2.30 | 1.31 | 4.04 | 0.0038 | 2.26 | 1.27 | 4.03 | 0.0056 | 1.77 | 0.93 | 3.38 | 0.082 |
| Rhinitis current (198) | 2.40 | 1.38 | 4.16 | 0.0019 | 2.26 | 1.27 | 4.00 | 0.0055 | 2.23 | 1.19 | 4.18 | 0.0124 |
| Rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (87) | 4.34 | 2.41 | 7.83 | <0.001 | 4.07 | 2.22 | 7.46 | <0.001 | 4.66 | 2.32 | 9.34 | <0.001 |
| Rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (8) | 14.0 | 3.25 | 60.3 | <0.001 | 9.87 | 2.24 | 43.6 | 0.0027 | 6.1 | 0.79 | 46.4 | 0.083 |
| Rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (78) | 3.22 | 1.74 | 5.96 | <0.001 | 2.96 | 1.57 | 5.55 | <0.001 | 3.67 | 1.79 | 7.52 | <0.001 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current (37) | 3.23 | 1.47 | 7.07 | 0.0034 | 3.15 | 1.41 | 7.06 | 0.0055 | 2.85 | 1.16 | 7.00 | 0.022 |
| Wheeze current, rhinitis current (52) | 2.64 | 1.29 | 5.37 | 0.0076 | 2.57 | 1.23 | 5.35 | 0.012 | 2.18 | 0.95 | 5.04 | 0.067 |
| Wheeze current, rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (25) | 3.31 | 1.32 | 8.30 | 0.011 | 3.47 | 1.31 | 9.17 | 0.013 | 3.13 | 1.01 | 9.69 | 0.048 |
| Wheeze current, rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (1) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (23) | 2.28 | 0.81 | 6.38 | 0.118 | 2.37 | 0.80 | 6.99 | 0.12 | 2.51 | 0.74 | 8.51 | 0.14 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current (73) | 2.88 | 1.53 | 5.40 | 0.0010 | 2.66 | 1.39 | 5.09 | 0.0032 | 2.47 | 1.19 | 5.13 | 0.0151 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (45) | 4.26 | 2.11 | 8.61 | <0.001 | 3.93 | 1.91 | 8.10 | <0.001 | 3.73 | 1.61 | 8.69 | 0.0022 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (6) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (41) | 2.79 | 1.29 | 6.04 | 0.0093 | 2.50 | 1.13 | 5.54 | 0.024 | 2.84 | 1.16 | 6.96 | 0.023 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current (23) | 3.69 | 1.45 | 9.37 | 0.0062 | 3.47 | 1.34 | 8.98 | 0.011 | 3.03 | 0.99 | 9.27 | 0.052 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (16) | 5.02 | 1.75 | 14.4 | 0.0026 | 4.91 | 1.67 | 14.4 | 0.0040 | 4.15 | 1.12 | 15.4 | 0.033 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (1) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (14) | 3.22 | 0.98 | 10.6 | 0.055 | 3.08 | 0.91 | 10.4 | 0.071 | 3.14 | 0.75 | 13.2 | 0.118 |
| OR | 95% CI | p | aOR † | 95% CI | p | aOR ‡ | 95% CI | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| At 9 years | ||||||||||||
| Wheeze current (56) | 3.47 | 1.78 | 6.76 | <0.001 | 3.84 | 1.91 | 7.73 | <0.001 | 3.64 | 1.65 | 8.02 | 0.0014 |
| Eczema current (108) | 1.97 | 1.09 | 3.56 | 0.025 | 2.02 | 1.10 | 3.71 | 0.024 | 2.55 | 1.32 | 4.91 | 0.0052 |
| Rhinitis current (291) | 5.00 | 2.40 | 10.4 | <0.001 | 4.90 | 2.31 | 10.4 | <0.001 | 3.96 | 1.83 | 8.59 | <0.001 |
| Rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (201) | 7.93 | 3.89 | 16.2 | <0.001 | 6.68 | 3.29 | 13.6 | <0.001 | 6.78 | 3.16 | 14.6 | <0.001 |
| Rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (45) | 12.5 | 6.28 | 24.8 | <0.001 | 11.3 | 5.50 | 23.3 | <0.001 | 9.0 | 4.00 | 20.0 | <0.001 |
| Rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (192) | 6.04 | 3.14 | 11.6 | <0.001 | 5.30 | 2.75 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 5.67 | 2.73 | 11.8 | <0.001 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current (16) | 6.72 | 2.40 | 18.8 | <0.001 | 7.10 | 2.41 | 20.9 | <0.001 | 7.09 | 2.12 | 23.7 | 0.0015 |
| Wheeze current, rhinitis current (46) | 4.14 | 2.06 | 8.33 | <0.001 | 4.50 | 2.18 | 9.32 | <0.001 | 3.92 | 1.73 | 8.90 | 0.0011 |
| Wheeze current, rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (37) | 3.96 | 1.84 | 8.54 | <0.001 | 4.02 | 1.82 | 8.88 | <0.001 | 3.96 | 1.63 | 9.63 | 0.0024 |
| Wheeze current, rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (9) | 31.9 | 6.44 | 158 | <0.001 | - | - | - | - | 36.5 | 6.44 | 207 | <0.001 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (35) | 3.11 | 1.38 | 7.02 | 0.0064 | 3.07 | 1.33 | 7.07 | 0.0087 | 3.36 | 1.35 | 8.36 | 0.0093 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current (77) | 2.69 | 1.44 | 5.02 | 0.0020 | 2.66 | 1.39 | 5.08 | 0.0033 | 3.46 | 1.71 | 7.00 | <0.001 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (56) | 3.25 | 1.64 | 6.43 | <0.001 | 2.92 | 1.44 | 5.94 | 0.0031 | 4.36 | 2.04 | 9.30 | <0.001 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (17) | 6.30 | 2.30 | 17.3 | <0.001 | 6.14 | 2.09 | 18.0 | 0.0011 | 6.97 | 2.32 | 21.0 | <0.001 |
| Eczema current, rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (54) | 3.02 | 1.50 | 6.08 | 0.0019 | 2.68 | 1.31 | 5.52 | 0.0075 | 4.01 | 1.86 | 8.66 | <0.001 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current (13) | 7.29 | 2.36 | 22.5 | <0.001 | 7.80 | 2.38 | 25.6 | <0.001 | 8.26 | 2.13 | 32.1 | 0.0023 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current, pan-allergen sensitization (12) | 6.08 | 1.86 | 19.8 | 0.0028 | 6.17 | 1.78 | 21.3 | 0.0043 | 8.26 | 2.13 | 32.1 | 0.0023 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current, Bet v 1 sensitization (5) | 33.9 | 3.72 | 308 | 0.0018 | - | - | - | - | 35.5 | 3.55 | 356 | 0.0024 |
| Wheeze current, eczema current, rhinitis current, Cry j 1 sensitization (11) | 4.77 | 1.35 | 16.8 | 0.015 | 4.69 | 1.26 | 17.4 | 0.022 | 6.12 | 1.48 | 25.4 | 0.012 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasudo, H.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Yang, L.; Saito-Abe, M.; Sato, M.; Miyaji, Y.; Shimada, M.; Hirai, S.; Toyokuni, K.; Ishikawa, F.; et al. Pollen Food Allergy Syndrome in Allergic March. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132658
Yasudo H, Yamamoto-Hanada K, Yang L, Saito-Abe M, Sato M, Miyaji Y, Shimada M, Hirai S, Toyokuni K, Ishikawa F, et al. Pollen Food Allergy Syndrome in Allergic March. Nutrients. 2022; 14(13):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132658
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasudo, Hiroki, Kiwako Yamamoto-Hanada, Limin Yang, Mayako Saito-Abe, Miori Sato, Yumiko Miyaji, Mami Shimada, Seiko Hirai, Kenji Toyokuni, Fumi Ishikawa, and et al. 2022. "Pollen Food Allergy Syndrome in Allergic March" Nutrients 14, no. 13: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132658
APA StyleYasudo, H., Yamamoto-Hanada, K., Yang, L., Saito-Abe, M., Sato, M., Miyaji, Y., Shimada, M., Hirai, S., Toyokuni, K., Ishikawa, F., Inuzuka, Y., Kabashima, S., Fukuie, T., & Ohya, Y. (2022). Pollen Food Allergy Syndrome in Allergic March. Nutrients, 14(13), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132658






