Changes in Phospholipid Composition of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex during Normal Ageing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Brain Tissue
2.3. Subcellular Fractionation
2.4. Lipid Extraction
2.5. Mass Spectrometry and Lipid Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Protein Concentration and Proportion of Phospholipid Classes in the Microsomal and Mitochondrial Membrane Fractions of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex
3.2. Abundant Phospholipid Molecules of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex
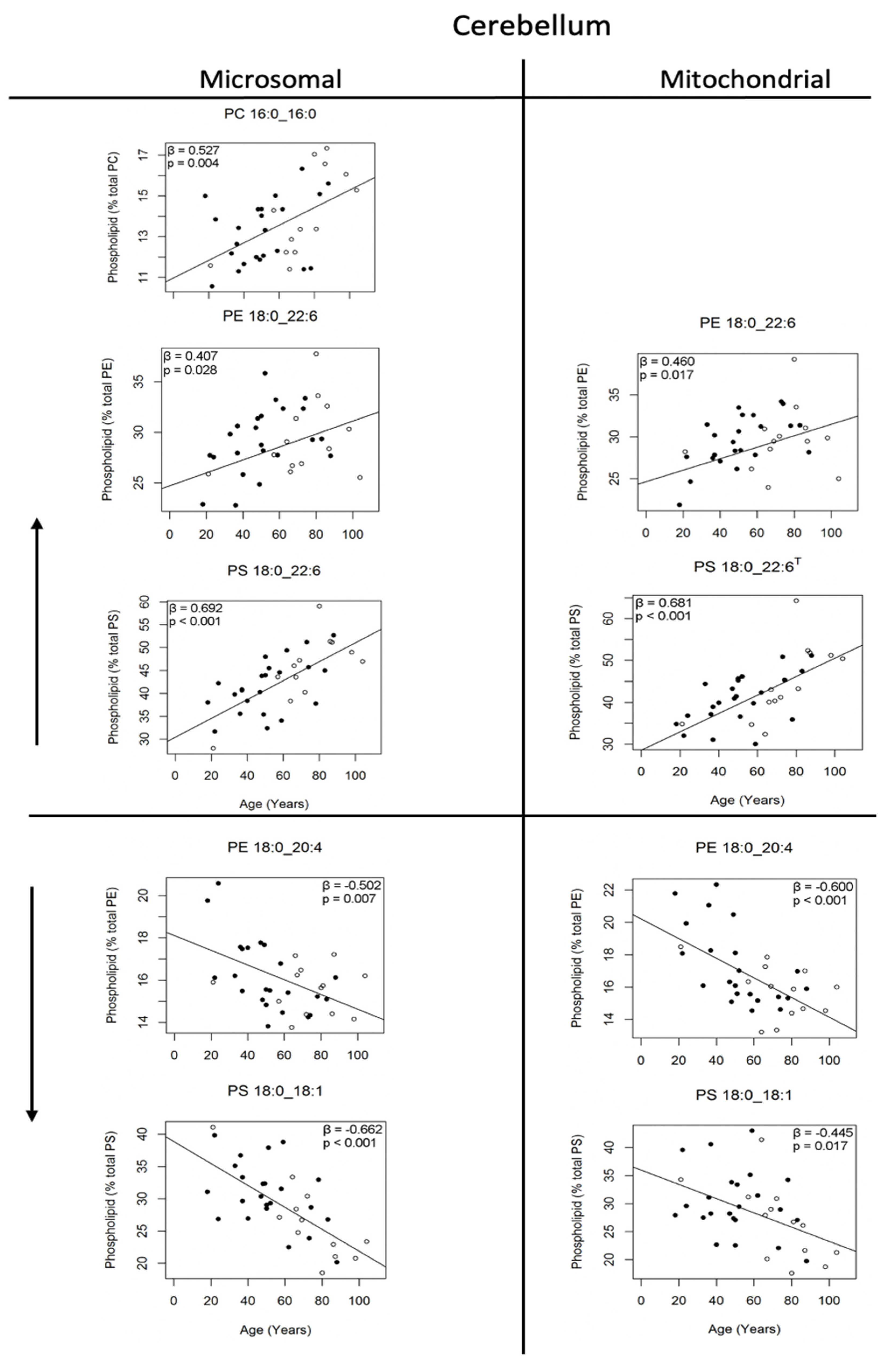
3.3. Changes in Phosphatidylcholine Molecules of the Human Cerebellum with Age
3.4. Changes in Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylserine Molecules of the Human Cerebellum with Age
3.5. Changes in Phosphatidylcholine Molecules of the Human Motor Cortex with Age
3.6. Changes in Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylserine Molecules of the Human Motor Cortex with Age
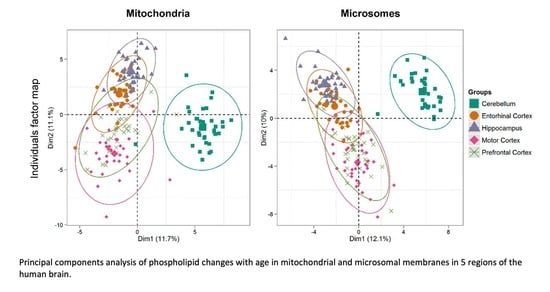
3.7. Hierarchical Clustering of Changes in Phospholipids Associated with Age in Five Areas of the Human Brain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- O’Brien, J.S.; Sampson, E.L. Lipid composition of the normal human brain: Gray matter, white matter, and myelin. J. Lipid Res. 1965, 6, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Else, P.L. The Highly Unnatural Fatty Acid Profile of Cells in Culture. Prog. Lipid Res. 2020, 77, 101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, S.E.; Freidrich, F.G.; Mitchell, T.W.; Truscott, R.J.W.; Else, P.L. Human prefrontal cortex phospholipids containing docosahexaenoic acid increase during normal ageing, whereas those containing arachidonic acid decrease. Neurobiol. Ageing 2015, 36, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, S.E.; Freidrich, F.G.; Mitchell, T.W.; Truscott, R.J.W.; Else, P.L. Decreases in Phospholipids Containing Adrenic and Arachidonic Acids Occur in the Human Hippocampus over the Adult Lifespan. Lipids 2015, 50, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.E.; Freidrich, F.G.; Mitchell, T.W.; Truscott, R.J.W.; Else, P.L. The phospholipid composition of the human entorhinal cortex remains relatively stable over 80 years of adult aging. Geroscience 2016, 38, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deeley, J.M.; Mitchell, T.W.; Wei, X.; Korth, J.; Nealon, J.R.; Blanksby, S.J.; Truscott, R.J.W. Human lens lipids differ markedly from those of commonly used experimnetal animals. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebisch, G.; Vizcaíno, J.A.; Köfeler, H.; Trötzmüller, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Schmitz, G.; Spencer, F.; Wakelam, M.J.O. Shorthand notation for lipid structures derived from mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, S.E.; Toledo, J.B.; Appleby, D.H.; Xie, S.X.; Wang, L.-S.; Back, Y.; Wolk, D.A.; Lee, E.B.; Miller, B.L.; Lee, M.-Y.; et al. Comparative survey of the topographical distribution of signature molecular lesions in major neurodegenerative diseases. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 4339–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E.; Bohl, J.; Lang, W. Alzheimer’s disease: Amyloid plaques in the cerebellum. J. Neurol. Sci. 1989, 93, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.C.; Cételat, G.; Desgranges, B.; Perchey, G.; Landeau, B.; de la Sayette, V.; Eustache, F. In vivo mapping of grey matterr loss with voxel-basedmorphometry in mild Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 2001, 14, 209–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L. Regional covariance patterns of gray matter alterations in Alzheimer’s disease and its replicability evaluation. J. Mag. Reson. Imaging 2014, 39, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, P.M.; Mega, M.S.; Woods, R.P.; Zoumalan, C.I.; Lindshield, C.J.; Blaton, E.; Moussai, J.; Holmes, C.J.; Cummings, J.L.; Toga, A.W. Cortical change in Alzheimer’s disease detected with a disease-specific population-based brain atlas. Cereb. Cortex 2001, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Holtzman, D.M.; McKeel, D.W.J. Plasmalogen deficiency in early Alzheimers disease subjects and in animal models: Molecular characterization using electronspray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderberg, M.; Edlund, C.; Alafuzoff, I.; Kristensson, K.; Dallner, G. Lipid composition in different regions of the brain in Alzheimer’s disease/senile dementia of Alzheimers type. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.B.; Oliveira, T.G.; Cotes, E.P.; Honig, L.S.; Duff, K.E.; Small, S.A.; Wenk, M.R.; Shui, G.; Di Paolo, G. Comparative lipidomic analysis of mouse and human brain with Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, M.R.; Lovell, M.A.; Yatin, M.; Dhillon, H.; Markesbery, W.R. Regional membrane phospholipid alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 1998, 23, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettegrew, J.W.; Panachalingam, K.; Hamilton, R.L.; McClure, R.J. Brain membrane phospholipid alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderberg, M.; Edlund, C.; Kristensson, K.; Dallner, G. Lipid compositions of different regions of the human brain during aging. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Else, P.L.; Kraffe, E. Docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid peroxidation: Its a within molecular cascade. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortie, C.H.; Hulbert, A.J.; Hancock, S.E.; Mitchell, T.W.; McAndrew, D.; Else, P.L. Of mice, pigs and humans:An analysis of mitochondrial phospholipids from mammals with very different maximal lifespans. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 70, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortie, C.H.; Else, P.L. An antioxidant-like action for non-peroxidisable phospholipids using ferrous iron as a peroxidation initiator. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornelius, F.; Habeck, M.; Kanai, R.; Toyoshima, C.; Karlish, S.J.D. General and specific lipid-protein interactions in Na,K-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balaban, R.S.; Nemoto, S.; Finkel, T. Mitochondria, oxidant, and aging. Cell 2005, 120, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, C.; Boafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; De Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E. Inflamm-ageing: An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabré, R.; Naudí, A.; Dominguez-Gonzalez, M.; Jové, M.; Ayala, V.; Mota-Martorell, N.; Pradas, I.; Nogueras, L.; Rué, M.; Portero-Otín, M.; et al. Lipid Profile in Human Frontal Cortex Is Sustained Throughout Healthy Adult Life Span to Decay at Advanced Ages. J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. 2017, 73, 703–710. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas, E.; Sies, H. The Lag Phase. Free Radic. Res. 1998, 28, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, V.; Fabelo, N.; Santpere, G.; Puig, B.; Marín, R.; Ferrer, I.; Díaz, M. Lipid alterations in lipid rafts from Alzheimer’s disease human brain cortex. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svennerholm, L.; Boström, K.; Jungber, B.; O’lsson, L. Membrane lipids of adult human brain: Lipid composition of frontal and temporal lobe in subjects of age 20 to 100 years. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderberg, M.; Edlund, C.; Kristensson, K.; Dallner, G. Fatty acid composition of brain phospholipids in aging and in Alzheimers disease. Lipids 1991, 26, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, J.D.; Benford, V.J.; Han, B.; Cantor, A.B. The relationship between age and the fatty acid composition of cerebral cortex and erythrocytes in human subjects. Brain Res. Bull. 2001, 56, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, R.K.; Liu, Y.; Jandacek, R.; Rider, T.; Tso, P. The ageing human orbitofrontal cortex: Decreasing polyunsaturated fatty acid composition and associated increases in lipogenic gene expression and stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2008, 78, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, T.; Taylor, H.; Love, S. Fatty acid composition of frontal, temporal and parietal neocortex in the normal human brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7248–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fatty Acid Combinations | Microsomal | Mitochondrial | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerebellum | Motor Cortex | Cerebellum | Motor Cortex | |||||||
| % of the PC, PE or PS | % Change | % of the PC, PE or PS | % Change | % of the PC, PE or PS | % Change | % of the PC, PE or PS | % Change | |||
| Increase | PC | 14:0_16:0 | - | - | 1.42 ± 0.02 | 15% | - | - | ||
| 16:0_16:0 | 13.55 ± 0.31 | 30% | - | - | - | |||||
| 16:0_18:2 | 1.18 ± 0.05 | 54% | 1.25 ± 0.05 | 51% | 1.10 ± 0.05 | 39% | 1.26 ± 0.05 | 59% | ||
| 16:0_22:6 | - | 4.00 ± 0.03 | 20% | - | ||||||
| PE | 16:0_22:6 | 6.21 ± 0.11 | 25% | 6.27 ± 0.12 | 34% | - | ||||
| 18:0_22:6 | 29.27 ± 0.56 | 20% | 29.54 ± 0.56 | 21% | - | |||||
| 18:1_22:6 | 2.86 ± 0.05 | 26% | 2.95 ± 0.07 | 33% | - | |||||
| 15:0_22:4/ O-16:0_22:4 | - | 0.65 ± 0.07 | 86% | - | ||||||
| 15:0_22:6/ O-16:0_22:6 | 1.66 ± 0.09 | 61% | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 83% | 1.73 ± 0.12 | 263% | - | |||
| O-18:1_22:5 | - | 1.36 ± 0.11 | 75% | - | ||||||
| O-18:1_22:6 | - | 1.99 ± 0.04 | 16% | 2.74 ± 0.06 | 22% | - | ||||
| PS | 18:0_22:6 | 42.91 ± 6.67 | 48% | 42.16 ± 1.22 | 50% | - | ||||
| 18:1_20:1 | 1.89 ± 0.70 | 129% | - | |||||||
| Decrease | PC | Lyso-18:1 | 0.86 ± 0.05 | 10% | - | |||||
| 16:0_20:1 | 1.54 ± 0.22 | 23% | 1.48 ± 0.21 | 27% | ||||||
| 16:0_20:4 | - | - | 3.59 ± 0.10 | 17% | ||||||
| 16:0_22:4 | 2.50 ± 0.07 | 22% | 2.89 ± 0.23 | 25% | 1.95 ± 0.15 | 41% | ||||
| 18:0_18:1 | 7.55 ± 0.17 | 18% | - | - | ||||||
| 18:0_20:4 | - | - | 1.71 ± 0.08 | 28% | - | - | ||||
| 18:1_22:6 | 1.12 ± 0.03 | 59% | - | - | ||||||
| PE | Lyso 22:4 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 38% | - | ||||||
| 16:0_22:4 | 0.78 ± 0.04 | 38% | - | - | ||||||
| 18:0_18:1 | 2.83 ± 0.08 | 27% | 2.79 ± 0.08 | 28% | - | |||||
| 18:0_20:4 | 15.97 ± 0.26 | 16% | 16.71 ± 0.38 | 25% | - | |||||
| 18:0_22:4 | 3.49 ± 0.14 | 36% | 3.36 ± 0.13 | 39% | - | |||||
| O-16:1_22:4 | - | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 45% | - | - | |||||
| O-16:1_22:5 | 1.09 ± 0.07 | 54% | - | |||||||
| 17:0_22:4/ O-18:0_22:4 | 1.31 ± 0.07 | 40% | - | |||||||
| PS | 18:0_18:1 | 29.88 ± 6.85 | 38% | - | 28.84 ± 1.06 | 30% | - | |||
| 18:0_20:1 | 2.13 ± 1.13 | 56% | - | - | - | |||||
| 18:0_20:2 | 1.10 ± 0.65 | 38% | - | - | - | |||||
| 18:0_22:4 | 6.12 ± 1.64 | 28% | - | 6.25 ± 0.23 | 37% | - | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hancock, S.E.; Friedrich, M.G.; Mitchell, T.W.; Truscott, R.J.W.; Else, P.L. Changes in Phospholipid Composition of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex during Normal Ageing. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122495
Hancock SE, Friedrich MG, Mitchell TW, Truscott RJW, Else PL. Changes in Phospholipid Composition of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex during Normal Ageing. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122495
Chicago/Turabian StyleHancock, Sarah E., Michael G. Friedrich, Todd W. Mitchell, Roger J. W. Truscott, and Paul L. Else. 2022. "Changes in Phospholipid Composition of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex during Normal Ageing" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122495
APA StyleHancock, S. E., Friedrich, M. G., Mitchell, T. W., Truscott, R. J. W., & Else, P. L. (2022). Changes in Phospholipid Composition of the Human Cerebellum and Motor Cortex during Normal Ageing. Nutrients, 14(12), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122495