Plasma Nitrate and Nitrite Kinetics after Single Intake of Beetroot Juice in Adult Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis and in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Composition of Nitrate-Enriched and Placebo Beetroot Juice
2.3. Blood, Dialysate, and Saliva Collection
2.4. Hemodialysis Procedure
2.5. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.6. Nitrate and Nitrite in Plasma, Saliva, and Dialysate
2.7. N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Potassium in Plasma
2.8. Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate in Plasma
2.9. Kinetic Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Populations
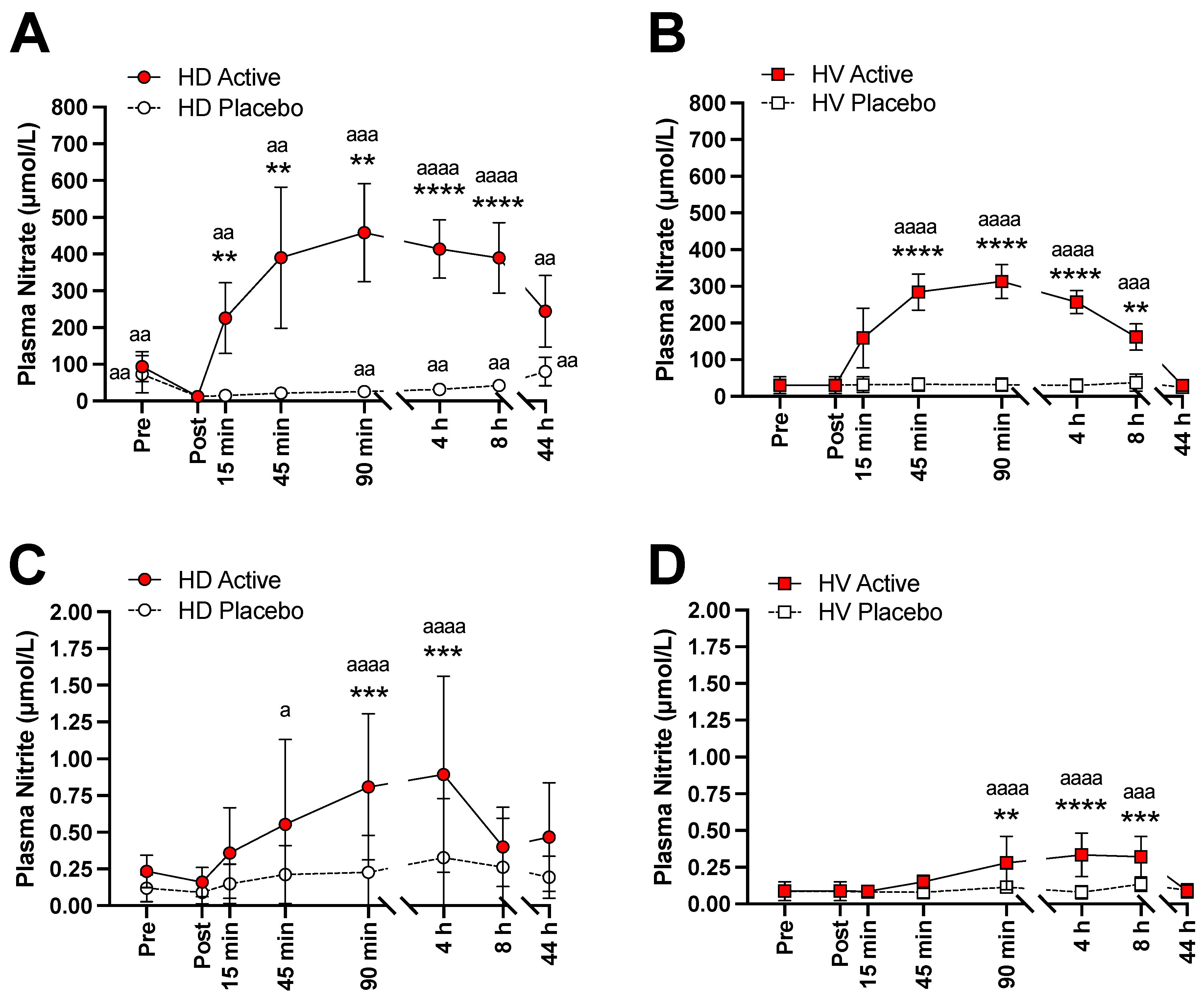
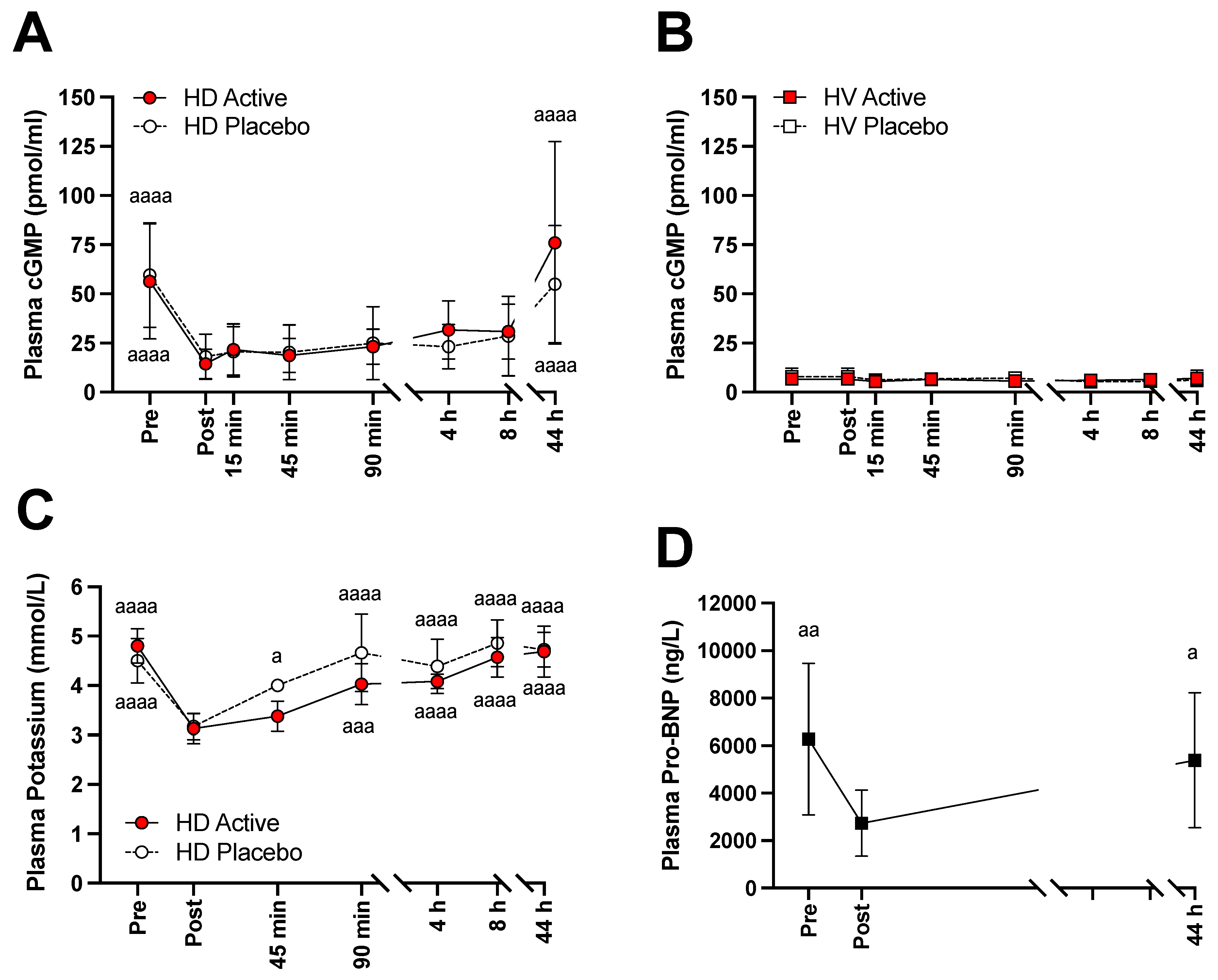
3.2. Changes of NO Markers, Potassium, and Pro-BNP
3.3. Kinetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Floege, J.; Drueke, T.B. Mineral and bone disorder in chronic kidney disease: Pioneering studies. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, Z.J.; Lu, Y.; Ji, N.; Kapke, A.; Selewski, D.T.; Dietrich, X.; Abbott, K.; Nallamothu, B.K.; Schaubel, D.E.; Saran, R.; et al. Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Young Adults with End-stage Renal Disease: An Analysis of the US Renal Data System. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlstrom, M. Nitric oxide signalling in kidney regulation and cardiometabolic health. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Gladwin, M.T.; Weitzberg, E. Strategies to increase nitric oxide signalling in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Gladwin, M.T.; Ahluwalia, A.; Benjamin, N.; Bryan, N.S.; Butler, A.; Cabrales, P.; Fago, A.; Feelisch, M.; Ford, P.C.; et al. Nitrate and nitrite in biology, nutrition and therapeutics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Carlstrom, M.; Larsen, F.J.; Weitzberg, E. Roles of dietary inorganic nitrate in cardiovascular health and disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstrom, M.; Montenegro, M.F. Therapeutic value of stimulating the nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway to attenuate oxidative stress and restore nitric oxide bioavailability in cardiorenal disease. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlstrom, M.; Cananau, C.; Checa, A.; Wide, K.; Sartz, L.; Svensson, A.; Wheelock, C.E.; Westphal, S.; Bekassy, Z.; Barany, P.; et al. Peritoneal dialysis impairs nitric oxide homeostasis and may predispose infants with low systolic blood pressure to cerebral ischemia. Nitric Oxide 2016, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia Martinez, A.; Rosa Diez, G.; Ferraris, V.; Coccia, P.A.; Ferraris, J.R.; Checa, A.; Wheelock, C.E.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Carlstrom, M.; et al. Removal of nitrate and nitrite by hemodialysis in end-stage renal disease and by sustained low-efficiency dialysis in acute kidney injury. Nitric Oxide 2020, 98, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, O.M.; Easton, C.; Shepherd, A.I.; Siervo, M.; Bailey, S.J.; Clifford, T. Dietary nitrate and population health: A narrative review of the translational potential of existing laboratory studies. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, L.S.; Arabi, S.M.; Feizy, Z.; Rezvani, R. The effect of beetroot inorganic nitrate supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. Nitric Oxide 2021, 115, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, C.P.; Liu, A.H.; Croft, K.D.; Considine, M.J.; Puddey, I.B.; Woodman, R.J.; Hodgson, J.M. Antibacterial mouthwash blunts oral nitrate reduction and increases blood pressure in treated hypertensive men and women. Am. J. Hypertens 2015, 28, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapil, V.; Haydar, S.M.; Pearl, V.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Ahluwalia, A. Physiological role for nitrate-reducing oral bacteria in blood pressure control. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 55, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersson, J.; Carlstrom, M.; Schreiber, O.; Phillipson, M.; Christoffersson, G.; Jagare, A.; Roos, S.; Jansson, E.A.; Persson, A.E.; Lundberg, J.O.; et al. Gastroprotective and blood pressure lowering effects of dietary nitrate are abolished by an antiseptic mouthwash. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govoni, M.; Jansson, E.A.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O. The increase in plasma nitrite after a dietary nitrate load is markedly attenuated by an antibacterial mouthwash. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Brown, M.A.; Tam, S.H.; Chan, M.C.; Whitworth, J.A. Effects of diet on measurement of nitric oxide metabolites. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 1997, 24, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hord, N.G.; Tang, Y.; Bryan, N.S. Food sources of nitrates and nitrites: The physiologic context for potential health benefits. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, M.; Winyard, P.G.; Fulford, J.; Anning, C.; Shore, A.C.; Benjamin, N. Dietary nitrate supplementation improves reaction time in type 2 diabetes: Development and application of a novel nitrate-depleted beetroot juice placebo. Nitric Oxide 2014, 40, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.J.; Patel, N.; Loukogeorgakis, S.; Okorie, M.; Aboud, Z.; Misra, S.; Rashid, R.; Miall, P.; Deanfield, J.; Benjamin, N.; et al. Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension 2008, 51, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlstrom, M.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Mechanisms underlying blood pressure reduction by dietary inorganic nitrate. Acta Physiol. 2018, 224, e13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ing, T.S.; Yu, A.W.; Wong, F.K.; Rafiq, M.; Zhou, F.Q.; Daugirdas, J.T. Collection of a representative fraction of total spent hemodialysate. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 25, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative. NKF-K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hemodialysis Adequacy: Update 2000. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, S7–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldau, R.; Kuhlmann, U.; Samadi, N.; Gross, M.; Graf, T.; Orlandini, G.; Marcelli, D.; Lange, H. Ionic dialysance measurement is urea distribution volume dependent: A new approach to better results. Artif. Organs 2002, 26, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, M.F.; Sundqvist, M.L.; Nihlen, C.; Hezel, M.; Carlstrom, M.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O. Profound differences between humans and rodents in the ability to concentrate salivary nitrate: Implications for translational research. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Takeda, S.; Kurokawa, S.; Kubo, T.; Fukuda, N.; Izumi, T. Cyclic GMP production by ANP, BNP, and NO during worsening and improvement of chronic heart failure. Jpn. Heart J. 2003, 44, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, M.S.S.; Eismark, F.; Goetze, J.P.; Gustafsson, F.; Wolsk, E. The contribution of cardiac and extracardiac factors to NT-proBNP concentrations in patients with advanced heart failure before and after left ventricular assist device implantation. Peptides 2021, 135, 170420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Bohm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstrom, M.; Wide, K.; Lundvall, M.; Cananau, C.; Svensson, A.; Lundberg, J.O.; Barany, P.; Krmar, R.T. Plasma nitrate/nitrite removal by peritoneal dialysis might predispose infants with low blood pressure to cerebral ischaemia. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Carlstrom, M.; Weitzberg, E. Metabolic Effects of Dietary Nitrate in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapil, V.; Khambata, R.S.; Robertson, A.; Caulfield, M.J.; Ahluwalia, A. Dietary nitrate provides sustained blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients: A randomized, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Hypertension 2015, 65, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velmurugan, S.; Gan, J.M.; Rathod, K.S.; Khambata, R.S.; Ghosh, S.M.; Hartley, A.; Van Eijl, S.; Sagi-Kiss, V.; Chowdhury, T.A.; Curtis, M.; et al. Dietary nitrate improves vascular function in patients with hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kemmner, S.; Lorenz, G.; Wobst, J.; Kessler, T.; Wen, M.; Gunthner, R.; Stock, K.; Heemann, U.; Burkhardt, K.; Baumann, M.; et al. Dietary nitrate load lowers blood pressure and renal resistive index in patients with chronic kidney disease: A pilot study. Nitric Oxide 2017, 64, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramick, M.G.; Kirkman, D.L.; Stock, J.M.; Muth, B.J.; Farquhar, W.B.; Chirinos, J.A.; Doulias, P.T.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Edwards, D.G. The effect of dietary nitrate on exercise capacity in chronic kidney disease: A randomized controlled pilot study. Nitric Oxide 2021, 106, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, H.; de Joode, M.; Hossein, I.J.; Henckens, N.F.T.; Guggeis, M.A.; Berends, J.E.; de Kok, T.; van Breda, S.G.J. The benefits and risks of beetroot juice consumption: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.B.D.; Cockburn, A.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Dogliotti, E.; Alessandro, D.D.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; Fürst, P.; Galli, C.; Verger, P.; et al. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in the Food chain on a request from the European Commission to perform a scientific risk assessment on nitrate in vegetables. EFSA J. 2008, 689, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speijers, G.; van den Brandt, P.A. Nitrite and potential endogenous formation of N-nitroso compounds; Safety evaluation of certain food additives, JECFA. WHO Food Addit. Ser. 2003, 50, 49–74. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, L.; Beaumier, L.; Ajami, A.M.; Young, V.R. Whole body nitric oxide synthesis in healthy men determined from [15N] arginine-to-[15N]citrulline labeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11460–11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakinis, A.; Jungersten, L.; Wennmalm, A. An 18oxygen inhalation method for determination of total body formation of nitric oxide in humans. Clin. Physiol. 1999, 19, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S.; Torregrossa, A.C.; Mian, A.I.; Berkson, D.L.; Westby, C.M.; Moncrief, J.W. Acute effects of hemodialysis on nitrite and nitrate: Potential cardiovascular implications in dialysis patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 58, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, M.L.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Carlstrom, M. Renal handling of nitrate in women and men with elevated blood pressure. Acta Physiol. 2021, 232, e13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.K.; Smallwood, M.J.; Benjamin, N.; D’Souza, R.J.; Shore, A.C.; Winyard, P.G.; Gilchrist, M. Renal nitrate clearance in chronic kidney disease. Nitric Oxide 2020, 97, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niizuma, S.; Iwanaga, Y.; Yahata, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Goto, Y.; Nakahama, H.; Miyazaki, S. Impact of left ventricular end-diastolic wall stress on plasma B-type natriuretic peptide in heart failure with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohsaka, S.; Okami, S.; Kanda, E.; Kashihara, N.; Yajima, T. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes Associated with Hyperkalemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Hospital-Based Cohort Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2021, 5, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, G.; Kim, J.; Mellstrom, C.; Ford, K.L.; Jenkins, N.C.; Tsang, C.; Evans, M.; McEwan, P. Serum potassium variability as a predictor of clinical outcomes in patients with cardiorenal disease or diabetes: A retrospective UK database study. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, E.N.M.; Dekker, F.W.; Le Cessie, S.; Hoorn, E.J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Hoogeveen, E.K. Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis-2 Study, G. Serum Potassium and Mortality Risk in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cohort Study. Kidney Med. 2022, 4, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.T.; Kang, Y.N.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, I.L.; Chang, W.C.; Fang, T.C.; Wu, M.S.; Kao, C.C. Efficacy and Safety of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Kidney Failure Patients Treated with Dialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.J.; Ekblom, B.; Sahlin, K.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Effects of dietary nitrate on blood pressure in healthy volunteers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2792–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Characteristics | Hemodialysis Patients (n = 8) | Healthy Volunteers (n = 7) | p |
| Age, years | 31 (25.75–38.75) | 36 (30–40) | 0.380 |
| Gender (male), n (%) | 4 (50) | 3 (42) | 0.999 |
| Body weight (a), kg | 53.3 (50.0–62.6) | 77.0 (60.3–84.2) | 0.048 |
| Height, m | 1.60 (1.54–1.64) | 1.67 (1.63–1.76) | 0.025 |
| Body mass index (b), kg/m2 | 20.9 (20.1–23.3) | 25.4 (22.7–27.2) | 0.302 |
| SBP (c), mmHg | 135 (119–147) | 105 (101–110) | 0.002 |
| DBP (c), mmHg | 85 (73–92) | 65 (62–70) | 0.020 |
| Dialysis vintage, months | 138.5 (75.75–201.5) | NA | − |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 4 (50) | NA | − |
| Ischemic cardiomyopathy, n (%) | 0 (0) | NA | − |
| Arrythmia, n (%) | 0 (0) | NA | − |
| Peripheral vascular disease, n (%) | 0 (0) | NA | − |
| Type 2 diabetes, n (%) | 0 (0) | NA | − |
| COPD n (%) | 1 (13) | NA | − |
| Previous renal Tx, n (%) | 7 (88) | NA | − |
| Smoking, n (%) | 2 (25) | NA | − |
| Hemodialysis Patients (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Active BJ (n = 8) | Placebo BJ (n = 8) | p |
| Pre-dialysis body weight, kg | 55.2 (52.7–64.5) | 55.3 (52.9–65.4) | 0.456 |
| Post-dialysis body weight, kg | 53.4 (49.4–62.6) *** | 53.4 (50.6–62.6) *** | 0.847 |
| Pre-HD SBP (b), mmHg | 137 (119–146) | 128 (118–149) | 0.675 |
| Post-HD SBP, mmHg | 114 (107–135) * | 129 (106–138) | 0.575 |
| 4 h post-HD SBP, mmHg | 119 (106–128) | 139 (116–140) | 0.200 |
| Pre-HD DBP (b), mmHg | 85.5 (67.5–93.8) | 80.5 (75.3–92.8) | 0.929 |
| Post-HD DBP, mmHg | 64.5 (56.0–81.0) * | 75.5 (58.0–85.0) * | 0.729 |
| 4 h post-HD DBP, mmHg | 75.0 (60.0–83.0) | 81.0 (72.0–85.0) | 0.212 |
| HD session length, min | 230 (209–239) | 233 (209–249) | 0.945 |
| Blood flow rate, mL/min | 383 (352–398) | 391 (349–398) | 0.813 |
| Total volume (c), L | 139 (136–142) | 133 (122–146) | 0.688 |
| Ultrafiltration, mL | 2332 (1734–3191) | 2811 (1978–3233) | 0.250 |
| Kt/Vurea | 2.49 (1.65–2.79) | 2.38 (1.73–2.80) | 0.712 |
| Kt/Vurea ≥ 1.2, n (%) | 8 (100) | 8 (100) | 0.999 |
| Residual urine, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.999 |
| Healthy Volunteers (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Active BJ (n = 7) | Placebo BJ (n = 7) | p |
| Body weight, kg | 77 (60.30–84.20) | 77 (60.30–84.20) | 0.999 |
| Baseline (b) SBP (c), mmHg | 100 (100–110) | 110 (102–110) | 0.464 |
| 4 h post-baseline SBP, mmHg | 100 (93–120) | 105 (90–120) | 0.803 |
| Baseline (b) DBP (c), mmHg | 70 (63–75) | 64 (60–66) | 0.123 |
| 4 h post-baseline DBP, mmHg | 70 (60–70) | 60 (60–70) | 0.748 |
| Active BJ | Placebo BJ | Active BJ/Placebo BJ | ||||
| AUClast (h × µmol/L) | Cmax (µmol/L) | AUClast (h × µmol/L) | Cmax (µmol/L) | AUClast Ratio | Cmax Ratio | |
| Hemodialysis Patients n = 8 | 14300 *** (9150–20900) | 485 *** (247–720) | 2250 (1510–3540) | 73.4 (45.5–133) | 6.34 (5.52–7.28) | 6.61 (4.75–9.19) |
| Healthy Volunteers n = 7 | 5640 ***/### (3810–7110) | 316 ***/### (233–383) | 1370 # (746–2470) | 41.1 (19.7–81.8) | 4.10 ## (3.21–5.24) | 7.70 (5.26–11.3) |
| Active BJ | Placebo BJ | Active BJ/Placebo BJ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUClast (h × µmol/L) | Cmax (µmol/L) | AUClast (h × µmol/L) | Cmax (µmol/L) | AUClast Ratio | Cmax Ratio | |
| Hemodialysis Patients n = 8 | 19.5 * (7.66–64.6) | 0.862 * (0.346–2.13) | 7.30 (2.96–31.1) | 0.273 (0.106–1.25) | 2.67 (1.82–3.94) | 3.16 (2.00–4.99) |
| Healthy Volunteers n = 7 | 9.75 *** (4.40–14.2) | 0.411 ***/# (0.216–0.619) | 4.93 (2.39–7.67) | 0.137 (0.0625–0.206) | 1.98 (1.90–2.06) | 3.01 (2.54–3.58) |
| Plasma Nitrate | Plasma Nitrite | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Corrected AUClast (h × µmol/L) | Corrected Cmax (µmol/L) | Corrected AUClast (h × µmol/L) | Corrected Cmax (µmol/L) |
| Hemodialysis Patients n = 8 | 9070 (6230–11800) | 338 (185–548) | 6.04 (0.414–25.5) | 0.467 (0.233–1.24) |
| Healthy Volunteers n = 7 | 4090 ### (3020–6780) | 282 (240–367) | 4.73 (2.37–7.70) | 0.301 (0.133–0.446) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heredia-Martinez, A.; Rosa-Diez, G.; Ferraris, J.R.; Sohlenius-Sternbeck, A.-K.; Nihlen, C.; Olsson, A.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Carlström, M.; Krmar, R.T. Plasma Nitrate and Nitrite Kinetics after Single Intake of Beetroot Juice in Adult Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis and in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122480
Heredia-Martinez A, Rosa-Diez G, Ferraris JR, Sohlenius-Sternbeck A-K, Nihlen C, Olsson A, Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Carlström M, Krmar RT. Plasma Nitrate and Nitrite Kinetics after Single Intake of Beetroot Juice in Adult Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis and in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122480
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeredia-Martinez, Agustina, Guillermo Rosa-Diez, Jorge R. Ferraris, Anna-Karin Sohlenius-Sternbeck, Carina Nihlen, Annika Olsson, Jon O. Lundberg, Eddie Weitzberg, Mattias Carlström, and Rafael T. Krmar. 2022. "Plasma Nitrate and Nitrite Kinetics after Single Intake of Beetroot Juice in Adult Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis and in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122480
APA StyleHeredia-Martinez, A., Rosa-Diez, G., Ferraris, J. R., Sohlenius-Sternbeck, A.-K., Nihlen, C., Olsson, A., Lundberg, J. O., Weitzberg, E., Carlström, M., & Krmar, R. T. (2022). Plasma Nitrate and Nitrite Kinetics after Single Intake of Beetroot Juice in Adult Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis and in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Nutrients, 14(12), 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122480







