Effects of Diastolic Blood Pressure on Brain Structures and Cognitive Functions in Middle and Old Ages: Longitudinal Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
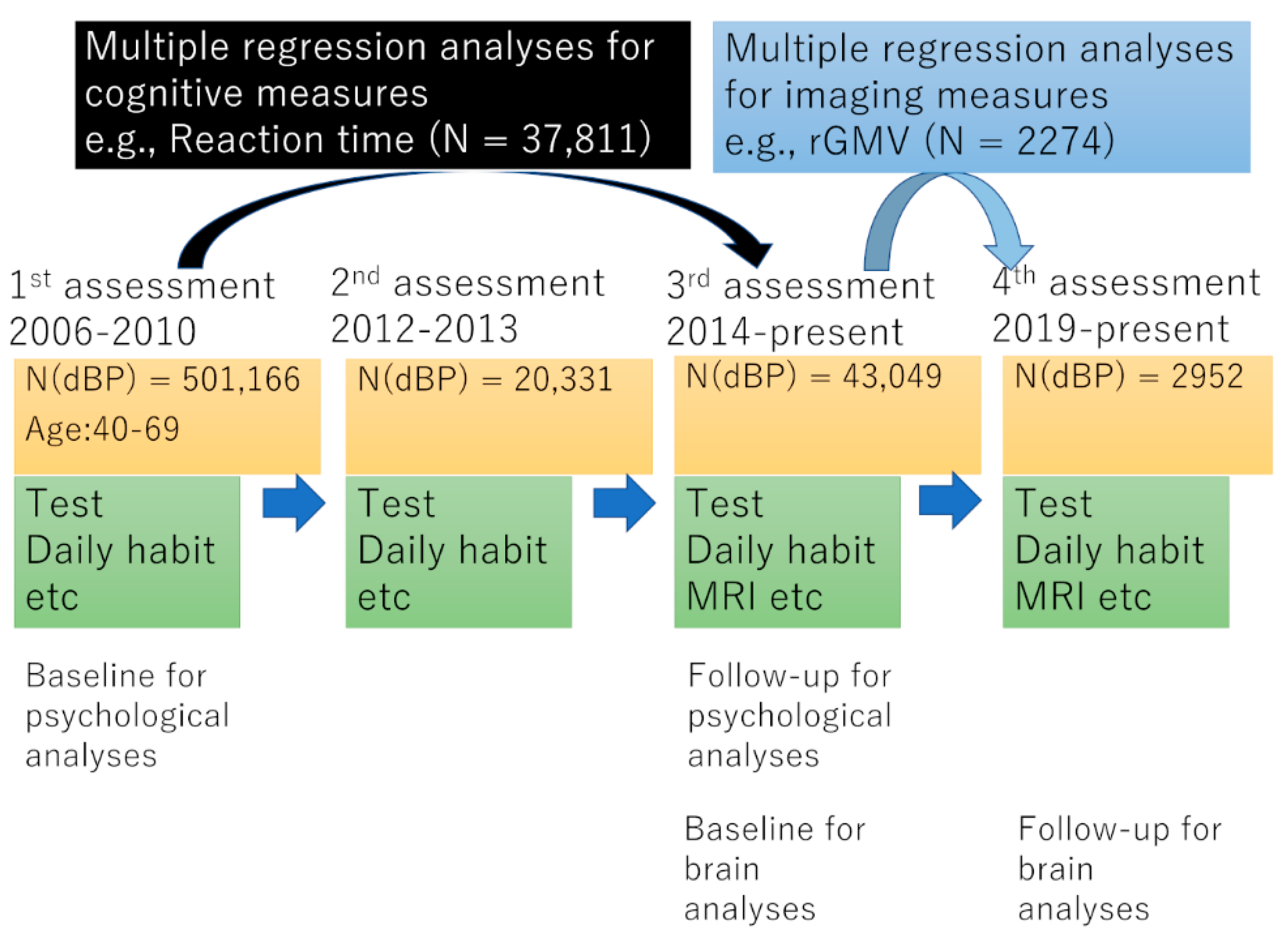
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Basic Baseline Data
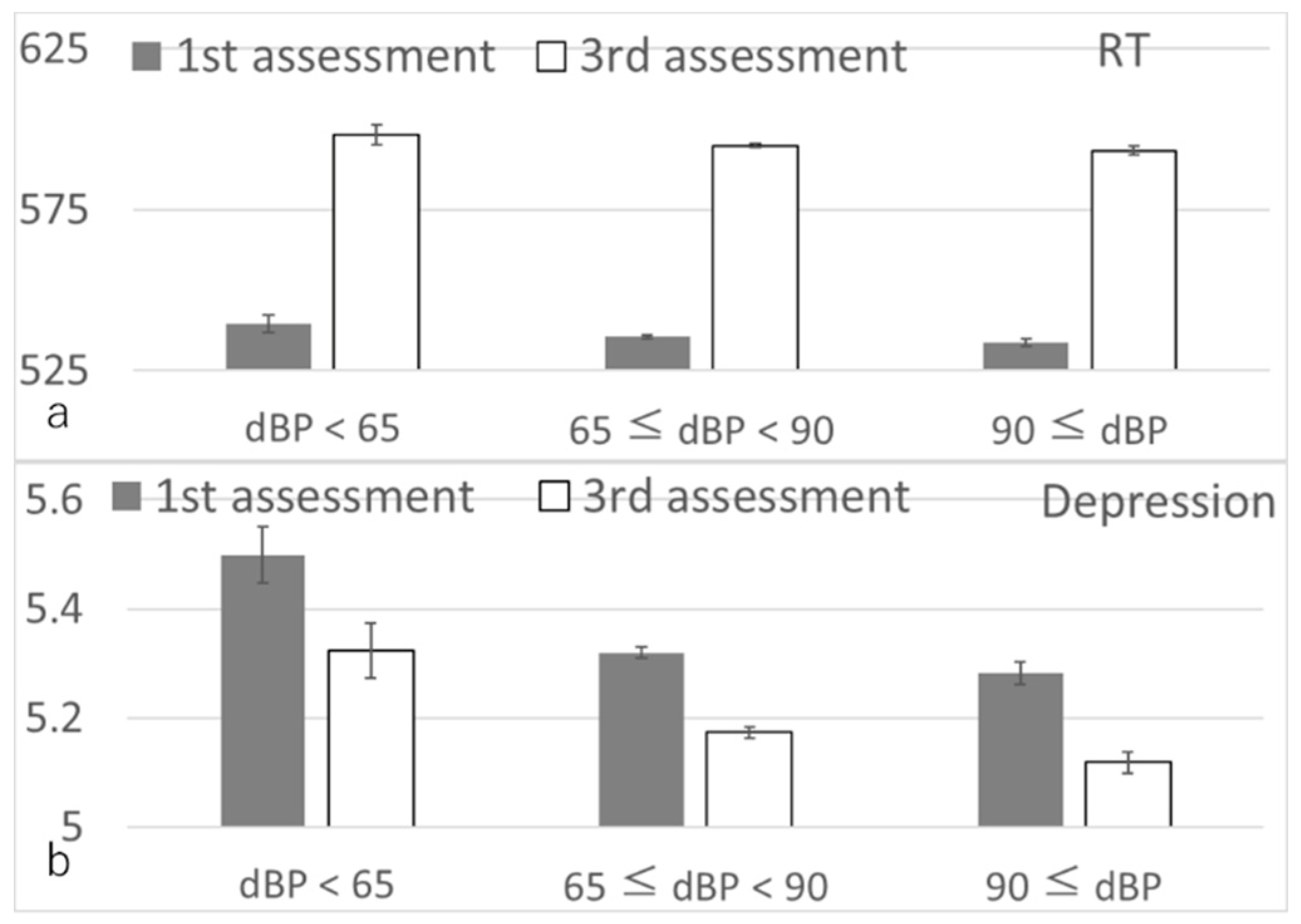
3.2. Longitudinal Psychological Analyses
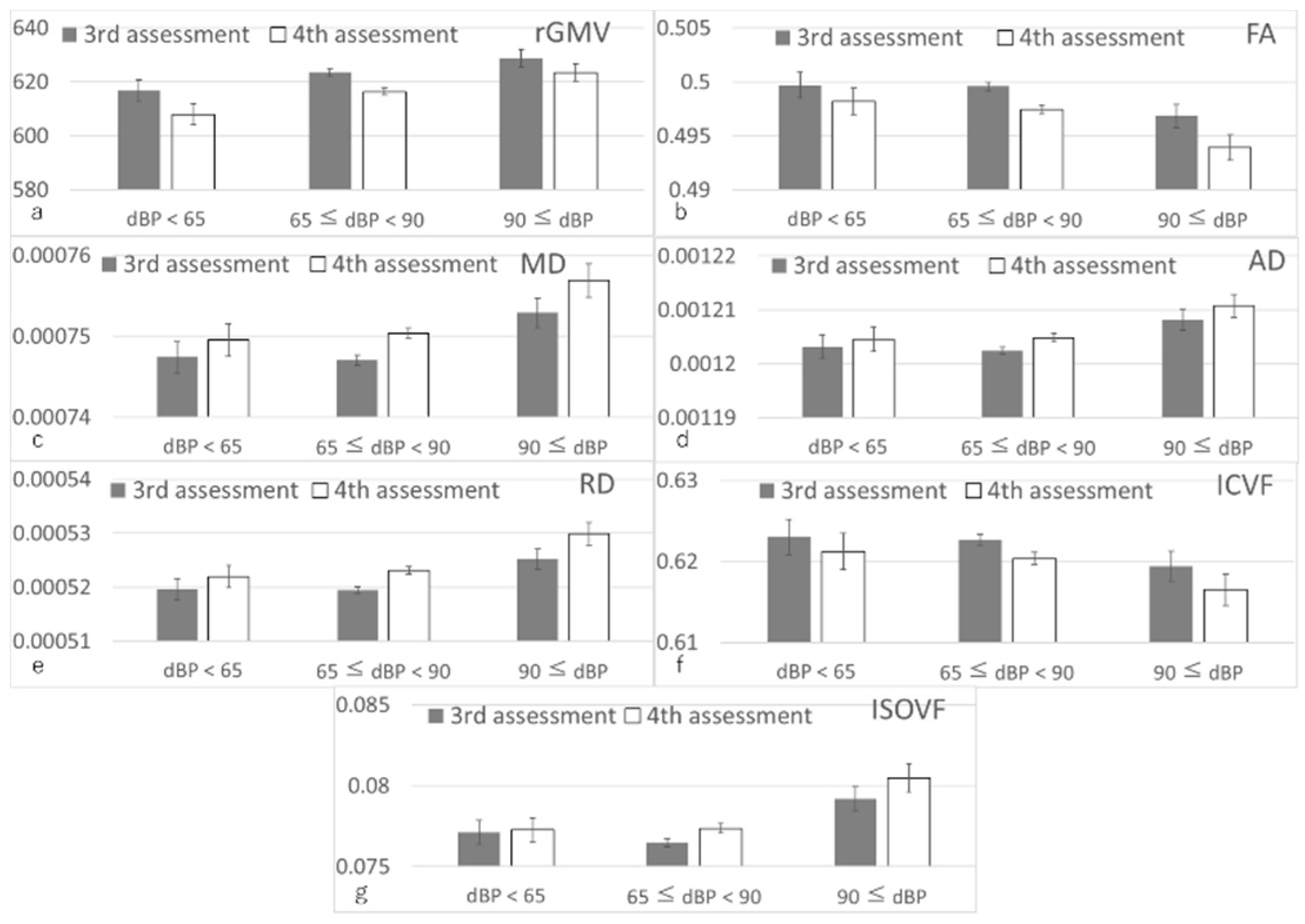
3.3. Longitudinal Brain Imaging Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Transparency
References
- Neaton, J.D.; Wentworth, D.N.; Cutler, J.; Stamler, J.; Kuller, L. Risk factors for death from different types of stroke. Ann. Epidemiol. 1993, 3, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglio, F.; Paglieri, C.; Rabbia, F.; Bisbocci, D.; Bergui, M.; Cerrato, P. Hypertension and cerebrovascular damage. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, M.C.; Weuve, J.; Gagne, J.J.; McQueen, M.B.; Viswanathan, A.; Blacker, D. The Association Between Blood Pressure and Incident Alzheimer Disease A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, C.; Viitanen, M.; Fastbom, J.; Winblad, B.; Fratiglioni, L. Blood pressure and dementia in persons 75+ years old: 3-year follow-up results from the Kungsholmen Project. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2001, 3, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproviero, W.; Winchester, L.; Newby, D.; Fernandes, M.; Shi, L.; Goodday, S.M.; Prats-Uribe, A.; Alhambra, D.P.; Buckley, N.J.; Nevado-Holgado, A.J. High blood pressure and risk of dementia: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study in the UK Biobank. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, V.; Hajjar, I. The relationship between blood pressure and cognitive function. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, G.; Casagrande, M. Effects of blood pressure on cognitive performance in aging: A systematic review. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.; van der Graaf, Y.; Visseren, F.L.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Geerlings, M.I.; Group, S.S. Hypertension and longitudinal changes in cerebral blood flow: The SMART-MR study. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufouil, C.; de Kersaint–Gilly, A.; Besancon, V.; Levy, C.; Auffray, E.; Brunnereau, L.; Alperovitch, A.; Tzourio, C. Longitudinal study of blood pressure and white matter hyperintensities: The EVA MRI Cohort. Neurology 2001, 56, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, C.; Abebe, K.Z.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Boudreau, R.; Jennings, J.R.; Venkatraman, V.; Harris, T.B.; Yaffe, K.; Satterfield, S.; Newman, A.B. Longitudinal systolic blood pressure characteristics and integrity of white matter tracts in a cohort of very old black and white adults. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.R.; Ritchie, S.J.; Tucker-Drob, E.M.; Liewald, D.C.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Davies, G.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Gale, C.R.; Bastin, M.E.; Deary, I.J. Ageing and brain white matter structure in 3513 UK Biobank participants. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andica, C.; Kamagata, K.; Hatano, T.; Saito, Y.; Ogaki, K.; Hattori, N.; Aoki, S. MR biomarkers of degenerative brain disorders derived from diffusion imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, P.; Seshadri, S.; Beiser, A.; Himali, J.J.; Au, R.; Fletcher, E.; Carmichael, O.; Wolf, P.A.; DeCarli, C. Effects of systolic blood pressure on white-matter integrity in young adults in the Framingham Heart Study: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartolowska, K.A.; Webb, A.J.S. Blood Pressure Determinants of Cerebral White Matter Hyperintensities and Microstructural Injury: UK Biobank Cohort Study. Hypertension 2021, 78, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchet, O.; Celle, S.; Roche, F.; Bartha, R.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Allali, G.; Annweiler, C. Blood pressure levels and brain volume reduction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1502–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.; Cai, H.; Liu, K.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L. The effect of Lactobacillus consumption on human blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 54, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morejón-Terán, Y.; Pizarro, R.; Mauritz, L.; Díaz, D.; Agüero, S.D. Association between dairy product intake and high blood pressure in Chilean adults. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2021, 62, E681. [Google Scholar]
- Sieber, R.; Bütikofer, U.; Egger, C.; Portmann, R.; Walther, B.; Wechsler, D. ACE-inhibitory activity and ACE-inhibiting peptides in different cheese varieties. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2010, 90, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Bertram, H.C.; Bonjour, J.P.; de Groot, L.C.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Feeney, E.L.; Garg, M.L.; Givens, I.; Kok, F.J.; Krauss, R.M.; et al. WHO draft guidelines on dietary saturated and trans fatty acids: Time for a new approach? BMJ 2019, 366, l4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Fernández, A.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Recio-Rodríguez, J.I.; Cavero-Redondo, I. Total dairy, cheese and milk intake and arterial stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Nutrients 2019, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qizilbash, N.; Gregson, J.; Johnson, M.E.; Pearce, N.; Douglas, I.; Wing, K.; Evans, S.J.; Pocock, S.J. BMI and risk of dementia in two million people over two decades: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Associations of BMI and Serum Urate with Developing Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e4688–e4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.J.; Pine, K.J.; Ellerbrock, I.; Weiskopf, N.; Mohammadi, S. NODDI-DTI: Estimating neurite orientation and dispersion parameters from a diffusion tensor in healthy white matter. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, C.D.; Johnsrude, I.S.; Ashburner, J.; Henson, R.N.A.; Friston, K.J.; Frackowiak, R.S.J. A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study of Ageing in 465 Normal Adult Human Brains. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnert, E.A.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Burchell, A.E.; Neumann, S.; Ratcliffe, L.E.; Manghat, N.E.; Harris, A.D.; Adams, Z.; Nightingale, A.K.; Wise, R.G. Is high blood pressure self-protection for the brain? Circ. Res. 2016, 119, e140–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, R. Diet and Dementia: A Prospective Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldsman, M.; Kindalova, P.; Husain, M.; Kosmidis, I.; Nichols, T.E. Spatial distribution and cognitive impact of cerebrovascular risk-related white matter hyperintensities. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 28, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, G.D.; McIntosh, A.M.; Russ, T.C.; Deary, I.J.; Gale, C.R. Psychological distress, neuroticism, and cause-specific mortality: Early prospective evidence from UK Biobank. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2016, 70, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehrband, F.; Clark, K.A.; Ullmann, J.F.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Leanage, G.; Reutens, D.C.; Yang, Z. Brain tissue compartment density estimated using diffusion-weighted MRI yields tissue parameters consistent with histology. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 3687–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Taki, Y.; Thyreau, B.; Sassa, Y.; Hashizume, H.; Sekiguchi, A.; Nagase, T.; Nouchi, R.; Fukushima, A.; Kawashima, R. White matter structures associated with empathizing and systemizing in young adults. Neuroimage 2013, 77, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, R.; Srikanth, R.; Baer, A.; Laurienti, P.J.; Burdette, J.H.; Hayasaka, S.; Flowers, L.; Wood, F.; Maldjian, J.A. Biological parametric mapping: A statistical toolbox for multimodality brain image analysis. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poline, J.-B.; Worsley, K.J.; Evans, A.C.; Friston, K.J. Combining spatial extent and peak intensity to test for activations in functional imaging. Neuroimage 1997, 5, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Taki, Y.; Hashizume, H.; Asano, K.; Asano, M.; Sassa, Y.; Yokota, S.; Kotozaki, Y.; Nouchi, R.; Kawashima, R. Impact of videogame play on the brain’s microstructural properties: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Krieger, A.M.; Yekutieli, D. Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 2006, 93, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, K.E.; Murphy, N.; Key, T.J. Diet and colorectal cancer in UK Biobank: A prospective study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Ohashi, Y.; Harada, A.; Taguri, M.; Kushiro, T.; Takahashi, A.; Nishinaga, M.; Soejima, H.; Ueshima, H. Four blood pressure indexes and the risk of stroke and myocardial infarction in Japanese men and women: A meta-analysis of 16 cohort studies. Circulation 2009, 119, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Gaser, C. Magnetic resonance-based morphometry: A window into structural plasticity of the brain. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—A technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligianni, F.; Carmichael, D.W.; Zhang, G.H.; Clark, C.A.; Clayden, J.D. NODDI and tensor-based microstructural indices as predictors of functional connectivity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, E.; Launer, L.J.; Egger, M.; Prince, M.J.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Wolters, F.J.; Egan, K. Body mass index in midlife and dementia: Systematic review and meta-regression analysis of 589,649 men and women followed in longitudinal studies. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2017, 8, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, G.; Zabzuni, D.; Bravi, E.; Piva, G.; De Noni, I.; Bighi, E.; Rossi, F. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the antihypertensive effects of Grana Padano DOP cheese consumption in mild-moderate hypertensive subjects. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7573–7581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klinedinst, B.S.; Le, S.T.; Larsen, B.; Pappas, C.; Hoth, N.J.; Pollpeter, A.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, L. Genetic Factors of Alzheimer’s Disease Modulate How Diet is Associated with Long-Term Cognitive Trajectories: A UK Biobank Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 78, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.-J.; Presse, N.; Rahme, E.; Ferland, G.; Bherer, L.; Chevalier, S. Milk, Yogurt, and Cheese Intake Is Positively Associated with Cognitive Executive Functions in Older Adults of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockey, M.; McGuinness, A.J.; Marx, W.; Rocks, T.; Jacka, F.N.; Ruusunen, A. Is dairy consumption associated with depressive symptoms or disorders in adults? A systematic review of observational studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3653–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allender, P.S.; Cutler, J.A.; Follmann, D.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Pryer, J.; Elliott, P. Dietary calcium and blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Taki, Y.; Hashizume, H.; Asano, K.; Asano, M.; Sassa, Y.; Yokota, S.; Kotozaki, Y.; Nouchi, R.; Kawashima, R. The impact of parent–child interaction on brain structures: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Taki, Y.; Hashizume, H.; Asano, K.; Asano, M.; Sassa, Y.; Yokota, S.; Kotozaki, Y.; Nouchi, R.; Kawashima, R. The Impact of Television Viewing on Brain Structures: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analyses. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.J.; Xiong, C.; Benzinger, T.L.; Fagan, A.M.; Goate, A.; Fox, N.C.; Marcus, D.S.; Cairns, N.J.; Xie, X.; Blazey, T.M. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P. Deprivation. J. Soc. Policy 1987, 16, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okbay, A.; Beauchamp, J.P.; Fontana, M.A.; Lee, J.J.; Pers, T.H.; Rietveld, C.A.; Turley, P.; Chen, G.-B.; Emilsson, V.; Meddens, S.F.W.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 74 loci associated with educational attainment. Nature 2016, 533, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Cox, S.R.; Adams, M.J.; Howard, D.M.; Lawrie, S.M.; Ritchie, S.J.; Bastin, M.E.; Deary, I.J.; McIntosh, A.M.; Whalley, H.C. Resting-State Connectivity and Its Association with Cognitive Performance, Educational Attainment, and Household Income in the UK Biobank. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, B.; Newby, D.; Lee, D.; Lyall, D.M.; Nevado-Holgado, A.J.; Evans, J.J.; Pell, J.P.; Lovestone, S.; Cavanagh, J. Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses of outdoor air pollution exposure and cognitive function in UK Biobank. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.N.; Huang, R.-Q.; Logan, S.M.; Yi, K.D.; Dillon, G.H.; Simpkins, J.W. Estrogens directly potentiate neuronal L-type Ca 2+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15148–15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, L.J.; Lawson, D.J.; Davies, N.M.; Pourcain, B.S.; Lewis, S.J.; Smith, G.D.; Hemani, G. Genetic evidence for assortative mating on alcohol consumption in the UK Biobank. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubchandani, J.; Brey, R.; Kotecki, J.; Kleinfelder, J.; Anderson, J. The Psychometric Properties of PHQ-4 Depression and Anxiety Screening Scale Among College Students. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2016, 30, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.L.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Bangerter, N.K.; Thomas, D.L.; Yacoub, E.; Xu, J.; Bartsch, A.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Andersson, J.L.R.; et al. Multimodal population brain imaging in the UK Biobank prospective epidemiological study. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Jenkinson, M.; Bangerter, N.K.; Andersson, J.L.; Griffanti, L.; Douaud, G.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Jbabdi, S.; Hernandez-Fernandez, M.; Vallee, E.; et al. Image processing and Quality Control for the first 10,000 brain imaging datasets from UK Biobank. NeuroImage 2017, 166, 400–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Voxel-based morphometry-the methods. Neuroimage 2000, 11, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daducci, A.; Canales-Rodríguez, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Dyrby, T.B.; Alexander, D.C.; Thiran, J.-P. Accelerated Microstructure Imaging via Convex Optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. NeuroImage 2015, 105, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, M.; Abraham, G.; Nelson, C.P.; Wood, A.M.; Sweeting, M.J.; Dudbridge, F.; Lai, F.Y.; Kaptoge, S.; Brozynska, M.; Wang, T. Genomic risk prediction of coronary artery disease in 480,000 adults: Implications for primary prevention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaizumi, T. The origin and clinical importance of white matter lesion. Jpn. J. Stroke 2016, 38, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Semplicini, A.; Maresca, A.; Boscolo, G.; Sartori, M.; Rocchi, R.; Giantin, V.; Forte, P.L.; Pessina, A.C. Hypertension in acute ischemic stroke: A compensatory mechanism or an additional damaging factor? Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Dependent Variables | N | Standardized Beta | T | p (Uncorrected) | p (FDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid intelligence | 12,827 | −0.002 (−0.019, 0.014) | −0.283 | 0.777 | 0.439 |
| Reaction time | 37,811 | −0.012 (−0.022, −0.003) | −2.478 | 0.013 | 0.019 |
| Visuospatial memory (number of errors) | 37,261 | −0.004 (−0.012, 0.005) | −0.834 | 0.404 | 0.270 |
| Depressive symptoms | 38,461 | −0.012 (−0.021, −0.003) | −2.589 | 0.010 | 0.019 |
| Dependent Variables | N | Standardized Beta | T | p (Uncorrected) | p (FDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rGMV | 2274 | 0.045 (0.002~0.088) | 2.067 | 0.039 | 0.037 |
| rWMV | 2274 | −0.022 (−0.065~0.021) | −0.991 | 0.322 | 0.237 |
| FA | 2240 | −0.066 (−0.11~−0.022) | −2.922 | 0.004 | 0.015 |
| MD | 2240 | 0.055 (0.012~0.098) | 2.502 | 0.012 | 0.019 |
| AD | 2240 | 0.044 (0.002~0.087) | 2.051 | 0.040 | 0.037 |
| RD | 2240 | 0.064 (0.021~0.107) | 2.933 | 0.003 | 0.015 |
| ICVF | 2240 | −0.05 (−0.093~−0.008) | −2.306 | 0.021 | 0.026 |
| ISOVF | 2240 | 0.043 (−0.001~0.087) | 1.929 | 0.054 | 0.044 |
| OD | 2240 | −0.014 (−0.055~0.027) | −0.682 | 0.496 | 0.304 |
| Dependent Variables | N | Level 1 (<Once/wk) Mean Change (95%CI) | Level 2 (Once/wk) Mean Change (95%CI) p (Level 1 vs. Level 2) | Level 3 (2–4 Times/wk) Mean Change (95%CI) p (Level 1 vs. Level 3) | Level 4 (≥5 Times/wk) Mean Change (95%CI) p (Level 1 vs. Level 4) | Group Level Difference p-Value (Uncorrected, FDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diastolic BP | 34,964 | −2.676 (−2.895~−2.458) | −2.597 (−2.795~−2.398) 0.594 | −2.747 (−2.874~−2.62) 0.589 | −3.267 (−3.494~−3.04) 2.63 × 10−4 | 7.28 × 10−5 3.82 × 10−4 |
| Fluid intelligence | 12,636 | −0.15 (−0.218~−0.083) - | −0.151 (−0.212~−0.089) 0.996 | −0.003 (−0.042~0.035) 2.25 × 10−4 | 0.09 (0.024~0.155) 7.95 × 10−7 | 1.21 × 10−8 1.27 × 10−7 |
| Reaction time | 37,185 | 59.5 (57.2–61.8) - | 60.6 (58.5~62.8) 0.467 | 59.3 (57.9~60.6) 0.899 | 56.8 (54.4~59.2) 0.114 | 0.123 0.215 |
| Visuospatial memory (errors) | 36,653 | −0.026 (−0.098~0.046) - | −0.07 (−0.135~−0.004) 0.377 | −0.123 (−0.165~−0.081) 0.024 | −0.198 (−0.272~−0.124) 0.001 | 0.007 0.018 |
| Depressive symptoms | 37,814 | −0.152 (−0.188~−0.115) - | −0.179 (−0.212~−0.146) 0.265 | −0.145 (−0.166~−0.124) 0.770 | −0.085 (−0.123~−0.048) 0.013 | 0.003 0.011 |
| rGMV | 2233 | −6655 (−7922~−5389) - | −6747 (−7851~−5644) 0.915 | −7219 (−7933~−6505) 0.448 | −7429 (−8589~−6271) 0.380 | 0.741 0.750 |
| rWMV | 2233 | −7298 (−8735~−5860) - | −7787 (−9040~−6534) 0.614 | −6586 (−7397~−5776) 0.399 | −6867 (−8182~−5551) 0.667 | 0.441 0.579 |
| FA | 2196 | −2.1 × 10−3 (−2.6 × 10−3~−1.6 × 10−3) - | −2.6 × 10−3 (−3.0 × 10−3~−2.1 × 10−3) 0.147 | −2.0 × 10−3 (−2.3 × 10−3~−1.7 × 10−3) 0.763 | −2.5 × 10−3 (−2.9 × 10−3~−2.0 × 10−3) 0.265 | 0.094 0.197 |
| MD | 2196 | 3.4 × 10−6 (2.4 × 10−6~4.5 × 10−6) - | 3.6 × 10−6 (2.7 × 10−6~4.5 × 10−6) 0.828 | 3.1 × 10−6 (2.5 × 10−6~3.7 × 10−6) 0.612 | 3.6 × 10−6 (2.6 × 10−6~4.6 × 10−6) 0.818 | 1 0.75 |
| AD | 2196 | 2.7 × 10−6 (1.3 × 10−6~4.1 × 10−6) - | 2.6 × 10−6 (1.3 × 10−6~3.8 × 10−6) 0.909 | 2.3 × 10−6 (1.5 × 10−6~3.1 × 10−6) 0.641 | 2.6 × 10−6 (1.3 × 10−6~4.0 × 10−6) 0.976 | 1 0.75 |
| RD | 2196 | 3.7 × 10−6 (2.8 × 10−6~4.7 × 10−6) - | 4.2 × 10−6 (3.3 × 10−6~5.0 × 10−6) 0.481 | 3.5 × 10−6 (3.0 × 10−6~4.0 × 10−6) 0.690 | 4.1 × 10−6 (3.2 × 10−6~4.9 × 10−6) 0.600 | 1 0.750 |
| ICVF | 2196 | −1.9 × 10−3 (−2.6 × 10−3~−1.2 × 10−3) - | −2.4 × 10−3 (−3.0 × 10−3~−1.8 × 10−3) 0.34 | −2.5 × 10−3 (−2.9 × 10−3~−2.1 × 10−3) 0.186 | −2.3 × 10−3 (−3.0 × 10−3~−1.6 × 10−3) 0.436 | 0.620 0.723 |
| ISOVF | 2196 | 1.2 × 10−3 (0.5 × 10−3~1.9 × 10−3) - | 1.1 × 10−3 (0.5 × 10−3~1.8 × 10−3) 0.846 | 0.6 × 10−3 (0.2 × 10−3~1.0 × 10−3) 0.14 | 1.0 × 10−3 (0.3 × 10−3~1.7 × 10−3) 0.634 | 0.337 0.506 |
| OD | 2196 | 4.7 × 10−4 (1.3 × 10−4~8.2 × 10−4) - | 5.3 × 10−4 (2.3 × 10−4~8.3 × 10−4) 0.773 | 3.8 × 10−4 (1.9 × 10−4~5.8 × 10−4) 0.679 | 5.2 × 10−4 (2.1 × 10−4~8.3 × 10−4) 0.821 | 0.812 0.750 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, R. Effects of Diastolic Blood Pressure on Brain Structures and Cognitive Functions in Middle and Old Ages: Longitudinal Analyses. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122464
Takeuchi H, Kawashima R. Effects of Diastolic Blood Pressure on Brain Structures and Cognitive Functions in Middle and Old Ages: Longitudinal Analyses. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122464
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakeuchi, Hikaru, and Ryuta Kawashima. 2022. "Effects of Diastolic Blood Pressure on Brain Structures and Cognitive Functions in Middle and Old Ages: Longitudinal Analyses" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122464
APA StyleTakeuchi, H., & Kawashima, R. (2022). Effects of Diastolic Blood Pressure on Brain Structures and Cognitive Functions in Middle and Old Ages: Longitudinal Analyses. Nutrients, 14(12), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122464





