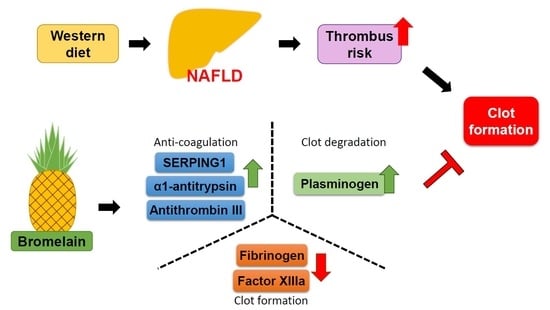
New Mechanisms of Bromelain in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Induced Deregulation of Blood Coagulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Histological Examination
2.4. Anticoagulant Activity
2.5. LC-MS/MS
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
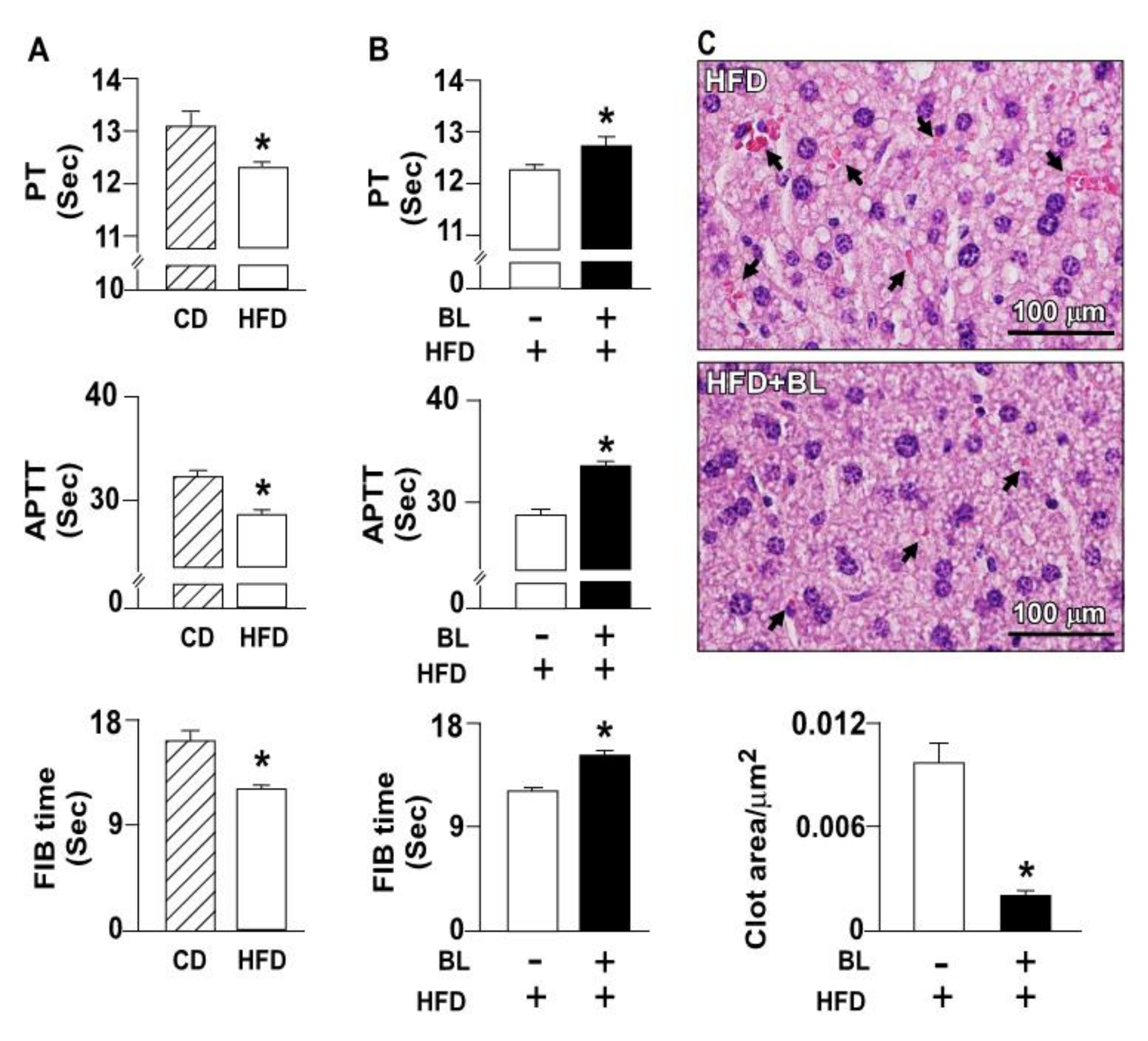
3.1. Bromelain Decreases Thrombus Formation in HFD-Fed Mice
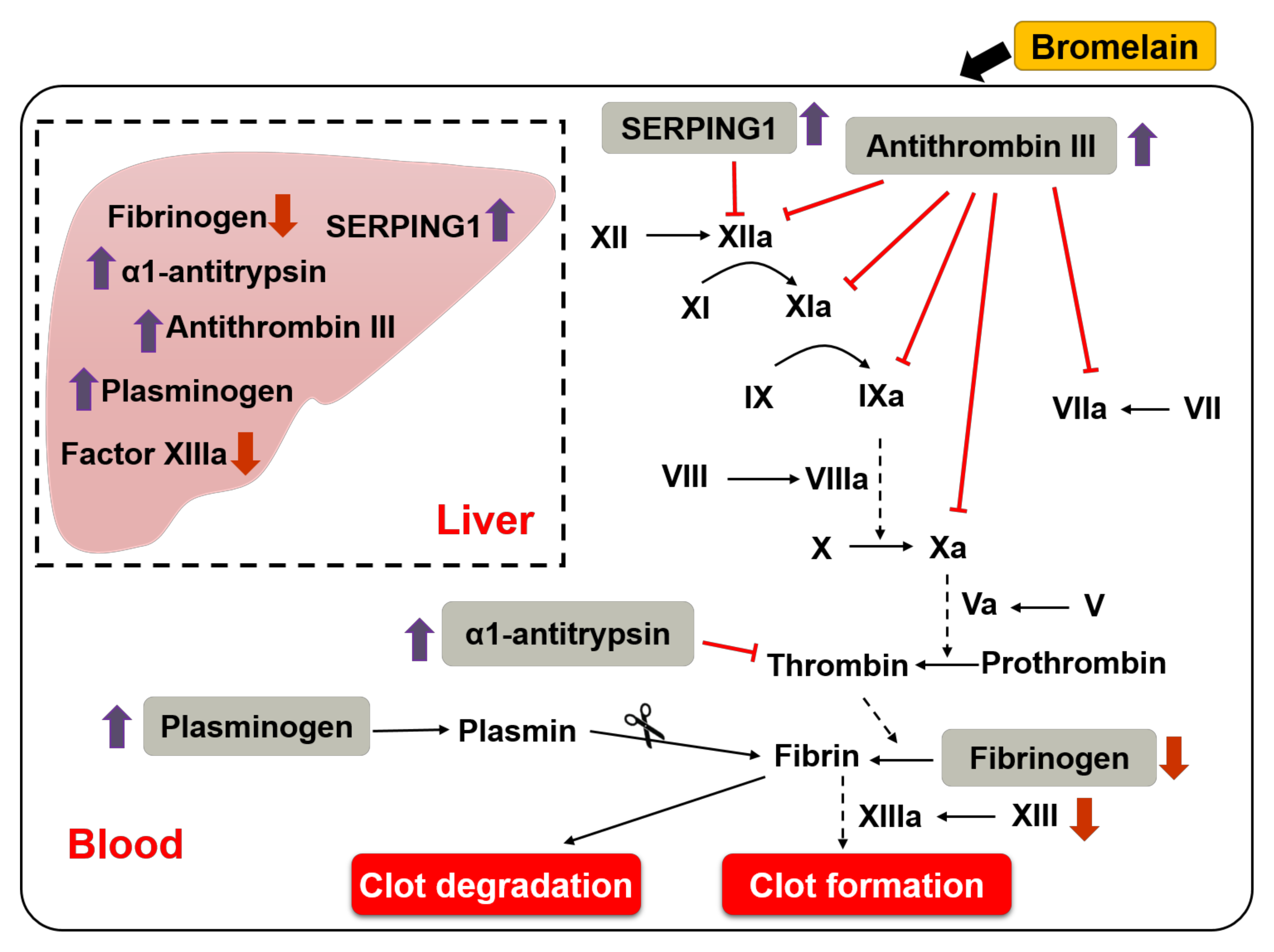
3.2. Effects of Bromelain on the Coagulation Cascade
3.3. Bromelain Increases Expression of ATIII, SERPING1, α1-Antitrypsin, Plasminogen, and Decreases Expression of FIB in the Liver and Plasma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaman, M.; Ehtram, A.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; Nusrat, S.; Khan, R.H. Amyloidogenic behavior of different intermediate state of stem bromelain: A biophysical insight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandanwale, A.; Langade, D.; Sonawane, D.; Gavai, P. A randomized, clinical trial to evaluate efficacy and tolerability of trypsin: Chymotrypsin as compared to serratiopeptidase and trypsin: Bromelain: Rutoside in wound management. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, Z.A.; Ahmad, T. Therapeutic uses of pineapple-extracted bromelain in surgical care-A review. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017, 67, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ramli, A.N.; Aznan, T.N.; Illias, R.M. Bromelain: From production to commercialisation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lencastre Novaes, L.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Lopes, A.M.; de Carvalho Santos-Ebinuma, V.; Mazzola, P.G.; Pessoa Junior, A. Stability, purification, and applications of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errasti, M.E.; Prospitti, A.; Viana, C.A.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Ramos, M.V.; Rotelli, A.E.; Caffini, N.O. Effects on fibrinogen, fibrin, and blood coagulation of proteolytic extracts from fruits of Pseudananas macrodontes, Bromelia balansae, and B. hieronymi (Bromeliaceae) in comparison with bromelain. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didisheim, P.; Lewis, J.H. Fibrinolytic and coagulant activities of certain snake venoms and proteases. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol Med. 1956, 93, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taussig, S.J.; Batkin, S. Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1988, 22, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Fernández, S.; Garcés-Rimón, M.; Vera, G.; Astier, J.; Landrier, J.F.; Miguel, M. High Fat/High Glucose Diet Induces Metabolic Syndrome in an Experimental Rat Model. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.L. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis. Model. Mech. 2009, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, P.D.; Beemath, A.; Olson, R.E. Obesity as a risk factor in venous thromboembolism. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 978–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvei, L.D.; Braekkan, S.K.; Smith, E.N.; Solomon, T.; Hindberg, K.; Frazer, K.A.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Hansen, J.B. Joint effects of prothrombotic genotypes and body height on the risk of venous thromboembolism: The Tromsø study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verrijken, A.; Francque, S.; Mertens, I.; Prawitt, J.; Caron, S.; Hubens, G.; Van Marck, E.; Staels, B.; Michielsen, P.; Van Gaal, L. Prothrombotic factors in histologically proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripodi, A.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Chantarangkul, V.; Primignani, M.; Fargion, S. Procoagulant imbalance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotronen, A.; Joutsi-Korhonen, L.; Sevastianova, K.; Bergholm, R.; Hakkarainen, A.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Lundbom, N.; Rissanen, A.; Lassila, R.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Increased coagulation factor VIII, IX, XI and XII activities in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; VanWagner, L.B.; Colangelo, L.A.; Lewis, C.E.; Henkel, A.; Ajmera, V.H.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Vaughan, D.E.; Khan, S.S. Association between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in young adulthood and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in midlife: Cardia. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.R. Hemostatic disorders associated with hepatobiliary disease. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 47, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, A.; Gnocchi, D.; Custodero, C.; Lenato, G.M.; Fiore, G.; Sabbà, C.; Mazzocca, A. Translational insight into prothrombotic state and hypercoagulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Thromb. Res. 2021, 198, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.E.; Flax, S.D.; Harris, N.S. Coagulation testing in the core laboratory. Lab. Med. 2017, 48, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinazzer, H. Hereditary and acquired antithrombin deficiency. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1999, 25, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, H.; Heikaus, L.; Long, A.T.; Naudin, C.; Schlüter, H.; Renné, T. The plasma contact system, a protease cascade at the nexus of inflammation, coagulation and immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, H.; Tan, B.H. Alpha-1-antitrypsin, an inhibitor for thrombin and plasmin. Clin. Chim. Acta 1967, 17, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Minno, M.N.; Tufano, A.; Rusolillo, A.; Di Minno, G.; Tarantino, G. High prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver in patients with idiopathic venous thromboembolism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 6119–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.A.; Chen, C.H.; Guo, B.C.; Kou, Y.R.; Lee, T.S. Bromelain confers protection against the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in male C57BL/6 mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnavelu, V.; Alitheen, N.B.; Sohila, S.; Kanagesan, S.; Ramesh, R. Potential role of bromelain in clinical and therapeutic applications. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seligman, B. Oral bromelains as adjuncts in the treatment of acute thrombophlebitis. Angiology 1969, 20, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.E. Fibrinolytic and antithrombotic action of bromelain may eliminate thrombosis in heart patients. Med. Hypotheses 1980, 6, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.H.; Butenas, S.; Ribarik, N.; Mann, K.G. Complex-dependent inhibition of factor VIIa by antithrombin III and heparin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Matsushita, T.; Mackman, N.; Ito, M.; Adachi, T.; Katsumi, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Takeshita, K.; Kojima, T.; Saito, H.; et al. Fatal thrombosis of antithrombin-deficient mice is rescued differently in the heart and liver by intercrossing with low tissue factor mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, N.R.; Travis, J. Inactivation of human thrombin in the presence of human α-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem. J. 1976, 159, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bafunno, V.; Divella, C.; Sessa, F.; Tiscia, G.L.; Castellano, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Margaglione, M.; Montinaro, V. De novo homozygous mutation of the C1 inhibitor gene in a patient with hereditary angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 748–750.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugno, M.; Bos, I.; Lubbers, Y.; Hack, C.E.; Agostoni, A. In vitro interaction of C1-inhibitor with thrombin. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2001, 12, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. Subcell. Biochem. 2017, 82, 405–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weisel, J.W. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Adv. Protein Chem. 2005, 70, 247–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszbek, L.; Yee, V.C.; Hevessy, Z. Blood coagulation factor XIII: Structure and function. Thromb. Res. 1999, 94, 271–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, O.F.; de Vries, C.; Hohmann, C.; Veerman, H.; Pannekoek, H. Interaction between plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) bound to fibrin and either tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) or urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA). Binding of t-PA/PAI-1 complexes to fibrin mediated by both the finger and the kringle-2 domain of t-PA. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinicke, R.M.; van der Wal, L.; Yokoyama, M. Effect of bromelain (Ananase) on human platelet aggregation. Experientia 1972, 28, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
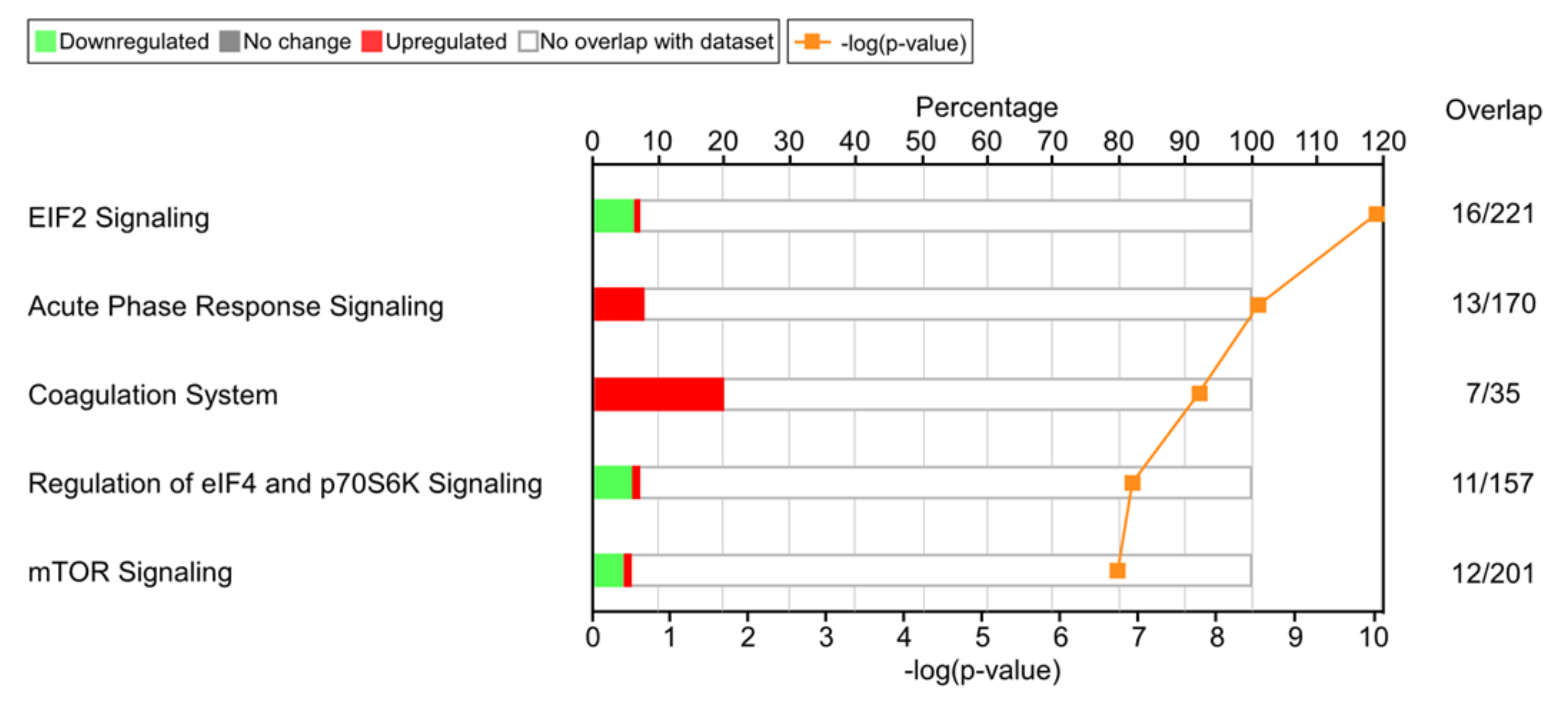
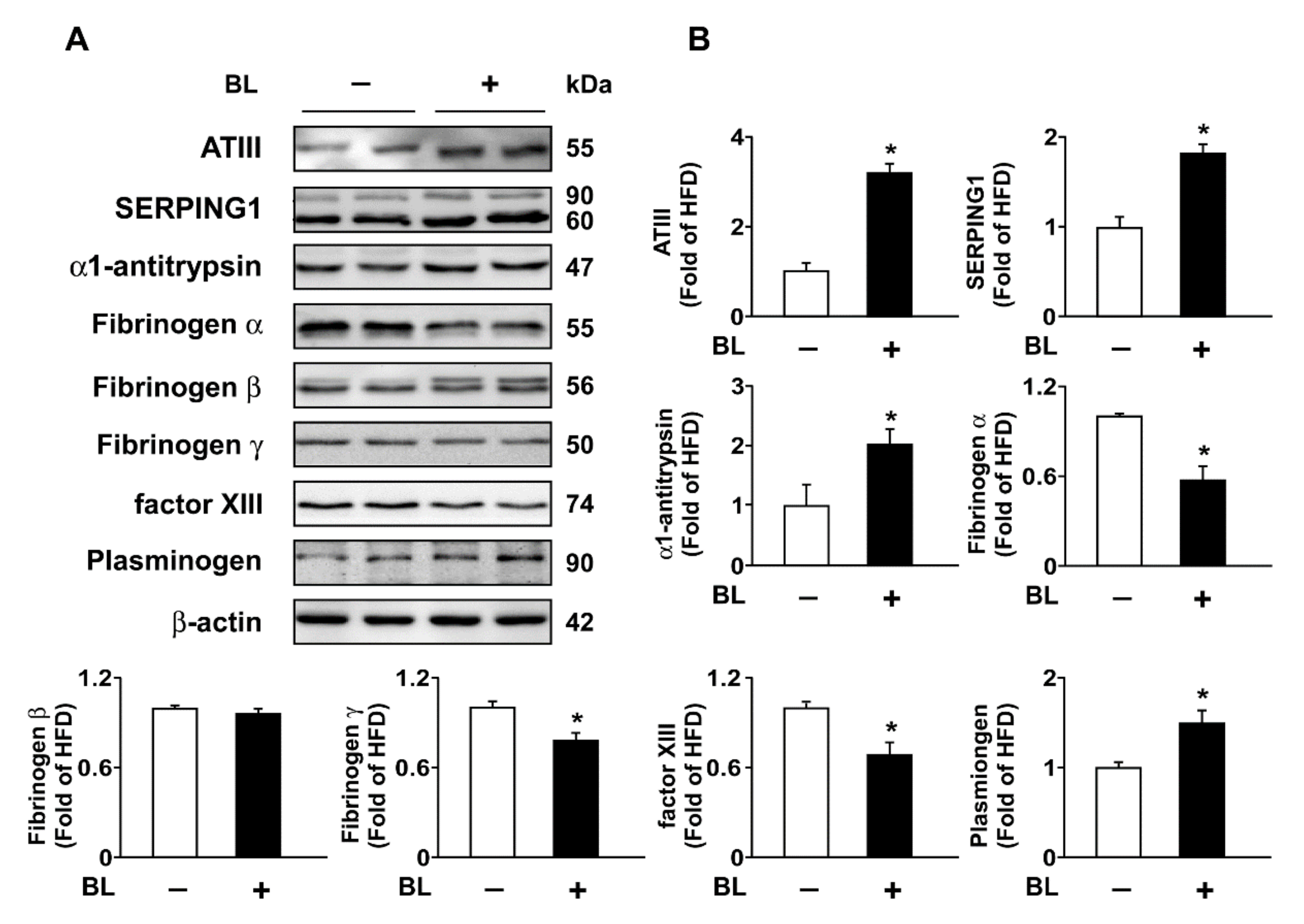

| Protein | HFD + BL vs. HFD | Regulation of Coagulation Activity | Intrinsic | Extrinsic | Common |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SERPING1 | ↑ | Negative | ✓ | ||
| Antithrombin III | ↑ | Negative | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Annexin A5 | − | Negative | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Plasma kallikrein | − | Positive/Negative | ✓ | ||
| Tissue factor pathway inhibitor | − | Negative | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 | − | Positive | ✓ | ✓ | |
| α1-antitrypsin | ↑ | Negative | ✓ | ||
| Prothrombin | − | Positive | ✓ |
| Protein | HFD + BL vs. HFD | Regulation of Coagulation Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Plasminogen | ↑ | Negative |
| α2-antiplasmin | − | Positive |
| Plasma kallikrein | − | Positive/Negative |
| Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 | − | Positive |
| Tissue plasminogen activator | − | Negative |
| Urokinase-type plasminogen activator | − | Negative |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, P.-A.; Wang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Guo, B.-C.; Huang, J.-W.; Lee, T.-S. New Mechanisms of Bromelain in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Induced Deregulation of Blood Coagulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112329
Hu P-A, Wang S-H, Chen C-H, Guo B-C, Huang J-W, Lee T-S. New Mechanisms of Bromelain in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Induced Deregulation of Blood Coagulation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112329
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Po-An, Sz-Han Wang, Chia-Hui Chen, Bei-Chia Guo, Jenq-Wen Huang, and Tzong-Shyuan Lee. 2022. "New Mechanisms of Bromelain in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Induced Deregulation of Blood Coagulation" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112329
APA StyleHu, P.-A., Wang, S.-H., Chen, C.-H., Guo, B.-C., Huang, J.-W., & Lee, T.-S. (2022). New Mechanisms of Bromelain in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Induced Deregulation of Blood Coagulation. Nutrients, 14(11), 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112329