Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
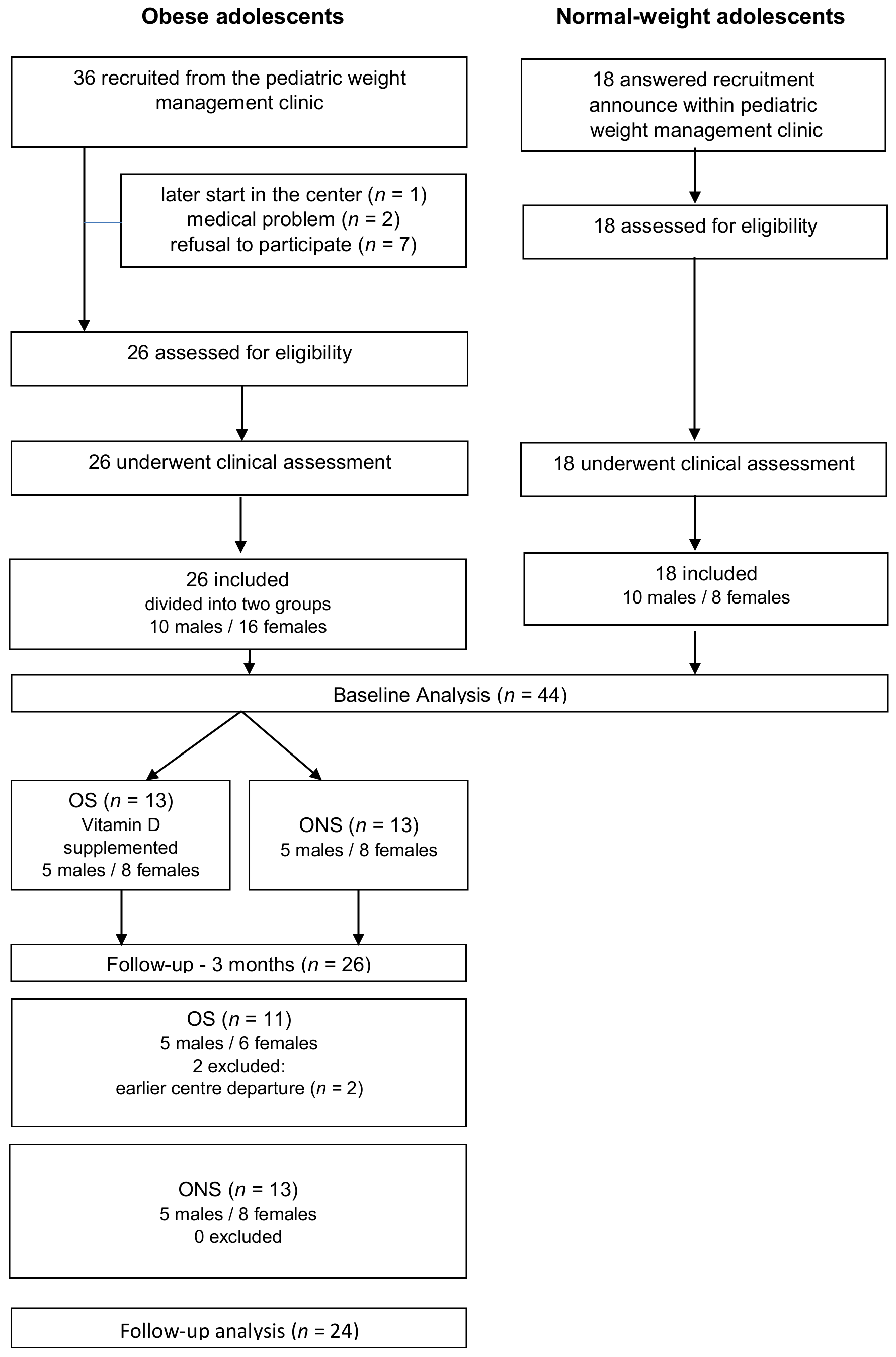
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Statistical Method
3. Results
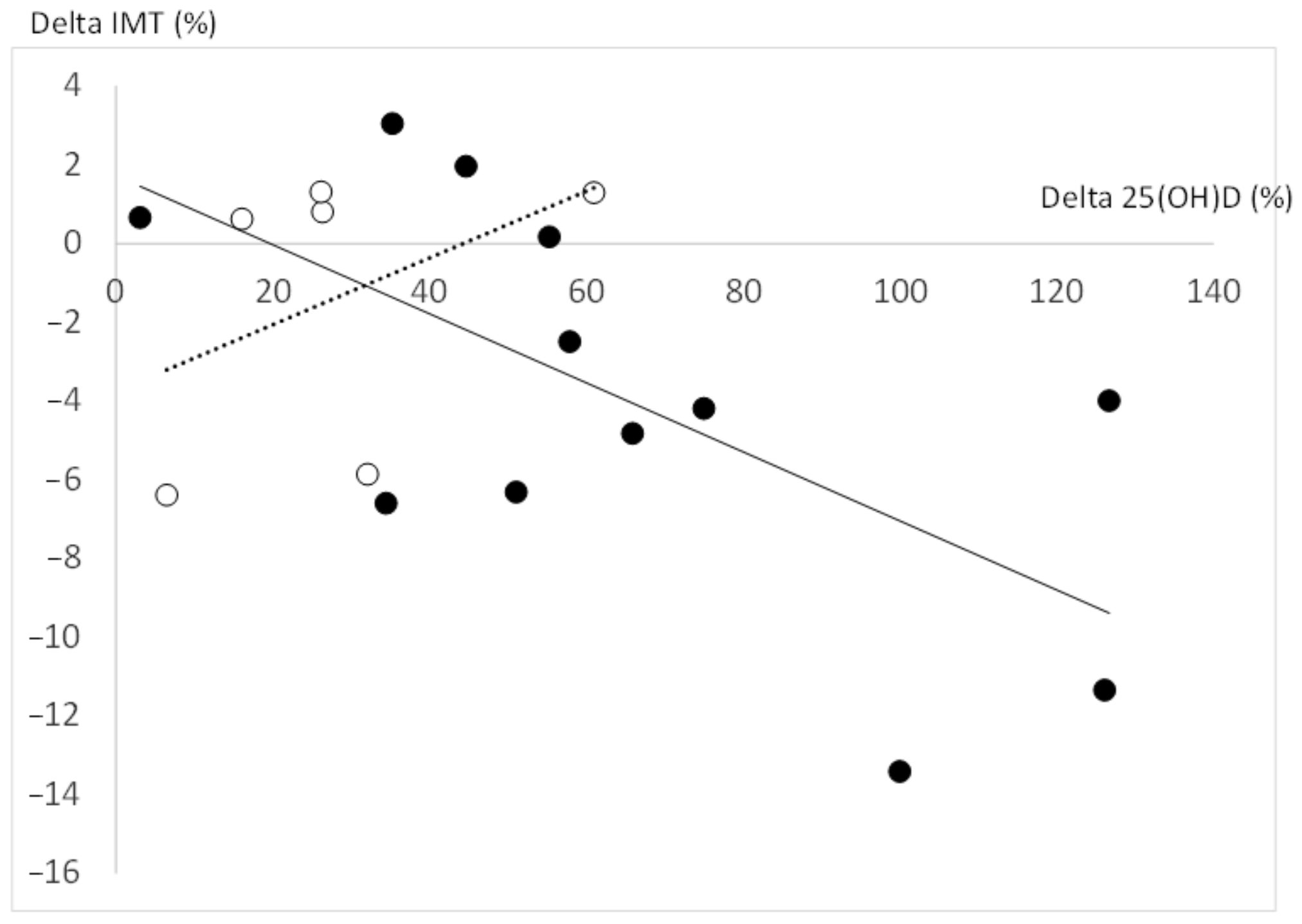
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alemzadeh, R.; Kichler, J.; Babar, G.; Calhoun, M. Hypovitaminosis D in obese children and adolescents: Relationship with adiposity, insulin sensitivity, ethnicity, and season. Metabolism 2008, 57, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganji, V.; Zhang, X.; Shaikh, N.; Tangpricha, V. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with prevalence of metabolic syndrome and various cardiometabolic risk factors in US children and adolescents based on assay-adjusted serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D data from NHANES 2001–2006. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, A.T.; Phillips, A.A.; Harris, K.C.; Sandor, G.G.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Devlin, A.M. Obesity and arterial stiffness in children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mheid, I.; Patel, R.; Murrow, J.; Morris, A.; Rahman, A.; Fike, L.; Kavtaradze, N.; Uphoff, I.; Hooper, C.; Tangpricha, V.; et al. Vitamin D status is associated with arterial stiffness and vascular dysfunction in healthy humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, O., Jr.; Filipovský, J.; Seidlerová, J.; Vaněk, J.; Dolejšová, M.; Vrzalová, J.; Cífková, R. The association between low 25-hydroxyvitamin D and increased aortic stiffness. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2012, 26, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.P.; Alvarez, J.A.; Dudenbostel, T.; Calhoun, D.; Griffin, R.; Wang, X.; Hanks, L.J.; Gower, B.A. Associations between vascular health indices and serum total, free and bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D in adolescents. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.J.; Scott, D.; Srikanth, V.; Ebeling, P. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on measures of arterial stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 84, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upala, S.; Sanguankeo, A.; Congrete, S.; Jaruvongvanich, V. Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on arterial stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2016, 50, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Stallmann-Jorgensen, I.S.; Pollock, N.K.; Harris, R.A.; Keeton, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Bassali, R.; Guo, D.H.; Thomas, J.; et al. A 16-week randomized clinical trial of 2000 international units daily vitamin D3 supplementation in black youth: 25-hydroxyvitamin D, adiposity, and arterial stiffness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4584–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.S.; Clifton, P.M.; Lister, N.; Keogh, J.B. Effect of weight loss induced by energy restriction on measures of arterial compliance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2016, 247, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skilton, M.R.; Yeo, S.Q.; Ne, J.Y.; Celermajer, D.S.; Caterson, I.D.; Lee, C.M. Weight loss and carotid intima-media thickness—A meta-analysis. Obesity 2017, 25, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannu, P.K.; Zhao, Y.; Soares, M.J. Reductions in body weight and percent fat mass increase the vitamin D status of obese subjects: A systematic review and metaregression analysis. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T.; de Sousa, G.; Alexy, U.; Kersting, M.; Andler, W. Vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone in obese children before and after weight loss. Eur J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Gow, M.; Baur, L.A.; Benitez-Aguirre, P.Z.; Tam, C.S.; Donaghue, K.C.; Craig, M.E.; Cowell, C.T.; Garnett, S.P. Effect of fat loss on arterial elasticity in obese adolescents with clinical insulin resistance: RESIST study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinet, A.; Morrissey, C.; Perez-Martin, A.; Goncalves, A.; Raverdy, C.; Masson, D.; Gayrard, S.; Carrere, M.; Landrier, J.F.; Amiot, M.J.; et al. supplementation reversed microvascular dysfunction in obese adolescents: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenchia, A.M.; Tosh, A.; Hillman, L.; Peterson, C. Correcting vitamin D insufficiency improves insulin sensitivity in obese adolescents: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.; Binkley, N.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Gordon, C.; Hanley, D.; Heaney, R.; Murad, M.; Weaver, C. Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, C.; Montero, D.; Raverdy, C.; Masson, D.; Amiot, M.J.; Vinet, A. Effects of Exercise Intensity on Microvascular Function in Obese Adolescents. Int J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.; Nottin, S.; Dauzat, M.; Obert, P. Femoral and axillary ultrasound blood flow during exercise: A methodological study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Walther, G.; Perez-Martin, A.; Roche, E.; Mercier, C.; Vinet, A. Leg arterial stiffness after weight loss in severely obese adolescents. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1676–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia del Giudice, E.; Grandone, A.; Cirillo, G.; Capristo, C.; Marzuillo, P.; Di Sessa, A.; Umano, G.R.; Ruggiero, L.; Perrone, L. Bioavailable Vitamin D in Obese Children: The Role of Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3949–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sollid, S.T.; Hutchinson, M.; Berg, V.; Fuskevåg, O.M.; Figenschau, Y.; Thorsby, P.M.; Jorde, R. Effects of vitamin D binding protein phenotypes and vitamin D supplementation on serum total 25(OH)D and directly measured free 25(OH)D. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourshahidi, L.K. Vitamin D and obesity: Current perspectives and future directions. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, L.; Anania, C.; Osborn, J.F.; Ferraro, F.; Bonci, E.; Olivero, E.; Chiesa, C. Low 25(OH)D3 levels are associated with total adiposity, metabolic syndrome, and hypertension in Caucasian children and adolescents. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Merrill, E.D.; Sandesara, P.B.; Schoeneberg, L.; Dai, H.; Raghuveer, G. Vitamin D, Low-Grade Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risk in Young Children: A Pilot Study. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2015, 36, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juonala, M.; Voipio, A.; Pahkala, K.; Viikari, J.S.; Mikkilä, V.; Kähönen, M.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Jula, A.; Burgner, D.; Sabin, M.A.; et al. Childhood 25-OH vitamin D levels and carotid intima-media thickness in adulthood: The cardiovascular risk in young Finns study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 4, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzotzas, T.; Papadopoulou, F.G.; Tziomalos, K.; Karras, S.; Gastaris, K.; Perros, P.; Krassas, G.E. Rising serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels after weight loss in obese women correlate with improvement in insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4251–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säidifard, N.; Tangestani, H.; Djafarian, K.; Shab-Bidar, S. Serum Vitamin D Level and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies and Randomized Control Trials. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvisalo, M.J.; Harmoinen, A.; Hakanen, M.; Paakkunainen, U.; Viikari, J.; Hartiala, J.; Lehtimäki, T.; Simell, O.; Raitakari, O.T. Elevated serum C-reactive protein levels and early arterial changes in healthy children. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Obese | Obese Subgroups | p-Value | Normal-Weight | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | (n = 26) | OS (n = 13) | ONS (n = 13) | OS vs. ONS | (n = 18) | All OA vs. NW |
| Age (year) | 14.2 (13.6–14.8) | 14.6 (13.6–14.8) | 14 (13.1–16.7) | 0.959 | 14.8 (13.3–15.3) | 0.535 |
| Boys/girls (n) | 10–16 | 5–8 | 5–8 | 1.0 | 10–8 | 0.728 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.5 (31.2–36.2) | 33.8 (31.3–36.5) | 32.7 (31.1–36.3) | 0.614 | 19.2 (18.5–20.2) | <0.0001 |
| BMI Z-score | 4.0 (3.5–4.5) | 3.9 (3.4–4.7) | 4.0 (3.4–4.6) | 0.959 | 0.0 (−0.3–0.7) | <0.0001 |
| Fat mass (%) | 41.4 (39.8–43.2) | 41.9 (39.8–43.6) | 41.1 (36.5–44.3) | 0.555 | 23.2 (18.4–27.7) | <0.0001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 112 (106–120) | 112 (106–123) | 113 (106–120.5) | 0.797 | 104 (100–108) | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 66 (62–68) | 59 (57–60) | 61 (59–68) | 0.039 | 60 (59–62) | 0.004 |
| Total 25(OH)D (nmol/L) | 38 (35.4–47.8) | 39 (38–55.8) | 34.5 (32–58.6) | 0.191 | 57 (48.1–67.7) | 0.002 |
| n deficiency in 25(OH)D | 8 | 1 | 7 | - | 0 | - |
| n insuficiency in 25(OH)D | 18 | 9 | 9 | - | 5 | - |
| Free 25(OH)D (pg/mL) | 4.1 (1.9–5.3) | 4.1 (1.9–5.3) | 4.1 (2.4–4.8) | 0.918 | 4.8 (2.6–6.2) | 0.006 |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 6.1 (3.3–10.1) | 7.9 (3.6–13.7) | 4.4 (2.3–10.1) | 0.331 | 0.3 (0.2–0.7) | <0.0001 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 2.6 (1.7–2.7) | 2.7 (1.8–2.9) | 2.3 (1.6–2.7) | 0.283 | 0.55 (0.5–1.1) | <0.0001 |
| CCA diameter (mm) | 5.73 (5.59–581) | 5.77 (5.53–5.87) | 5.70 (5.31–5.82) | 0.355 | 5.05 (4.84–5.24) | <0.0001 |
| CCA compliance (mm2/mmHg) | 0.11 (0.09–0.12) | 0.10 (0.06–0.16) | 0.11 (0.08–0.12) | 0.923 | 0.16 (0.12–0.18) | 0.0017 |
| CCA-IMT (mm) | 0.64 (0.63–0.67) | 0.63 (0.62–0.66) | 0.66 (0.62–0.68) | 0.342 | 0.61 (0.59–0.63) | 0.0186 |
| All Obese | p-Value | Changes from Baseline (in %) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Variables | Baseline | 3 Months | OS | ONS | ||
| Total 25(OH)D (mmol/L) | 38.0 (35.4–47.8) | 67.0 (57.0–71.6) | <0.0001 | 55.2 (38.1–72.0) | 34.9 (8.1–70.9) | 0.132 |
| Free 25(OH)D (mmol/L) | 4.1 (1.9–5.3) | 5.9 (4.1–8.3) | 0.0001 | 59.4 (36.3–77.4) | 27.4 (8.6–60.6) | 0.336 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.5 (31.2–36.2) | 30.3 (29.6–32.5) | <0.0001 | −8.5 (−11.2–−6.3) | −7.8 (−10.9–−5.6) | 0.649 |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 6.1 (3.3–10.1) | 2.0 (0.9–4.5) | 0.0002 | −48.8 (−81.6–−0.35) | −65 (−81.1–48) | 0.331 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 2.6 (1.7–2.7) | 1.6 (1.1–1.9) | 0.007 | −36.9 (−76.9–1.7) | −36.3 (−60.3–−12.8) | 1 |
| Carotid diameters (mm) | 5.73 (5.59–5.81) | 5.66 (5.46–5.83) | 0.678 | 0 (−1.1–2.5) | −1.5 (−4.4–3.5) | 0.434 |
| Carotid compliance (mm2/mmHg) | 0.11 (0.09–0.12) | 0.12 (0.10–0.15) | 0.05 | 2.35 (−9.8–18.2) | 15.5 (−5.3–58.1) | 0.305 |
| Intima-media thickness (mm) | 0.64 (0.63–0.67) | 0.63 (0.62–0.67) | 0.034 | −3.25 (−7.3–0.9) | 0.61 (−6.4–2.1) | 0.599 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morrissey, C.; Amiot, M.-J.; Goncalves, A.; Raverdy, C.; Masson, D.; Tardivel, C.; Gayrard, S.; Carrère, M.; Landrier, J.-F.; Vinet, A.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112296
Morrissey C, Amiot M-J, Goncalves A, Raverdy C, Masson D, Tardivel C, Gayrard S, Carrère M, Landrier J-F, Vinet A, et al. Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112296
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorrissey, Christopher, Marie-Josèphe Amiot, Aurelie Goncalves, Cecile Raverdy, Delphine Masson, Catherine Tardivel, Sandrine Gayrard, Myriam Carrère, Jean-Francois Landrier, Agnes Vinet, and et al. 2022. "Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112296
APA StyleMorrissey, C., Amiot, M.-J., Goncalves, A., Raverdy, C., Masson, D., Tardivel, C., Gayrard, S., Carrère, M., Landrier, J.-F., Vinet, A., & Perez-Martin, A. (2022). Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents. Nutrients, 14(11), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112296








