Comparison of Ferric Sodium EDTA in Combination with Vitamin C, Folic Acid, Copper Gluconate, Zinc Gluconate, and Selenomethionine as Therapeutic Option for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Improvement in Inflammatory Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
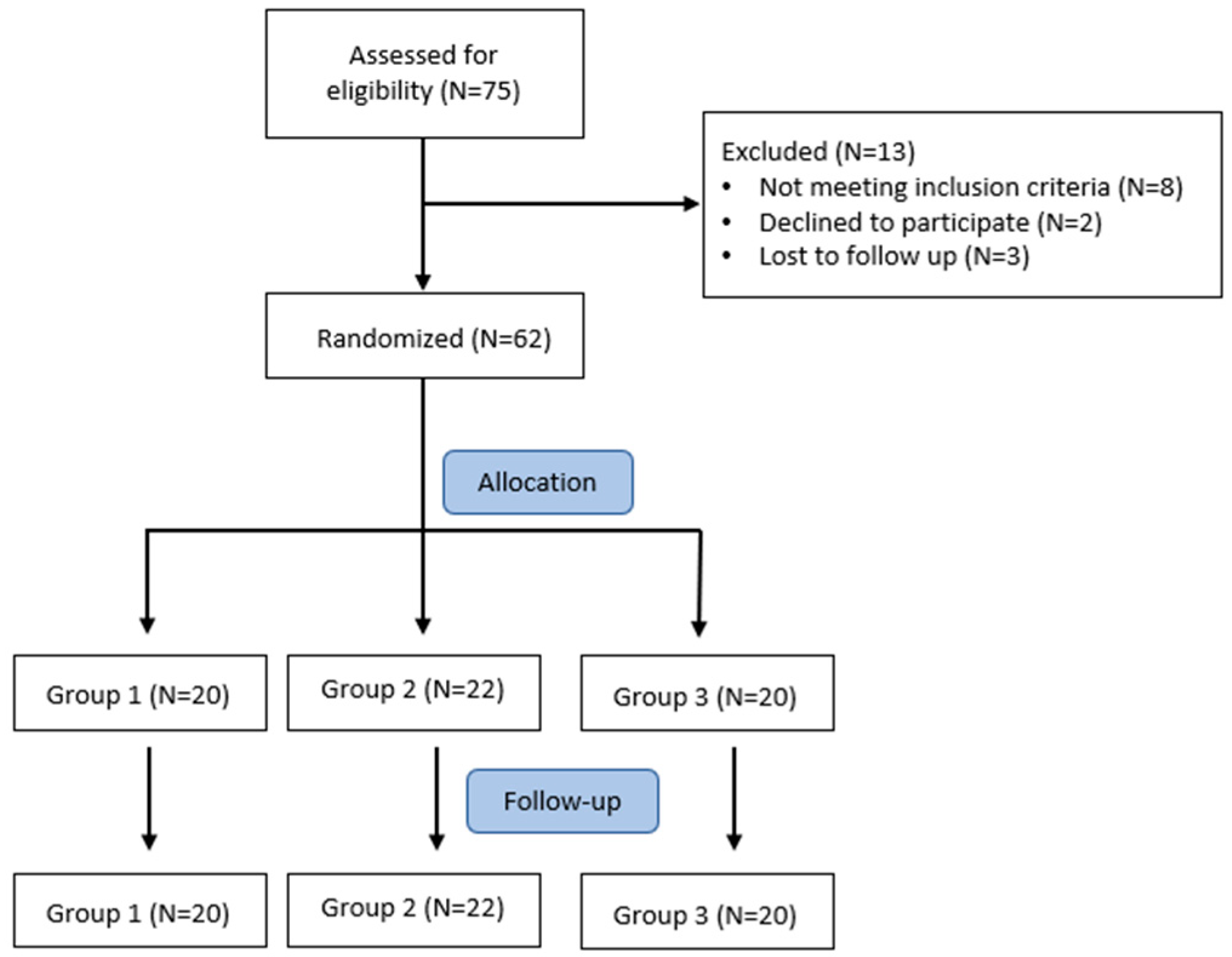
2. Materials and Methods
- Ferrous sulfate prolonged-release tablets (Ferro-grad®, Teofarma s.r.l., Pavia, Italy) 1 tab/day, containing 105 mg of ferrous ion for 6 months (Group 1; N = 20);
- Ferric sodium EDTA in combination with vitamin C, folic acid, copper gluconate, zinc gluconate, and selenomethionine (Ferachel Forte®, AQMA Italia S.p.A., Milan, Italy) 1 tab/day, containing 30 mg of ferric ion for 6 months (Group 2; N = 22);
- Ferric liposomal formulation (Ferroabi30®, Abi pharmaceutical s.r.l., Rome, Italy) 1 tab/day, containing 30 mg of ferric ion for 6 months (Group 3; N = 20).
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramy, M.H.; Streja, E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Burden of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Beyond Erythropoietin. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 52–75. [Google Scholar]
- Babitt, J.L.; Lin, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Hepcidin Regulation: Implications for the Anemia of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, A.A.; Walther, C.P.; Richardson, P.A.; Shah, M.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Navaneethan, S.D. Prevalence, correlates and outcomes of absolute and functional iron deficiency anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 36, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gafter-Gvili, A.; Schechter, A.; Rozen-Zvi, B. Iron Deficiency Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Acta Haematol 2019, 142, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaschella, C. Iron deficiency anemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Ganz, T.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Assessment and Management NICE Guideline. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng203/resources/chronic-kidney-disease-assessment-and-management-pdf-66143713055173 (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Anemia Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Intern. Suppl. 2012, 2, 279–335. [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe, L.E.K.; Thomas, W.; Glen, J.; Padhi, S.; Pordes, B.A.J.; Wonderling, D.; Connell, R.; Stephens, S.; Mikhail, A.I.; Fogarty, D.G.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Iron Deficiency in CKD: A Summary of the NICE Guideline Recommendations and Their Rationale. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G.; Duranti, D.; Duranti, E. Short study on the use of oral Ferric Sodium EDTA in association with vitamin C, folic acid, copper gluconate, zinc gluconate and selenomethionine, in patients with advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Renal. Dis. 2021, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo, L.; Marchitto, N.; Curcio, A.; Romano, A.; Bilo, L.L.; Pironti, M.; Raimondi, G. The best therapeutic option for oral treatment of secondary anaemia in chronic kidney disease: Role of Ferric Sodium EDTA, in association with Vitamin C, Folic acid, Copper gluconate, Zinc Gluconate and Selenomethionine. Nephrol. Renal. Dis. 2021, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchitto, N.; Curcio, A.; Iannarelli, N.; Petrucci, A.; Romano, A.; Pironti, M.; Paparello, P.T.; Raimondi, G. A pilot study on secondary anaemia in “frailty” patients treated with the Ferric Sodium EDTA in combination with vitamin C, folic acid, copper gluconate, zinc gluconate and selenomethionine: Safety of treatment explored by HRV non-linear analysis as predictive factor of cardiovascular tolerability. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7776–7783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchitto, N.; Sindona, F.; Pannozzi, A.; Petrucci, A.; Fusco, L.; Dalmaso, S.G.; Raimondi, G. Role of Ferric Sodium EDTA associated with vitamin C, folic acid, copper gluconate, zinc gluconate and selenomethionine administration in patients with secondary anaemia. Effects on hemoglobin value and cardiovascular risk. Health Sci. J. 2019, 13, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto, N.; Petrucci, A.; Fusco, L.; Curcio, A.; Romano, A.; Pironti, M.; Raimondi, G. Effect of Ferric Sodium EDTA administration, in combination with vitamin C, folic acid, copper gluconate, zinc gluconate and selenomethionine, on cardiovascular risk evaluation: Exploration of the HRV frequency domain. Clin. Pract. 2019, 16, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Curcio, A.; Romano, A.; Marchitto, N.; Pironti, M.; Raimondi, G. Efficacy and Safety of a New Formulation of Ferric Sodium EDTA Associated with Vitamin C, Folic Acid, Copper Gluconate, Zinc Gluconate and Selenomethionine Administration in Patients with Secondary Anaemia. J. Blood Lymph 2018, 8, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Ma, A.G.; Yang, F.; Zhang, F.Z.; Jiang, D.C.; Li, Y. Moderate NaFeEDTA and ferrous sulfate supplementation can improve both hematologic status and oxidative stress in anemic pregnant women. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 514–520. [Google Scholar]
- Van Thuy, P.; Berger, J.; Nakanishi, Y.; Khan, N.C.; Lynch, S.; Dixon, P. The use of NaFeEDTA-fortified fish sauce is an effective tool for controlling iron deficiency in women of childbearing age in rural Vietnam. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2596–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignini, P.; Mangiafico, L.; Padula, F.; D’Emidio, L.; Dugo, N.; Aloisi, A.; Giorlandino, C.; Vitale, S.G. Supplementation with a dietary multicomponent (Lafergin(®)) based on Ferric Sodium EDTA (Ferrazone(®)): Results of an observational study. J. Prenat. Med. 2015, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Sun, J.; Miao, H.; Yu, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, Z.; Lu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; et al. Therapeutic effects of NaFeEDTA-fortified soy sauce in anaemic children in China. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 11, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herter-Aeberli, I.; Eliancy, K.; Rathon, Y.; Loechl, C.U.; Marhône Pierre, J.; Zimmermann, M.B. In Haitian women and preschool children, iron absorption from wheat flour-based meals fortified with sodium iron EDTA is higher than that from meals fortified with ferrous fumarate, and is not affected by Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthayya, S.; Thankachan, P.; Hirve, S.; Amalrajan, V.; Thomas, T.; Lubree, H.; Agarwal, D.; Srinivasan, K.; Hurrell, R.F.; Yajnik, C.S.; et al. Iron fortification of whole wheat flour reduces iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia and increases body iron stores in Indian school-aged children. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longfils, P.; Monchy, D.; Weinheimer, H.; Chavasit, V.; Nakanishi, Y.; Schümann, K. A comparative intervention trial on fish sauce fortified with NaFe-EDTA and FeSO4+citrate in iron deficiency anemic school children in Kampot, Cambodia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teshome, E.M.; Otieno, W.; Terwel, S.R.; Osoti, V.; Demir, A.Y.; Andango, P.E.A.; Prentice, A.M.; Verhoef, H. Comparison of home fortification with two iron formulations among Kenyan children: Rationale and design of a placebo-controlled non-inferiority trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.S.; Yin, J.Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, Z.X.; Regina, M.P.; Chen, J.S.; Chen, C.M. Effect of NaFeEDTA-Fortified Soy Sauce on Anemia Prevalence in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Regil, L.M.; Jefferds, M.E.D.; Peña-Rosas, J.P. Point-of-use fortification of foods with micronutrient powders containing iron in children of preschool and school-age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD009666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhan, S.; Xia, Y.; Lee, L. Effect of sodium iron ethylenediaminetetra-acetate (NaFeEDTA) on haemoglobin and serum ferritin in iron-deficient populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheers, N. Regulatory Effects of Cu, Zn, and Ca on Fe Absorption: The Intricate Play between Nutrient Transporters. Nutrients 2013, 5, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.; Tripathi, S.K. Folic Acid Revisited. Ind. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 33, 322–342. [Google Scholar]
- Semba, R.D.; Ferrucci, L.; Cappola, A.R.; Ricks, M.O.; Ray, A.L.; Xue, Q.L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fried, L.P. Low Serum Selenium Is Associated with Anemia Among Older Women Living in the Community: The Women’s Health and Aging Studies I and II. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2006, 112, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Locatelli, F.; Mazzaferro, S.; Yee, J. Iron Therapy Challenges for the Treatment of Nondialysis CKD Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Takasawa, K. Impact of Inflammation on Ferritin, Hepcidin and the Management of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.; de Benoist, B.; Dary, O.; Hurrell, R. Guidelines on Food Fortification with Micronutrients. World Health Organization: 2006. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/43412/9241594012_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS). Scientific Opinion on the use of ferric sodium EDTA as a source of iron added for nutritional purposes to foods for the general population (including food supplements) and to foods for particular nutritional uses. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compendium of Food Additive Specifications. Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives 68th Meeting 2007. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/a1447e/a1447e.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Begum, S.; Latunde-Dada, G.O. Anemia of Inflammation with An Emphasis on Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. New Recommendations to Manage Risk of Allergic Reactions with Intravenous Iron Containing Medicines (EMA/579491/2013). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/intravenous-iron-containing-medicinal-products-article-31-referral-new-recommendations-manage-risk_en.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2022).
| Variable | Group 1 (N = 20) | Group 2 (N = 22) | Group 3 (N = 20) | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male/female, N | 10/10 | 11/11 | 11/9 | - |
| Age (years), mean (±SD) | 68.3 (2.8) | 72.3 (7.5) | 68.05 (1.7) | - |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), | 46.15 (2.2) | 36.45 (8.5) | 47.80 (3.5) | <0.001 |
| Hb (g/dL), mean (±SD) | 10.46 (0.22) | 10.70 (0.23) | 10.59 (0.14) | 0.023 |
| Sideremia (μg/dL), mean (±SD) | 28.15 (1.96) | 38.18 (7.17) | 27.10 (1.87) | 0.004 |
| TSAT (%), mean (±SD) | 16.85 (3.15) | 19.95 (3.07) | 17.45 (4.32) | 0.041 |
| Ferritin (μg/L), mean (±SD) | 279.10 (33.53) | 249.68 (37.50) | 269.45 (56.94) | 0.170 |
| CRP (mg/dL), mean (±SD) | 4.56 (0.30) | 4.05 (0.36) | 4.63 (0.15) | 0.001 |
| Hepcidin (ng/mL), mean (±SD) | 19.01 (0.39) | 18.85 (0.44) | 18.92 (0.48) | 0.442 |
| Blood Parameters, Mean (±SD) | Group (N = 20) | Group 2 (N = 22) | Group 3 (N = 20) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | p Value | T0 | T1 | p Value | T0 | T1 | p Value | |
| Hb (g/dL) | 10.46 (0.22) | 10.42 (0.19) | 0.780 | 10.70 (0.23) | 11.91 (0.21) | <0.001 | 10.59 (0.14) | 10.78 (0.22) | <0.001 |
| Sideremia (μg/dL) | 28.15 (1.96) | 30.65 (4.07) | 0.117 | 38.18 (7.17) | 63.59 (8.28) | <0.001 | 27.10 (1.87) | 33.05 (3.26) | <0.001 |
| TSAT (%) | 16.85 (3.15) | 17.11 (4.51) | 0.874 | 19.95 (3.07) | 36.72 (4.28) | <0.001 | 17.45 (4.32) | 19.60 (2.73) | <0.001 |
| Ferritin (μg/L) | 279.10 (33.53) | 291.75 (38.17) | <0.001 | 249.68 (37.50) | 164.73 (28.73) | <0.001 | 269.45 (56.94) | 217.70 45.86) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 4.56 (0.30) | 4.53 (0.21) | 0.576 | 4.05 (0.36) | 1.52 (0.32) | <0.001 | 4.63 (0.15) | 4.06 (0.63) | 0.012 |
| Hepcidin (ng/mL) | 19.01 (0.39) | 18.85 (0.44) | 0.673 | 18.85 (0.44) | 8.90 (1.18) | <0.001 | 18.92 (0.48) | 18.62 (0.63) | 0.245 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giliberti, A.; Curcio, A.; Marchitto, N.; Di Lullo, L.; Paolozzi, F.; Nano, F.; Pironti, M.; Raimondi, G. Comparison of Ferric Sodium EDTA in Combination with Vitamin C, Folic Acid, Copper Gluconate, Zinc Gluconate, and Selenomethionine as Therapeutic Option for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Improvement in Inflammatory Status. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102116
Giliberti A, Curcio A, Marchitto N, Di Lullo L, Paolozzi F, Nano F, Pironti M, Raimondi G. Comparison of Ferric Sodium EDTA in Combination with Vitamin C, Folic Acid, Copper Gluconate, Zinc Gluconate, and Selenomethionine as Therapeutic Option for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Improvement in Inflammatory Status. Nutrients. 2022; 14(10):2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102116
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiliberti, Antonella, Annalisa Curcio, Nicola Marchitto, Luca Di Lullo, Fulvia Paolozzi, Fabiana Nano, Michele Pironti, and Gianfranco Raimondi. 2022. "Comparison of Ferric Sodium EDTA in Combination with Vitamin C, Folic Acid, Copper Gluconate, Zinc Gluconate, and Selenomethionine as Therapeutic Option for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Improvement in Inflammatory Status" Nutrients 14, no. 10: 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102116
APA StyleGiliberti, A., Curcio, A., Marchitto, N., Di Lullo, L., Paolozzi, F., Nano, F., Pironti, M., & Raimondi, G. (2022). Comparison of Ferric Sodium EDTA in Combination with Vitamin C, Folic Acid, Copper Gluconate, Zinc Gluconate, and Selenomethionine as Therapeutic Option for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Improvement in Inflammatory Status. Nutrients, 14(10), 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102116







