Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Healthy Diet and/or Physical Activity during Pregnancy: An Umbrella Review
Highlights
- Both diet and physical activity interventions independently reduce the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
- Whether the effect of combined interventions, involving both diet and physical activity, tends to be protective, however, is less clear.
- The systematic reviews included were of a relatively low quality, and high variability was observed in the definition of interventions.
- Our results highlight the need to perform more clinical trials of a higher quality and approach interventions and systematic reviews in a way that aligns with the current standards.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria for the Selection of Systematic Reviews
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
- -
- Gestational diabetes mellitus, gestational diabetes.
- -
- Activit*, physical activity, exercise, sport, training, fitness.
- -
- Eating behaviors, feeding behaviors, eating habits, food habits, dietary habits, feeding patterns, dietary pattern, diet.
- -
- Systematic review, meta-analysis.
- -
- Diabetes mellitus type 1, diabetes mellitus type 2, T2D, DM2, treatment.
2.3. Study Selection and Extraction Data
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Overlapping Synthesis
2.6. Data Synthesis
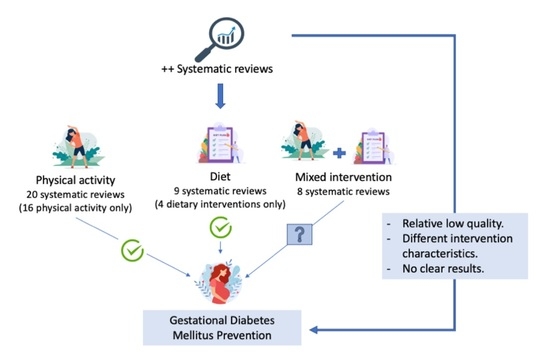
3. Results
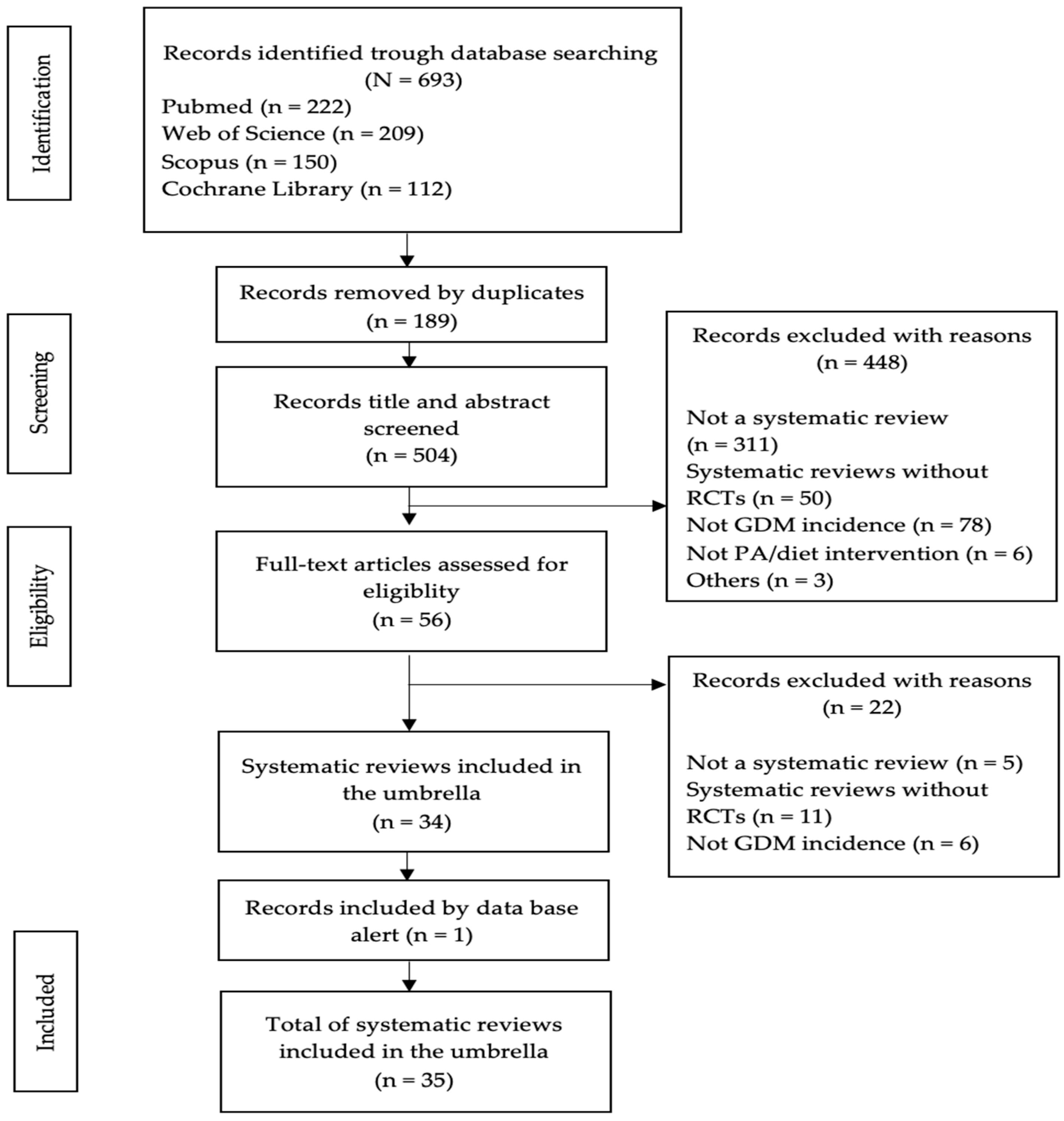
3.1. Literature Search
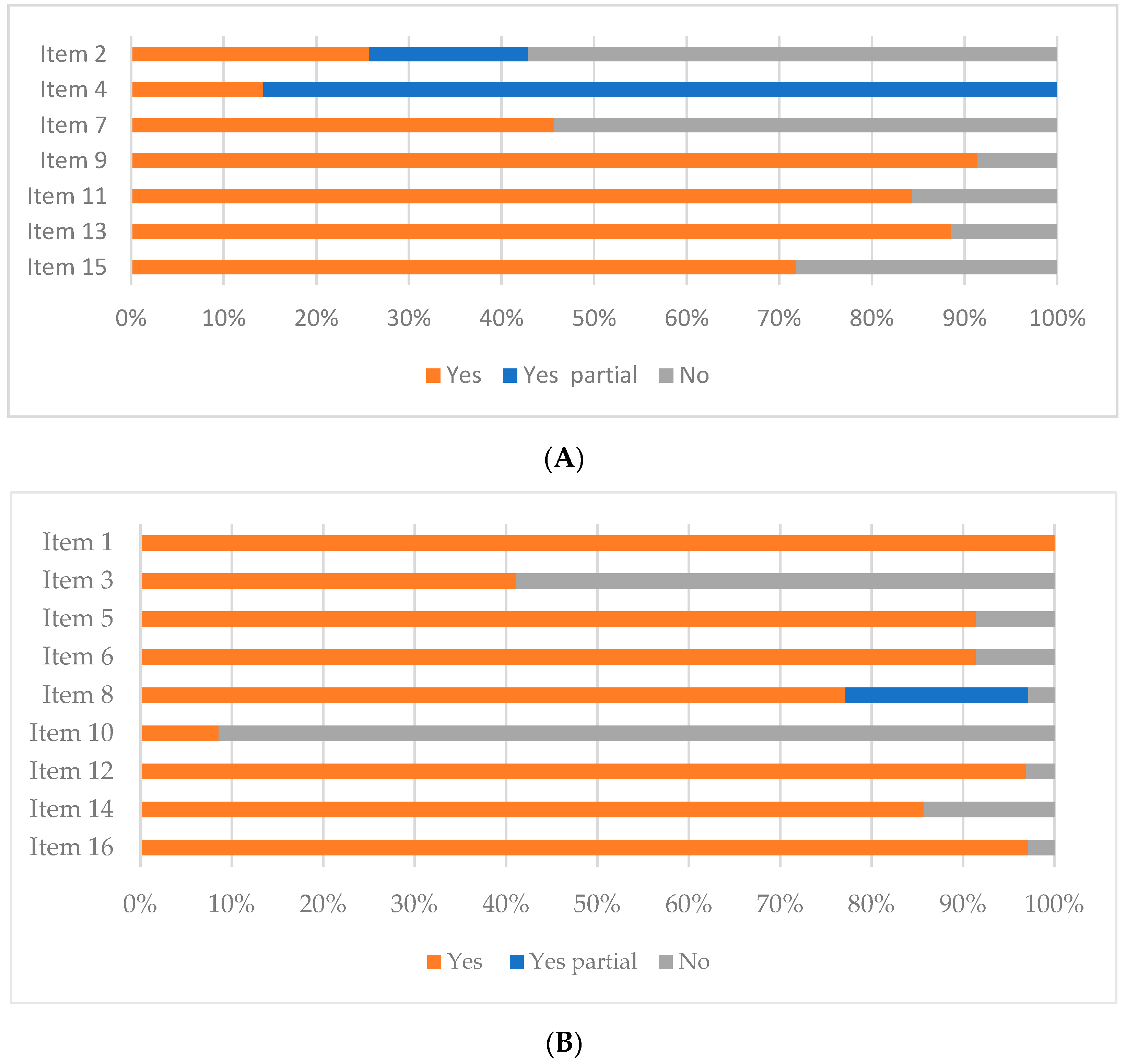
3.2. Quality Assessment of the Systematic Reviews
3.3. Overlapping between Reviews
3.4. Main Results
3.4.1. Interventions
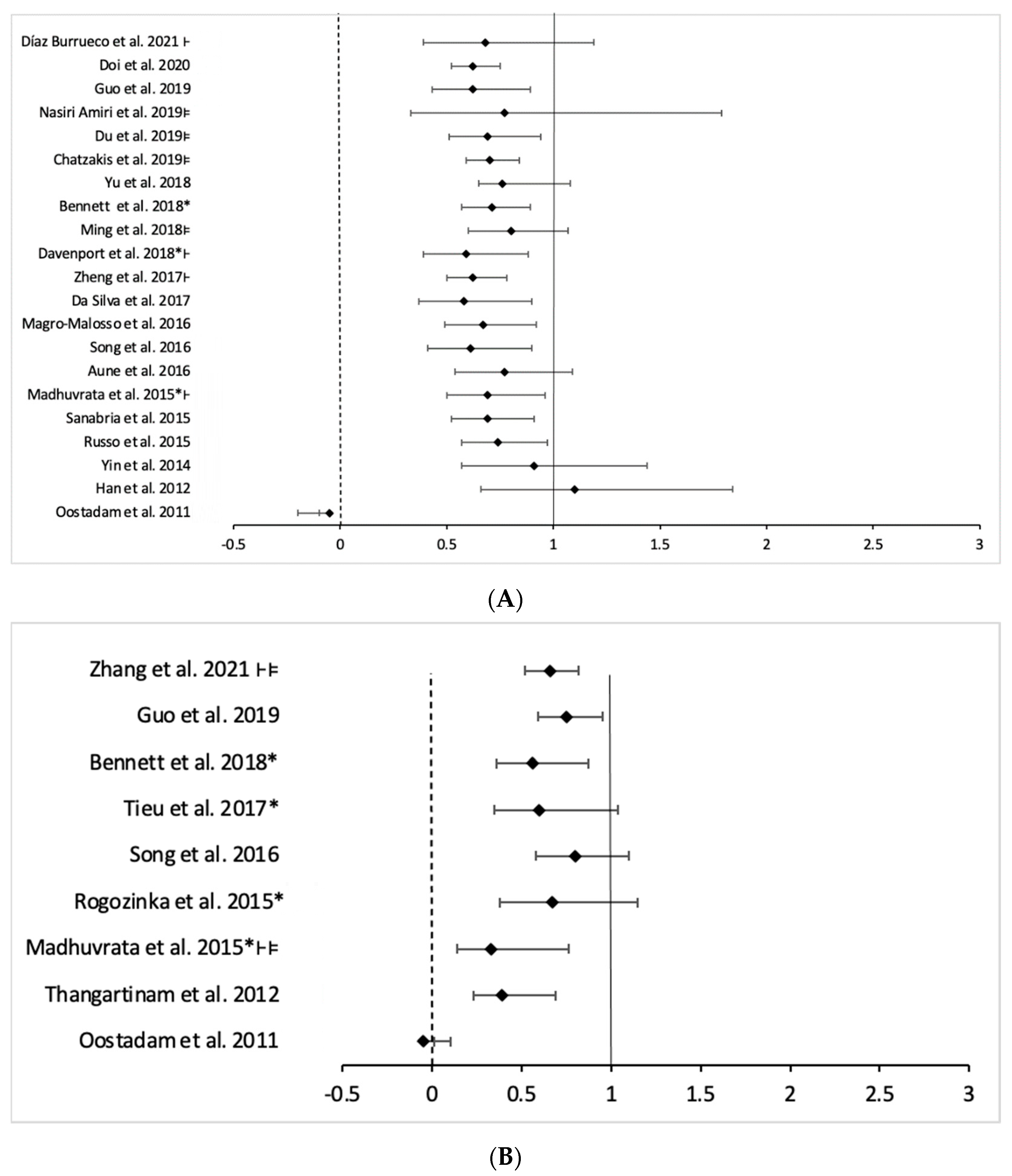
3.4.2. Prevention of GDM
- (a)
- Physical activity intervention
- (b)
- Diet intervention
- (c)
- Mixed intervention
3.5. Results from Studies with GDM as Not a Principal Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.-J.; Chao-Qing, T.; Hu, C.-L.; Zhu, M.; Tian, C.-Q.; Li, L. Is gestational diabetes mellitus an independent risk factor for macrosomia: A meta-analysis? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 291, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billionnet, C.; Mitanchez, D.; Weill, A.; Nizard, J.; Alla, F.; Hartemann, A.; Jacqueminet, S. Gestational diabetes and adverse perinatal outcomes from 716,152 births in France in 2012. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Vigo, P.; Álvarez-Silvares, E.; Alves-Pérez, M.T.; Domínguez-Sánchez, J.; González-González, A. Incidencia y Factores Clínicos de Riesgo de Diabetes Mellitus En Mujeres Con Diabetes Gestacional Previa. Ginecol. Obstet. Mex. 2016, 84, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kramer, C.K.; Campbell, S.; Retnakaran, R. Gestational Diabetes and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hormones 2020, 19, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nerenberg, K.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Dasgupta, K. Gestational Diabetes and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy as Vascular Risk Signals: An Overview and Grading of the Evidence. Can. J. Cardiol. 2014, 30, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; Rao, Y.; Sharma, M.; Zhao, Y. Prevalence and Determinants of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.-C.; Hung, C.-H.; Chan, T.-F.; Lin, K.-C.; Hsu, Y.-Y.; Tzeng, Y.-L. The risk factors for gestational diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study. Midwifery 2016, 42, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zheng, L.; Ye, P.; Wei, D.; Chen, D. Analysis of risk factors related to gestational diabetes mellitus. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 59, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, C.J. Gestational diabetes: Risk factors and recent advances in its genetics and treatment. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Available online: https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/gestational-diabetes/how-will-this-impact-my-baby (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Kapustin, R.V.; Arzhanova, O.N.; Bespalova, O.N.; Pakin, V.S.; Ailamazyan, E.K. Abnormal Weight Gain as a Factor in the Development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Akusherstvo I Ginekol. 2016, 5, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesi, L.; Moscatiello, S.; Malavolti, M.; Marzocchi, R.; Marchesini, G. Physical activity for the prevention and treatment of metabolic disorders. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De la Iglesia, R.; Loria-Kohen, V.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Reglero, G.; Ramirez de Molina, A. Dietary Strategies Implicated in the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagnild, J.M.; Hinshaw, K.; Pollard, T. Associations of sedentary time and self-reported television time during pregnancy with incident gestational diabetes and plasma glucose levels in women at risk of gestational diabetes in the UK. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Rawal, S. Dietary iron intake, iron status, and gestational diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1672S–1680S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olmedo-Requena, R.; Gómez-Fernández, J.; Amezcua-Prieto, C.; Mozas-Moreno, J.; Khan, K.S.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J. Pre-Pregnancy Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davenport, M.H.; Ruchat, S.M.; Poitras, V.J.; Jaramillo Garcia, A.; Gray, C.E.; Barrowman, N.; Skow, R.J.; Meah, V.L.; Riske, L.; Sobierajski, F.; et al. Prenatal exercise for the prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; Henriksen, T.; Saugstad, O.D.; Tonstad, S. Physical activity and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 967–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.; Li, J.; Leng, J.; Ma, R.C.; Yang, X. Lifestyle intervention can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, R.J.; Alsweiler, J.; Moore, A.E.; Brown, S.; Middleton, P.; Shepherd, E.; Crowther, C.A. Interventions to prevent women from developing gestational diabetes mellitus: An overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD012394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.J.; Walker, R.E.; Blumfield, M.L.; Gwini, S.-M.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.; Wan, Y.; Dickinson, H.; Truby, H. Interventions designed to reduce excessive gestational weight gain can reduce the incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhuvrata, P.; Govinden, G.; Bustani, R.; Song, S.; Farrell, T.A. Prevention of gestational diabetes in pregnant women with risk factors for gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Obstet. Med. 2015, 8, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, M. Influence of exercise intervention on gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, J.; Shepherd, E.; Middleton, P.; Crowther, C.A. Dietary advice interventions in pregnancy for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1, CD006674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Wells, G.A.; Boers, M.; Andersson, N.; Hamel, C.; Porter, A.C.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; Bouter, L.M. Development of AMSTAR: A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shea, A. AMSTAR-2: Herramienta de Evaluación Crítica de Revisiones Sis- Temáticas de Estudios de Intervenciones de Salud. BMJ 2017, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, D.; Antoine, S.-L.; Mathes, T.; Neugebauer, E.A.; Eikermann, M. Systematic review finds overlapping reviews were not mentioned in every other overview. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoth, K.; Chandan, J.S.; Marshall, T.; Thangaratinam, S.; Thomas, G.N.; Nirantharakumar, K.; Adderley, N.J. Association between the reproductive health of young women and cardiovascular disease in later life: Umbrella review. BMJ 2020, 371, m3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, E.; Gomersall, J.C.; Tieu, J.; Han, S.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Combined diet and exercise interventions for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD010443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougioukas, K.I.; Liakos, A.; Tsapas, A.; Ntzani, E.; Haidich, A.-B. Preferred reporting items for overviews of systematic reviews including harms checklist: A pilot tool to be used for balanced reporting of benefits and harms. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 93, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaruk, B.; Galczak-Kondraciuk, A.; Forczek, W.; Grantham, W.; Charmas, M. The Effectiveness of Regular Exercise Programs in the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus—A Systematic Review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2019, 74, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamminpää, R.; Vehviläinen-Julkunen, K.; Schwab, U. A systematic review of dietary interventions for gestational weight gain and gestational diabetes in overweight and obese pregnant women. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1721–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skouteris, H.; Morris, H.; Nagle, C.; Nankervis, A. Behavior Modification Techniques Used to Prevent Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, S.A.; Furuya-Kanamori, L.; Toft, E.; Musa, O.A.; Mohamed, A.M.; Clark, J.; Thalib, L. Physical activity in pregnancy prevents gestational diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 168, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri-Amiri, F.; Sepidarkish, M.; Shirvani, M.A.; Habibipour, P.; Tabari, N.S.M. The effect of exercise on the prevention of gestational diabetes in obese and overweight pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, M.-C.; Ouyang, Y.-Q.; Nie, X.-F.; Huang, Y.; Redding, S.R. Effects of physical exercise during pregnancy on maternal and infant outcomes in overweight and obese pregnant women: A meta-analysis. Birth 2019, 46, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xie, R.; Shen, C.; Shu, L. Effect of exercise during pregnancy to prevent gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2017, 31, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzakis, C.; Goulis, D.G.; Mareti, E.; Eleftheriades, M.; Zavlanos, A.; Dinas, K.; Sotiriadis, A. Prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus in overweight or obese pregnant women: A network meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 158, 107924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro-Malosso, E.R.; Saccone, G.; Di Mascio, D.; Di Tommaso, M.; Berghella, V. Exercise during pregnancy and risk of preterm birth in overweight and obese women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ming, W.-K.; Ding, W.; Zhang, C.J.P.; Zhong, L.; Long, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; et al. The effect of exercise during pregnancy on gestational diabetes mellitus in normal-weight women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, S.G.; Ricardo, L.I.; Evenson, K.R.; Hallal, P.C. Leisure-Time Physical Activity in Pregnancy and Maternal-Child Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanabria-Martinez, G.; Garcia-Hermoso, A.; Poyatos-Leon, R.; Alvarez-Bueno, C.; Sanchez-Lopez, M.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions on preventing gestational diabetes mellitus and excessive maternal weight gain: A meta-analysis. BJOG 2015, 122, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, L.M.; Nobles, C.; Ertel, K.A.; Chasan-Taber, L.; Whitcomb, B.W. Physical Activity Interventions in Pregnancy and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.-N.; Li, X.-L.; Tao, T.-J.; Luo, B.-R.; Liao, S.-J. Physical activity during pregnancy and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Middleton, P.; Crowther, C.A. Exercise for pregnant women for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 7, CD009021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Burrueco, J.R.; Cano-Ibáñez, N.; Martín-Peláez, S.; Khan, K.S.; Amezcua-Prieto, C. Effects on the maternal-fetal health outcomes of various physical activity types in healthy pregnant women. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 262, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Weng, S.; Wang, C.; Yuan, P.; Tang, S. Effect of Mediterranean diet for pregnant women: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieu, J.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Dietary Advice in Pregnancy for Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Tieu, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.Y.; Shu, J.; Fu, X.H.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Ji, M.X.; Liu, X.M.; Yu, T.T.; Sheng, J.Z.; Huang, H.F. Improving the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions for gestational diabetes prevention: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. BJOG 2019, 126, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogozinska, E.; Marlin, N.; Betran, A.P.; Astrup, A.; Bogaerts, A.; Cecatti, J.G.; Devlieger, R.; Dodd, J.M.; El Beltagy, N.; Facchinetti, F.; et al. Effect of diet and physical activity based interventions in pregnancy on gestational weight gain and pregnancy outcomes: Meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. BMJ 2017, 358, j3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogozinska, E.; Marlin, N.; Jackson, L.; Rayanagoudar, G.; Ruifrok, A.E.; Dodds, J.; Molyneaux, E.; Van Poppel, M.N.; Poston, L.; Vinter, C.A.; et al. Effects of antenatal diet and physical activity on maternal and fetal outcomes: Individual patient data meta-analysis and health economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2017, 21, 1–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, C.M.; Grivell, R.M.; Dodd, J.M. Systematic review of antenatal dietary and lifestyle interventions in women with a normal body mass index. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2016, 95, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogozińska, E.; Chamillard, M.; Hitman, G.A.; Khan, K.S.; Thangaratinam, S. Nutritional Manipulation for the Primary Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bain, E.; Crane, M.; Tieu, J.; Han, S.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Diet and Exercise Interventions for Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteng-Ntim, E.; Varma, R.; Croker, H.; Poston, L.; Doyle, P. Lifestyle interventions for overweight and obese pregnant women to improve pregnancy outcome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thangaratinam, S.; Rogozinska, E.; Jolly, K.; Glinkowski, S.; Duda, W.; Borowiack, E.; Roseboom, T.; Tomlinson, J.; Walczak, J.; Kunz, R.; et al. Interventions to reduce or prevent obesity in pregnant women: A systematic review. Health Technol. Assess. 2012, 16, 1–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oostdam, N.; Van Poppel, M.N.; Wouters, M.G.; Van Mechelen, W. Interventions for Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Women’s Health 2011, 20, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overlapping | N | CCA | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activity as only intervention | |||
| Reviews of RCTs with pregnant women in general published since 2015 | 11 | 26.28% | Very high |
| Reviews of RCTs with high-risk women published since 2015 | 6 | 19.26% | Very high |
| Reviews of RCTs with pregnant women in general published before 2015 | 3 | 37.5% | Very high |
| Diet as only intervention | 4 | 25.39% | Very high |
| Mixed intervention | 5 | 36.49% | Very high |
| Systematic Review ID | RCTs Number | Participant Included in Intervention and Control Group (N/n) | Association Measurement | I2 (p) | Quality (Amstar 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oostdam et al., 2011 [59] | 3 | 125/113 | RD −0.05 (−0.20–0.10) | 66 (0.05) | Critically low | |
| Han et al., 2012 [47] | 5 | 437/389 | RR 1.10 (0.66–1.84) | 0 (0.37) | Low | |
| Yin et al., 2014 [46] | 5 | 497/450 | RR 0.91 (0.57–1.44) | 26 (0.25) | Critically low | |
| Russo et al., 2015 [45] | 10 | 569/520 | RR 0.74 (0.57–0.97) | 12 (0.33) | Critically low | |
| Sanabria-Martínez et al., 2015 [44] | 8 | N.A. | RR 0.69 (0.52–0.91) | 0 (0.61) | Critically low | |
| Madhuvrata et al., 2015 * [23] | 3 | 76/76 | OR 0.77 (0.33–1.79) | 0 (0.53) | Moderate | |
| Aune et al., 2016 [19] | 12 | 9804 ** | RR 0.69 (0.50–0.96) | 30.2 (0.15) | Critically low | |
| Song et al., 2016 [20] | 10 | 4161 ** | RR 0.77 (0.54–1.09) | N.A. | Critically low | |
| Da Silva et al., 2017 [43] | 10 | 1883/1907 | RR 0.67 (0.49–0.92) | 33 (0.14) | Critically low | |
| Zheng et al., 2017 [24] | 7 | 550/563 | OR 0.62 (0.43–0.89) | 37 (0.19) | Critically low | |
| Ming et al., 2018 * [42] | 9 | 1472/1509 | RR 0.58 (0.37–0.90) | 46 (0.07) | Low | |
| Davenport et al., 2018 [18] | 27 | 7568/7198 | OR 0.62 (0.52–0.75) | 0 (0.51) | High | |
| Bennett et al., 2018 [22] | 10 | 2981 ** | RR 0.62 (0.50–0.78) | 0 (0.90) | Moderate | |
| Yu et al., 2018 [39] | 6 | 651/719 | RR 0.59 (0.39–0.88) | 46 (0.11) | Critically low | |
| Chatzakis et al., 2019 * [40] | 14 | 575/589 | RR 0.80 (0.60–1.07) | 30 | Low | |
| Du et la., 2019 * [38] | 13 | 550/572 | RR 0.71 (0.57–0.89) | 0 (0.52) | Low | |
| Makaruk et al., 2019 [33] | 10 | 1747/2013 | N.A. | N.A. | Critically low | |
| Nasiri-Amiri et al., 2019 * [37] | 8 | 727/714 | RR 0.76 (0.65–1.08) | 50 (0.05) | Critically low | |
| Guo et al., 2019 [51] | 19 | 5883 ** | RR 0.70 (0.95–0.84) | N.A. | Critically low | |
| Doi et al., 2020 * [36] | 11 | 722/745 | RR 0.69 (0.51–0.94) | 23.2 (0.02) | Low | |
| Systematic Review ID | RCTs Number | Participant Included in Intervention and Control Group (N/n) | Association Measurement | I2 (p) | Quality (Amstar 2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oostdam et al., 2011 [59] | 7 | 449/364 | RD −0.05 (−0.10–−0.01) | 41 (0.12) | Critically low |
| Madhuvrata et al., 2015 * [23] | 3 | 202/207 | OR 0.33 (0.14–0.76) | 26 (0.26) | Moderate |
| Rogozińska et al., 2015 [55] | 6 | 725/754 | RR 0.67 (0.38–1.15) | 52 (0.06) | Moderate |
| Song et al., 2016 [20] | 5 | 1279 ** | RR 0.80 (0.58–1.10) | - | Critically low |
| Tieu et al., 2017 [25] | 11 | 628/652 | RR 0.60 (0.35–1.04) | 56 (0.07) | High |
| Bennett et al., 2018 [22] | 9 | 3388 ** | RR 0.56 (0.36–0.87) | 53 (0.03) | Moderate |
| Lamminpää et al., 2018 [34] | 15 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | Critically low |
| Guo et al., 2019 [51] | 11 | 2838 ** | RR 0.75 (0.59–0.95) | N.A. | Critically low |
| Zhang et al., 2020 *** [49] | 2 | 911/937 | OR 0.66 (0.52–0.82) | 0 (0.85) | Critically low |
| Study ID | RCTs Number | Participant Included in Intervention and Control Group (N/n) | Association Measurement | I2(p) | Quality (Amstar 2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bain et al., 2015 [56] | 13 | 1903/1841 | RR 0.92 (0.68–1.23) | 43.13 (0.06) | Low |
| Madhuvrata et al., 2015 * [23] | 6 | 562/526 | OR 1.44 (0.96–2.14) | 0 (0.93) | Moderate |
| Rogozińska et al., 2015 [55] | 12 | 2399/2346 | RR 0.95 (0.76–1.18) | 23 (0.21) | Moderate |
| Song et al., 2016 [20] | 14 | 6047 ** | RR 0.85 (0.70–1.03) | N.A. | Critically low |
| Shepherd et al., 2017 [31] | 19 | 3353/3280 | RR 0.85 (0.71–1.01) | 42 (0.03) | High |
| Davenport et al., 2018 [18] | 22 | 575/550 | OR 0.90 (0.74–1.10) | 30 (0.09) | High |
| Bennett et al., 2018 [22] | 22 | 7274 ** | RR 0.90 (0.77–1.05) | 33 (0.072) | Moderate |
| Guo et al., 2019 [51] | 18 | 7024 ** | RR 0.86 (0.71–1.04) | N.A. | Critically low |
| Systematic Reviews with GDM as Not the Principal Outcome | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCTs Number | Participant Included in Intervention and Control Group (N/n) | Association Measurement | I2 (p) | Quality (Amstar 2) | |
| Physical activity | |||||
| Magro-Malosso et al., 2017 * [41] | 7 | 623/727 | RR 0.61 (0.41–0.90) | - | Critically low |
| Díaz-Burrueco et al., 2021 [48] | 5 | 782/1091 | OR 0.68 (0.39–1.19) | - | Low |
| Diet | |||||
| Thangaratinam et al., 2012 [58] | 3 | 409 ** | RR 0.39 (0.23–0.69) | 21 (0.001) | Critically Low |
| Mixed intervention | |||||
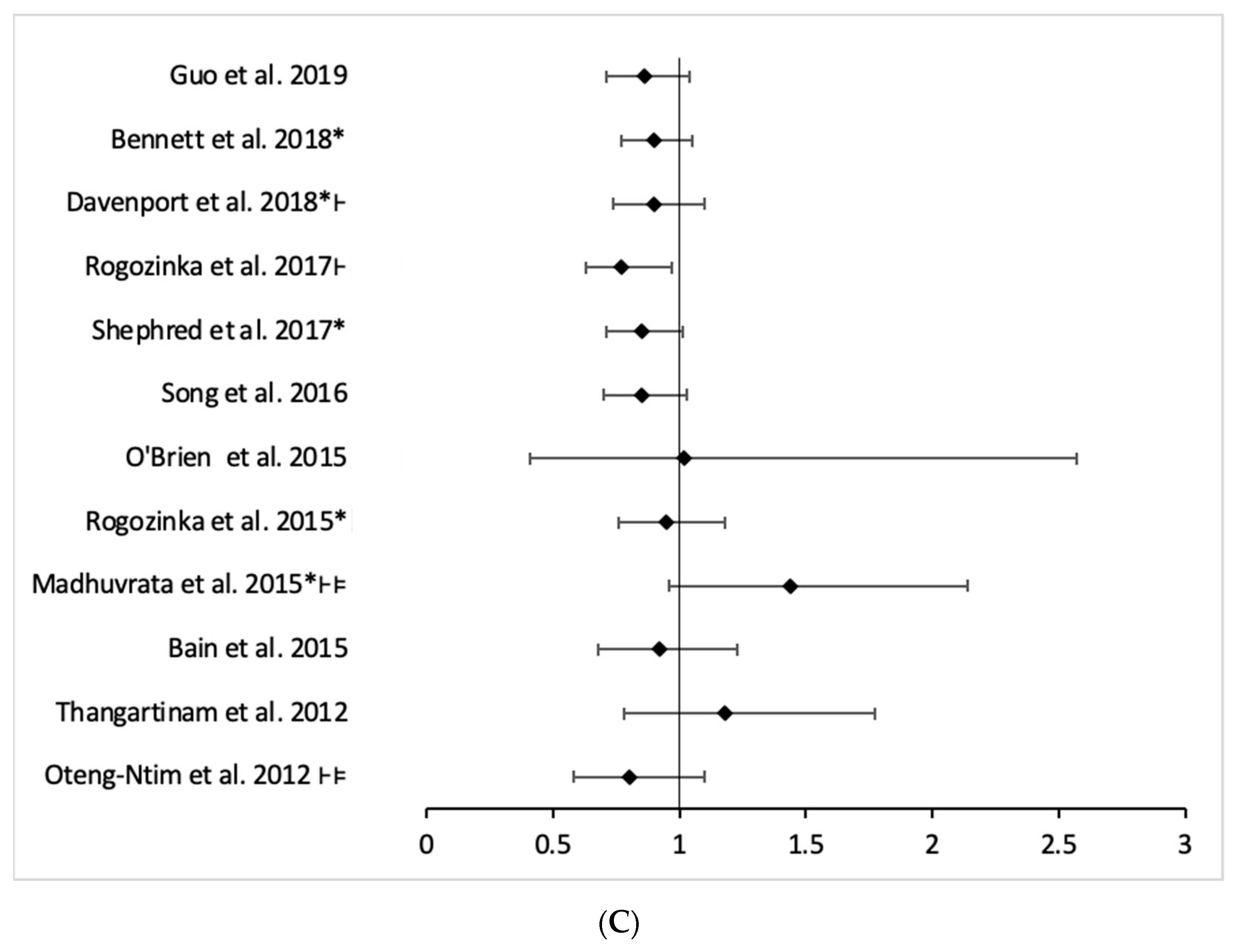
| Rogozinska et al., 2017 [53] | 31 | 5710/5408 | OR 0.77 (0.63–0.94) | 38 (0.02) | Low |
| O’brien et al., 2016 [54] | 2 | 243 ** | RR 1.02 (0.41–2.57) | - | Critically Low |
| Thangaratinam et al., 2012 [58] | 6 | 1233 ** | RR 1.18 (0.78–1.77) | 0 (0.44) | Critically Low |
| Oteng-Ntim Et al., 2012 * [57] | 6 | 526/491 | OR 0.80 (0.58–1.10) | 62 (0.002) | Critically Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kouiti, M.; Hernández-Muñiz, C.; Youlyouz-Marfak, I.; Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Mozas-Moreno, J.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J. Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Healthy Diet and/or Physical Activity during Pregnancy: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102066
Kouiti M, Hernández-Muñiz C, Youlyouz-Marfak I, Salcedo-Bellido I, Mozas-Moreno J, Jiménez-Moleón JJ. Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Healthy Diet and/or Physical Activity during Pregnancy: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients. 2022; 14(10):2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102066
Chicago/Turabian StyleKouiti, Malak, Cristian Hernández-Muñiz, Ibtissam Youlyouz-Marfak, Inmaculada Salcedo-Bellido, Juan Mozas-Moreno, and José Juan Jiménez-Moleón. 2022. "Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Healthy Diet and/or Physical Activity during Pregnancy: An Umbrella Review" Nutrients 14, no. 10: 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102066
APA StyleKouiti, M., Hernández-Muñiz, C., Youlyouz-Marfak, I., Salcedo-Bellido, I., Mozas-Moreno, J., & Jiménez-Moleón, J. J. (2022). Preventing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Healthy Diet and/or Physical Activity during Pregnancy: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients, 14(10), 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102066