Postnatal Choline Supplementation Rescues Deficits in Synaptic Plasticity Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure
Abstract
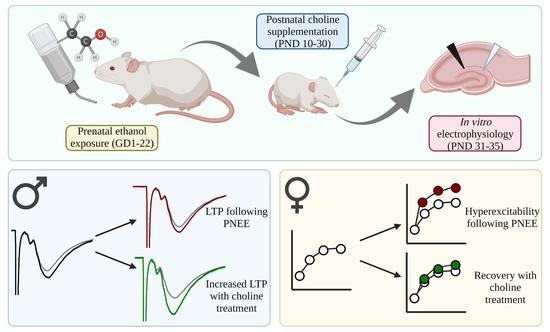
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Breeding
2.2. Prenatal Diet Conditions
2.3. Postnatal Choline Supplementation
2.4. In Vitro Electrophysiology
2.5. Statistics & Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reduced Body Weight following PNEE
3.2. Basal Changes in Excitability Evident in Female PNEE Offspring
3.3. Postnatal Choline Supplementation Ameliorated Deficits in PNEE Male Offspring LTP
3.4. PNEE Increased LTP in Female Offspring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattson, S.N.; Crocker, N.; Nguyen, T.T. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Neuropsychological and Behavioral Features. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2011, 21, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, P.; Chambers, C.D.; Kalberg, W.O.; Zellner, J.; Feldman, H.; Buckley, D.; Kopald, D.; Hasken, J.M.; Xu, R.; Honerkamp-Smith, G.; et al. Prevalence of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders in 4 US Communities. JAMA 2018, 319, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, S.; Lange, S.; Poznyak, V.; Chudley, A.E.; Shield, K.D.; Reynolds, J.N.; Murray, M.; Rehm, J. Population-based prevalence of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder in Canada. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skagerstróm, J.; Chang, G.; Nilsen, P. Predictors of Drinking During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. J. Women’s Health 2011, 20, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denny, C.H.; Acero, C.S.; Naimi, T.S.; Kim, S.Y. Consumption of Alcohol Beverages and Binge Drinking Among Pregnant Women Aged 18–44 Years—United States, 2015–2017. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehme, F.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Cox, A.; Patten, A.; Giles, E.; Brocardo, P.S.; Christie, B.R. Voluntary exercise induces adult hippocampal neurogenesis and BDNF expression in a rodent model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocardo, P.S.; Boehme, F.; Patten, A.; Cox, A.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Christie, B.R. Anxiety- and depression-like behaviors are accompanied by an increase in oxidative stress in a rat model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Protective effects of voluntary physical exercise. Neuropharmacology 2011, 62, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redila, V.A.; Olson, A.K.; Swann, S.E.; Mohades, G.; Webber, A.J.; Weinberg, J.; Christie, B.R. Hippocampal cell proliferation is reduced following prenatal ethanol exposure but can be rescued with voluntary exercise. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, B.R.; Swann, S.E.; Fox, C.J.; Froc, D.; Lieblich, S.E.; Redila, V.; Webber, A. Voluntary exercise rescues deficits in spatial memory and long-term potentiation in prenatal ethanol-exposed male rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, A.R.; Brocardo, P.S.; Christie, B.R. Omega-3 supplementation can restore glutathione levels and prevent oxidative damage caused by prenatal ethanol exposure. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, A.R.; Sickmann, H.M.; Dyer, R.A.; Innis, S.M.; Christie, B.R. Omega-3 fatty acids can reverse the long-term deficits in hippocampal synaptic plasticity caused by prenatal ethanol exposure. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 551, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murawski, N.J.; Moore, E.M.; Thomas, J.D.; Riley, E.P. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: From animal models to human studies. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2015, 37, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline: Critical Role During Fetal Development and Dietary Requirements in Adults. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeisel, S.H.; da Costa, K.-A. Choline: An essential nutrient for public health. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiedeman, A.M.; Barr, S.I.; Green, T.J.; Xu, Z.; Innis, S.M.; Kitts, D.D. Dietary Choline Intake: Current State of Knowledge Across the Life Cycle. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallace, T.C.; Blusztajn, J.K.; Caudill, M.A.; Klatt, K.C.; Natker, E.; Zeisel, S.H.; Zelman, K.M. Choline: The Underconsumed and Underappreciated Essential Nutrient. Nutr. Today 2018, 53, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, E. Could we be overlooking a potential choline crisis in the United Kingdom? BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2019, 2, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caudill, M.A.; Strupp, B.J.; Muscalu, L.; Nevins, J.E.H.; Canfield, R.L. Maternal choline supplementation during the third trimester of pregnancy improves infant information processing speed: A randomized, double-blind, controlled feeding study. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahnfleth, C.; Canfield, R.; Nevins, J.; Caudill, M.; Strupp, B. Prenatal Choline Supplementation Improves Child Color-location Memory Task Performance at 7 Y of Age (FS05-01-19). Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzz048.FS05-01-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caudill, M.A.; Obeid, R.; Derbyshire, E.; Bernhard, W.; Lapid, K.; Walker, S.J.; Zeisel, S.H. Building better babies: Should choline supplementation be recommended for pregnant and lactating mothers? Literature overview and expert panel consensus. Eur. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 2, 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Wurtman, R.J. Developmental changes in rat blood choline concentration. Biochem. J. 1981, 198, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornford, E.M.; Braun, L.D.; Oldendorf, W.H. Developmental Modulations of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability as an Indicator of Changing Nutritional Requirements in the Brain. Pediatr. Res. 1982, 16, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inazu, M. Functional Expression of Choline Transporters in the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; La Fiette, M.H.; Quinn, V.R.; Riley, E.P.; Thomas, J.D.; La Fiette, M.H.; Quinn, V.R.; Riley, E.P. Neonatal choline supplementation ameliorates the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on a discrimination learning task in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2000, 22, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; Idrus, N.M.; Monk, B.; Dominguez, H.D. Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates behavioral alterations associated with prenatal alcohol exposure in rats. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; Abou, E.J.; Dominguez, H.D. Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates the adverse effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on development in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2009, 31, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idrus, N.M.; Breit, K.; Thomas, J.D. Dietary choline levels modify the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 59, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, S.W.; Molteno, C.D.; Meintjes, E.M.; Senekal, M.S.; Lindinger, N.M.; Dodge, N.C.; Zeisel, S.H.; Duggan, C.P.; Jacobson, J.L.; Carter, R. Feasibility and Acceptability of Maternal Choline Supplementation in Heavy Drinking Pregnant Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.W.; Carter, R.C.; Molteno, C.D.; Stanton, M.E.; Herbert, J.S.; Lindinger, N.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Dodge, N.C.; Hoyme, H.E.; Zeisel, S.H.; et al. Efficacy of Maternal Choline Supplementation During Pregnancy in Mitigating Adverse Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Growth and Cognitive Function: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, F.L.; Molteno, C.D.; Warton, C.M.R.; Wintermark, P.; Lindinger, N.M.; Dodge, N.C.; Zöllei, L.; van der Kouwe, A.J.; Carter, R.C.; Jacobson, J.L.; et al. Maternal choline supplementation mitigates alcohol exposure effects on neonatal brain volumes. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekdash, R.A.; Zhang, C.; Sarkar, D.K. Gestational Choline Supplementation Normalized Fetal Alcohol-Induced Alterations in Histone Modifications, DNA Methylation, and Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) Gene Expression in β-Endorphin-Producing POMC Neurons of the Hypothalamus. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akison, L.K.; Kuo, J.; Reid, N.; Boyd, R.N.; Moritz, K. Effect of Choline Supplementation on Neurological, Cognitive, and Behavioral Outcomes in Offspring Arising from Alcohol Exposure During Development: A Quantitative Systematic Review of Clinical and Preclinical Studies. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1591–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, S.H.; Williams, J.K.; Thomas, J.D. Choline supplementation attenuates learning deficits associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in the rat: Effects of varying the timing of choline administration. Brain Res. 2008, 1237, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; Biane, J.S.; O’Bryan, K.A.; O’Neill, T.M.; Dominguez, H.D. Choline supplementation following third-trimester-equivalent alcohol exposure attenuates behavioral alterations in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 121, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Fink, B.A.; Hoecker, H.L.; Boys, C.J.; Radke, J.P.; Kroupina, M.G.; Miller, N.C.; Brearley, A.M.; et al. Choline supplementation in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fink, B.A.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Boys, C.J.; Sandness, K.E.; Radke, J.P.; Miller, N.C.; Lindgren, C.; Brearley, A.M.; et al. Four-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of choline for neurodevelopment in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Risbud, R.D.; Mattson, S.; Chambers, C.D.; Thomas, J.D. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of choline supplementation in school-aged children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, R.F.; Hannigan, J.H. Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the hippocampus: Spatial behavior, electrophysiology, and neuroanatomy. Hippocampus 2000, 10, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, M.P.; Valenzuela, C.F. Repeated third trimester-equivalent ethanol exposure inhibits long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region of neonatal rats. Alcohol 2010, 44, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontaine, C.J.; Patten, A.R.; Sickmann, H.M.; Helfer, J.L.; Christie, B.R. Effects of pre-natal alcohol exposure on hippocampal synaptic plasticity: Sex, age and methodological considerations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.J.; McDonald, R.J.; Savage, D.D. Prenatal exposure to moderate levels of ethanol can have long-lasting effects on hippocampal synaptic plasticity in adult offspring. Hippocampus 1997, 7, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, C.J.; Pinar, C.; Yang, W.; Pang, A.F.; Suesser, K.E.; Choi, J.S.J.; Christie, B.R. Impaired Bidirectional Synaptic Plasticity in Juvenile Offspring Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kervern, M.; de Ferron, B.S.; Alaux-Cantin, S.; Fedorenko, O.; Antol, J.; Naassila, M.; Pierrefiche, O. Aberrant NMDA-dependent LTD after perinatal ethanol exposure in young adult rat hippocampus. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartzwelder, H.; Farr, K.; Wilson, W.; Savage, D. Prenatal exposure to ethanol decreases physiological plasticity in the hippocampus of the adult rat. Alcohol 1988, 5, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M.L.; Diaz, M.; Iuso, A.; Everett, J.C.; Valenzuela, C.F.; Caldwell, K.K. Moderate Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Reduces Plasticity and Alters NMDA Receptor Subunit Composition in the Dentate Gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sickmann, H.; Patten, A.; Morch, K.; Sawchuk, S.; Zhang, C.; Parton, R.; Szlavik, L.; Christie, B. Prenatal ethanol exposure has sex-specific effects on hippocampal long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 2013, 24, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Zhang, T. Spatial cognition and sexually dimorphic synaptic plasticity balance impairment in rats with chronic prenatal ethanol exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 256, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterness, A.K.; Christie, B.R. Prenatal ethanol exposure enhances NMDAR-dependent long-term potentiation in the adolescent female dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 2010, 22, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, A.R.; Sawchuk, S.; Wortman, R.C.; Brocardo, P.S.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Christie, B.R. Prenatal ethanol exposure impairs temporal ordering behaviours in young adult rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 299, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, B. Evidence for two physiologically distinct perforant pathways to the fascia dentata. Brain Res. 1980, 199, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.; Moradpour, F.; Eadie, B.; Shin, J.; Kannangara, T.; Delaney, K.; Christie, B. Electrophysiological identification of medial and lateral perforant path inputs to the dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 2013, 252, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, A.R.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Wortman, R.C.; Noonan, A.; Brocardo, P.S.; Christie, B.R. Effects of ethanol exposure during distinct periods of brain development on hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 1076–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meck, W.H.; Williams, C.L.; Cermak, J.M.; Blusztajn, J.K. Developmental periods of choline sensitivity provide an ontogenetic mechanism for regulating memory capacity and age-related dementia. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2008, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, G.; Jablonski, S.; Schiffino, F.; Cyr, S.S.; Stanton, M.; Klintsova, A. Exercise and environment as an intervention for neonatal alcohol effects on hippocampal adult neurogenesis and learning. Neuroscience 2014, 265, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berman, R.F.; Hannigan, J.H.; ASperry, M.; Zajac, C.S. Prenatal alcohol exposure and the effects of environmental enrichment on hippocampal dendritic spine density. Alcohol 1996, 13, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, J.H.; O’Leary-Moore, S.K.; Berman, R.F. Postnatal environmental or experiential amelioration of neurobehavioral effects of perinatal alcohol exposure in rats. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille-Bille, A.; Bellia, F.; García, A.M.J.; Miranda-Morales, R.S.; D’Addario, C.; Pautassi, R.M. Early exposure to environmental enrichment modulates the effects of prenatal ethanol exposure upon opioid gene expression and adolescent ethanol intake. Neuropharmacology 2019, 165, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaie, C.I.; Hausknecht, K.A.; Wang, R.; Dezfuli, P.H.; Haj-Dahmane, S.; Kane, C.J.M.; Sigurdson, W.J.; Shen, R. Prenatal Ethanol Exposure and Postnatal Environmental Intervention Alter Dopaminergic Neuron and Microglia Morphology in the Ventral Tegmental Area During Adulthood. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 44, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschen, K.E.; McKeown, S.E.; Roth, T.L.; Klintsova, A. Impact of exercise and a complex environment on hippocampal dendritic morphology, B dnf gene expression, and DNA methylation in male rat pups neonatally exposed to alcohol. Dev. Neurobiol. 2016, 77, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y. A review of interventions against fetal alcohol spectrum disorder targeting oxidative stress. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 71, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrus, N.M.; Thomas, J.D. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Experimental Treatments and Strategies for Intervention. Alcohol Res. Health 2011, 34, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ernst, A.M.; Gimbel, B.A.; de Water, E.; Eckerle, J.K.; Radke, J.P.; Georgieff, M.K.; Wozniak, J.R. Prenatal and Postnatal Choline Supplementation in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2022, 14, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, A.A.; Lauterborn, J.C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, W.; Cox, C.D.; Gall, C.M.; Lynch, G. Prepubescent female rodents have enhanced hippocampal LTP and learning relative to males, reversing in adulthood as inhibition increases. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H. What Choline Metabolism Can Tell Us About the Underlying Mechanisms of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portales-Casamar, E.; Lussier, A.A.; Jones, M.J.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Edgar, R.D.; Mah, S.M.; Barhdadi, A.; Provost, S.; Lemieux-Perreault, L.-P.; Cynader, M.S.; et al. DNA methylation signature of human fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Epigenetics Chromatin 2016, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lussier, A.A.; Morin, A.M.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Salmon, J.; Weinberg, J.; Reynolds, J.N.; Pavlidis, P.; Chudley, A.E.; Kobor, M.S. DNA methylation as a predictor of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobben, J.M.; Krzyzewska, I.M.; Venema, A.; Mul, A.N.; Polstra, A.; Postma, A.V.; Smigiel, R.; Pesz, K.; Niklinski, J.; AChomczyk, M.; et al. DNA methylation abundantly associates with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and its subphenotypes. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garro, A.J.; McBeth, D.L.; Lima, V.; Lieber, C.S. Ethanol Consumption Inhibits Fetal DNA Methylation in Mice: Implications for the Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1991, 15, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, C.; Halder, D.; Jung, K.H.; Chai, Y.G. Gestational Alcohol Exposure Altered DNA Methylation Status in the Developing Fetus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otero, N.K.H.; Thomas, J.D.; Saski, C.A.; Xia, X.; Kelly, S.J. Choline Supplementation and DNA Methylation in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex of Rats Exposed to Alcohol During Development. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balaraman, S.; Idrus, N.M.; Miranda, R.; Thomas, J.D. Postnatal choline supplementation selectively attenuates hippocampal microRNA alterations associated with developmental alcohol exposure. Alcohol 2017, 60, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monk, B.R.; Leslie, F.M.; Thomas, J.D. The effects of perinatal choline supplementation on hippocampal cholinergic development in rats exposed to alcohol during the brain growth spurt. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smiley, J.F.; Bleiwas, C.; Canals-Baker, S.; Williams, S.Z.; Sears, R.; Teixeira, C.M.; Wilson, D.A.; Saito, M. Neonatal ethanol causes profound reduction of cholinergic cell number in the basal forebrain of adult animals. Alcohol 2021, 97, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruivo, L.M.T.-G.; Mellor, J.R. Cholinergic modulation of hippocampal network function. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2013, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carito, V.; Ceccanti, M.; Ferraguti, G.; Coccurello, R.; Ciafrè, S.; Tirassa, P.; Fiore, M. NGF and BDNF Alterations by Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knipper, M.; da Penha Berzaghi, M.; Blöchl, A.; Breer, H.; Thoenen, H.; Lindholm, D. Positive Feedback between Acetylcholine and the Neurotrophins Nerve Growth Factor and Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Rat Hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.D.; Thomas, J.D. Adolescent Choline Supplementation Attenuates Working Memory Deficits in Rats Exposed to Alcohol During the Third Trimester Equivalent. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pyapali, G.K.; Turner, D.A.; Williams, C.L.; Meck, W.H.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Prenatal dietary choline supplementation decreases the threshold for induction of long-term potentiation in young adult rats. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Pup Sex Ratio (Male/Female) | Total Number of Pups | Gestation Length (Days) | Dam Weight (% Change) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (litters = 10) | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 11.0 ± 0.5 | 21.5 ± 0.2 | 156.6 ± 7.9% |
| PNEE (litters = 13) | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 9.3 ± 0.7 | 22.0 ± 0.1% | 137.4 ± 4.7% |
| Males | Females | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slice (n), Animal (a), Litter (l) | PTP | LTP | Slice (n), Animal (a), Litter (l) | PTP | LTP | |
| Control + Saline | n = 14, a = 6, l = 6 | 110.6 ± 12.3% | 63 ± 11.5% | n = 11, a = 6, l = 5 | 114.9 ± 15.0% | 48.3 ± 7.4% |
| Control + Choline | n = 10, a = 4, l = 3 | 119.6 ± 9.6% | 52.7 ± 11.7% | n = 14, a = 5, l = 3 | 93.6 ± 6.3% | 45.9 ± 5.8% |
| PNEE + Saline | n = 13, a = 6, l = 5 | 79.3 ± 9.4% | 36.0 ± 5.4% | n = 12, a = 4, l = 4 | 97.8 ± 12.6% | 53.0 ± 4.8% |
| PNEE + Choline | n = 13, a = 5, l = 5 | 106.5 ± 9.5% | 76.0 ± 10.1% | n = 13, a = 4, l = 4 | 107.1 ± 8.8% | 69.5 ± 10.9% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grafe, E.L.; Wade, M.M.M.; Hodson, C.E.; Thomas, J.D.; Christie, B.R. Postnatal Choline Supplementation Rescues Deficits in Synaptic Plasticity Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102004
Grafe EL, Wade MMM, Hodson CE, Thomas JD, Christie BR. Postnatal Choline Supplementation Rescues Deficits in Synaptic Plasticity Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure. Nutrients. 2022; 14(10):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102004
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrafe, Erin L., Mira M. M. Wade, Claire E. Hodson, Jennifer D. Thomas, and Brian R. Christie. 2022. "Postnatal Choline Supplementation Rescues Deficits in Synaptic Plasticity Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure" Nutrients 14, no. 10: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102004
APA StyleGrafe, E. L., Wade, M. M. M., Hodson, C. E., Thomas, J. D., & Christie, B. R. (2022). Postnatal Choline Supplementation Rescues Deficits in Synaptic Plasticity Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure. Nutrients, 14(10), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102004