An Avocado Extract Enriched in Mannoheptulose Prevents the Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Avocado Extract
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Body Composition and Food Intake
2.4. Metabolism
2.5. Insulin Sensitivity
2.6. Blood Lipids
2.7. Oxidative Stress
2.8. Western Blot for mTOR Signaling and ELISA for Leptin and Adiponectin
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
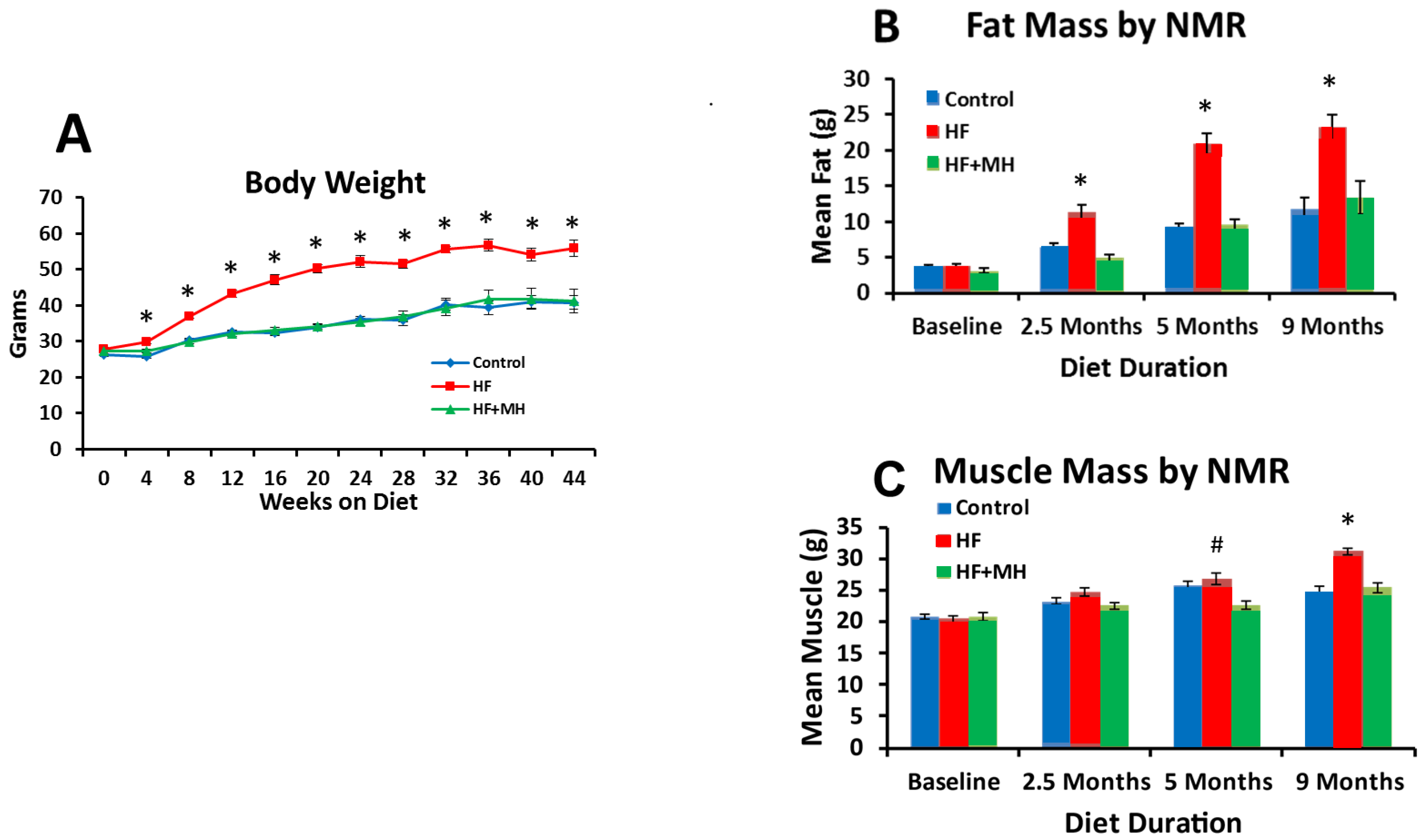
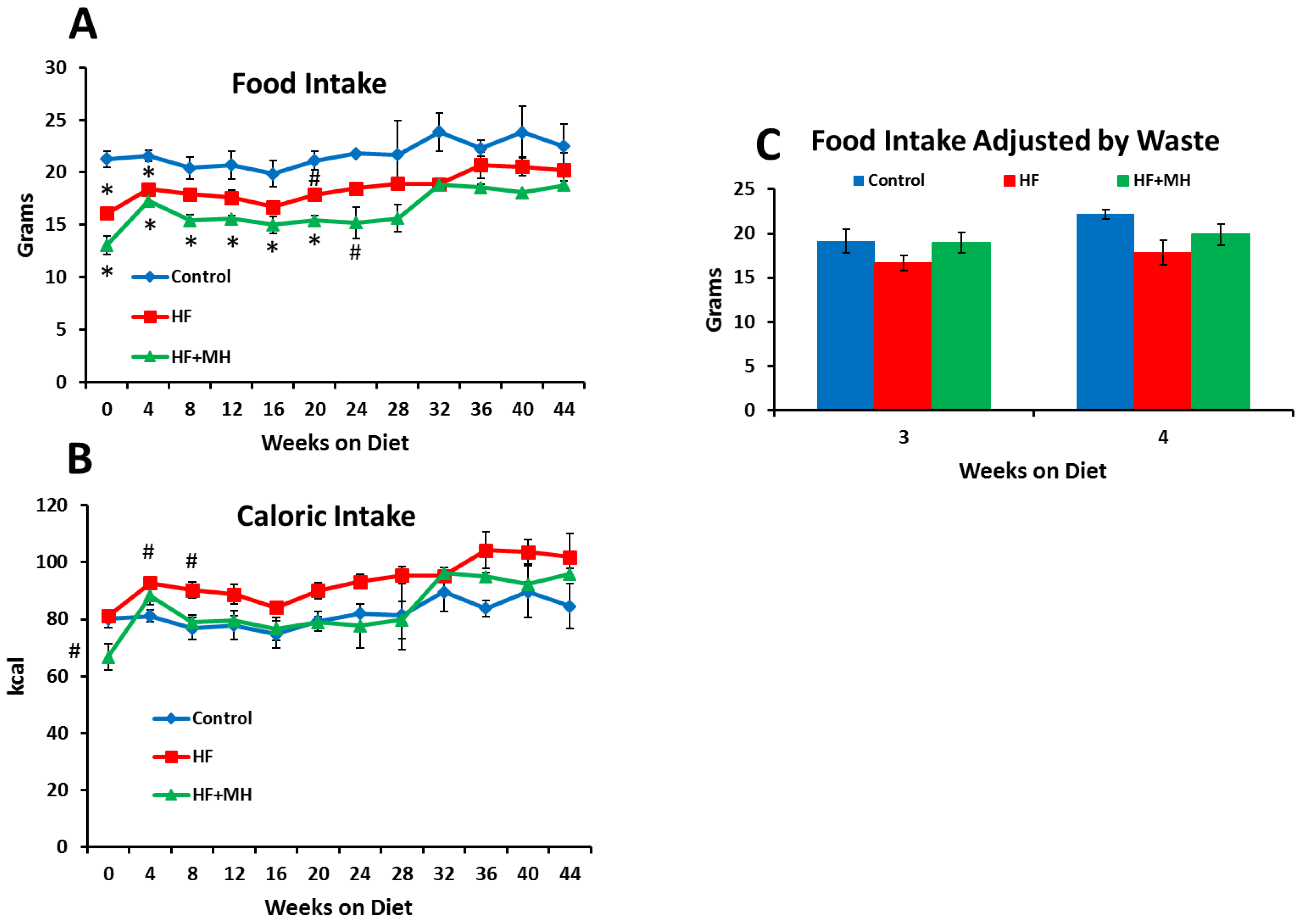
3.1. Body Composition and Food Intake
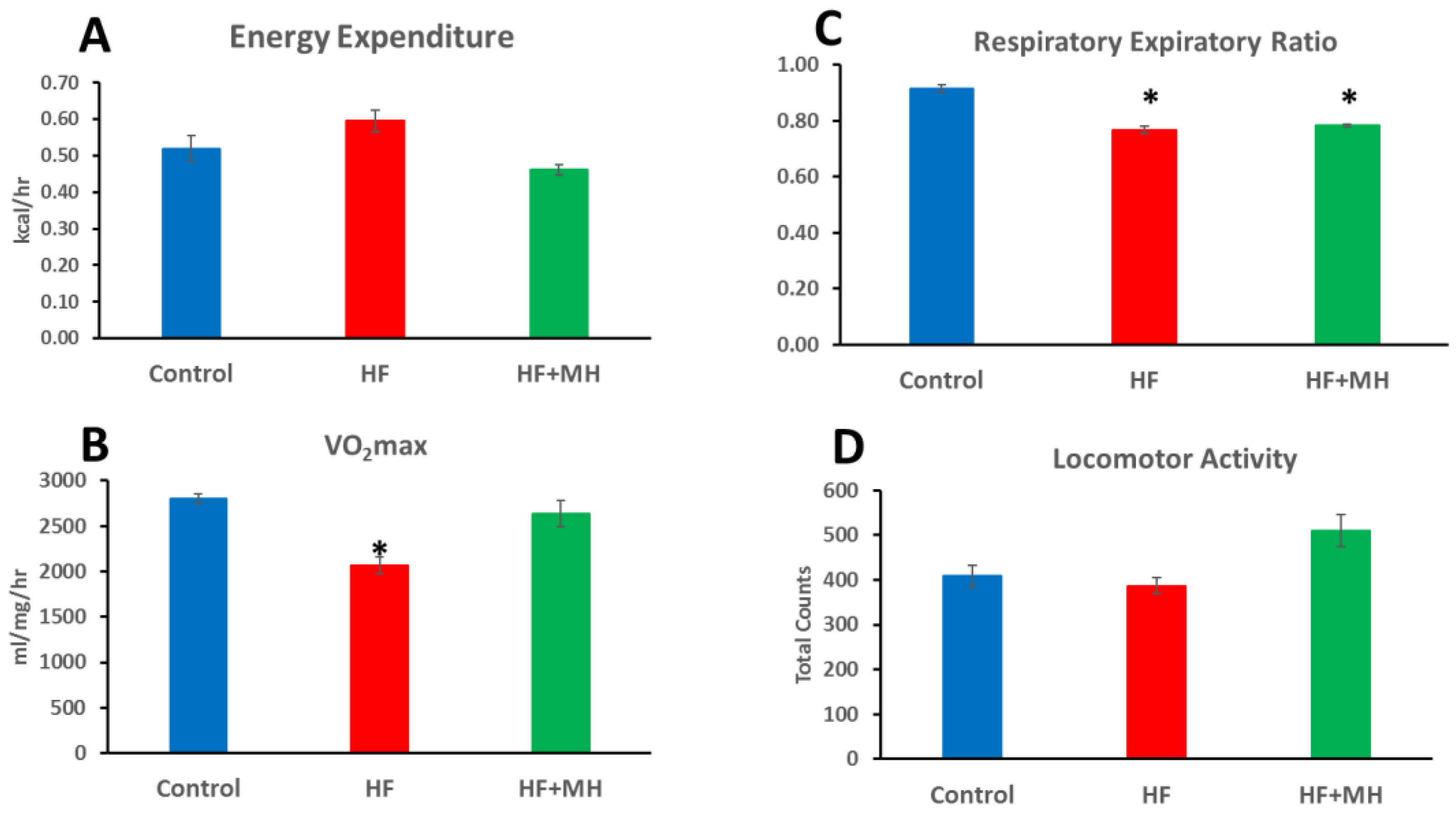
3.2. Metabolism
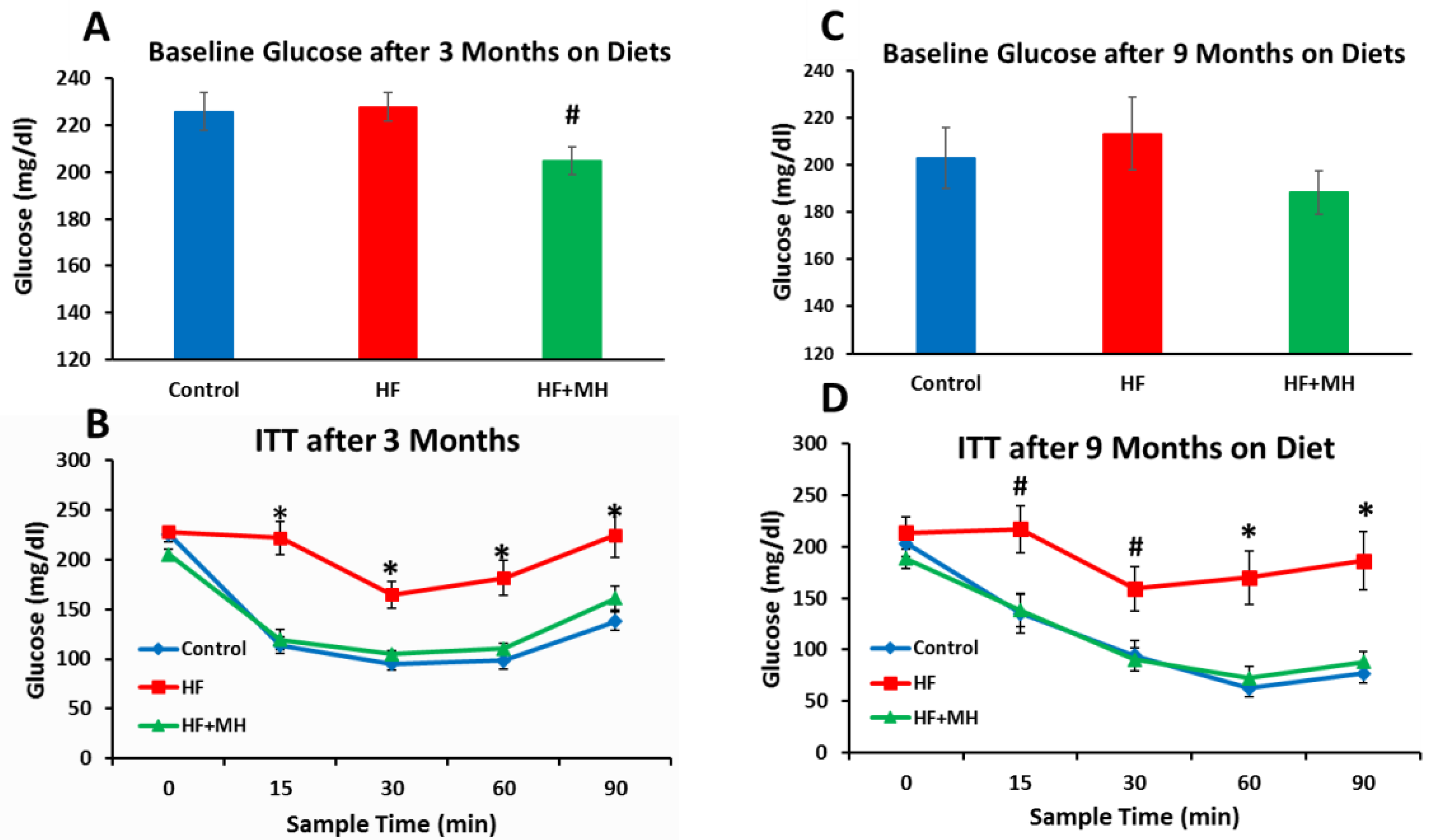
3.3. Glucose Levels and Insulin Sensitivity
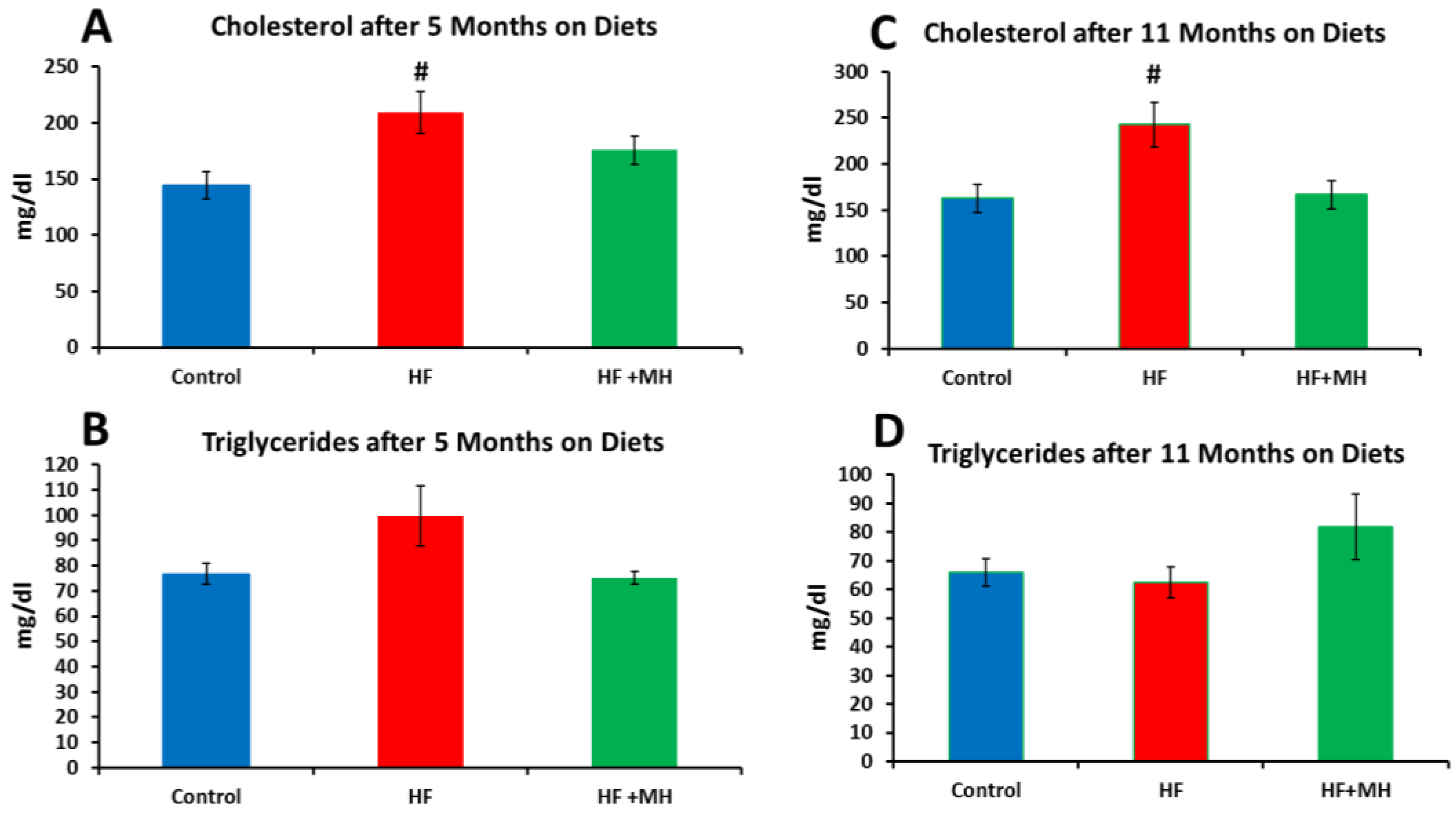
3.4. Blood Lipids
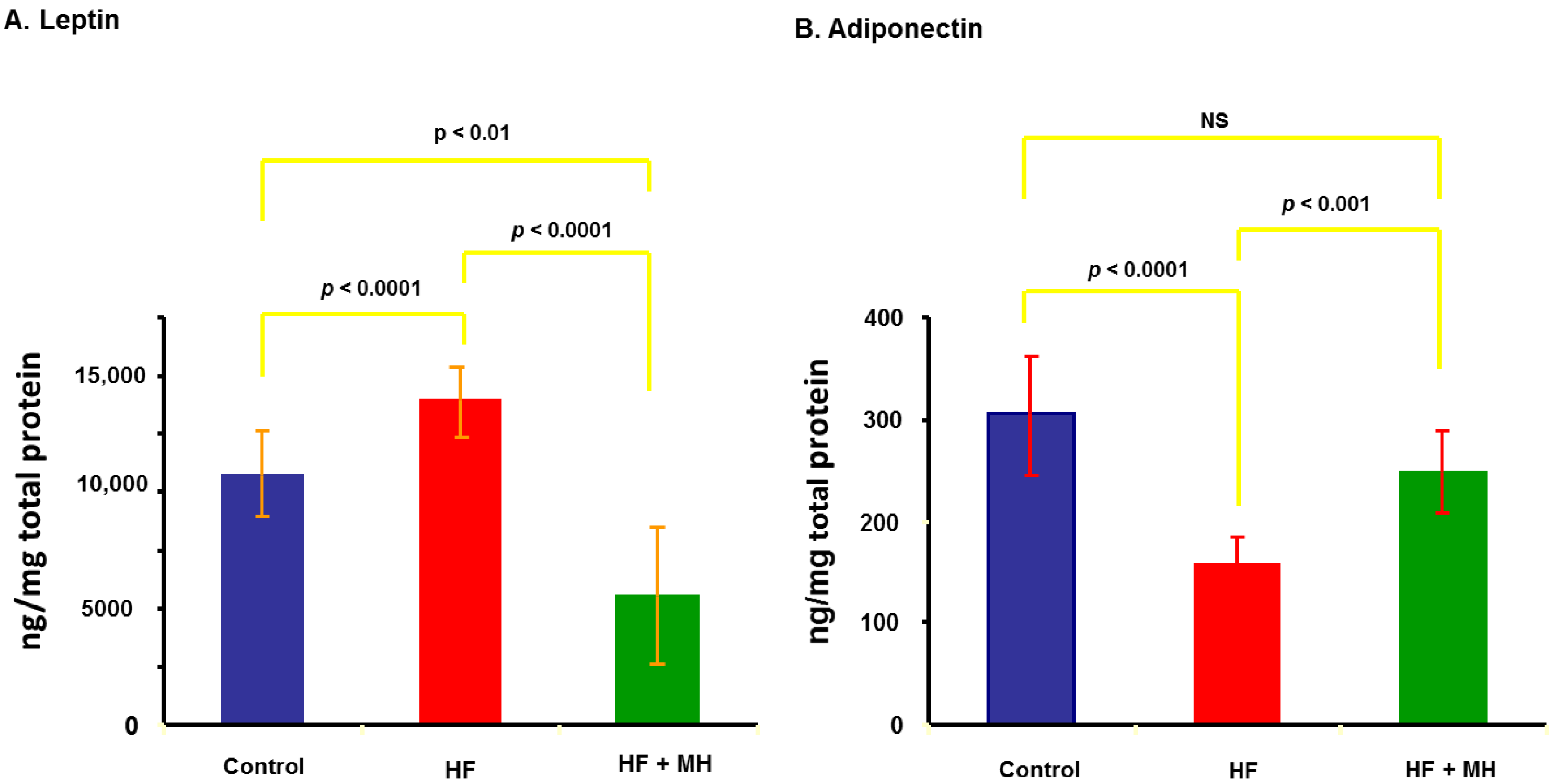
3.5. Leptin and Adiponectin
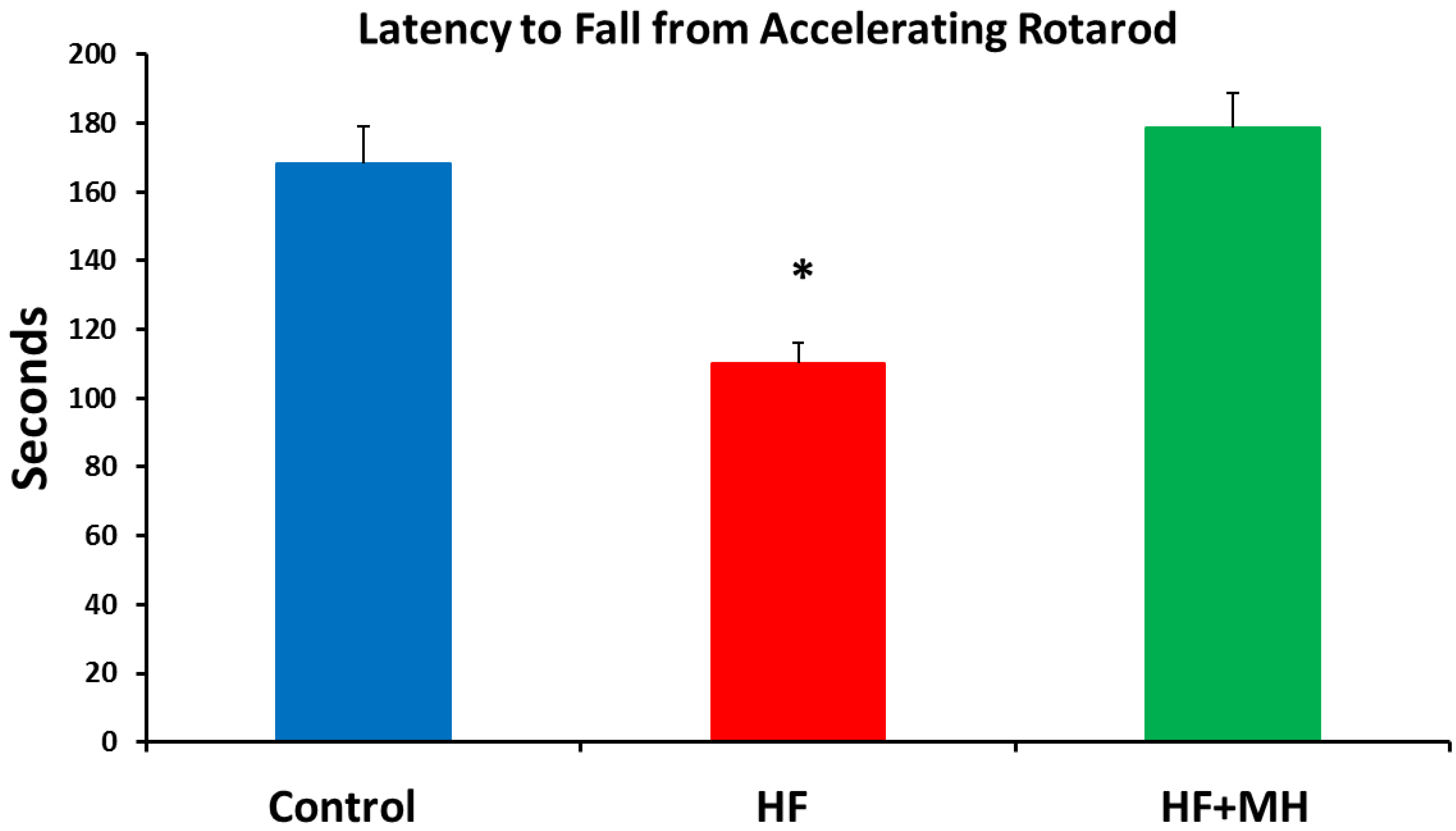
3.6. Rotarod
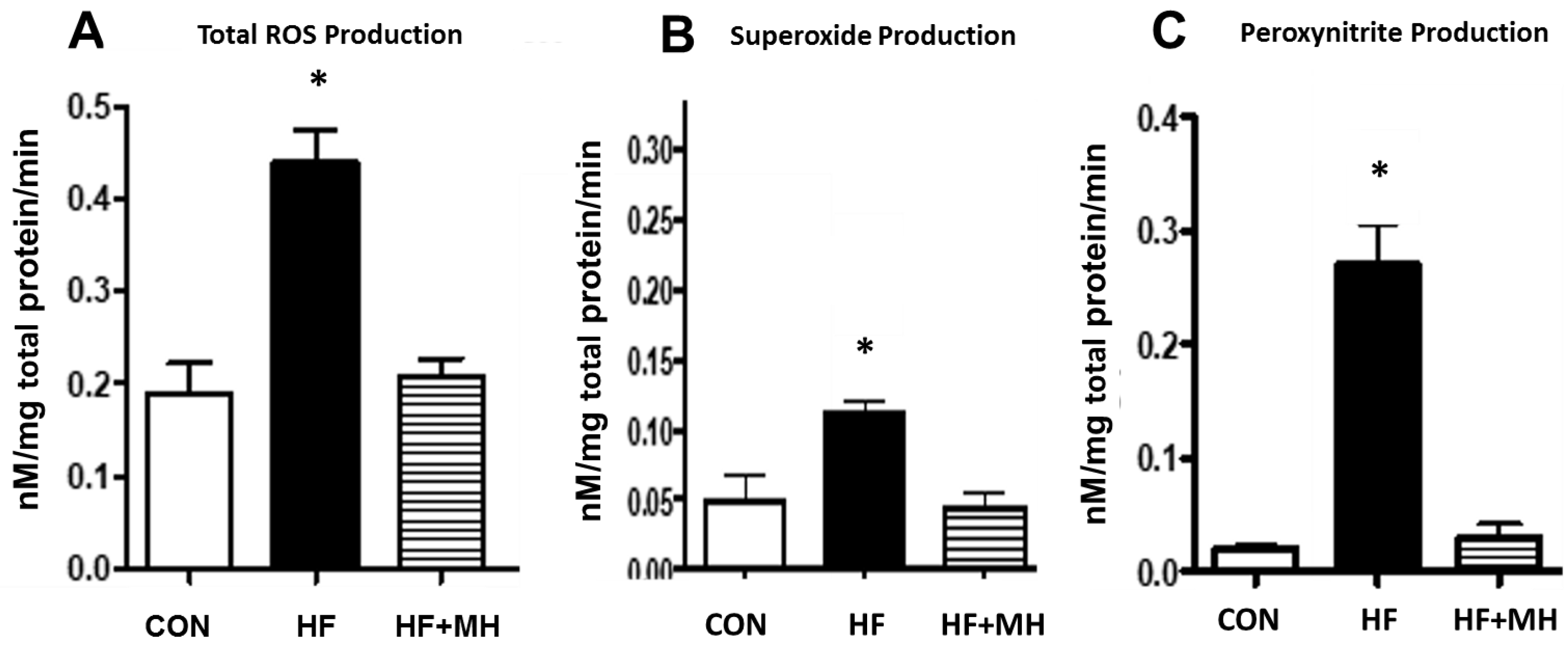
3.7. Oxidative Stress
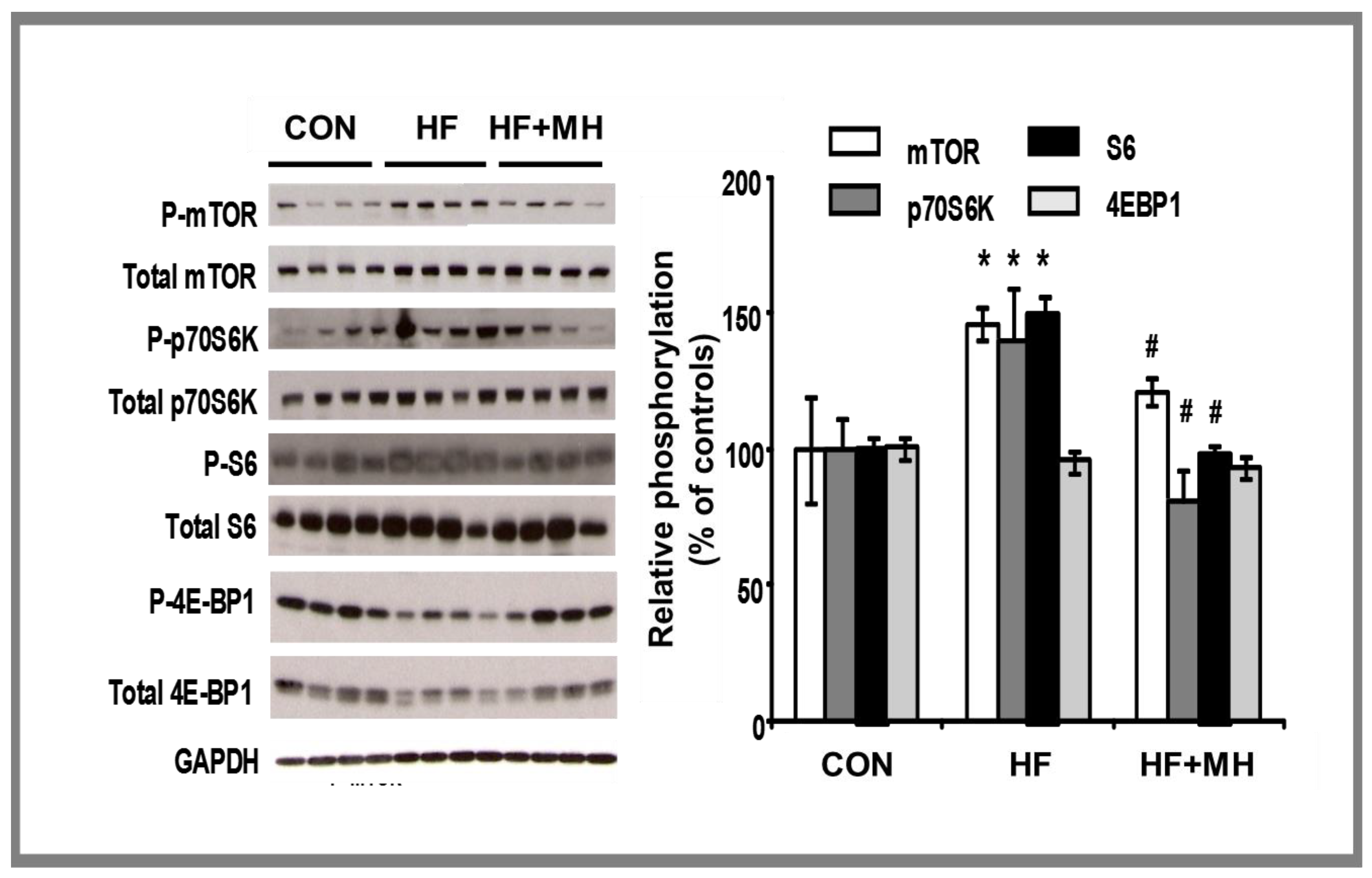
3.8. mTOR Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018; NCHS Data Brief, No 360; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020.
- Gadde, K.M.; Martin, C.K.; Berthoud, H.R.; Heymsfield, S.B. Obesity: Pathophysiology and management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.W.; Kim, S. Comprehensive review of current and upcoming anti-obesity drugs. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. An overview of dietary supplements on obesity and type 2 diabetes: Efficacy and mechanisms. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Risi, R.; Masi, D.; Caputi, A.; Balena, A.; Rossini, G.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Manfrini, S.; et al. Current evidence to propose different food supplements for weight loss: A comprehensive review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, D.K.; Pistell, P.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, Y.; Massimino, S.; Davenport, G.M.; Hayek, M.; Roth, G.S. Characterization and mechanisms of action of avocado extract enriched in mannoheptulose as a candidate calorie restriction mimetic. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7367–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, D.J.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Perera, S.; Low, M.; Basu, A.; Devi, O.A.; Barooah, M.S.; Guang, C.; Papoutsis, K. The odyssey of bioactive compounds in avocado (Persea americana) and their health benefits. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viktora, J.K.; Johnson, B.F.; Penhos, J.C.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Wolff, F.W. Effect of ingested mannoheptulose in animals and man. Metabolism 1969, 18, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev-Ran, A.; Laor, J.; Vins, M.; Simon, E. Effect of intravenous infusion of D-mannoheptulose on blood glucose and insulin levels in man. J. Endocrin. 1970, 47, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.S.; Lane, M.A.; Ingram, D.K. Caloric restriction mimetics: The next phase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1057, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, D.K.; Zhu, M.; Mamczarz, J.; Zou, S.; Lane, M.A.; Roth, G.S.; de Cabo, R. Calorie restriction mimetics: An emerging research field. Aging Cell 2006, 5, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, D.K.; Roth, G.S. Glycolytic inhibition as a strategy for developing calorie restriction mimetics. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, D.K.; Roth, G.S. Calorie restriction mimetics: Can you have your cake and eat it, too? Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 20C, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, D.K.; Roth, G.S. Glycolytic inhibition: An effective strategy for developing calorie restriction mimetics. Geroscience 2021, 43, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasschaert, J.; Kadiata, M.M.; Malaisse, W.J. Effects of D-mannoheptulose upon D-glucose metabolism in tumoral pancreatic islet cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2001, 226, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Escalante, M.L.; Coop-Gamas, F.; Cervantes-Rodríguez, M.; Méndez-Iturbide, D.; Aranda-González, I.I. The effect of diet on oxidative stress and metabolic diseases-Clinically controlled trials. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobore, T.O. Towards a comprehensive theory of obesity and a healthy diet: The causal role of oxidative stress in food addiction and obesity. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 384, 112560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledda, A.; Annunziata, G.; Tenore, G.C.; Palmas, V.; Manzin, A.; Velluzzi, F. Diet-derived antioxidants and their role in inflammation, obesity and gut microbiota modulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovski, G.; Das, D.K. Does autophagy take a front seat in lifespan extension? J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2543–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichhart, T. mTOR as regulator of lifespan, aging, and cellular senescence: A mini-review. Gerontology 2018, 64, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfay, S.Z.; Bertling, I.; Bower, J.P. D-mannoheptulose and perseitol in ‘Hass’ avocado: Metabolism in seed and mesocarp tissue. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 79, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Board, M.; Colquhoun, A.; Newsholme, E.A. High Km glucose-phosphorylating (glucokinase) activities in a range of tumor cell lines and inhibition of rates of tumor growth by the specific enzyme inhibitor mannoheptulose. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, N.; Soorapan, R.; Haque, M.; Sriramula, S.; Francis, J. TNF-alpha induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and cardiac dysfunction: Restoration by superoxide dismutase mimetic tempol. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H2726–H2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ebenezer, P.J.; Dasuri, K.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; Francis, J.; Mariappan, N.; Gao, Z.; Ye, J.; Bruce-Keller, A.; Keller, J.N. Aging is associated with hypoxia and oxidative stress in adipose tissue: Implications for adipose function. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E5990607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryyti, R.; Hämäläinen, M.; Peltola, R.; Moilanen, E. Beneficial effects of lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.) supplementation on metabolic and inflammatory adverse effects induced by high-fat diet in a mouse model of obesity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, O.; Kim, H.S. Dietary chokeberry and dried jujube fruit attenuates high-fat and high-fructose diet-induced dyslipidemia and insulin resistance via activation of the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway in C57BL/6 J mice. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, N.A.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, I.G.; Roh, G.S.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, G.J.; et al. Anti-diabetic effects of ethanol extract from bitter melon in mice fed a high-fat diet. Dev. Reprod. 2017, 21, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, A.G.; Ribot, J.; Priego, T.; Vazquez, I.; Frank, S.; Palou, A.; Buchwald-Werner, S. Consumption of a mango fruit powder protects mice from high-fat induced insulin resistance and hepatic fat accumulation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ding, Z.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P.; Mu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, L. Jamun (Eugenia jambolana Lam.) Fruit extract prevents obesity by modulating the gut microbiome in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1801307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Li, M.; Ding, X.; Fan, S.; Guo, L.; Gu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, L.; Jiang, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of Fortunella margarita fruit extract on metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Edirisinghe, I.; Burton-Freeman, B. Avocado fruit on postprandial markers of cardio-metabolic risk: A randomized controlled dose response trial in overweight and obese men and women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Bordi, P.L.; Fleming, J.A.; Hill, A.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Effect of a moderate fat diet with and without avocados on lipoprotein particle number, size and subclasses in overweight and obese adults: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tao, L.; Hao, L.; Stanley, T.H.; Huang, K.H.; Lambert, J.D.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. A moderate-fat diet with one avocado per day increases plasma antioxidants and decreases the oxidation of small, dense LDL in adults with overweight and obesity: A randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.G.; Walk, A.M.; Thompson, S.V.; Reeserc, G.E.; Erdman, J.W., Jr.; Burda, N.A.; Holscher, H.D.; Khana, N.A. Effects of 12-week avocado consumption on cognitive function among adults with overweight and obesity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2020, 148, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Tcheng, M.; Roma, A.; Buraczynski, M.; Jayanth, P.; Rea, K.; Akhtar, T.A.; Spagnuolo, P.A. Avocatin B protects against lipotoxicity and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, M.A.; Ingram, D.K.; Roth, G.S. 2-deoxy-D-glucose feeding in rats mimics physiological effects of calorie restriction. J. Anti-Aging Med. 1998, 1, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.E.; Strong, R.; Allison, D.B.; Ames, B.N.; Astle, C.M.; Atamna, H.; Fernandez, E.; Flurkey, K.; Javors, M.A.; Nadon, N.L.; et al. Acarbose, 17--estradiol, and nordihydroguaiaretic acid extend mouse lifespan preferentially in males. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, R.A.; Gibbs, V.K.; Smith, D.L., Jr. Targeting glucose metabolism for healthy aging. Nutr. Healthy Aging 2016, 4, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.E.; Strong, R.; Alavez, S.; Astle, C.M.; DiGiovanni, J.; Fernandez, E.; Flurkey, K.; Garratt, M.; Gelfond, J.A.L.; Javors, M.A.; et al. Acarbose improves health and lifespan in aging HET3 mice. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, S.; Priebs, J.; Kuhlow, D.; Growth, M.; Priebe, S.; Mansfeld, J.; Merry, T.L.; Dubuis, S.; Laube, B.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; et al. D-Glucosamine supplementation extends life span of nematodes and of ageing mice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zheng, J.; Ren, L.; Jiao, S.; Feng, C.; Du, Y.; Liu, H. Glucosamine ameliorates symptoms of high-fat diet-fed mice by reversing imbalanced gut microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 694107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.S.; Ji-Won Park, J.-W.; Nam, M.-S.; Hyeongjin Cho, H.; Han, I.-O. Glucosamine enhances body weight gain and reduces insulin response in mice fed chow diet but mitigates obesity, insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance in mice high-fat diet. Metabolism 2014, 64, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooding, M.A.; Davenport, G.; Atkinson, J.L.; Duncan, I.J.H.; Shoveller, A.K. Dietary avocado-derived mannoheptulose results in increased energy expenditure after a 28-day feeding trial in cats. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2014, 12, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- McKnight, L.L.; Flickinger, E.A.; France, J.; Davenport, G.M.; Shoveller, A.K. Mannoheptulose has differential effects on fasting and postprandial energy expenditure and respiratory quotient in adult Beagle dogs fed diets of different macronutrient contents. J. Nutr. Sci. 2014, 3, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, L.L.; Eyre, R.; Gooding, M.A.; Davenport, G.M.; Shoveller, A.K. Dietary mannoheptulose increases fasting serum glucagon like peptide-1 and post-prandial serum ghrelin concentrations in adult Beagle dogs. Animals 2015, 5, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, L.L.; Flickinger, E.A.; Davenport, G.M.; France, J.; Shoveller, A.K. Dietary mannoheptulose has differential effects on fasting and post-prandial glucose oxidation in Labrador Retrievers. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2014, 43, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, L.L.; Root-McCaig, J.; Wright, D.; Davenport, G.M.; France, J.; Shoveller, A.K. Dietary mannoheptulose does not significantly alter daily energy expenditure in adult Labrador Retrievers. PLoS ONE 2016, 10, e143324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Macronutrient | % (w/w) |
|---|---|
| Protein | 3.3 |
| Moisture | 4.4 |
| Ash | 10.2 |
| Fat | 10.7 |
| Sugars | |
| Mannoheptulose | 13.7 |
| Perseitol | 8.1 |
| Glucose | 0.5 |
| Fructose | 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pistell, P.J.; Utsuki, T.; Francis, J.; Ebenezer, P.J.; Terrebonne, J.; Roth, G.S.; Ingram, D.K. An Avocado Extract Enriched in Mannoheptulose Prevents the Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010155
Pistell PJ, Utsuki T, Francis J, Ebenezer PJ, Terrebonne J, Roth GS, Ingram DK. An Avocado Extract Enriched in Mannoheptulose Prevents the Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010155
Chicago/Turabian StylePistell, Paul J., Tadanobu Utsuki, Joseph Francis, Philip J. Ebenezer, Jennifer Terrebonne, George S. Roth, and Donald K. Ingram. 2022. "An Avocado Extract Enriched in Mannoheptulose Prevents the Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet in Mice" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010155
APA StylePistell, P. J., Utsuki, T., Francis, J., Ebenezer, P. J., Terrebonne, J., Roth, G. S., & Ingram, D. K. (2022). An Avocado Extract Enriched in Mannoheptulose Prevents the Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients, 14(1), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010155





