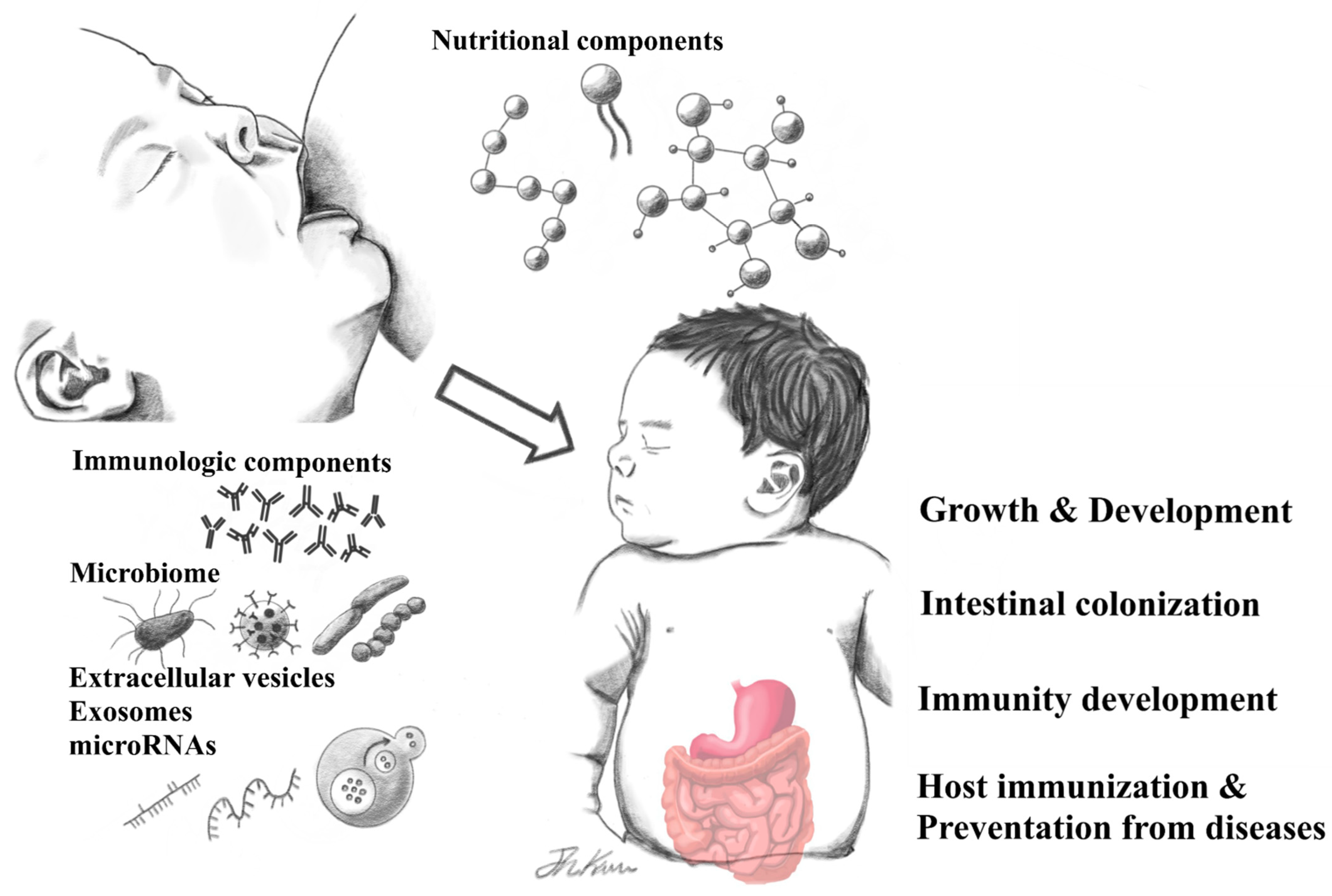
Human Breast Milk Composition and Function in Human Health: From Nutritional Components to Microbiome and MicroRNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nutritional Components of HBM and Associated Human Health Benefits
3. Immunologic Components of HBM and Associated Human Health Benefits
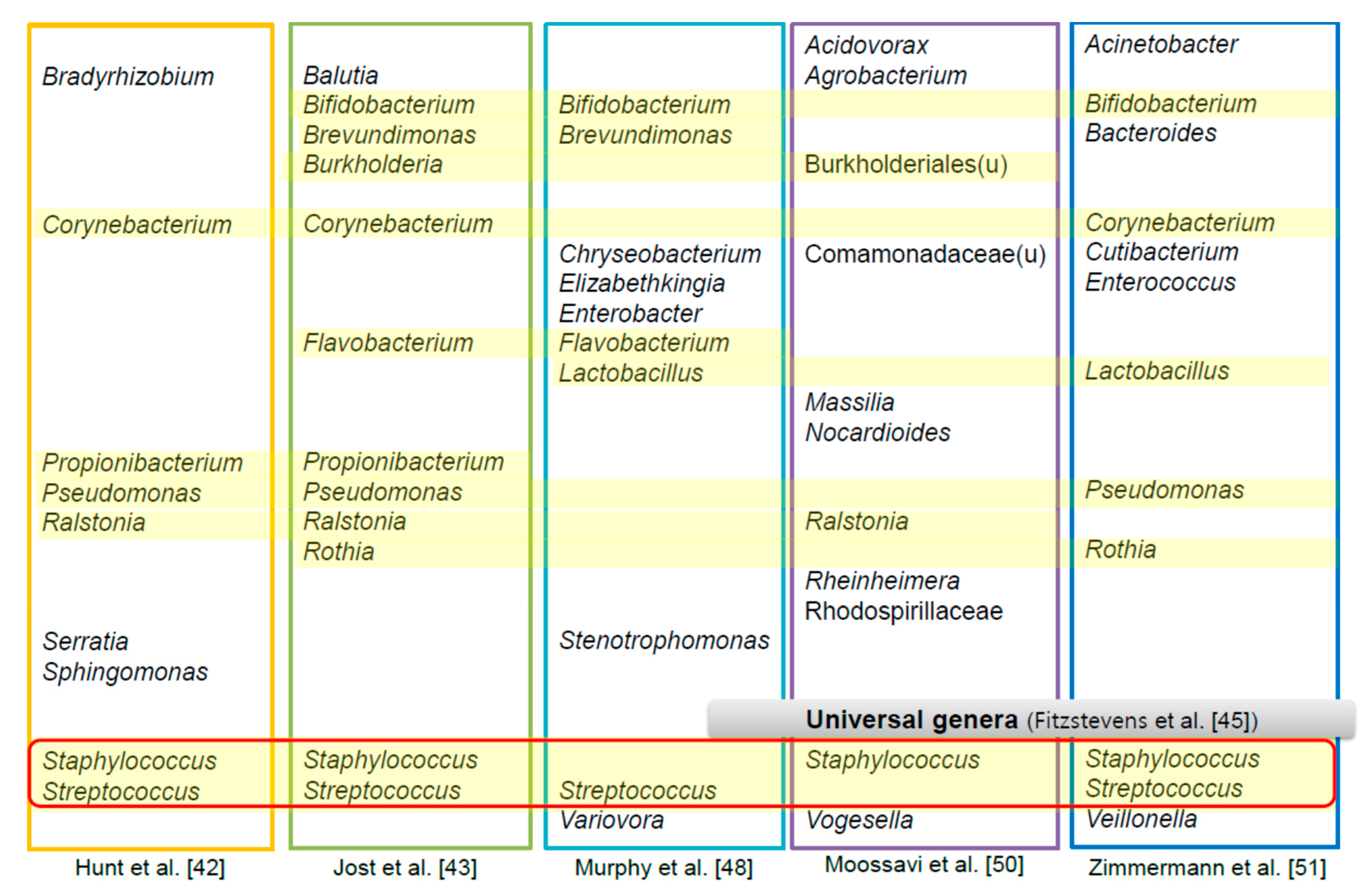
4. The HBM-Derived Microbiome
5. Relationship between the HBM Microbiome and Human Health
6. HBM-Derived Exosomes and microRNA in Relation to Human Health and Disease
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: Nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Components of human breast milk: From macronutrient to microbiome and microRNA. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, C.R.; Ling, P.R.; Blackburn, G.L. Review of Infant Feeding: Key Features of Breast Milk and Infant Formula. Nutrients 2016, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellote, C.; Casillas, R.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Castell, M.; Moretones, M.G.; López-Sabater, M.C.; Franch, A. Premature delivery influences the immunological composition of colostrum and transitional and mature human milk. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Shim, K.S.; Yi, D.Y.; Lim, I.S.; Chae, S.A.; Yun, S.W.; Lee, N.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S. Macronutrient Analysis of Human Milk according to Storage and Processing in Korean Mother. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, S.; Chung, M.; Raman, G.; Chew, P.; Magula, N.; DeVine, D.; Trikalinos, T.; Lau, J. Breastfeeding and maternal and infant health outcomes in developed countries. Evid. Rep. Technol. Assess. 2007, 153, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni, C.; Braegger, C.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Puntis, J.; Shamir, R.; et al. Breast-feeding: A commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosca, F.; Giannì, M.L. Human milk: Composition and health benefits. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2017, 39, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksen, K.G.; Christensen, S.H.; Lind, M.V.; Michaelsen, K.F. Human milk composition and infant growth. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, N.J.; Kampmann, B.; Mehring Le-Doare, K. Human breast milk: A review on its composition and bioactivity. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, S.N.; Hustead, D.S.; Mackey, A.D.; Singhal, A.; Marriage, B.J. Is the macronutrient intake of formula-fed infants greater than breast-fed infants in early infancy? J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 891201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Luca, A.; Hankard, R.; Alexandre-Gouabau, M.C.; Ferchaud-Roucher, V.; Darmaun, D.; Boquien, C.Y. Higher concentrations of branched-chain amino acids in breast milk of obese mothers. Nutrition 2016, 32, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delplanque, B.; Gibson, R.; Koletzko, B.; Lapillonne, A.; Strandvik, B. Lipid Quality in Infant Nutrition: Current Knowledge and Future Opportunities. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saarela, T.; Kokkonen, J.; Koivisto, M. Macronutrient and energy contents of human milk fractions during the first six months of lactation. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Noguera, M.F.; Calvache, J.A.; Bonfill Cosp, X. Supplementation with long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) to breastfeeding mothers for improving child growth and development. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, Cd007901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Z.R.; Green, R.S.; Holzman, I.R.; Lin, J. Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B. Human milk proteins: Key components for the biological activity of human milk. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2004, 554, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerdal, B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1537s–1543s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telemo, E.; Hanson, L.A. Antibodies in milk. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 1996, 1, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.M.; Lawrence, R.A. Breast milk and infection. Clin. Perinatol. 2004, 31, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishna, K.P.; Macadangdang, B.R.; Rogers, M.B.; Tometich, J.T.; Firek, B.A.; Baker, R.; Ji, J.; Burr, A.H.P.; Ma, C.; Good, M.; et al. Maternal IgA protects against the development of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive proteins in breast milk. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2013, 49 (Suppl. 1), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, L.S.; Parks, O.B.; Good, M. A Review of the Immunomodulating Components of Maternal Breast Milk and Protection Against Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Nutrients 2019, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarramala, D.S.; Prakash, P.; Ranade, D.S.; Doshi, S.; Kulkarni, P.P.; Bhaumik, P.; Rao, C.P. Cytotoxicity of apo bovine α-lactalbumin complexed with La3+ on cancer cells supported by its high resolution crystal structure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.C.S.; Nadeem, A.; Svanborg, C. HAMLET—A protein-lipid complex with broad tumoricidal activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 15, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisuda, A.; Ho, J.C.S.; Kandiyal, P.S.; Ng, J.T.; Ambite, I.; Butler, D.S.C.; Háček, J.; Wan, M.L.Y.; Tran, T.H.; Nadeem, A.; et al. Bladder cancer therapy using a conformationally fluid tumoricidal peptide complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 8, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamiri, F.; Riesbeck, K.; Hakansson, A.P. HAMLET, a protein complex from human milk has bactericidal activity and enhances the activity of antibiotics against pathogenic Streptococci. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2019, 63, e01193-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosvenor, C.E.; Picciano, M.F.; Baumrucker, C.R. Hormones and growth factors in milk. Endocr. Rev. 1993, 14, 710–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Díaz, J.; Fontana, L.; Gil, A. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Immune System Development. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurl, S.; Munzert, M.; Boehm, G.; Matthews, C.; Stahl, B. Systematic review of the concentrations of oligosaccharides in human milk. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moukarzel, S.; Bode, L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and the Preterm Infant: A Journey in Sickness and in Health. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantscher-Krenn, E.; Zherebtsov, M.; Nissan, C.; Goth, K.; Guner, Y.S.; Naidu, N.; Choudhury, B.; Grishin, A.V.; Ford, H.R.; Bode, L. The human milk oligosaccharide disialyllacto-N-tetraose prevents necrotising enterocolitis in neonatal rats. Gut 2012, 61, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, C.E.; Litov, R.E.; Thormar, H. Antimicrobial activity of lipids added to human milk, infant formula, and bovine milk. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1995, 6, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, A.; Ostovar, K. Microbiological Characterization of Human Milk1. J. Food Prot. 1977, 40, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidelman, A.I.; Szilagyi, G. Patterns of bacterial colonization of human milk. Obs. Gynecol. 1979, 53, 550–552. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C. Maternal transmission of infectious pathogens in breast milk. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2001, 37, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkila, M.P.; Saris, P.E. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by the commensal bacteria of human milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiminez, E.; Marin, M.L.; Xaus, J.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Human milk is a source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut. J. Pediatrics 2003, 143, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Delgado, S.; Maldonado, A.; Rodriguez, J.M. Assessment of the bacterial diversity of breast milk of healthy women by quantitative real-time PCR. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Jimenez, E.; Heilig, H.; Fernandez, L.; Marin, M.L.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Rodriguez, J.M. Isolation of bifidobacteria from breast milk and assessment of the bifidobacterial population by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative real-time PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, K.M.; Foster, J.A.; Forney, L.J.; Schutte, U.M.; Beck, D.L.; Abdo, Z.; Fox, L.K.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Characterization of the diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in human milk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.; Chassard, C. Assessment of bacterial diversity in breast milk using culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olivares, M.; Diaz-Ropero, M.P.; Martin, R.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Xaus, J. Antimicrobial potential of four Lactobacillus strains isolated from breast milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzstevens, J.L.; Smith, K.C.; Hagadorn, J.I.; Caimano, M.J.; Matson, A.P.; Brownell, E.A. Systematic Review of the Human Milk Microbiota. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togo, A.; Dufour, J.C.; Lagier, J.C.; Dubourg, G.; Raoult, D.; Million, M. Repertoire of human breast and milk microbiota: A systematic review. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Manara, S.; Zolfo, M.; Truong, D.T.; Scholz, M.; Armanini, F.; Ferretti, P.; Gorfer, V.; Pedrotti, A.; Tett, A.; et al. Studying Vertical Microbiome Transmission from Mothers to Infants by Strain-Level Metagenomic Profiling. mSystems 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.; Curley, D.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; O’Shea, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. The Composition of Human Milk and Infant Faecal Microbiota over the First Three Months of Life: A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.Y.; Park, J.; Yi, D.Y. Comprehensive Analysis of the Effect of Probiotic Intake by the Mother on Human Breast Milk and Infant Fecal Microbiota. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moossavi, S.; Sepehri, S.; Robertson, B.; Bode, L.; Goruk, S.; Field, C.J.; Lix, L.M.; de Souza, R.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; et al. Composition and Variation of the Human Milk Microbiota Are Influenced by Maternal and Early-Life Factors. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 324–335.e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Breast milk microbiota: A review of the factors that influence composition. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Bender, J.M.; Yang, S.; Rollie, A.; Adisetiyo, H.; Zabih, S.; Lincez, P.J.; Bittinger, K.; et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatrics 2017, 171, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordy, K.; Gaufin, T.; Mwangi, M.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Lee, D.J.; Adisetiyo, H.; Woodward, C.; Pannaraj, P.S.; Tobin, N.H.; et al. Contributions to human breast milk microbiome and enteromammary transfer of Bifidobacterium breve. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0219633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramsay, D.T.; Kent, J.C.; Owens, R.A.; Hartmann, P.E. Ultrasound imaging of milk ejection in the breast of lactating women. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescigno, M.; Urbano, M.; Valzasina, B.; Francolini, M.; Rotta, G.; Bonasio, R.; Granucci, F.; Kraehenbuhl, J.-P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Uhr, T. Induction of Protective IgA by Intestinal Dendritic Cells Carrying Commensal Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Collado, M.C.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Mira, A. The human milk microbiome changes over lactation and is shaped by maternal weight and mode of delivery. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Rochat, F.; Chassard, C. Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Lugli, G.A.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Ferrario, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Viappiani, A.; Ferretti, P.; Gorfer, V.; et al. Exploring Vertical Transmission of Bifidobacteria from Mother to Child. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7078–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jara, S.; Sánchez, M.; Vera, R.; Cofré, J.; Castro, E. The inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus spp. isolated from breast milk on gastrointestinal pathogenic bacteria of nosocomial origin. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nantavisai, K.; Puttikamonkul, S.; Chotelersak, K.; Taweechotipatr, M. In Vitro Adhesion Property and Competition against Enteropathogens of Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Thai Infants. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 40, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Turroni, F.; Peano, C.; Pass, D.A.; Foroni, E.; Severgnini, M.; Claesson, M.J.; Kerr, C.; Hourihane, J.; Murray, D.; Fuligni, F. Diversity of bifidobacteria within the infant gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Factors influencing the intestinal microbiome during the first year of life. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, e315–e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Analysis of the human breast milk microbiome and bacterial extracellular vesicles in healthy mothers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.U.; Kim, W.H.; Jeong, C.H.; Yi, D.Y.; Min, H. More than Nutrition: Therapeutic Potential of Breast Milk-Derived Exosomes in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Giardino Torchia, M.L.; Lawson, G.W.; Karp, C.L.; Ashwell, J.D.; Mazmanian, S.K. Outer membrane vesicles of a human commensal mediate immune regulation and disease protection. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryant, W.A.; Stentz, R.; Le Gall, G.; Sternberg, M.J.E.; Carding, S.R.; Wilhelm, T. In Silico Analysis of the Small Molecule Content of Outer Membrane Vesicles Produced by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Indicates an Extensive Metabolic Link between Microbe and Host. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, K.; Underwood, M.A. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 135, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullinane, M.; Amir, L.H. In Response to “Microbial Diversity in Milk of Women With Mastitis: Potential Role of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci, Viridans Group Streptococci, and Corynebacteria”. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, S.; Arroyo, R.; Martín, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. PCR-DGGE assessment of the bacterial diversity of breast milk in women with lactational infectious mastitis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, S.; Arroyo, R.; Jiménez, E.; Marín, M.L.; del Campo, R.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Staphylococcus epidermidis strains isolated from breast milk of women suffering infectious mastitis: Potential virulence traits and resistance to antibiotics. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.H.; Vaidya, Y.H.; Patel, R.J.; Pandit, R.J.; Joshi, C.G.; Kunjadiya, A.P. Culture independent assessment of human milk microbial community in lactational mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbaniak, C.; Gloor, G.B.; Brackstone, M.; Scott, L.; Tangney, M.; Reid, G. The Microbiota of Breast Tissue and Its Association with Breast Cancer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5039–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashed, M.H.; Bayraktar, E.; Helal, G.K.; Abd-Ellah, M.F.; Amero, P.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C. Exosomes: From Garbage Bins to Promising Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlassov, A.V.; Magdaleno, S.; Setterquist, R.; Conrad, R. Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, S.; Elbaum Shiff, Y.; Golan-Gerstl, R. Milk-derived exosomes (MDEs) have a different biological effect on normal fetal colon epithelial cells compared to colon tumor cells in a miRNA-dependent manner. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollaei, H.; Safaralizadeh, R.; Rostami, Z. MicroRNA replacement therapy in cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 12369–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaweed, M.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Kakulas, F. MicroRNAs in Breastmilk and the Lactating Breast: Potential Immunoprotectors and Developmental Regulators for the Infant and the Mother. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13981–14020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. MicroRNAs: Milk’s epigenetic regulators. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, B.; Singh, A.K.; Rotllan, N.; Price, N.; Fernández-Hernando, C. MicroRNAs and lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Hernando, C.; Suárez, Y.; Rayner, K.J.; Moore, K.J. MicroRNAs in lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2011, 22, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy-Aksel, A.; Zampa, F.; Schratt, G. MicroRNAs and synaptic plasticity--a mutual relationship. Philos Trans. R Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrillo-Lozano, E.; Sebastián-Valles, F.; Knott-Torcal, C. Circulating microRNAs in Breast Milk and Their Potential Impact on the Infant. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Human Breast Milk Composition and Function in Human Health: From Nutritional Components to Microbiome and MicroRNAs. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093094
Yi DY, Kim SY. Human Breast Milk Composition and Function in Human Health: From Nutritional Components to Microbiome and MicroRNAs. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093094
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Dae Yong, and Su Yeong Kim. 2021. "Human Breast Milk Composition and Function in Human Health: From Nutritional Components to Microbiome and MicroRNAs" Nutrients 13, no. 9: 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093094
APA StyleYi, D. Y., & Kim, S. Y. (2021). Human Breast Milk Composition and Function in Human Health: From Nutritional Components to Microbiome and MicroRNAs. Nutrients, 13(9), 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093094