Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 Protects against Antibiotic-Induced Functional and Compositional Changes in Human Fecal Microbiome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
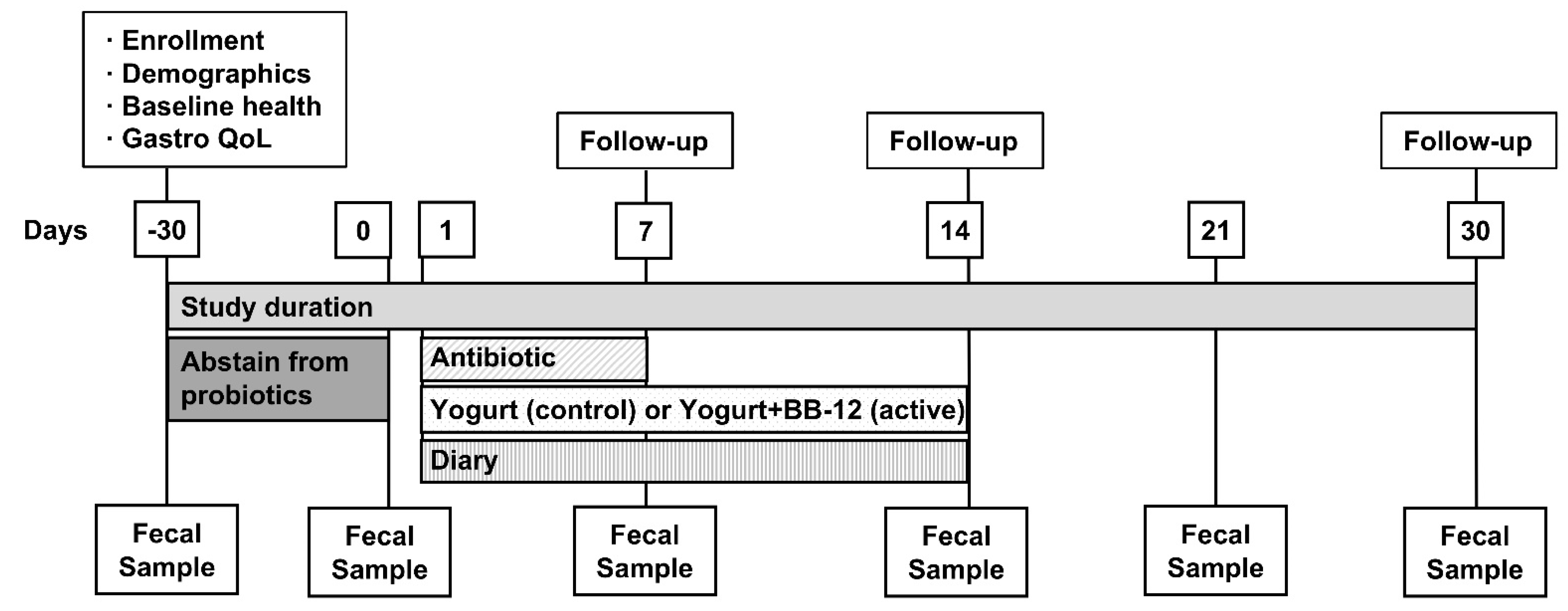
2.1. Study Design and Regulatory Approval
2.2. Participants
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Blinding
2.5. Randomization
2.6. Compliance
2.7. SCFA Analysis
2.8. Microbial DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.9. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
2.10. Sample Size Calculation
2.11. Other Data Collected
3. Results
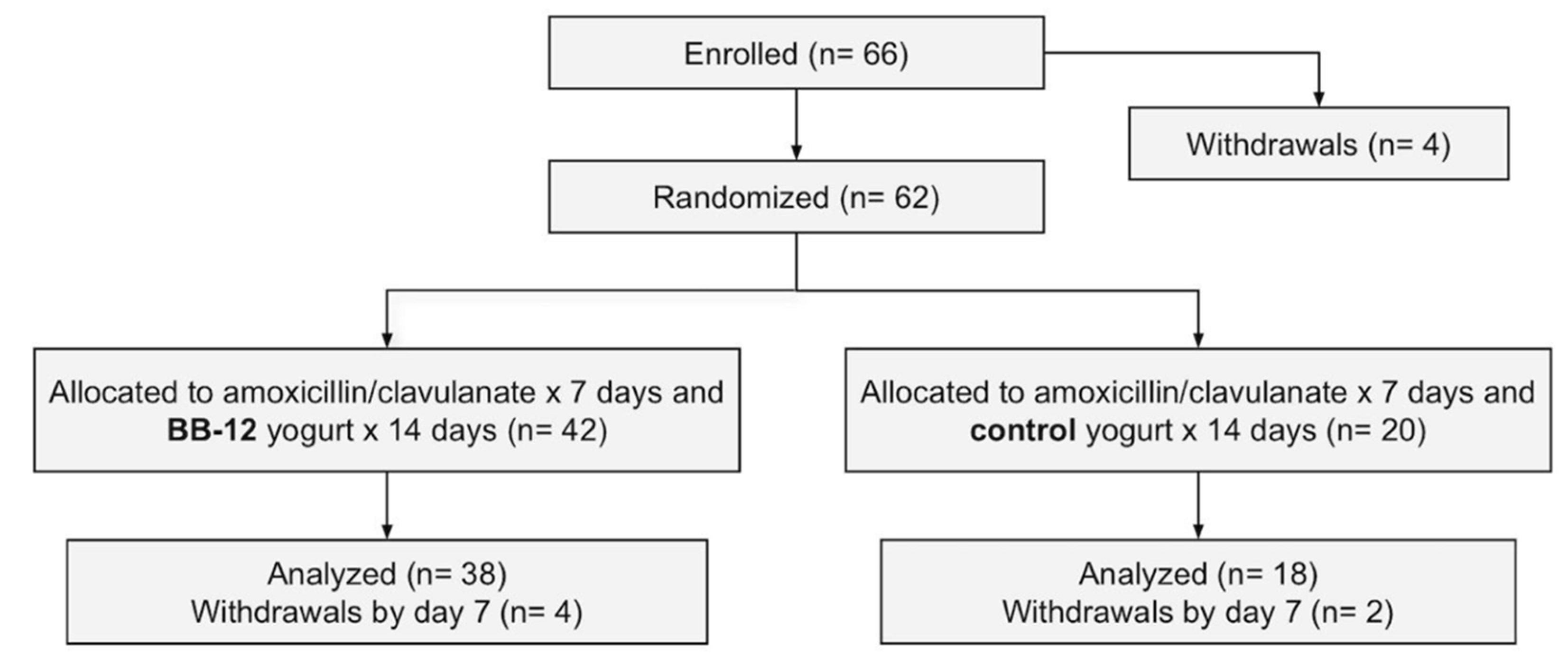
3.1. Participant Flow and Baseline Characteristics
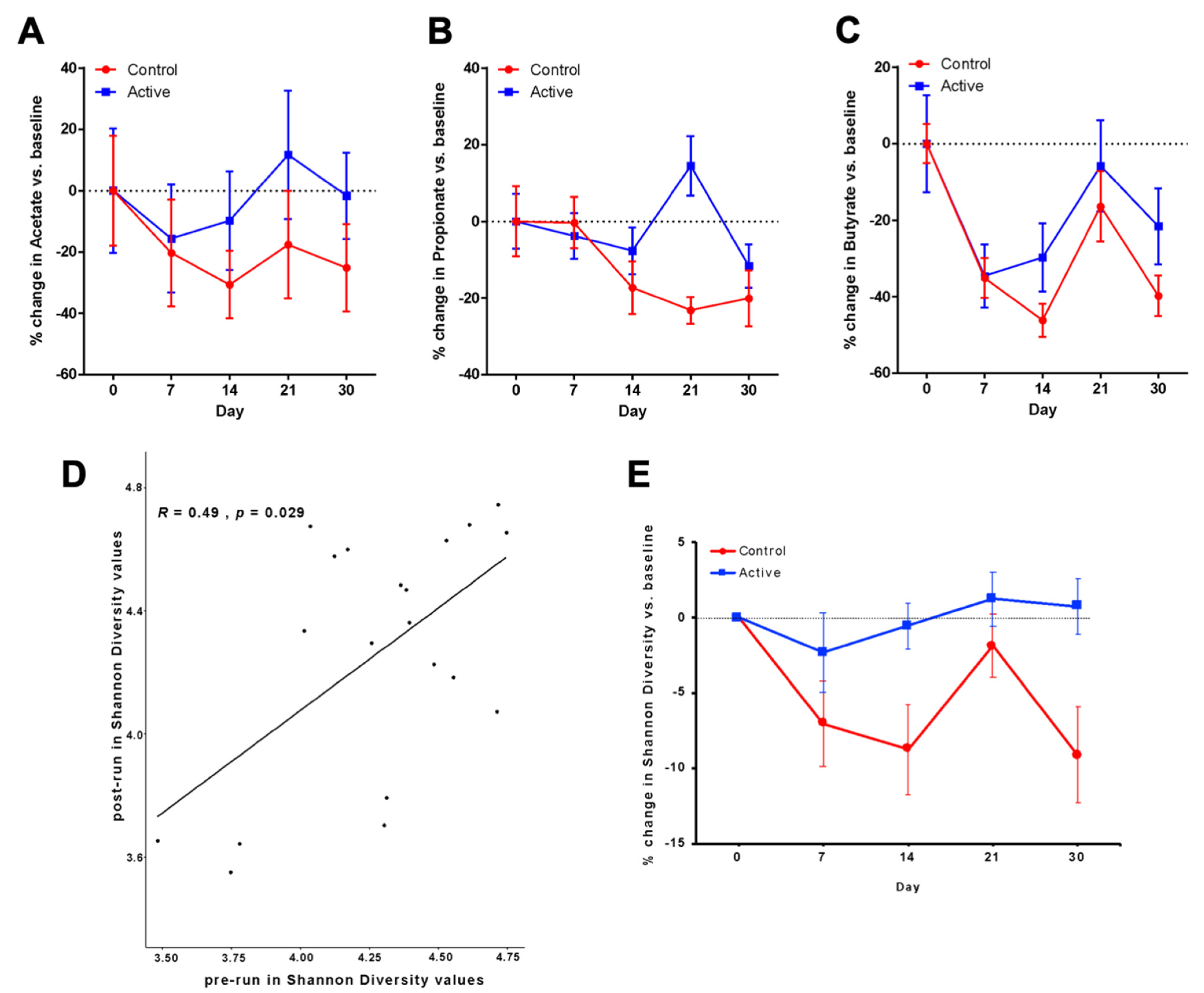
3.2. Primary Outcomes after Antibiotic Administration Measured by SFCA Analyses
3.3. Relative Risk for Improvement
3.4. Area under the Curve Analysis of Change in Acetate
3.5. Propionate and Butyrate Measured after Antibiotic Administration
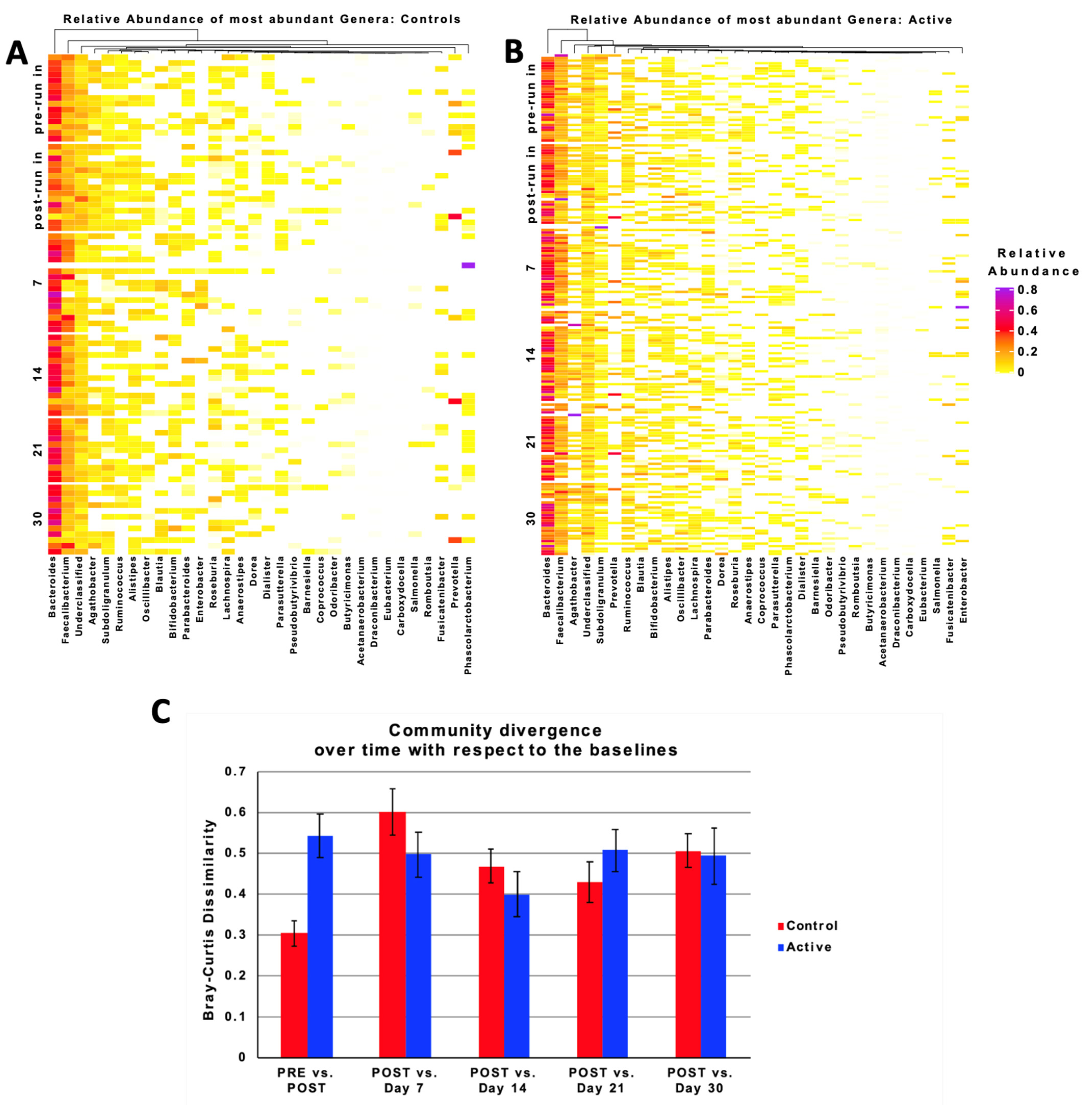
3.6. Microbiota Analyses
3.7. Taxonomic Characteristics and Changes over Time
3.8. Relative Abundance
3.9. Clinical Outcomes and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAD | antibiotic-associated diarrhea |
| ASV | amplicon sequence variants |
| AUC | area under curve |
| BB-12 | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 |
| HEI-2015 | healthy eating index–2015 |
| IND | investigational new drug |
| LEfSe | linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| SCFA | short-chain fatty acid |
References
- Tuohy, K.M.; Rouzaud, G.C.; Bruck, W.M.; Gibson, G.R. Modulation of the Human Gut Microflora towards Improved Health Using Prebiotics—Assessment of Efficacy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, H.J. Role of Colonic Short-Chain Fatty Acid Transport in Diarrhea. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethlefsen, L.; Huse, S.; Sogin, M.L.; Relman, D.A. The Pervasive Effects of an Antibiotic on the Human Gut Microbiota, as Revealed by Deep 16S RRNA Sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, L.; Relman, D.A. Incomplete Recovery and Individualized Responses of the Human Distal Gut Microbiota to Repeated Antibiotic Perturbation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4554–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, V.B.; Schmidt, T.M. Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea Accompanied by Large-Scale Alterations in the Composition of the Fecal Microbiota. J. Clin. Micro. 2004, 42, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clausen, M.R.; Bonnen, H.; Tvede, M.; Mortensen, P.B. Colonic Fermentation to Short-Chain Fatty Acids Is Decreased in Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Gastroenterology 1991, 101, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycook, J.H.; Scanlan, P.D. Ecological and Evolutionary Responses to Antibiotic Treatment in the Human Gut Microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan-Yulzari, A.; Turta, O.; Belogolovski, A.; Ziv, O.; Kunz, C.; Perschbacher, S.; Neuman, H.; Pasolli, E.; Oz, A.; Ben-Amram, H.; et al. Neonatal Antibiotic Exposure Impairs Child Growth during the First Six Years of Life by Perturbing Intestinal Microbial Colonization. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Coin-Aragüez, L.; Roca-Rodríguez, M.D.M.; Muñoz-Garach, A.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Cardona, F.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Tinahones, F.J.H. Pylori Eradication with Antibiotic Treatment Causes Changes in Glucose Homeostasis Related to Modifications in the Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romick-Rosendale, L.E.; Haslam, D.B.; Lane, A.; Denson, L.; Lake, K.; Wilkey, A.; Watanabe, M.; Bauer, S.; Litts, B.; Luebbering, N.; et al. Antibiotic Exposure and Reduced Short Chain Fatty Acid Production after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turck, D.; Bernet, J.P.; Marx, J.; Kempf, H.; Giard, P.; Walbaum, O.; Lacombe, A.; Rembert, F.; Toursel, F.; Bernasconi, P.; et al. Incidence and Risk Factors of Oral Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in an Outpatient Pediatric Population. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 37, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.K.; Van, R.; Mason, E.H.; Norris, D.M.; Pickering, L.K. Prospective Study of Toxigenic Clostridium Difficile in Children given Amoxicillin/Clavulanate for Otitis Media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1996, 15, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, J.M.; Phillips, A.; Wiisanen, R. Comparative Safety and Efficacy of Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin/Clavulanate in the Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1993, 12, S122–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elstner, C.L.; Lindsay, A.N.; Book, L.S.; Matsen, J.M. Lack of Relationship of Clostridium Difficile to Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Children. Pediatr Infect. Dis. J. 1983, 2, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, L.V. Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Treatments for Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Dig. Dis. 1998, 16, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaugerie, L.; Flahault, A.; Barbut, F.; Atlan, P.; Lalande, V.; Cousin, P.; Cadilhac, M.; Petit, J.C. Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhoea and Clostridium Difficile in the Community. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 17, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, J.A.; Davis, R.L.; Dowell, S.F.; Metlay, J.P.; Soumerai, S.B.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Higham, M.; Miller, Z.; Miroshnik, I.; Pedan, A.; et al. Reducing Antibiotic Use in Children: A Randomized Trial in 12 Practices. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, J.A.; Metlay, J.P.; Davis, R.L.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Dowell, S.F.; Platt, R. Antimicrobial Use in Defined Populations of Infants and Young Children. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2000, 154, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Flaster, N.; Casanello, A.L.; Curcio, D. Assessing Risk Factors, Mortality, and Healthcare Utilization Associated with Clostridioides Difficile Infection in Four Latin American Countries. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Braz. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebel, R.; Vojtilová, L.; Husa, P. Clostridium Difficile Infection: An Update on Treatment and Prevention. Vnitr. Lek. 2020, 66, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert Consensus Document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jungersen, M.; Wind, A.; Johansen, E.; Christensen, J.; Stuer-Lauridsen, B.; Eskesen, D. The Science behind the Probiotic Strain Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB-12®. Microorganisms 2014, 2, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, C.; Johansen, E.; Pedersen, M.B. Complete Genome Sequence of Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis BB-12, a Widely Consumed Probiotic Strain. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2467–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merenstein, D.J.; Smith, K.H.; Scriven, M.; Roberts, R.F.; Sanders, M.E.; Petterson, S. The Study to Investigate the Potential Benefits of Probiotics in Yogurt, a Patient-Oriented, Double-Blind, Cluster-Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.P.; Ba, Z.; Sanders, M.E.; D′Amico, F.J.; Roberts, R.F.; Smith, K.H.; Merenstein, D.J. Safety of Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis (B. Lactis) Strain BB-12-Supplemented Yogurt in Healthy Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merenstein, D.J.; Tan, T.P.; Molokin, A.; Smith, K.H.; Roberts, R.F.; Shara, N.M.; Mete, M.; Sanders, M.E.; Solano-Aguilar, G. Safety of Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. Lactis (B. Lactis) Strain BB-12-Supplemented Yogurt in Healthy Adults on Antibiotics: A Phase I Safety Study. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merenstein, D.; Gonzalez, J.; Young, A.G.; Roberts, R.F.; Sanders, M.E.; Petterson, S. Study to Investigate the Potential of Probiotics in Children Attending School. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lin, K.; Sequeira, C.; Borchers, C.H. An Isotope-Labeled Chemical Derivatization Method for the Quantitation of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Human Feces by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 854, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, J.B.; Humphrys, M.S.; Robinson, C.K.; Settles, M.L.; Ott, S.; Fu, L.; Yang, H.; Gajer, P.; He, X.; McComb, E.; et al. Ultrahigh-Throughput Multiplexing and Sequencing of >500-Base-Pair Amplicon Regions on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 Platform. MSystems 2019, 4, e00029-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of RRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoverstad, T.; Carlstedt-Duke, B.; Lingaas, E.; Midtvedt, T.; Norin, K.E.; Saxerholt, H.; Steinbakk, M. Influence of Ampicillin, Clindamycin, and Metronidazole on Faecal Excretion of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Healthy Subjects. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1986, 21, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoverstad, T.; Carlstedt-Duke, B.; Lingaas, E.; Norin, E.; Saxerholt, H.; Steinbakk, M.; Midtvedt, T. Influence of Oral Intake of Seven Different Antibiotics on Faecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Excretion in Healthy Subjects. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1986, 21, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Pannucci, T.E.; Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Lerman, J.L.; Tooze, J.A.; Wilson, M.M.; Reedy, J. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Reedy, J.; Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Pannucci, T.E.; Subar, A.F.; Wilson, M.M.; Lerman, J.L.; Tooze, J.A. Applications of the Healthy Eating Index for Surveillance, Epidemiology, and Intervention Research: Considerations and Caveats. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Bashiardes, S.; Zur, M.; Regev-Lehavi, D.; Ben-Zeev Brik, R.; Federici, S.; et al. Post-Antibiotic Gut Mucosal Microbiome Reconstitution Is Impaired by Probiotics and Improved by Autologous FMT. Cell 2018, 174, 1406–1423.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, N.T.; Maw, A.; Tmanova, L.L.; Pino, A.; Ancy, K.; Crawford, C.V.; Simon, M.S.; Evans, A.T. Timely Use of Probiotics in Hospitalized Adults Prevents Clostridium Difficile Infection: A Systematic Review With Meta-Regression Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1889–1900.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldenberg, J.Z.; Yap, C.; Lytvyn, L.; Lo, C.K.-F.; Beardsley, J.; Mertz, D.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the Prevention of Clostridium Difficile-Associated Diarrhea in Adults and Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, CD006095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Goldenberg, J.Z.; Humphrey, C.; El Dib, R.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the Prevention of Pediatric Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnadower, D.; Tarr, P.I.; Casper, T.C.; Gorelick, M.H.; Dean, J.M.; O’Connell, K.J.; Mahajan, P.; Levine, A.C.; Bhatt, S.R.; Roskind, C.G.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG versus Placebo for Acute Gastroenteritis in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Guarino, A.; Hojsak, I.; Indrio, F.; Kolacek, S.; Shamir, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; Weizman, Z. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Use of Probiotics for Management of Acute Gastroenteritis: A Position Paper by the ESPGHAN Working Group for Probiotics and Prebiotics. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, G.L.; Ko, C.W.; Bercik, P.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Sultan, S.; Weizman, A.V.; Morgan, R.L. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Role of Probiotics in the Management of Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Grześkowiak, Ł.; Salminen, S. Probiotic Strains and Their Combination Inhibit in Vitro Adhesion of Pathogens to Pig Intestinal Mucosa. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Meriluoto, J.; Salminen, S. Role of Commercial Probiotic Strains against Human Pathogen Adhesion to Intestinal Mucus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubitowski, T.B.; Poll, B.G.; Natarajan, N.; Pluznick, J.L. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Delivery: Assessing Exogenous Administration of the Microbiome Metabolite Acetate in Mice. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Interplay between Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Host Energy Metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and Their Role as Members of the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanders, M.E.; Benson, A.; Lebeer, S.; Merenstein, D.J.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Shared Mechanisms among Probiotic Taxa: Implications for General Probiotic Claims. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Control n = 20 | Active/BB-12 n = 42 | Not Randomized n = 4 | Total n = 66 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Mean (sd) | 29.4 (8.1) | 29.6 (10.3) | 31.8 (21.6) | 29.7 (10.6) |
| Race | American Indian or Alaska Native | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Asian | 3 | 6 | 3 | 12 | |
| Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Black or African American | 5 | 8 | 0 | 13 | |
| White | 11 | 28 | 1 | 40 | |
| More than one race | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Unknown/Not Reported | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ethnicity (Hispanic or Latino origin) | Yes | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| No | 18 | 36 | 4 | 58 | |
| Unknown/Not Reported | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | |
| Health insurance status | Yes | 20 | 41 | 4 | 65 |
| No | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Household smoking | Yes | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| No | 20 | 44 | 0 | 64 | |
| Marital status | Married | 4 | 10 | 0 | 14 |
| Living with a partner | 2 | 5 | 0 | 7 | |
| Single | 14 | 26 | 3 | 43 | |
| Separated | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Divorced | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Widowed | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Annual gross total income | Less than $15,000 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 7 |
| $15,000–$29,999 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 | |
| $30,000–$49,999 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 6 | |
| $50,000–$74,999 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 6 | |
| $75,000–$99,999 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 11 | |
| $100,000–$150,999 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | |
| $150,000–$200,000 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| More than $200,000 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 11 | |
| Prefer not to answer | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Unknown/Not Reported | 6 | 5 | 1 | 12 | |
| Control | Active/BB-12 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetate (µM) | Acetate (µM) | |||||||||
| Mean ± SD | Median | Range | N | % Change | Mean ± SD | Median | Range | N | % Change | |
| Day 0 | 53.1 ± 18.0 | 53.0 | 22.1–85.9 | 12 | N/A | 45.2 ± 20.3 | 38.7 | 13.7–93.6 | 29 | N/A |
| Day 7 | 42.3 ± 17.5 | 40.3 | 18.8–72.1 | 12 | −20.3% | 38.1 ± 17.6 | 39.6 | 4.4–74.8 | 27 | −15.6% |
| Day 14 | 36.8 ± 11.1 | 33.6 | 23.9–60.5 | 12 | −30.6% | 40.8 ± 16.1 | 40.1 | 11.0–79.1 | 29 | −9.7% |
| Day 21 | 43.8 ± 17.6 | 43.9 | 15.8–69.2 | 12 | −17.6% | 50.5 ± 20.9 | 50.9 | 18.8–98.9 | 29 | 11.7% |
| Day 30 | 39.8 ± 14.3 | 40.9 | 15.4–58.1 | 10 | −25.1% | 44.5 ± 14.1 | 47.2 | 18.1–66.1 | 26 | −1.6% |
| Control | Active/BB-12 | |||||||||
| Propionate (µM) | Propionate (µM) | |||||||||
| Mean ± SD | Median | Range | N | % Change | Mean ± SD | Median | Range | N | % Change | |
| Day 0 | 14.3 ± 9.1 | 12.2 | 3.8–34.0 | 12 | N/A | 13.0 ± 7.2 | 10.6 | 3.8–32.2 | 29 | N/A |
| Day 7 | 14.3 ± 6.7 | 13.0 | 3.9–29.2 | 12 | −0.3% | 12.5 ± 6.0 | 12.5 | <0.5–25.9 | 25 | −3.8% |
| Day 14 | 11.8 ± 6.9 | 10.6 | 5.1–32.4 | 12 | −17.3% | 12.0 ± 6.1 | 11.0 | 3.7–31.8 | 29 | −7.7% |
| Day 21 | 11.0 ± 3.5 | 11.2 | 5.7–18.9 | 11 | −23.2% | 14.8 ± 7.8 | 13.4 | 5.6–45.6 | 29 | 14.5% |
| Day 30 | 11.4 ± 7.3 | 8.4 | 4.5–27.3 | 11 | −20.1% | 11.5 ± 5.7 | 10.8 | 2.1–26.0 | 26 | −11.6% |
| Control | Active/BB-12 | |||||||||
| Butyrate (µM) | Butyrate (µM) | |||||||||
| Mean ± SD | Median | Range | N | % Change | Mean ± SD | Median | Range | N | % Change | |
| Day 0 | 12.7 ± 6.2 | 13.3 | <0.5–21.0 | 11 | N/A | 12.7 ± 8.4 | 9.6 | 5.3–38.1 | 29 | N/A |
| Day 7 | 9.0 ± 5.3 | 8.9 | <0.5–16.4 | 11 | −35.1% | 8.3 ± 5.7 | 6.6 | ND–22.6 | 24 | −34.6% |
| Day 14 | 7.4 ± 4.3 | 5.9 | 2.2–16.8 | 12 | −46.2% | 8.9 ± 6.1 | 8.1 | 1.1–31.0 | 29 | −29.7% |
| Day 21 | 11.6 ± 9.2 | 8.9 | 1.1–30.5 | 11 | −16.4% | 11.9 ± 7.8 | 10.8 | 1.1–37.1 | 29 | −5.8% |
| Day 30 | 8.3 ± 5.3 | 6.3 | 0.8–19.0 | 11 | −39.8% | 9.9 ± 4.0 | 9.8 | 1.0–17.5 | 26 | −21.6% |
| Time Point | Baseline Health | Post Run-in | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 30 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptom, Number of Reports (%) | C † | A ‡ | Total § | C | A | Total | C | A | Total | C | A | Total | C | A | Total |
| Group n | 20 | 42 | 66 | 20 | 40 | 61 | 18 | 38 | 56 | 17 | 38 | 55 | 16 | 36 | 52 |
| Loose stool | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 (44) | 10 (26) | 18 | 5 (29) | 6 (16) | 11 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Constipation | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Fever | |||||||||||||||
| Flatulence | 3 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 12 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Lack/Loss of Appetite | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Stomach Pain | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Rash | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Vomiting | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Allergic Reaction | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Dyspepsia | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||
| Nausea | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 8 | ||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||
| Headache | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||
| Light-headed | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Migraine | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Passing undigested food | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Rectal pain | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Ringing in ears | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Runny nose | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Subconjunctival hemorrhage | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Unable to fall asleep after waking at night | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Yeast Infection | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merenstein, D.; Fraser, C.M.; Roberts, R.F.; Liu, T.; Grant-Beurmann, S.; Tan, T.P.; Smith, K.H.; Cronin, T.; Martin, O.A.; Sanders, M.E.; et al. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 Protects against Antibiotic-Induced Functional and Compositional Changes in Human Fecal Microbiome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082814
Merenstein D, Fraser CM, Roberts RF, Liu T, Grant-Beurmann S, Tan TP, Smith KH, Cronin T, Martin OA, Sanders ME, et al. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 Protects against Antibiotic-Induced Functional and Compositional Changes in Human Fecal Microbiome. Nutrients. 2021; 13(8):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082814
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerenstein, Daniel, Claire M. Fraser, Robert F. Roberts, Tian Liu, Silvia Grant-Beurmann, Tina P. Tan, Keisha Herbin Smith, Tom Cronin, Olivia A. Martin, Mary Ellen Sanders, and et al. 2021. "Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 Protects against Antibiotic-Induced Functional and Compositional Changes in Human Fecal Microbiome" Nutrients 13, no. 8: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082814
APA StyleMerenstein, D., Fraser, C. M., Roberts, R. F., Liu, T., Grant-Beurmann, S., Tan, T. P., Smith, K. H., Cronin, T., Martin, O. A., Sanders, M. E., Lucan, S. C., & Kane, M. A. (2021). Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 Protects against Antibiotic-Induced Functional and Compositional Changes in Human Fecal Microbiome. Nutrients, 13(8), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082814






