The Effects of 12-Week Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Single-Blind Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol of the Study
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Bioelectric Impedance Analysis
2.2.2. Quadriceps Ultrasound
2.2.3. Liver Frailty Index
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Basal Evaluation
4.3. Modifications Induced by Treatment
4.4. Muscle Performance Analysis
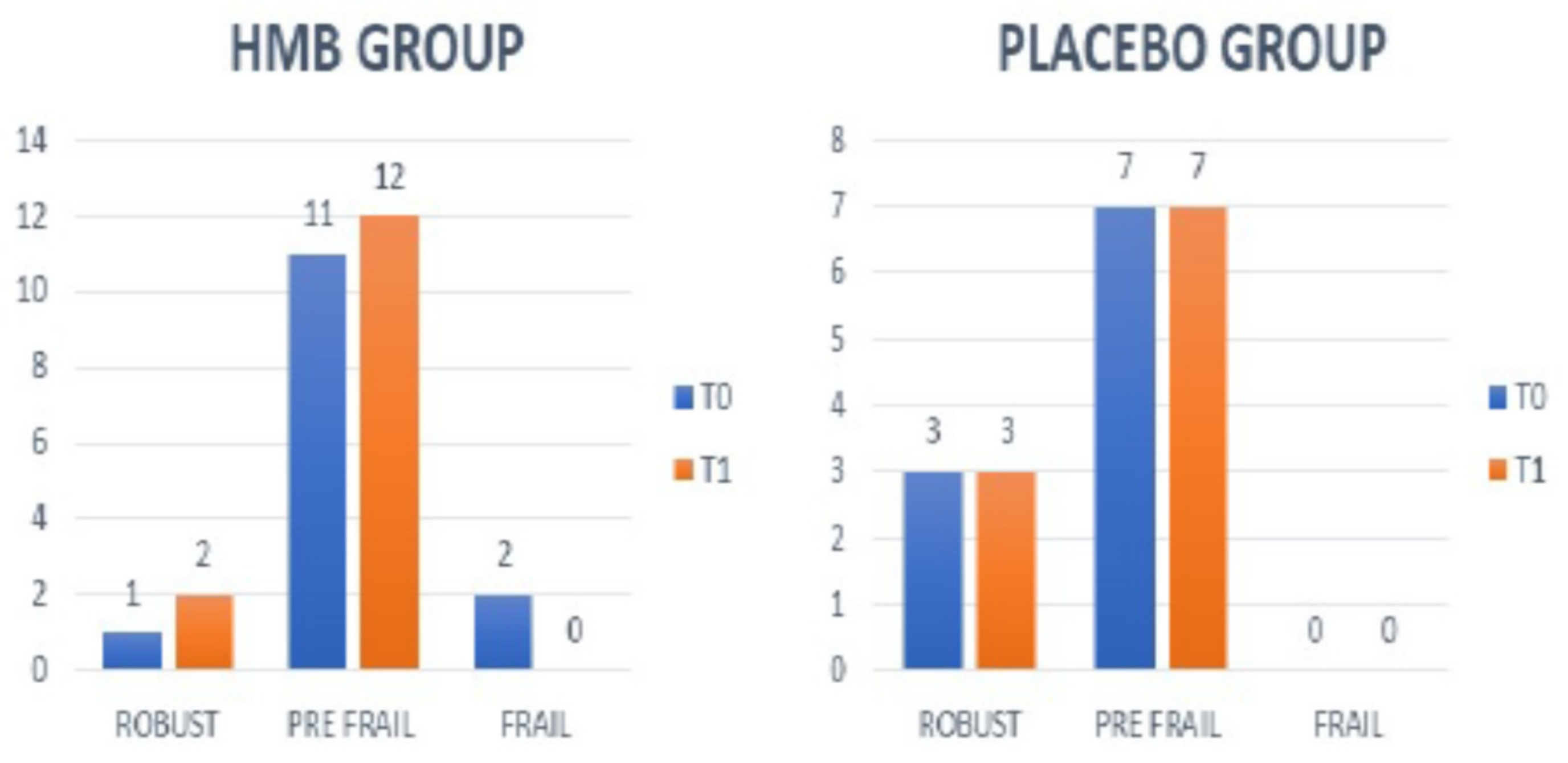
4.5. Frailty
4.6. Liver Function, Disease Severity, and Safety of HMB
4.7. Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score and Animal Naming Test
4.8. Food Diary and Daily Physical Activity
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bot, D.; Droop, A.; Lucassen, C.J.; van Veen, M.E.; van Vugt, J.L.A.; Shahbazi Feshtali, S.; Leistra, E.; Tushuizen, M.E.; van Hoek, B. Both muscle quantity and quality are predictors of waiting list mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 42, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternostro, R.; Bardach, C.; Hofer, B.S.; Scheiner, B.; Schwabl, P.; Asenbaum, U.; Ba-Ssalamah, A.; Scharitzer, M.; Bucscis, T.; Simbrunner, B.; et al. Prognostic impact of sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients stratified by different severity of portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, B.; Nardelli, S.; Pigliacelli, A.; Di Cola, S.; Farcomeni, A.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Gioia, S.; Ginanni Corradini, S.; Lucidi, C.; Mennini, G.; et al. The additive value of sarcopenia, myosteatosis and hepatic encephalopathy in the predictivity of model for end-stage liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Merli, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Muscle Alterations Are Associated With Minimal and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucidi, C.; Lattanzi, B.; Di Gregorio, V.; Incicco, S.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Venditti, M.; Riggio, O.; Merli, M. A low muscle mass increases mortality in compensated cirrhotic patients with sepsis. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Meza-Junco, J.; Baracos, V.E.; Sawyer, M.B.; Pang, J.X.Q.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Myers, R.P. Inclusion of Sarcopenia Within MELD (MELD- Sarcopenia) and the Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 16, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.C.; Ganger, D.R.; Volk, M.L.; Dodge, J.L.; Dunn, M.A.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Kappus, M.R.; Rahimi, R.S.; Ladner, D.P.; Boyarsky, B.; et al. Association of Frailty and Sex with Wait List Mortality in Liver Transplant Candidates in the Multicenter Functional Assessment in Liver Transplantation (FrAILT) Study. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Goldberg, D.S.; Kaplan, D.E.; Sundaram, V.; Taddei, T.H.; Mahmud, N. Patient Frailty Is Independently Associated with the Risk of Hospitalization for Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Liver Transpl. 2021, 27, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, R.; Díaz, L.A.; Rivas, V.; Fuentes-López, E.; Zalaquett, M.; Bruera, M.J.; Gonzalez, C.; Mezzano, G.; Benìtez, C. Frailty and reduced gait speed are independently related to mortality of cirrhotic patients in long-term follow-up. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 25, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.C.; Dodge, J.L.; Kappus, M.R.; Dunn, M.A.; Volk, M.L.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Ganger, D.R.; Rahimi, R.; McCulloch, C.; Haugen, C.E.; et al. Changes in frailty are associated with waitlist mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Covinsky, K.; Dodge, J.; Boscardin, W.J.; Segev, D.L.; Roberts, J.P.; Feng, S. Development of a novel frailty index to predict mortality in patients with end-stage. Hepatology 2017, 66, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Low, G.; Mourtzakis, M.; Zenith, L.; Myers, R.P.; Abraldes, J.G.; Shaheen, A.A.M.; Qamar, H.; Mansoor, N.; Carbonneau, M.; et al. A model to identify Sarcopenia in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Sarcopenia: What should a pharmacist know? Farm. Hosp. 2017, 41, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlinger-Romero, F.; Guimarães-Ferreira, L.; Giannocco, G.; Nunes, M.T. Chronic supplementation of beta- hydroxy-beta methylbutyrate (HMβ) increases the activity of the GH/IGF-I axis and induces hyperinsulinemia in rats. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2011, 21, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.J.; Wilson, J.M.; Manninen, A.H. Effects of betahydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) on exercise performance and body composition across varying levels of age, sex, and training experience: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 23, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorotto, M.L.; Schwartz, R.J.; Delaughter, M.C. Persistent IGF-1 overexpression in skeletal muscle transiently enhances DNA accretion and growth. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton-Davis, E.; Shoturma, D.I.; Musaro, A.; Rosenthal, N.; Sweeney, H.L. Viral mediated expression of IGF-I blocks the aging-related loss of skeletal muscle function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, H.J.; Mukerji, P.; Tisdale, M.J. Attenuation of proteasome-induced proteolysis in skeletal muscle by {beta}-hydroxy-{beta}-methylbutyrate in cancer-induced muscle loss. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Aversa, Z.; Alamdari, N.; Castillero, E.; Muscaritoli, M.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Hasselgren, P. β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) prevents dexamethasone-induced myotube atrophy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girón, M.D.; Vílchez, J.D.; Salto, R.; Manzano, M.; Sevillano, N.; Campos, N.; Argilès, J.M.; Rueda, R.; Lòpez-Pedrosa, J.M. Conversion of leucine to β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate by α-keto isocaproate dioxygenase is required for a potent stimulation of protein synthesis in L6 rat myotubes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornasio, R.; Riederer, I.; Butler-Browne, G.; Mouly, V.; Uni, Z.; Halevy, O. Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) stimulates myogenic cell proliferation, differentiation and survival via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oktaviana, J.; Zanker, J.; Vogrin, S.; Duque, G. The Effect of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) on Sarcopenia and Functional Frailty in Older Persons: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 2019, 23, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, B.; Giusto, M.; Albanese, C.; Mennini, G.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Farcomeni, A.; Ginanni Corradini, S.; Rossi, M.; Merli, M. The Effect of 12 Weeks of β-Hydroxy-β-Methyl-Butyrate Supplementation after Liver Transplantation: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merli, M.; Berzigotti, A.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnovale, E.M. Tabella di Composizione Degli Alimenti. Istituto Nazionale della Nutrizione; EDRA: Milano, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Salvini, S.; Parpinel, M.; Gnagnarella, P.; Maisonneuve, P.; Turrini, A. Banca Dati di Composizione degli Alimenti per Studi Epidemiologici in Italia; Istituto Europeo di Oncologia: Reggio Calabria, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Acta 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campagna, F.; Montagnese, S.; Ridola, L.; Senzolo, M.; Schiff, S.; De Rui, M.; Pasquale, C.; Nardelli, S.; Pentassuglio, I.; Merkel, C.; et al. The animal naming test: An easy tool for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2017, 66, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weissenborn, K.; Ennen, J.C.; Schomerus, H.; Rückert, N.; Hecker, H. Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Vetrovsky, T.; Dadova, K.; Pallarès, J.G.; Steffl, M. Health Benefits of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) Supplementation in Addition to Physical Exercise in Older Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta- Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia from mechanism to diagnosis and treatment in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Román, E.; García-Galcerán, C.; Torrades, T.; Herrera, S.; Marìn, A.; Donate, M.; Alvarado-Tapias, E.; Malouf, J.; Nàcher, L.; Serra-Grima, R.; et al. Effects of an Exercise Programme on Functional Capacity, Body Composition and Risk of Falls in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.; Gow, P.J.; Testro, A.; Chapman, B.; Sinclair, M. Exercise physiology in cirrhosis and the potential benefits of exercise interventions: A review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, J.; Spence, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Brotto, L.; Edens, N.K.; Garvey, S.M.; Brotto, M. Cellular and physiological effects of dietary supplementation with β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) and β-alanine in late middle-aged mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holeček, M. Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation and skeletal muscle in healthy and muscle-wasting conditions. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, U.S.U.; Brook, M.S.; Selby, A.; Quinlan, J.; Boereboom, C.; Abdulla, H.; Franchi, M.; Narici, M.V.; Phillips, B.E.; Williams, J.W.; et al. A double-blind placebo controlled trial into the impacts of HMB supplementation and exercise on free-living muscle protein synthesis, muscle mass and function, in older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stout, J.R.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Fukuda, D.H.; Kendall, K.L.; Moon, J.R.; Hoffman, J.R.; Wilson, J.M.; Oliver, J.S.; Mustad, V.A. Effect of calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (CaHMB) with and without resistance training in men and women 65+ yrs: A randomized, double- blind pilot trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tateyama, M.; Naoe, H.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, K.; Narahara, S.; Tokunaga, T. Loss of skeletal muscle mass affects the incidence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: A case control study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, M.; Giusto, M.; Lucidi, C.; Giannelli, G.; Pentassuglio, I.; Di Gregorio, V.; Lattanzi, B.; Riggio, O. Muscle depletion increases the risk of overt and minimal hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a prospective study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013, 28, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Placebo Group (10 Patients) | HMB Group (14 Patients) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56 ± 4.6 | 59.2 ± 8.4 | 0.3 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 6 (60) | 9 (64.3) | 0.8 |
| Etiology of cirrhosis n (%) | 0.05 | ||
| Virus | 7(70) | 2 (14.2) | |
| Alcohol | 1 (10) | 4 (28.6) | |
| Virus + alcohol | 1 (10) | 4 (28.6) | |
| Post-Nash | 1 (10) | 4 (28.6) | |
| Esophageal varices n (%) | 0.5 | ||
| Absent | 4 (40) | 4 (28.6) | |
| F1 | 3 (30) | 5 (35.7) | |
| F2 + F3 | 3 (30) | 5 (35.7) | |
| Child–Pugh class n (%) | 0.7 | ||
| A | 9 (90) | 12 (85.8) | |
| B | 1 (10) | 2 (14.2) | |
| C | 0 | 0 | |
| MELD | 9.8 ± 3.2 | 9 ± 2.7 | 0.5 |
| PhA (°) | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 0.1 |
| Fat mass—BIA (kg) | 31.4 ± 9.9 | 26.4 ± 14 | 0.3 |
| Lean mass—BIA (kg) | 33.5 ± 7.9 | 31.8 ± 5.9 | 0.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.8 ± 4.3 | 29.6 ± 6.8 | 0.9 |
| HG (kg) | 32.4 ± 12.6 | 26.1 ± 11.3 | 0.2 |
| CST (s) | 12.2 ±5.1 | 14.2 ± 5.1 | 0.3 |
| 6MWT (m) | 387 ± 96 | 361.4 ± 68 | 0.4 |
| LFI | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.4 | 0.01 |
| PHES | −1 ± 3 | −2 ± 1.5 | 0.3 |
| ANT | 21 ± 6.5 | 17 ± 6.1 | 0.2 |
| Protein/kg consumption at T0 (gr/kg) | 0.89 ± 0.4 | 0.94 ± 0.3 | 0.8 |
| Calorie consumption at T0 (Kcal/24 h) | 1811 ± 400 | 1600 ± 338 | 0.2 |
| Diet regimen at T0 n (%) | 0.5 | ||
| Hypocaloric diet n | 9 (90) | 13 (93) | |
| Normocaloric diet n | 1 (10) | 1 (7) | |
| Hypercaloric diet n | 0 | 0 | |
| IPAQ questionnaire results n (%) | 0.4 | ||
| Inactive | 3 (30) | 5 (36) | |
| Sufficiently active | 7 (70) | 9 (64) | |
| Active | 0 | 0 |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMB GROUP (14 patients) | |||
| Lean mass/h2 (kg/h2) | 11.1 ± 1.6 | 11.1 ± 1.7 | 11.2 ± 1.6 |
| Fat mass/h2 (kg/h2) | 9.3 ± 5.2 | 9.4 ± 5.1 | 9.4 ± 4.9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.6 ± 6.8 | 29.4 ± 6.8 | 29.2 ± 6.7 |
| PhA (°) | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 4.9 ± 0.8 | 4.8 ± 0.2 |
| PLACEBO GROUP (10 patients) | |||
| Lean mass/h2 (kg/h2) | 11.3 ± 2.1 | 11.4 ± 2.1 | 11.4 ± 2 |
| Fat mass/h2 (kg/h2) | 10.7 ± 3.4 | 10.6 ± 3.8 | 10.3 ± 3.9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.9 ± 4.4 | 29.9 ± 4.3 | 29.6 ± 4.6 |
| PhA (°) | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.7 | 5.2 ± 0.7 |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMB GROUP (13 patients) | |||
| TPI (mm/h2) | 4.9 ± 1.8 | 5.4 ± 1.8 * | 5.4 ± 1.7 * |
| TWI (mm/h2) | 10.2 ± 2.5 | 10.6 ± 2.3 | 10.7 ± 2.5 |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
| PLACEBO GROUP (11 patients) | |||
| TPI (mm/h2) | 5.6 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 5.4 ± 1.3 |
| TWI (mm/h2) | 10.2 ± 2.2 | 10.2 ± 2.2 | 10.2 ± 2.3 |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMB GROUP (14 patients) | |||
| HG (kg) | 26 ± 11.3 | 28.7± 13.4 | 29.1 ± 13.4 |
| FCS (s) | 14.2 ± 5 | 11.7 ± 2.6 * | 11.7 ± 2.3 * |
| 6MWT (m) | 361.8 ± 68 | 409.4 ± 58 * | 407.3 ± 73 * |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
| PLACEBO GROUP (10 patients) | |||
| HG (kg) | 32.4 ± 12.6 | 32.6 ± 12.7 | 33.4 ± 13.5 |
| FST (s) | 12.2 ± 5.1 | 11.7 ± 4.3 | 11.7 ± 4 |
| 6MWT (m) | 387 ± 97 | 405 ± 72 | 396 ± 63 |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMB GROUP (14 patients) | |||
| Liver Frailty Index | 4.1 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 0.4 * | 3.6 ± 0.6 * |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | |
| PLACEBO GROUP (10 patients) | |||
| Liver Frailty Index | 3.5 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lattanzi, B.; Bruni, A.; Di Cola, S.; Molfino, A.; De Santis, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; Merli, M. The Effects of 12-Week Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Single-Blind Pilot Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072296
Lattanzi B, Bruni A, Di Cola S, Molfino A, De Santis A, Muscaritoli M, Merli M. The Effects of 12-Week Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Single-Blind Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072296
Chicago/Turabian StyleLattanzi, Barbara, Angelo Bruni, Simone Di Cola, Alessio Molfino, Adriano De Santis, Maurizio Muscaritoli, and Manuela Merli. 2021. "The Effects of 12-Week Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Single-Blind Pilot Study" Nutrients 13, no. 7: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072296
APA StyleLattanzi, B., Bruni, A., Di Cola, S., Molfino, A., De Santis, A., Muscaritoli, M., & Merli, M. (2021). The Effects of 12-Week Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Single-Blind Pilot Study. Nutrients, 13(7), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072296








