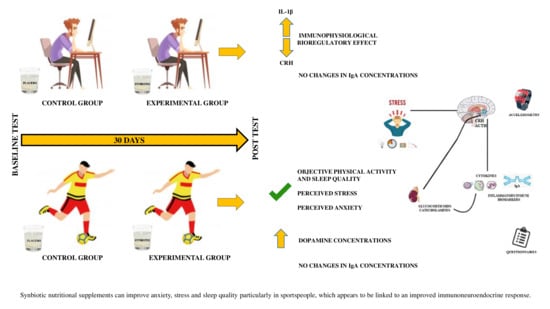
Differential Health Effects on Inflammatory, Immunological and Stress Parameters in Professional Soccer Players and Sedentary Individuals after Consuming a Synbiotic. A Triple-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
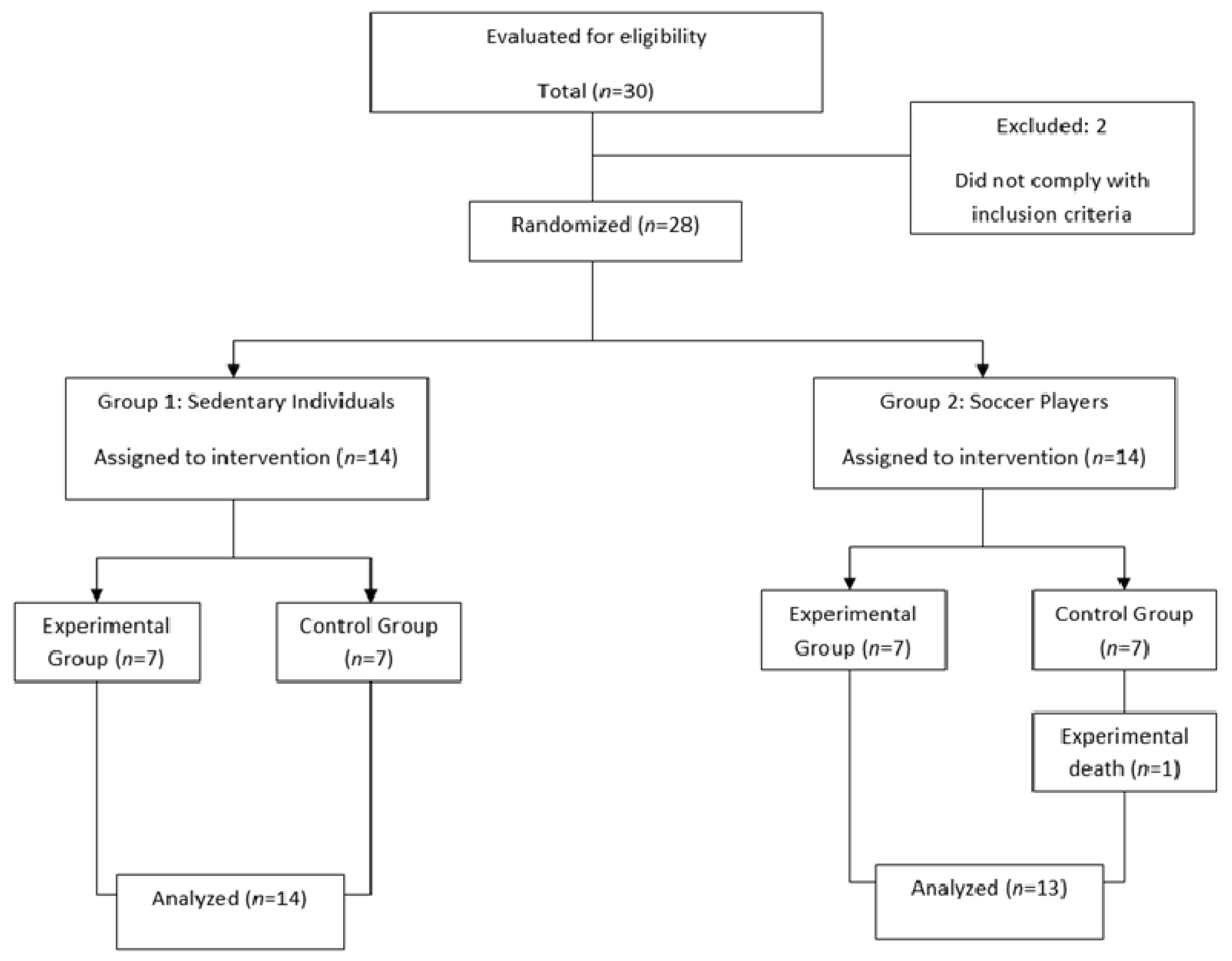
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Synbiotic
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Objective Determination of Levels of Physical Activity, Sedentary Lifestyle, and Sleep Quality: Accelerometry
2.5. Determination of Perceived Levels of General Health, Stress, Anxiety, Fatigue, Depression, and Sleep Quality: Questionnaires
2.6. Blood and Saliva Sampling
2.7. Determination of Metabolic Profile
2.8. Determination of Immuno-Neuroendocrine Parameters
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Effects of the Synbiotic on Physical Activity Levels, Sedentary Lifestyle, and Sleep Quality Objectively Determined by Accelerometry
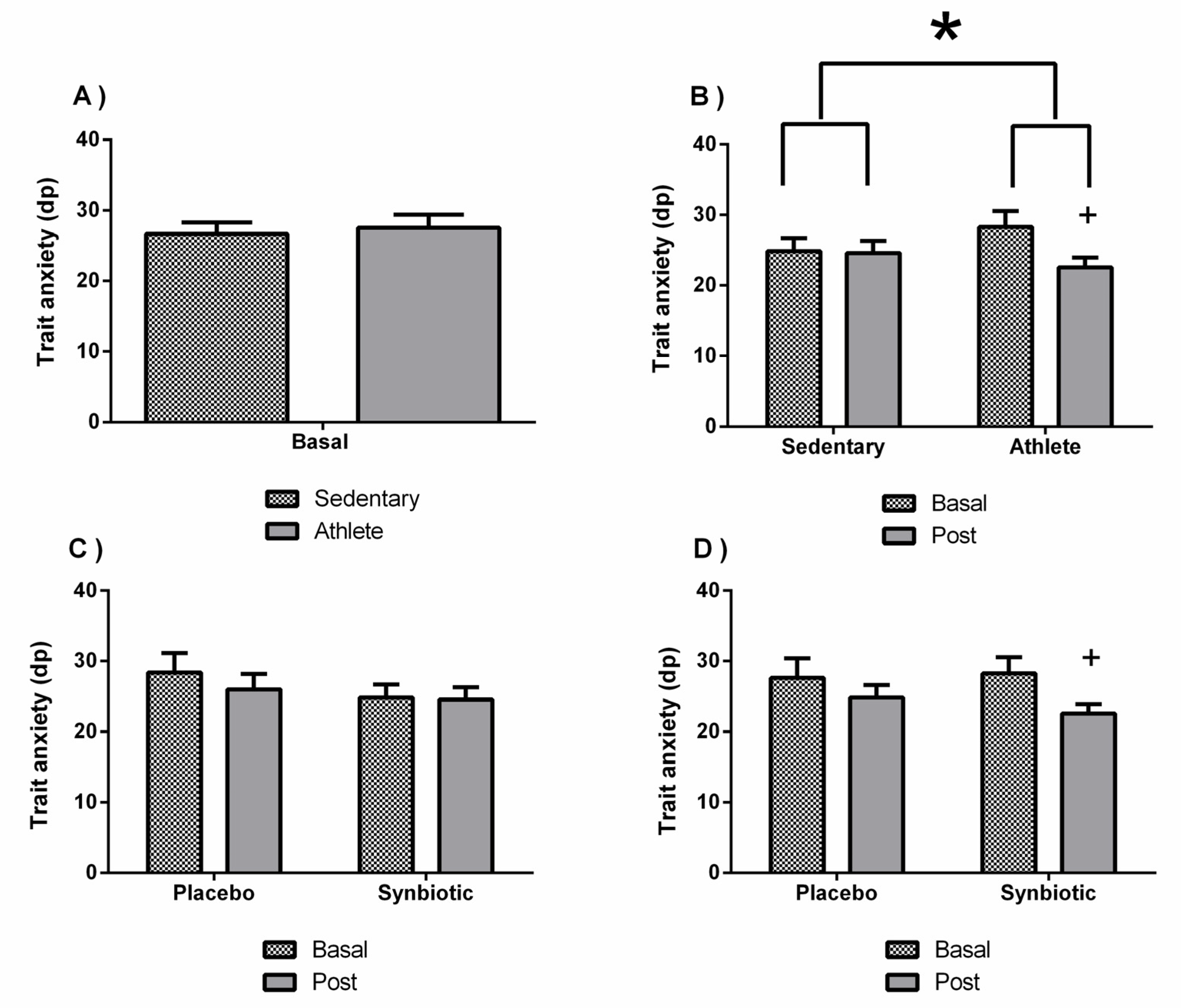
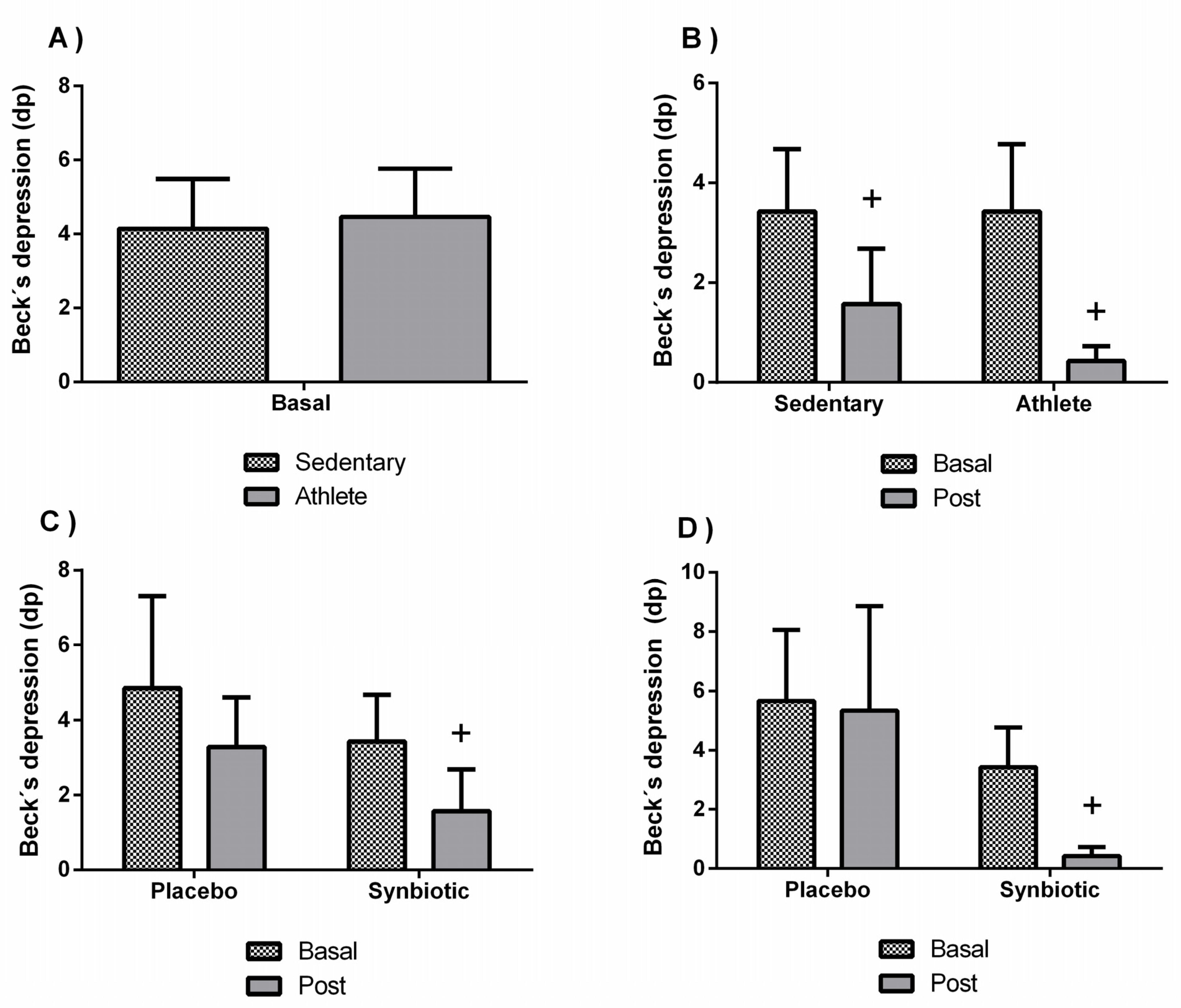
3.2. Effects of the Synbiotic on Perceived Levels of General Health, Stress, Anxiety, Fatigue, Depression, and Sleep Quality
3.3. Effects of the Synbiotic on Metabolic Profile
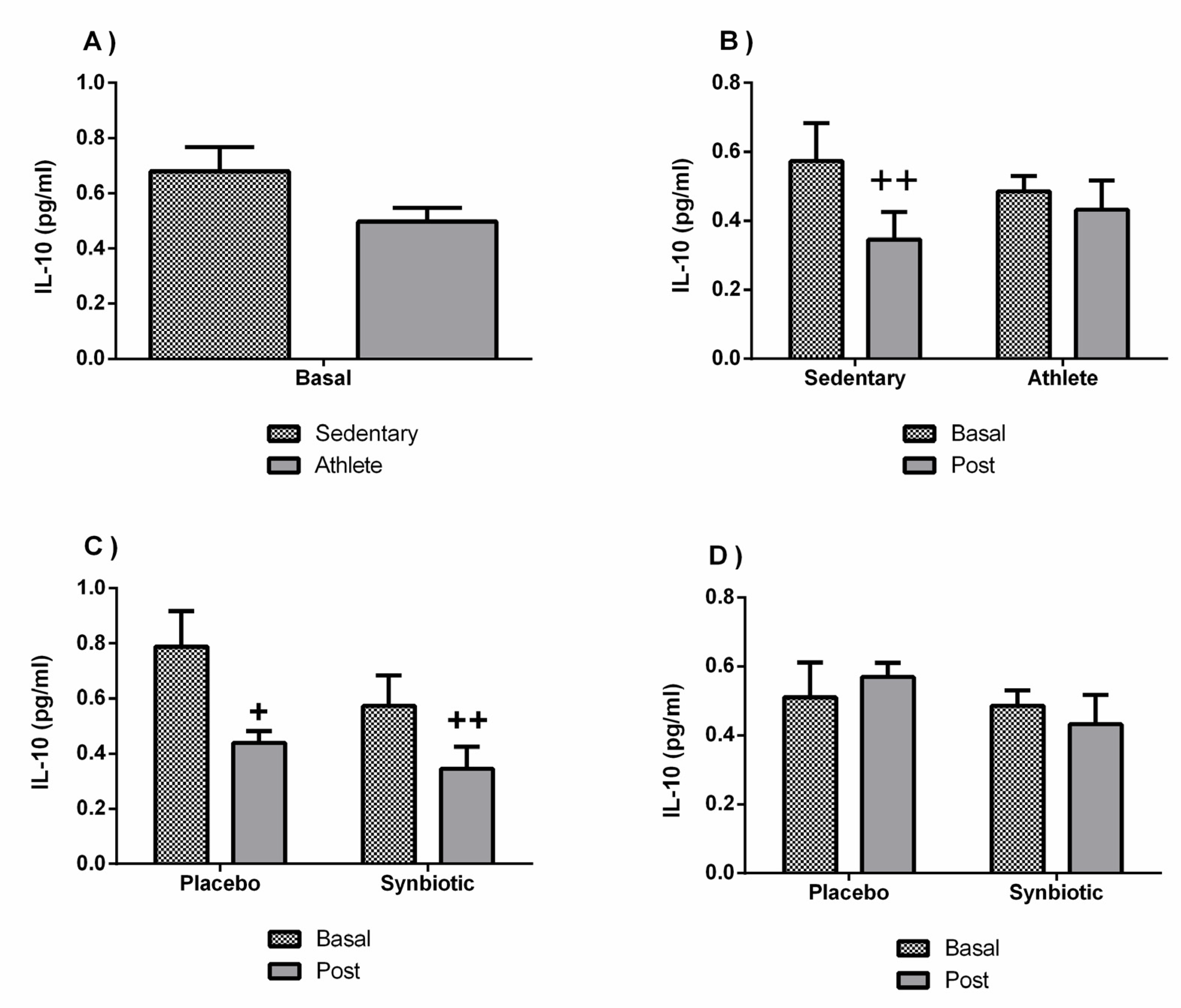
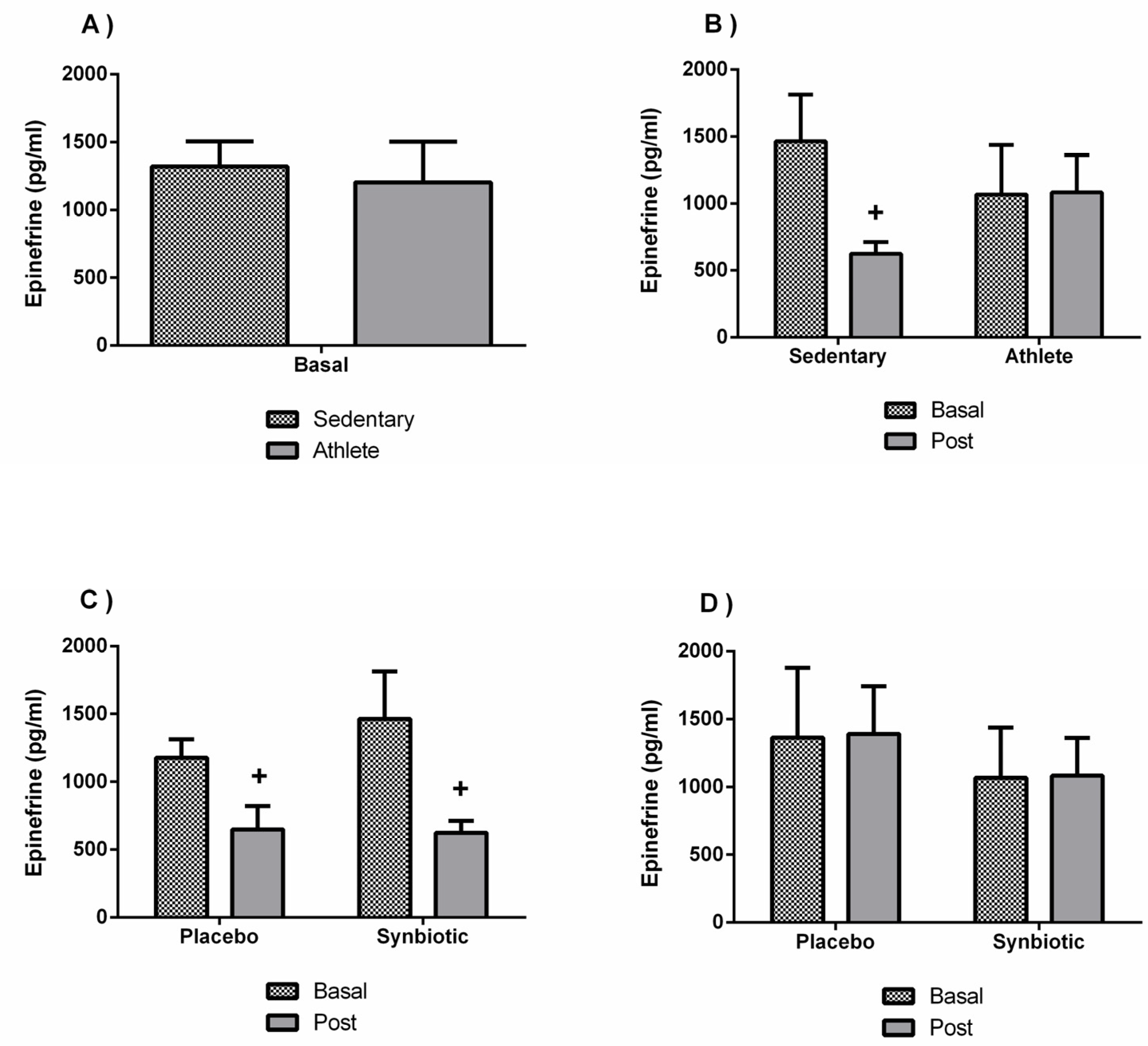
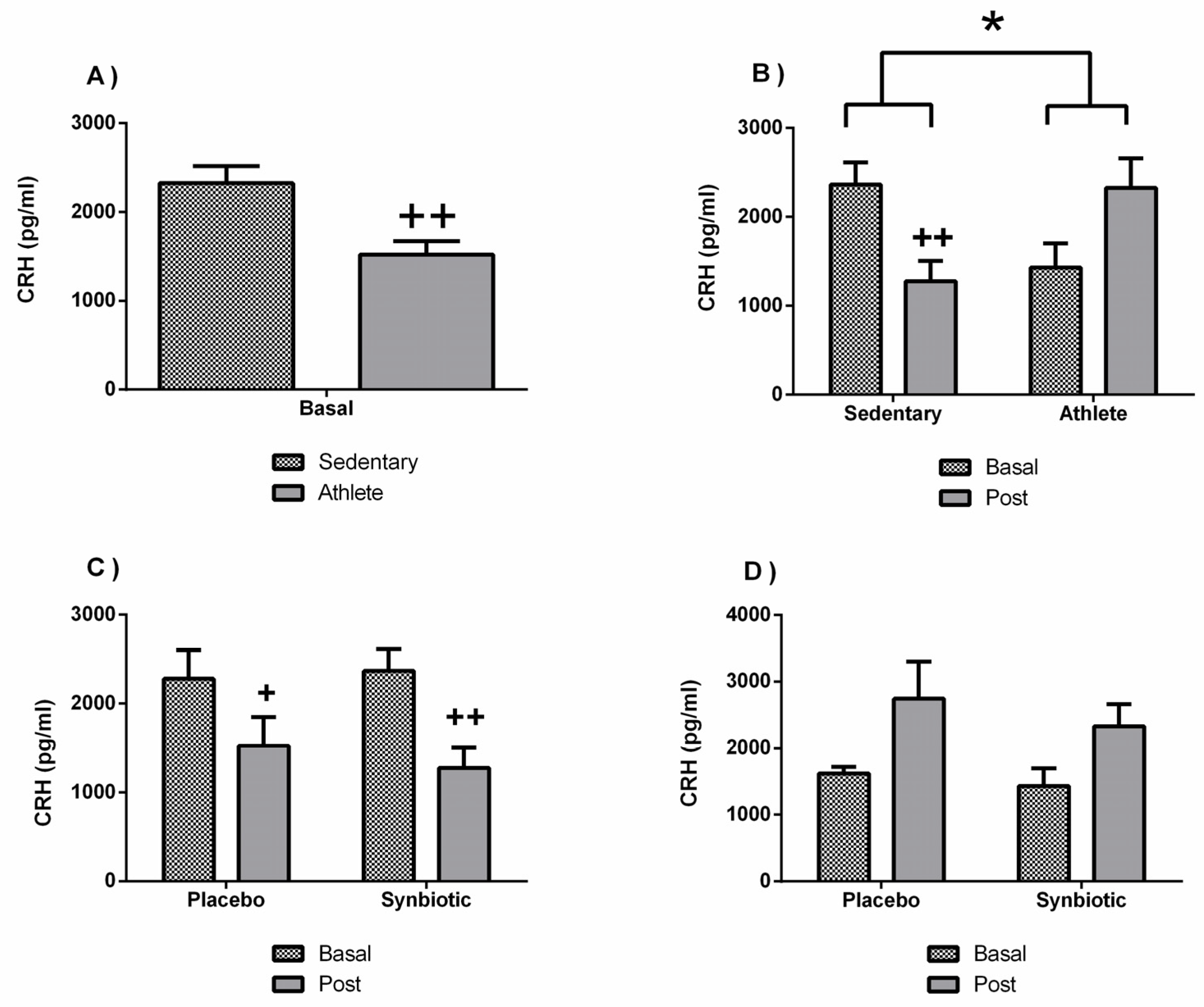
3.4. Effects of the Synbiotic on Inflammatory, Immunological, and Stress Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleeson, M.; Nieman, D.C.; Pedersen, B.K. Exercise, nutrition and immune function. J. Sports Sci. 2004, 22, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, R.L.; Gleeson, M.; Cox, A.; Callister, R.; Dorrington, M.; D’este, C.; Pang, G.; Pyne, D.; Fricker, P.; Henriksson, A. Reversal in fatigued athletes of a defect in interferon? Secretion after administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekkonen, R.A.; Vasankari, T.J.; Vuorimaa, T.; Haahtela, T.; Julkunen, I.; Korpela, R. The effect of probiotics on respiratory infections and gastrointestinal symptoms during training in marathon runners. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2007, 17, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A.J.; Pyne, D.B.; Saunders, P.U.; Fricker, P.A. Oral administration of the probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum VRI-003 and mucosal immunity in endurance athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, D.B.; West, N.P.; Cox, A.J.; Cripps, A.W. Probiotics supplementation for athletes-clinical and physiological effects. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, M.M.; Verdenelli, M.C.; Silvi, S.; Cecchini, C.; Gabbianelli, R.; Amadio, E.; Orpianesi, C.; Cresci, A. Knowledge and acceptance of functional foods: A preliminary study on influence of a synbiotic fermented milk on athlete health. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics 2017, 12, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cencic, A.; Chingwaru, W. The role of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and food supplements in intestinal health. Nutrients 2010, 2, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.F.; Murphy, E.F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Lucey, A.J.; Humphreys, M.; Hogan, A.; Hayes, P.; O’Reilly, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; Wood-Martin, R.; et al. Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut 2014, 63, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Mach, N. Exercise-induced stress behavior, gut-microbiota-brain axis and diet: A systematic review for athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, M.A.; Collazos, M.E.; Barriga, C.; De la Fuente, M.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Ortega, E. Effect of age on adherence and chemotaxis capacities of peritoneal macrophages. Influence of physical activity stress. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1994, 75, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E. Neuroendocrine mediators in the modulation of phagocytosis by exercise: Physiological implications. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2003, 9, 70–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, E. The “bioregulatory effect of exercise” on the innate/inflammatory responses. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 72, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, E.; Martin-Cordero, L.; Garcia, J.J.; Gerhmann, M.; Multhoff, G.; Ortega, E. Exercise-induced extracellular 72 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp72) stimulates neutrophil phagocytic and fungicidal capacities via TLR-2. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, N.P.; Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B.; Nieman, D.C.; Dhabhar, F.S.; Shephard, R.J.; Oliver, S.J.; Bermon, S.; Kajeniene, A. Position statement part two: Maintaining immune health. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 17, 64–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ortega, E.; García, J.J.; Bote, M.E.; Martín-Cordero, L.; Escalante, Y.; Saavedra, J.M.; Northoff, H.; Giraldo, E. Exercise in fibromyalgia and related inflammatory disorders: Known effects and unknown chances. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 15, 42–65. [Google Scholar]
- Martarelli, D.; Verdenelli, M.C.; Scuri, S.; Cocchioni, M.; Silvi, S.; Cecchini, C.; Pompei, P. Effect of a probiotic intake on oxidant and antioxidant parameters in plasma of athletes during intense exercise training. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.P.; Pyne, D.B.; Peake, J.M.; Cripps, A.W. Probiotics, immunity and exercise: A review. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 15, 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, A.V.; Leite, G.; Resende, A.; Blachier, F.; AH, L., Jr. Exercise, nutrition and gut microbiota: Possible links and consequences. Int. J. Sports Exerc. Med. 2017, 3, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilagut, G.; Ferrer, M.; Rajmil, L.; Rebollo, P.; Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Quintana, J.M.; Santed, R.; Valderas, J.M.; Ribera, A.; Domingo-Salvany, A.; et al. El Cuestionario de Salud SF-36 español: Una década de experiencia y nuevos desarrollos. Gac Sanit 2005, 19, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darviri, C.; Alexopoulos, E.C.; Artemiadis, A.K.; Tigani, X.; Kraniotou, C.; Darvyri, P.; Chrousos, G.P. The Healthy Lifestyle and Personal Control Questionnaire (HLPCQ): A novel tool for assessing self-empowerment through a constellation of daily activities. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gonzalez-Reigosa, F.; Martinez-Urrutia, A.; Natalicio, L.F.; Natalicio, D.S. The state-trait anxiety inventory. Interam J. Psychol. 1971, 5, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, T.R.; Wang, X.S.; Cleeland, C.S.; Morrissey, M.; Johnson, B.A.; Wendt, J.K.; Huber, S.L. The rapid assessment of fatigue severity in cancer patients: Use of the Brief Fatigue Inventory. Cancer 1999, 85, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. Beck depression inventory (BDI). Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrese, M.; Schrezenmeir, A.J. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. In Food Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, K.R.; Naik, S.R.; Vakil, B.V. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics-a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, B.; Mandal, N.C. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics-in health improvement by modulating gut microbiota: The concept revisited. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 410–420. [Google Scholar]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, Y.H.; Kim, H.I. The correlation between sleeping-time and numerical change of intestinal normal flora in psychiatric insomnia patients. Bull. Nat. Sci. Chungbuk Natl. Univ. 1987, 1, 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.E.; Kamerow, D.B. Epidemiologic study of sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders: An opportunity for prevention? JAMA 1989, 262, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerlo, P.; Sgoifo, A.; Suchecki, D. Restricted and disrupted sleep: Effects on autonomic function, neuroendocrine stress systems and stress responsivity. Sleep Med. Rev. 2008, 12, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Bisson, J.-F.; Rougeot, C.; Pichelin, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; et al. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; van Hemert, S.; Bosch, J.A.; Colzato, L.S. A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.K.; Allerton, D.M.; Ansley-Robson, P.; Hemmings, K.; Cox, M.; Costa, R.J. Does short-term high dose probiotic supplementation containing lactobacillus casei attenuate exertional-heat stress induced endotoxaemia and cytokinaemia? Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2016, 26, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.K.; Teixeira, A.M.; Rosado, F.; Cox, M.; Costa, R.J.S. High-dose probiotic supplementation containing Lactobacillus casei for 7 days does not enhance salivary antimicrobial protein responses to exertional heat stress compared with placebo. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2016, 26, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepner, Y.; Hoffman, J.R.; Shemesh, E.; Stout, J.R.; Church, D.D.; Varanoske, A.N.; Zelicha, H.; Shelef, I.; Chen, Y.; Frankel, H.; et al. Combined effect of Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 and HMB supplementation on muscle integrity and cytokine response during intense military training. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 123, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamprecht, M.; Frauwallner, A. Exercise, intestinal barrier dysfunction and probiotic supplementation. Med. Sport Sci. 2012, 59, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.P.; Pyne, D.B.; Cripps, A.; Christophersen, C.T.; Conlon, M.A.; Fricker, P.A. Gut Balance, a synbiotic supplement, increases fecal Lactobacillus paracasei but has little effect on immunity in healthy physically active individuals. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.D.; Suckling, C.A.; Peedle, G.Y.; Murphy, J.A.; Dawkins, T.G.; Roberts, M.G. An exploratory investigation of endotoxin levels in novice long distance triathletes, and the effects of a multi-strain probiotic/prebiotic, antioxidant intervention. Nutrients 2016, 8, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, I.; Torres-Piles, S.; Ortega, E. Innate/inflammatory bioregulation and clinical effectiveness of whole-body hyperthermia (balneotherapy) in elderly patients with osteoarthritis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, V.; Gleeson, M.; Folland, J.P. Salivary IgA as a risk factor for upper respiratory infections in elite professional athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Tauler, P. Daily probiotic’s (Lactobacillus casei Shirota) reduction of infection incidence in athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Jazayeri, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Solati, Z.; Mohammadpour, N.; Asemi, Z.; Adab, Z.; Djalali, M.; Tehrani-Doost, M.; Hosseini, M.; et al. The effects of probiotics on mental health and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial in petrochemical workers. Nutr. NeuroSci. 2016, 19, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, R.D.; Desbonnet, L.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome: Stress, health and disease. Mamm. Genome 2014, 25, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, L.M.; Rabelo, P.C.; Moraes, M.M.; Teixeira-Coelho, F.; Coimbra, C.C.; Wanner, S.P.; Soares, D. Physical exercise-induced fatigue: The role of serotonergic and dopaminergic systems. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenkov, I.J.; Chrousos, G.P. Stress hormones, proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, and autoimmunity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 966, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A.; Ballieux, R.E. Corticotropin-releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides in the modulation of immune function. In Psychoneuroimmunology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 429–446. [Google Scholar]




| Sedentary Individuals | Soccer Players | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Placebo (n = 7) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | Placebo (n = 6) | Synbiotic (n = 7) |
| Age (years) | 24.31 ± 3.94 | 23.04 ± 2.09 | 21.9 ± 2.77 | 20.66 ± 1.39 |
| Weight (Kg) | 79.81 ± 8.05 | 77.47 ± 13.47 | 73.95 ± 6.42 | 70.57 ± 6.75 |
| Height (cm) | 183.97 ± 7.30 | 176.23 ± 4.49 | 180.6 ± 8.57 | 178.23 ± 4.78 |
| Sedentary Individuals | Soccer Players | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 7) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | Placebo (n = 6) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | |||||
| Variable | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post |
| Kilocalories (Kcal/week) | 12,185.89 ± 3052.62 | 10,031.14 ± 209.75 ** | 9971.39 ± 6062.77 | 10,311.45 ± 6416.28 | 8485.81 ± 1572.13 | 8706.6 ± 2808.90 | 7856.41 ± 1619.90 | 8359.98 ± 1590.97 * |
| METS (mL O2/kg × min) | 1.52 ± 0.13 | 1.44 ± 0.10 * | 1.43 ± 0.21 | 1.46 ± 0.24 | 1.4 ± 0.08 | 1.46 ± 0.16 | 1.37 ± 0.08 | 1.49 ± 0.16 * |
| MVPA (min) | 1289.85 ± 332.09 | 1036.57 ± 188.80 * | 1081.28 ± 458.38 | 1081.14 ± 525.82 | 1091.66 ± 257.39 | 1103.16 ± 316.51 | 949.28 ± 231 | 952.85 ± 227.19 |
| Steps (total/week) | 81866 ± 11,746.98 | 66,338.85 ± 7987.85 | 70,175 ± 17,506.86 | 67,588 ± 20,406.6 | 73,096 ± 13,529.34 | 68,058.66 ± 13,787.82 | 65,676 ± 11,799.4 | 689,48.42 ± 12,447.45 |
| Sedentary bouts (>1 min) | 112.42 ± 17.92 | 104 ± 16.32 | 113.71 ± 27.34 | 114.14 ± 22.32 | 132.83 ± 22.65 | 114.16 ± 34.74 | 127 ± 10.36 | 120 ± 9.52 |
| Sleep Latency (min) | 1.12 ± 0.64 | 1.58 ± 0.83 | 1.91 ± 1.19 | 1.55 ± 1.22 | 0.87 ± 0.49 | 0.67 ± 0.49 | 1.38 ± 0.97 | 0.88 ± 0.74 * |
| Sleep efficiency (%) | 87.75 ± 2.87 | 87.23 ± 3.64 | 91.44 ± 3.16 | 91.04 ± 2.18 | 89.19 ± 3.31 | 89.6 ± 2.45 | 87.46 ± 6.09 | 90.8 ± 3.17 * |
| Sedentary Individuals | Soccer Players | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 7) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | Placebo (n = 6) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | |||||
| Variable | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post |
| SF-36 | 78.38 ± 13.82 | 79.2 ± 12.89 | 77.34 ± 8.62 | 79.45 ± 8.78 | 79.36 ± 9.95 | 80.72 ± 11.39 | 81.21 ± 9.01 | 88.5 ± 5.96 ** |
| Sleep Quality (HLPCQ) | 5.28 ± 2.42 | 5.14 ± 1.06 | 6.14 ± 1.95 | 5.71 ± 2.13 | 5.16 ± 2.78 | 5.66 ± 3.14 | 5.71 ± 2.21 | 6.42 ± 1.98 |
| State anxiety (STAI) | 30.14 ± 3.28 | 30.57 ± 3.9 | 27 ± 4.54 | 27.28 ± 3.45 | 29 ± 5.25 | 29.83 ± 2.71 | 30.85 ± 6.86 | 26.28 ± 6.57 |
| Brief Fatigue Inventory (BFI) | 2.92 ± 2.12 | 3.38 ± 2.04 | 2.98 ± 1.78 | 1.72 ± 0.63 | 5.55 ± 3.01 | 3.43 ± 2.53 | 3.5 ± 2.2 | 2.45 ± 1.92 |
| Sedentary Individuals | Soccer Players | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 7) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | Placebo (n = 6) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | |||||
| Variable | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 82 ± 6.45 | 79.71 ± 7.25 | 87.42 ± 9.6 | 81.85 ± 9.33 | 89 ± 6.09 | 86.33 ± 6.05 | 88.28 ± 7.88 | 83.57 ± 6.39 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 169.28 ± 20.61 | 169.57 ± 15.95 | 154.71 ± 31.23 | 154.14 ± 29.82 | 143.5 ± 17.09 | 141 ± 28.93 | 171.14 ± 22.93 | 164.85 ± 21.25 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 96.85 ± 37.72 | 80.42 ± 33.52 | 60.14 ± 23.83 | 60 ± 27.09 | 40.83 ± 19.34 | 56.16 ± 31.13 | 61.85 ± 23.31 | 78.71 ± 44.35 |
| Sedentary Individuals | Soccer Players | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 7) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | Placebo (n = 6) | Synbiotic (n = 7) | |||||
| Variable | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post | Basal | Post |
| Cortisol (µg/dL) | 16.53 ± 5.45 | 15.43 ± 5.19 | 14.6 ± 5.12 | 14.39 ± 6.29 | 16.29 ± 7.29 | 16.92 ± 4.4 | 10.65 ± 6.57 | 14.49 ± 4.74 |
| ACTH (pg/mL) | 869.07 ± 657.69 | 512.01 ± 250.23 | 848.29 ± 481.56 | 839.96 ± 515.46 | 733.82 ± 369.02 | 834.72 ± 389.89 | 1000.21 ± 802.89 ± | 953.68 ± 531.82 |
| Serotonin (ng/mL) | 34.19 ± 58.38 | 35.19 ± 72.27 | 29.17 ± 20.92 | 15.23 ± 16.32 | 98.09 ± 123.3 * | 79.06 ± 95.94 | 171.3 ± 211.99 * | 81.35 ± 85.81 |
| Norepinephrine (pg/mL) | 3766.19 ± 429.55 | 3410.59 ± 573.88 | 3937.12 ± 348.35 | 3474.2 ± 340.75 | 3964.81 ± 355.3 | 3874.09 ± 416.97 | 4085.99 ± 171.22 | 3743.15 ± 391.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quero, C.D.; Manonelles, P.; Fernández, M.; Abellán-Aynés, O.; López-Plaza, D.; Andreu-Caravaca, L.; Hinchado, M.D.; Gálvez, I.; Ortega, E. Differential Health Effects on Inflammatory, Immunological and Stress Parameters in Professional Soccer Players and Sedentary Individuals after Consuming a Synbiotic. A Triple-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041321
Quero CD, Manonelles P, Fernández M, Abellán-Aynés O, López-Plaza D, Andreu-Caravaca L, Hinchado MD, Gálvez I, Ortega E. Differential Health Effects on Inflammatory, Immunological and Stress Parameters in Professional Soccer Players and Sedentary Individuals after Consuming a Synbiotic. A Triple-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041321
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuero, Carmen Daniela, Pedro Manonelles, Marta Fernández, Oriol Abellán-Aynés, Daniel López-Plaza, Luis Andreu-Caravaca, María Dolores Hinchado, Isabel Gálvez, and Eduardo Ortega. 2021. "Differential Health Effects on Inflammatory, Immunological and Stress Parameters in Professional Soccer Players and Sedentary Individuals after Consuming a Synbiotic. A Triple-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study" Nutrients 13, no. 4: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041321
APA StyleQuero, C. D., Manonelles, P., Fernández, M., Abellán-Aynés, O., López-Plaza, D., Andreu-Caravaca, L., Hinchado, M. D., Gálvez, I., & Ortega, E. (2021). Differential Health Effects on Inflammatory, Immunological and Stress Parameters in Professional Soccer Players and Sedentary Individuals after Consuming a Synbiotic. A Triple-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients, 13(4), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041321