Abstract
Background: Intestinal failure (IF) is defined as reduction in functioning gut mass below the minimal amount necessary for adequate digestion and absorption. In most cases, IF results from intrinsic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (digestive IF) (DIF); few cases arise from digestive vascular components, gut annexed (liver and pancreas) and extra-digestive organs or from systemic diseases (non-digestive IF) (NDIF). The present review revised etiology and treatments of DIF and NDIF, with special focus on the pathophysiological mechanisms, whereby NDIF develops. Methods: We performed a comprehensive search of published literature from January 2010 to the present by selecting the following search strings: “intestinal failure” OR “home parenteral nutrition” OR “short bowel syndrome” OR “chronic pseudo-obstruction” OR “chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction” OR “autoimmune enteropathy” OR “long-term parenteral nutrition”. Results: We collected overall 1656 patients with well-documented etiology of IF: 1419 with DIF (86%) and 237 with NDIF (14%), 55% males and 45% females. Among DIF cases, 66% had SBS and among NDIF cases 90% had malabsorption/maldigestion. Conclusions: The improved availability of diagnostic and therapeutic tools has increased prevalence and life expectancy of rare and severe diseases responsible for IF. The present review greatly expands the spectrum of knowledge on the pathophysiological mechanisms through which the diseases not strictly affecting the intestine can cause IF. In view of the rarity of the majority of pediatric IF diseases, the development of IF Registries is strongly required; in fact, through information flow within the network, the Registries could improve IF knowledge and management.
1. Introduction
The term “intestinal failure” (IF) was defined originally by Fleming and Remington in 1981 to describe a state of “reduction in functioning gut mass below the minimal amount necessary for adequate digestion and absorption of food” [1]. Therefore, according to IF guidelines in adults, a “decreased absorption of macronutrients and/or water and electrolytes due to loss of gut function and need for Parenteral Nutrition (PN) should be both simultaneously present to define IF [2]. In children, IF derives from several diseases needing PN guaranteeing at least 75% of caloric requirements for not less than 1 month or at least 50% for not less than 3 months [3].
In most cases, IF is caused by diseases intrinsic to the gastrointestinal tract (digestive IF); few cases arise from digestive vascular components, gut annexed (liver and pancreas) and extra-digestive organs or from systemic diseases (non-digestive IF) [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The distinction between digestive IF (DIF) and non-digestive IF (NDIF) was first reported in a survey on Home Parenteral Nutrition (HPN) by the French group in 2007 [4] and confirmed in a later survey by the same group in 2016 [25].
Despite the multiplicity of diseases recognized as causes of IF, the pathophysiological mechanisms through which they trigger the gastrointestinal dysfunction are few and are common to DIF and NDIF. Three main pathophysiological mechanisms are recognized in children: short bowel syndrome (SBS), dysmotility and malabsorption/maldigestion. SBS derives from reduced intestinal length following neonatal or post-neonatal resections due to congenital or acquired gut diseases [26]. Dysmotility includes each disorder of muscular layers or enteric nervous system impeding the physiologic flux of intestinal content [15]. Finally, malabsorption/maldigestion derives from bowel pathologies not related with reduced length or impaired enteric muscular or nervous system [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,18,19,20,21,23]. While it is clear how DIF can develop from diseases directly affecting the intestine, it is instead less obvious and recognized how NDIF could develop. Furthermore, NDIF is generally the consequence of rare diseases beginning early in childhood and poorly understood. Therefore, we planned the present review to revise etiology and treatments of DIF and NDIF, with special focus on the pathophysiological mechanisms whereby NDIF develops.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
We performed a comprehensive search of published literature from January 2010 to the present on the PubMed database by selecting the following search strings: “intestinal failure” OR “home parenteral nutrition” OR “short bowel syndrome” OR “chronic pseudo-obstruction” OR “chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction” OR “autoimmune enteropathy” OR “long-term parenteral nutrition”. References retrieved from pertinent articles were also included.
Results were filtered according to:
(a) Age: 0–18 years; (b) Species: Humans; (c) Language: English.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
(1) SBS, dysmotility and malabsorption/maldigestion deriving from disorders of digestive vascular components, gut annexed organs (liver and pancreas) and extra-digestive organs or from systemic diseases and,
(2) Documented PN treatments.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
(1) Unclear primary diagnosis;
(2) PN started as exclusive nutritional support without mention of underlying gastrointestinal dysfunction;
(3) Duplicate articles from the same center.
Three authors (AD, GC, ES) separately screened the studies for eligibility. Articles were screened in two stages. First, titles and abstracts were reviewed to identify potentially relevant articles. Full texts of those abstracts which met the inclusion criteria were retrieved and independently reviewed in the second stage of the assessment.
2.4. Data Extraction, Synthesis and Analysis
Data obtained from the selected articles were gathered and entered into tables. The following information was collected: author; year; publication; Country; patients’ number; gender; primary diseases for each IF case.
2.5. Endpoints
(1) Primary endpoints were etiology of DIF and NDIF and pathophysiological mechanisms whereby NDIF develops;
(2) Secondary endpoint was the therapeutic strategy of IF.
Etiology of DIF and NDIF was based on the systematic literature search; pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment strategies were drawn from articles included in the systematic review as well as from further pertinent and relevant papers.
3. Results
The systematic literature search identified 935 potentially relevant articles that matched the search criteria (see Figure 1). After considering our inclusion and exclusion criteria 38 articles were selected (See Figure 1 and Table 1) and 2052 patients were collected. However, all cases where etiology was unclear and where PN was used as nutritional support, not clearly needed for gastro-intestinal dysfunction, were excluded. In detail we collected overall 1656 patients with well-documented etiology of IF: 1419 with DIF (86%) and 237 with NDIF (14%), 55% males and 45% females. Etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms in DIF and NDIF are reported in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively; as shown, 66% of all cases of DIF were due to SBS while 90% of all cases of NDIF derived from malabsorption/maldigestion.
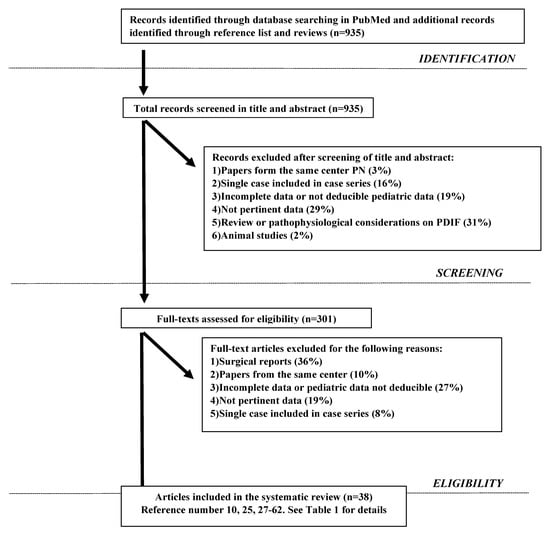
Figure 1.
Search Strategy.

Table 1.
Summary of the studies selected for the review.

Table 2.
Summary of the causes of Digestive Intestinal Failure (DIF).

Table 3.
Summary of the causes of Non-digestive Intestinal Failure (NDIF).
3.1. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of NDIF
3.1.1. Intestinal Fistulas
Interestingly, our review identified only one patient with high-output fistula as cause of NDIF. The patient was a 15-year-old boy with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with history of chronic constipation who developed megacolon, intestinal perforation and post-operative multiple entero-cutaneous fistulas. The high output from fistula required long-term PN [30]. This is the first case of IF due to fistula in children; however, it could be argued that the true cause of IF was the severe dysmotility complicated by intestinal perforation and entero-cutaneous fistula [30].
3.1.2. Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS)
Mesenteric ischemia. Interrupted blood flow in a bowel area supplied by superior or inferior mesenteric artery can result in intestinal infarction and necrosis needing resection, often causing SBS. Mesenteric ischemia can derive from thromboembolic occlusion or vasospasm and it can be confused with necrotizing enterocolitis. Cardiac and abdominal surgery are the main triggers for non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia [63,64,65,66,67]. Kawasaki disease [50] has also been reported as cause of mesenteric occlusive ischemia in a 7-month-old infant. This infant developed digestive symptoms (diarrhea and vomiting) up to clear signs and symptoms of abdominal obstruction combined with bilious vomiting and imaging of small-bowel occlusion with superior mesenteric and splenic ischemia. He underwent intestinal resection with reduced bowel length which caused SBS with long-term dependence on PN.
Meconium ileus. It is the earliest clinical manifestation of cystic fibrosis, which presents as neonatal bowel obstruction of the distal small bowel in a subset of infants with severe cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulatory mutations and pancreatic insufficiency [68]. In the simple form, viscid meconium physically obstructs terminal ileum that induces small intestine obstruction and dilation [68]. In the complex form the dilation is complicated by prenatal volvulus, ischemic necrosis, intestinal atresia, or perforation and extrusion of the meconium into the peritoneum [68]. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulatory is responsible for both Cl−and HCO3–excretion; HCO3–plays a relevant role in chelating Ca2+ associated with the tight matrix of normally exocytosed mucins within the gut lumen, contributing to form normal and well-hydrated mucus [69]. Abnormal cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulatory results in abnormal HCO3 secretion and consequent decreased luminal pH. This creates an acidic and dehydrated environment in which the tight matrix of exocytosed mucins is not disrupted appropriately, resulting in thick and dehydrated mucus [69]. The abnormally acidic luminal environment also increases stool albumin, minerals and protein-bound carbohydrates [68,69,70].
Multiple atresia. Multiple intestinal atresia, early bowel inflammation and severe combined immunodeficiency have been found associated to tetratricopeptide repeat domain 7A mutations [32,54,71,72,73,74,75]. Proteins encoded by tetratricopeptide repeat domain 7A are involved in polarization and differentiation of intestinal and likely thymic epithelial cells; mutations in this domain dysregulate the distribution of α-integrin and actin in the epithelial surface, leading to tissue architecture disorganization from fetal stage [71]. Multiple intestinal atresia and stenosis requires early surgery and intestinal resection causing SBS [54,71,73,74].
3.1.3. Dysmotility
Esophageal dysmotility, gastric outlet obstruction, small-bowel obstruction. This pattern of dysmotility can occur in patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis, a digestive disorder characterized by gastric and intestinal eosinophilic infiltration. Clinical phenotypes can differ according to gut layers at highest eosinophilic infiltration [76]. Muscle layer infiltration, ranging from 13 to 70% of all cases, affects stomach and duodenum and it can result in gastrointestinal occlusion and short term IF [76]. Chronic granulomatous disease involves digestive tracts in up to 50% of all cases leading, in some cases, to esophageal dysmotility, gastric outlet obstruction and small-bowel obstruction requiring short term PN [77].
Alternating diarrhea and constipation. Neonatal onset of alternating diarrhea and constipation episodes can cause IF as recognized in MEDNIK (mental retardation, enteropathy, deafness, neuropathy, ichthyosis and keratodermia) syndrome [78]. MEDNIK syndrome combines clinical and biochemical signs of the two classic disorders of copper metabolism: Menkes’s disease and Wilson’s disease [78,79].
Recurrent paralytic ileus. Gitelman syndrome, an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder with chronic hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, hypocalciuria and hypomagnesemia, can be cause of recurrent paralytic ileus [80]. In the present review two patients had recurrent paralytic ileus due to Gitelman’s syndrome [29]. Interestingly the present review identified a single case of electrolytes imbalance resulting in recurrent paralytic ileus following chronic diuretics administration in the context of pediatric falsification in Munchausen by proxy [29]. The need for increasingly invasive means of nutritional support due to intestinal dysfunction has indeed been reported as a potential feature of pediatric falsification [81].
Severe MRGE delayed gastric emptying and jejunal dysmotility. Amyoplasia, the most common form of arthrogryposis due to fatty–fibrous replacement of muscle [82], can be complicated by severe neuro-enteric dysfunction, which needs increasingly invasive means of nutritional support up to PN. [29]. Sanjad-Sakati syndrome is instead an autosomal recessive disorder which causes hypoparathyroidism, recurrent hypocalcemia, recurrent paralytic ileus, congenital growth retardation, seizures and typical facial dysmorphism [29,61]. It has been found associated to early development of IF requiring PN in one young girl [29].
Pediatric intestinal pseudo-obstruction (PIPO). PIPO has been reported associated to the Sanjad-Sakati syndrome [61] (see above) as well as to the Treacher Collins syndrome, which is caused by mutations in genes involved in neuroepithelial apoptosis during embryogenesis [38]. The child with Treacher Collins syndrome has been reported in the present review to have nutritional difficulties and digestive intolerance since birth; PIPO was suspected during childhood based on jejunal feeding intolerance and need for total PN. Histopathological confirmation was achieved on surgical rectal findings that showed enlarged ganglionic myenteric plexus [38]. The second patient with PIPO affected by Sanjad-Sakati syndrome was firstly evaluated for intermittent abdominal distension, bilious vomiting, and constipation when he was 6 years old. Plain abdominal radiographs and contrast barium swallow with follow-through showed dilated loops of intestine. Then, he underwent laparotomy due to increasing abdominal distension and respiratory difficulty, that excluded any identifiable structural causes of obstruction [61]. Histopathology found fibrotic changes of the longitudinal smooth muscle layer consistent with visceral myopathy. The child had satisfactory weight gain and maintained metabolic balance with total PN [61].
3.1.4. Malabsorption/Maldigestion
Protein losing enteropathy (PLE). PLE is the most common pathophysiological mechanism leading to IF for malabsorption/maldigestion. PLE can occur in the context of primary or secondary disorders of lymphatics, which causes leakage of protein-rich chyle into the intestinal lumen, enteric protein loss, hypoalbuminemia, hypoproteinemia, lymphopenia, low fat-soluble vitamins deficiency and increased concentration of fecal α1-antitrypsin [19,20,21]. Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia is the congenital dilation of intestinal lymphatics [27,83,84]. The first case was reported by Waldmann et al. [27,85]; since then, nearly 200 cases of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia have been globally reported [27,83,86]. The classical symptoms are bilateral or unilateral lower limb edema, intermittent diarrhea, steatorrhea and fat-soluble vitamin deficiency, but pleural effusion or ascites can also develop [86]. Intestinal lymphangiectasia in Hennekam syndrome can also include genitalia and face edema, facial dysmorphisms and mental retardation [87]. Fontan pathway obstruction, pulmonary artery branch stenosis, increased pulmonary vascular resistance, elevated atrial pressures related to atrio-ventricular-valve regurgitation, arrhythmias and diastolic dysfunction can cause lymphatics dilation due to high systemic venous pressure, generally in infants younger than 3 years old [19,21,88,89]. Interestingly, following Fontan operation leakage of liver lymph through dilated hepato-duodenal lymphatic connections in duodenum has been also demonstrated [90]. Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD) can develop as complication of allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) [91,92] and is a further cause of PLE. Acute GVHD most commonly involves skin, liver and gastrointestinal tract in up to 60% of patients [93,94,95]. Gastrointestinal involvement may result in PLE and persistent anorexia, secretory diarrhea, abdominal pain and/or hemorrhage [96,97]. Furthermore, the subtype of eosinophilic gastroenteritis, involving only the mucosa layer of the gut can lead to PLE [76]. Finally, congenital disorders of glycosylation, a heterogeneous group of rare genetic disorders due to defects in protein, lipid or proteoglycan glycosylation, may present as severe PLE [98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105].
Autoimmune enteropathy. Autoimmune enteropathy has now been recognized as part of more complex pictures of immunodeficiency, such as immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) [49] and therefore, it may be regarded as cause of NDIF [24]. In the past autoimmune enteropathy has been considered instead a form of DIF; in such perspective Unsworth and Walker-Smith first described a sub-group of infants with severe and protracted diarrhea, not responding to dietary restriction, with circulating gut autoantibodies and/or associated autoimmune diseases and lack of severe immunodeficiency [106]. In the present review two patients with autoimmune enteropathy were affected by IPEX, a primary immunodeficiency caused by mutations in FOXP3 gene, which encodes an essential transcription factor required for maintenance of thymus-derived regulatory T cells [107]. IPEX occurs in infancy with type-1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia and a variety of skin lesions, including eczema, ichthyosiform dermatitis, psoriatic dermatitis and alopecia universalis [107]. Protracted high-volume diarrhea, due to autoimmune enteropathy, is generally the major presenting feature [107].
Inflammation. Primary immunodeficiency can lead to IF by severe inflammation. In particular, tetratricopeptide repeat domain 7A mutations [32,54] (see also above) can cause severe exfoliate apoptotic enterocolitis and perianal fistula responding to steroids [32]. Furthermore, chronic inflammation is often seen in patients with chronic granulomatous disease (see above) and it is related to exuberant and persistent tissue granuloma formation [108,109,110], clinically and radiographically indistinguishable from Crohn’s disease [109,111,112,113,114]. Cystic fibrosis patients can also develop non-specific intestinal inflammation. The non-functional cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulatory on the apical membrane of secretory and absorptive epithelial cells decreases chloride and water secretion resulting in precipitation of secretions, intra-ductal obstructions, inflammation, tissue damage, and fibrosis [115]. Capsule endoscopy can show mucosal ulceration and erythema [116,117].
Intractable osmotic diarrhea. Osmotic intractable diarrhea (stool anion gap > 50, fecal pH < 6 and fasting test positive) [118] can occur in enteric anendocrinosis and enteric dysendocrinosis. Enteric anendocrinosis is due to mutations in Neurogenin-3, a basic helix-loop-helix transcriptional factor that drives the development of endocrine cell in both the pancreas and intestine [119,120,121]. These mutations cause lacking intestinal entero-endocrine cells [39] and early or later presentation of diabetes mellitus [119,120,121]. Enteric dysendocrinosis is caused by mutations of the gene encoding for prohormone convertase 1/3, a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease essential for the conversion of prohormones in the bioactive form. It is expressed in endocrine cells in the gut, in arcuate and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus, and in β-cells of the pancreas, where it has a well-defined role in processing proinsulin. Neonates with nonfunctional prohormone convertase 1/3 show IF and additional endocrine abnormalities such as diabetes insipidus, growth hormone deficiency, primary hypogonadism, adrenal insufficiency, and hypothyroidism [53].
3.2. Management
The main thread of nutritional strategy in any case of IF is to integrate the maximum tolerated amount of Enteral Nutrition (EN) with the ongoing PN support. The objective of nutritional work-up should be reaching intestinal autonomy, which depends on the type of IF. From a prognostic point of view Shaffer et al. defined as Type I IF an acute, short-term, and usually self-limiting condition [3]. Type II is instead considered as prolonged acute condition, requiring complex multi-disciplinary care and PN over weeks or months. It is possible that some forms of Type II IF may evolve in Type III IF. Type III IF, also called chronic IF, occurs in metabolically stable patients, who require PN over months or years and may be reversible or irreversible [2].
The strategies to treat/improve/revert IF may be summarized as follows:
(1) Specific treatments that could reverse the underlying disease responsible for IF (e.g., hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in primary immunodeficiency);
(2) Treatments allowing to improve/revert the pathophysiological mechanism leading to IF (e.g., nutritional treatments, steroids and octreotide in PLE);
(3) Treatments for chronic DIF and NDIF able to reduce PN dependency over time (e.g., analog of glucagon like peptide 2 and surgical procedures to increase mucosal surface area in SBS or prokinetic drugs in PIPO [15,21,22,26,27,29,49,62,81,82,83,84,85,86,90,122,123,124]
The advances in EN tolerance over time and the progressive decreasing in calories and fluids provided by PN will be the clinical markers of successful application of specific and non-specific therapies.
In Table 4 we report the main therapeutic options available to combine with nutritional management in DIF and NDIF.

Table 4.
Therapeutic approach in Intestinal Failure.
4. Discussion
The present review provides new insights on NDIF only occasionally and not systematically focused on literature. We observed that overall, 14% of patients require prolonged PN treatments due to diseases not strictly inherent to intestine. In 2007 Colomb and coll [3] found a prevalence of NDIF of 24%; this survey included, nevertheless, patients without clear intestinal dysfunction but requiring PN as nutritional support as well as patients with metabolic diseases, probably including mitochondrial disorders, now considered as causes of DIF [15]. Mitochondrial disorders are multi-systemic diseases affecting predominantly organs or systems with high-energy metabolism such as central nervous system, heart and skeletal muscle [125]. Gastrointestinal complaints could be gastrointestinal dysmotility, gastroparesis, progressive intestinal pseudo-obstruction, abdominal pain, dilation and dysmotility of the oesophagus, stomach and the small intestines, and malabsorption with progressive malnutrition [126]. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy, the prototype of mitochondrial IF with pseudo-obstruction, is a rare autosomal recessive disease due to defects in the thymidine phosphorylase gene, encoding the enzyme responsible for the conversion of deoxynucleosides (deoxythymidine and deoxyuridine) [127]. Pathological accumulation of deoxythimidine and deoxyuridine leads to the typical manifestations of the disease [127,128]. Digestive symptoms are early satiety, nausea, vomiting, dysphagia, gastro-esophageal reflux, abdominal pain and pseudo-obstruction or diarrhea, probably due to dysfunctional network of intestinal Cajal cells, that is the pacemakers of the gut [126].
A more recent survey by the French Group [25] found a prevalence of NDIF of 14%. Therefore, from an epidemiological perspective we can conclude that the prevalence of NDIF may be established as for more than 10%.
In more general terms the prevalence of pediatric IF has dramatically increased over time. Previous papers reported IF prevalence ranging from 2 and 6.8 per 1,000,000 of inhabitants in developed Countries [13,128,129]. In Italy in 2016, we observed prevalence and incidence of 14.12 and 1.41 par million inhabitants ≤19 years, respectively [36]. A comparable trend has been demonstrated in UK where IF prevalence has risen from 4.4/million in 1993 to 13.9/million in 2010 and to 14.5/million in 2012 [130].
Management of IF requires a close interplay between several actors in a multidisciplinary scenario where technical skills should be shared to offer the best and most tailored treatment to each patient. Nutritional work-up is only a part of the complex management of IF patients and it does not differ between DIF and NDIF. IF patients have highly specialized needs, and their care should be provided by centers of excellence providing sufficient surgical, medical, dietetic and nursing expertise to treat long-term IF and home parenteral nutrition (HPN) [36]. HPN should be proposed as soon as possible to the family when indicated [36]. IF patients who have developed severe complications that make PN unsafe should be cared in centers with expertise in IF and intestinal transplantation [131,132].
Over the last 25 years, the outcome of IF has transformed from almost certain death in childhood to a high chance of survival into adult life, even when still PN-dependent [133]. Therefore, the challenge is now to find therapeutic approaches able to reduce the dependency on PN over time. Relevant advances in the most recent years, have been seen in the field of immunodeficiencies and SBS, together accounting for the 63.5% of all causes of IF in the present review.
It is now known that many forms of autoimmune enteropathy, in the past considered as causes of DIF, are clinical manifestations of primary immunodeficiency [24]. The main curative treatment of IF combined with immunodeficiency is the hematopoietic stem cells transplantation [49]; therefore, the prognosis of autoimmune enteropathies has strongly changed, because PN is now considered as bridge to hematopoietic stem cells transplantation and not as a long-term treatment as in the past [24].
Furthermore, surgery and hormonal therapy have enriched the therapeutic armamentarium of SBS.
The impact of surgery on weaning off PN was assessed by a recent systematic literature review [122]. It found that surgery has low benefit in terms of intestinal adaptation and therefore it should not be proposed to all patients with SBS, but only to selected candidates. Main requirements to refer for surgery should be radiologically evident bowel dilation associated with signs or symptoms of small bowel bacterial overgrowth, such as failure of advancing enteral nutrition and poor growth. Early signs of intestinal failure-associated liver disease (IFALD) should also be considered, if associated with intestinal dilation, as a factor in favor of eligibility for surgery [122].
Clinical trials have proven safety, tolerability, and efficacy of the recombinant form of GLP-2 in the treatment of SBS-intestinal failure in children [123,134]. In the first published case series, outside clinical trials, Ramos Boluda et al. [135] reported a substantial improvement in the outcome for SBS children and they considered their outcome even better than that reported in the paediatric clinical pivotal study. Therefore, in the future, surgery and hormonal therapy, tailored on the single patient, could be promising strategies to improve the prognosis of SBS.
5. Conclusions
The improved availability of diagnostic and therapeutic tools has increased both the prevalence and life expectancy of rare and severe diseases responsible for IF. Current knowledge about pathophysiological mechanisms of the diseases has led to identify previously unrecognized extra-digestive causes of IF. The present review greatly expands the spectrum of knowledge on the pathophysiological mechanisms through which the diseases not strictly affecting the intestine can cause IF. In view of the rarity of the majority of pediatric IF diseases, the development of IF Registries is strongly required; in fact, through information flow within the network the Registries could not only improve the knowledge about the causes of IF, but also allow management to be shared.
Author Contributions
All authors actively participated in the research and in the article preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We thank Lorenzo Guglielmi for editing and reviewing the English language.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fleming, C.R.; Remington, M. Intestinal failure. In Nutrition and the Surgical Patient; Hill, G.L., Ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1981; pp. 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- Pironi, L.; Arends, J.; Bozzetti, F.; Cuerda, C.; Gillanders, L.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Joly, F.; Kelly, D.; Lal, S.; Staun, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on chronic intestinal failure in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 247–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, G.; Barabino, A.; Gambarara, M.; Diamanti, A.; Martelossi, S.; Guarino, A. Network approach to the child with primary intestinal failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, S61–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomb, V.; Dabbas-Tyan, M.; Taupin, P.; Talbotec, C.; Révillon, Y.; Jan, D.; De Potter, S.; Gorski-Colin, A.-M.; Lamor, M.; Herreman, K.; et al. Long-term Outcome of Children Receiving Home Parenteral Nutrition: A 20-year Single-center Experience in 302 Patients. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 44, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrin, G.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Passariello, A.; Elce, A.; Amato, F.; Di Costanzo, M.; Castaldo, G.; Canani, R.B. Congenital Diarrheal Disorders: An Updated Diagnostic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4168–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canani, R.B.; Pezzella, V.; Amoroso, A.; Cozzolino, T.; Di Scala, C.; Passariello, A. Diagnosing and treating intolerance to carbohydrates in children. Nutrients 2016, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Schwerd, T.; Koletzko, S.; Shah, N.; Kammermeier, J.; Elkadri, A.; Ouahed, J.; Wilson, D.C.; Travis, S.P.; Turner, D.; et al. The Diagnostic Approach to Monogenic Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 990–1007.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriati, T.; Cardile, S.; Papadatou, B.; Romano, C.; Knafelz, D.; Bracci, F.; Diamanti, A. Pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: Specificity of very early onset. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Hébuterne, X.; Van Gossum, A.; Messing, B.; Lyszkowska, M.; Colomb, V.; Forbes, A.; Micklewright, A.; Villares, J.M.M.; Thul, P.; et al. Candidates for Intestinal Transplantation: A Multicenter Survey in Europe. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hizarcioglu-Gulsen, H.; Saltik-Temizel, I.N.; Demir, H.; Gurakan, F.; Ozen, H.; Yuce, A. Intractable diarrhea of infancy: 10 years of experience. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker-Smith, J.A. Intractable diarrhea of infancy. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 1, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Catassi, C.; Fabiani, E.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Barera, G.; Guarino, A. Severe and protracted diarrhea: Results of the 3-year SIGENP multicenter survey. Working Group of the Italian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology (SIGENP). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 29, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, A.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Russo, S.; Albano, F.; Guandalini, S.; Capano, G.; Cucchiara, S.; Vairano, P.; Liguori, R.; Casola, A.; et al. Etiology and Risk Factors of Severe and Protracted Diarrhea. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1995, 20, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, N.S.; Kang, I.S.; Suh, Y.L. Protracted Diarrhea: Results of the Five-year Survey in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapar, N.; Saliakellis, E.; Benninga, M.A.; Borrelli, O.; Curry, J.; Faure, C.; De Giorgio, R.; Gupte, G.; Knowles, C.H.; Staiano, A.; et al. Pediatric intestinal pseudo-obstruction: Evidence and consensus-based rec-ommendations from an ESPGHAN-Led expert group. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 991–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, K.H. Parenteral nutrition use in children with cancer. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e28000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Honda, M.; Yoshii, D.; Isono, K.; Hayashida, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Inomata, Y. Living Donor Liver Transplantation for Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 1: Two Reported Cases. Transpl. Proc. 2017, 49, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecke, A.R.; Heinz-Erian, P.; Müller, T. Congenital Sodium Diarrhea: A Form of Intractable Diarrhea, With a Link to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braamskamp, M.J.; Dolman, K.M.; Tabbers, M.M. Clinical practice. Protein-losing enteropathy in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Lloyd, D.R.; Williams, M.D.; Darbyshire, P.J.; Booth, I.W. Gastrointestinal and nutritional sequelae of bone marrow transplantation. Arch. Dis. Child. 1996, 75, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Johnson, J.N.; Driscoll, D.J.; O’Leary, P.W. Protein-Losing Enteropathy and the Fontan Operation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutanen, A.; Wales, P.W. Etiology and prognosis of pediatric short bowel syndrome. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 27, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posovszky, C. Congenital intestinal diarrheal diseases: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, P.M.; Cutz, E.; Goulet, O. Immune and autoimmune enteropathies. Ann. Nestlé 2006, 64, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, E.A.; Lambe, C.; Talbotec, C.; Pigneur, B.; Lacaille, F.; Garnier-Lengliné, H.; Petit, L.-M.; Poisson, C.; Rocha, A.; Corriol, O.; et al. Outcome of home parenteral nutrition in 251 children over a 14-y period: Report of a single center. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O.; Ruemmele, F.; Lacaille, F.; Colomb, V. Irreversible Intestinal Failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Srivastava, A.; Tambe, A. Clinical profile, response to therapy, and outcome of children with primary intes-tinal lymphangiectasia. Dig. Dis. 2019, 37, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRusso, K.; Schaack, G.; Fung, T.; McGregor, K.; Long, J.; Dumas, M.P.; Attari, Z.; Yousef, Y.; Girgis, H.; Raghunathan, R. Should you pick the PICC? Prolonged use of peripherally inserted central venous catheters in children with intestinal failure. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti, A.; Fusaro, F.; Caldaro, T.; Capriati, T.; Candusso, M.; Nobili, V.; Borrelli, O. Pediatric Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction: Impact of Neonatal and Later Onset on Clinical and Nutritional Outcomes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemrani, B.; McLeod, E.; Rogers, E.; Lawrence, J.; Feldman, D.; Evans, V.; Shalley, H.; Bines, J. Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: An Unusual Cause of Chronic Intestinal Failure in a Child. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, e14–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, Y.Z.; Bunster, M.I.H.; Bayón, M.L.C.; Osiac, L.R.; Lorca, J.C.; Reus, G.A.; Antilef, R.M.; Balboa, P.; Cors, C.; De la Fuente, G. Home parenteral nutrition in pediatric patients with intestinal insufficiency. Rev. Chil. Pediatría 2019, 90, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Fayard, J.; Collardeau, S.; Bertrand, Y.; Cordier, M.-P.; Malcus, C.; Dubois, R.; Mure, P.-Y.; Basile, G.D.S.; Louazon, T.; Rohmer, B.; et al. TTC7A mutation must be considered in patients with repeated intestinal atresia associated with early inflammatory bowel disease: Two new case reports and a literature review. Archives de Pédiatrie 2018, 25, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, B.P.; Hazekamp, C.; Samnaliev, M.; Ozonoff, A. Analysis of healthcare institutional costs of pediatric home parenteral nu-trition central line infections. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, e77–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnar, R.; Lumia, M.; Pakarinen, M.; Merras-Salmio, L. Children With Intestinal Failure Undergoing Intestinal Rehabilitation Are at Risk for Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merras-Salmio, L.; Mutanen, A.; Ylinen, E.; Rintala, R.; Koivusalo, A.; Pakarinen, M.P. Pediatric Intestinal Failure: The Key Outcomes for the First 100 Patients Treated in a National Tertiary Referral Center During 1984-2017. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, A.; Capriati, T.; Gandullia, P.; Di Leo, G.; Lezo, A.; Lacitignola, L.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Gatti, S.; D’Antiga, L.; Verlato, G.; et al. Pediatric chronic intestinal failure in Italy: Report from the 2016 survey on be-half of Italian society for gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition (SIGENP). Nutrients 2017, 9, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blotte, C.; Styers, J.; Zhu, H.; Channabasappa, N.; Piper, H.G. A comparison of Broviac® and peripherally inserted central catheters in children with in-testinal failure. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giabicani, E.; Lemale, J.; Dainese, L.; Boudjemaa, S.; Coulomb, A.; Tounian, P.; Dubern, B. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in a child with Treacher Collins syndrome. Arch. Pédiatrie 2017, 24, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germán-Díaz, M.; Rodriguez-Gil, Y.; Cruz-Rojo, J.; Charbit-Henrion, F.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Manzanares, J.M.-L.; Moreno-Villares, J.M. A New Case of Congenital Malabsorptive Diarrhea and Diabetes Secondary to Mutant Neurogenin-3. Pediatr. 2017, 140, e20162210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, J.; Daoud, Y.; Styers, J.; Journeycake, J.M.; Channabasappa, N.; Piper, H.G. Central venous thrombosis in children with intestinal failure on long-term parenteral nutrition. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stýblová, J.; Kalousová, J.; Adamcová, M. Paediatric home parenteral nutrition in the Czech Republic and its devel-opment: Multicentre retrospective study 1995–2011. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 71, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimura, Y.; Morioka, I.; Hisamatsu, C.; Yokoyama, N.; Taniguchi-Ikeda, M.; Yokozaki, H.; Murayama, K.; Ohtake, A.; Itoh, K.; Takeshima, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex IV deficiency complicated with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in a neonate. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, S.; Ahmed, N.; Forget, S. Outcomes of patients with intestinal failure after the development and implementa-tion of a multidisciplinary team. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pichler, J.; Watson, T.; McHugh, K.; Hill, S. Prevalence of Gallstones Compared in Children With Different Intravenous Lipids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabel-Chambaud, E.; N’Guyen, M.; Valdeyron, M.L. Dramatic increase of associated complications in children with intestinal failure. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 815–819. [Google Scholar]
- Mezoff, E.A.; Fei, L.; Troutt, M.; Klotz, K.; Kocoshis, S.A.; Cole, C.R. Ethanol Lock Efficacy and Associated Complications in Children With Intestinal Failure. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelis, E.G.; Roskott, A.M.; Dijkstra, G. Presentation of a nation wide multicenter registry of intestinal failure and intes-tinal transplantation. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, J.; Simchowitz, V.; Macdonald, S. Comparison of liver function with two new/mixed intravenous lipid emul-sions in children with intestinal failure. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, A.D.; Goyal, A.; Davison, J.M.; Regueiro, M.D.; Roche, R.L.; Ranganathan, S. Pediatric autoimmune enteropathy: An entity frequently associated with immunodeficiency disorders. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 27, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godart, F.; Bakhti, O.M.; Bonnevalle, M. Intestinal ischaemia as a severe presentation of Kawasaki disease leading to short-bowel syndrome. Cardiol. Young 2014, 24, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duro, D.; Mitchell, P.D.; Mehta, N.M. Variability of resting energy expenditure in infants and young children with intes-tinal failure-associated liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney-Martin, G.; Kosar, C.; Campbell, A.; Avitzur, Y.; Wales, P.W.; Steinberg, K.; Harrison, D.; Chambers, K. Plasma Aluminum Concentrations in Pediatric Patients Receiving Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.G.; Lindberg, I.; Solorzano-Vargas, R.S. Congenital proprotein convertase 1/3 deficiency causes malabsorptive diarrhea and other endocrinopathies in a pediatric cohort. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, E.M.; Majewski, J.; Alirezaie, N.; Fernandez, I.; Casals, F.; Patey, N.; Decaluwe, H.; Gosselin, I.; Haddad, E.; Hodgkinson, A.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies mutations in the geneTTC7Ain French-Canadian cases with hereditary multiple intestinal atresia. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubesie, A.C.; Heubi, J.E.; Kocoshis, S.A.; Henderson, C.J.; Mezoff, A.G.; Rao, M.B.; Cole, C.R. Vitamin D Deficiency and Low Bone Mineral Density in Pediatric and Young Adult Intestinal Failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derepas, C.; Kosar, C.; Avitzur, Y.; Wales, P.W.; Courtney-Martin, G. Decreased Bone Turnover Markers in Children on Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) for Intestinal Failure (IF). J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 39, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlier, C. Helping children who require long-term parenteral nutrition. Nurs. Child. Young People 2013, 25, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieroni, K.P.; Nespor, C.; Ng, M. Evaluation of ethanol lock therapy in pediatric patients on long-term parenteral nutri-tion. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javid, P.J.; Malone, F.R.; Bittner, R. The optimal timing of referral to an intestinal failure program: The relationship be-tween hyperbilirubinemia and mortality. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti, A.; Bizzarri, C.; Basso, M.S. How does long-term parenteral nutrition impact the bone mineral status of chil-dren with intestinal failure? J. Bone Miner Metab. 2010, 28, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, K.; Moammarb, H.; Mitra, D.K. Visceral myopathy causing chronic intestinal pseudo obstruction and intestinal failure in a child with Sanjad-Sakati syndrome. J. Ped. Surg. 2010, 45, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, J.; Prajapati, P.; Ogola, G.; Channabasappa, N.; Drews, B.; Piper, H.G. Predicting time to full enteral nutrition in children after significant bowel resection. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcos, O.; Nuzzo, A. Gastro-Intestinal Vascular Emergencies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boley, S.J.; Brandt, L.J.; Sammartano, R.J. History of mesenteric ischemia. The evolution of a diagnosis and management. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 77, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, D.G.; Beach, J.M. Mesenteric Ischemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, I.A.; Swenson, O. Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion in Infancy and Childhood. N. Engl. J. Med. 1960, 263, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebra, A.; Brown, M.F.; Hirschl, R.B.; McGeehin, K.; O’Neill, J.A.; Norwood, W.I.; Ross, A.J. Mesenteric ischemia in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1993, 28, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, M.; Houwen, R. Meconium ileus in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, S32–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyle, B.E.; Borowitz, D.S.; Glick, P.L. A review of pathophysiology and management of fetuses and neonates with meco-nium ileus for the pediatric surgeon. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 47, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.A.; Yang, N.; Quinton, P.M. Normal mouse intestinal mucus release requires cystic fibrosis transmembrane regula-tor-dependent bicarbonate secretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigorgne, A.E.; Farin, H.F.; Lemoine, R.; Mahlaoui, N.; Lambert, N.; Gil, M.; Schulz, A.; Philippet, P.; Schlesser, P.; Abrahamsen, T.G.; et al. TTC7A mutations disrupt intestinal epithelial apicobasal polarity. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, I.; Patey, N.; Marchand, V.; Birlea, M.; Maranda, B.; Haddad, E.; Decaluwe, H.; Le Deist, F. Multiple Intestinal Atresia With Combined Immune Deficiency Related to TTC7A Defect Is a Multiorgan Pathology. Medicine 2014, 93, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Giliani, S.; Lanzi, G. Whole-exome sequencing identifies tetratricopeptide repeat domain 7A (TTC7A) muta-tions for combined immunodeficiency with intestinal atresias. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammermeier, J.; Dziubak, R.; Pescarin, M. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of inflammatory bowel disease presenting before the age of 2 years. J. Crohns. Colitis 2017, 11, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, R.K.; Coccia, P.F.; Talmadge, J.E. Donor immune reconstitution after liver-small bowel transplantation for multi-ple intestinal atresia with immunodeficiency. Blood 2004, 103, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkara, T.; Rawla, P.; Yarlagadda, K.S.; Gaduputi, V. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: Diagnosis and clinical perspectives. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Mayer, L. Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Disorders in Patients With Primary Immunodeficiency. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, D.; Travaglini, L.; Drouin, C.A. MEDNIK syndrome: A novel defect of copper metabolism treatable by zinc acetate therapy. Brain 2013, 136, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, D.; Dionisi-Vici, C. AP1S1 defect causing MEDNIK syndrome: A new adaptinopathy associated with defective copper metabolism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1314, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, U.; Lakkas, Y.; Asole, D. Gitelman’s syndrome presenting as recurrent paralytic ileus due to chronic renal tub-ular K+ wasting. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2010, 58, 322–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, P.E.; Bursch, B.; Beck, D. Discriminating pediatric condition falsification from chronic intestinal pseu-do-obstruction in toddlers. Child Maltreat 2002, 7, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.G.; Aldinger, K.A.; Tanaka, K.I. Amyoplasia Revisited. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164, 700–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kong, M.-S. Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia diagnosed by endoscopy following the intake of a high-fat meal. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 167, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, H.J.; Nimmo, M. Intestinal lymphangectasia in adults. World J. Gastrointest Oncol. 2011, 3, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Steinfeld, J.L.; Dutcher, T.F.; Davidson, J.D.; Gordon, R.S., Jr. The role of the gastrointestinal system in “idio-pathic hypoproteinemia”. Gastroenterology 1961, 41, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Tang, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W. Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia: Four case reports and a review of the litera-ture. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 3466–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siham, A.S.; Rawahi, Y.A.J.; Abdoon, H. Octreotide in Hennekam syndrome-associated intestinal lymphangiectasia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6333–6337. [Google Scholar]
- Al Balushi, M.D.A.; Andrew, S. Mackie. Protein-Losing Enteropathy Following Fontan Palliation. Canadian. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Itkin, M.; Piccoli, D.A.; Nadolski, G.; Rychik, J.; DeWitt, A.; Pinto, E.; Rome, J.; Dori, Y. Protein-Losing Enteropathy in Patients With Congenital Heart Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Yamagami, T.; Kato, T.; Hirota, T.; Yoshimatsu, R.; Masunami, T.; Nishimura, T. The effectiveness of lymphangiography as a treatment method for various chyle leakages. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, J.L.; Levine, J.E.; Reddy, P.; Holler, E. Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet 2009, 373, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratwohl, A.; Baldomero, H.; Passweg, J.F.; Frassoni, F.; Niederwieser, D.; Schmitz, N.; Urbano-Ispizua, A. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological malignancies in Europe. Leukemia 2003, 17, 941–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsohn, D.A.; Vogelsang, G.B. Acute graft versus host disease. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassereddine, S.; Rafei, H.; Elbahesh, E.; Tabbara, I. Acute Graft Versus Host Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, M.; Wang, Z.; Horowitz, M.M.; Gale, R.P. 2013 report from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Trans-plant Research (CIBMTR): Current uses and outcomes of hematopoietic cell transplants for blood and bone marrow disorders. Clin. Transpl. 2013, 8, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, P.J.; McDonald, G.B.; Sanders, J.E. Increasingly frequent diagnosis of acute gastrointestinal graft-versus-host dis-ease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004, 10, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fløisand, Y.; Lazarevic VLAertens, J. Safety and effectiveness of Vedolizumab in patients with steroid-refractory gas-trointestinal acute graft-versus-host disease: Retrospective Record Review. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeken, J.; Péanne, R. What is new in CDG? J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeze, H.H.; Aebi, M. Altered glycan structures: The molecular basis of congenital disorders of glycosylation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damen, G.; De Klerk, H.; Huijmans, J.; Hollander, J.D.; Sinaasappel, M. Gastrointestinal and Other Clinical Manifestations in 17 Children With Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation Type Ia, Ib, and Ic. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, Y.S.; Bode, L.; Freeze, H.H.; Leebeek, F.W.; Zandbergen, A.A.; Wilson, J.P. Using heparin therapy to reverse protein-losing enteropathy in a patient with CDG-Ib. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 5, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentilin Boyer, M.; de Lonlay, P.; Seta, N. Failure to thrive and intestinal diseases in congenital disorders of glycosyla-tion. Arch. Pediatr. 2003, 10, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeken, J.; Matthijs, G.; Saudubray, J.-M.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Bertini, E.; De Lonlay, P.; Henri, H.; Carchon, H.; Schollen, E.; Van Schaftingen, E. Phosphomannose Isomerase Deficiency: A Carbohydrate-Deficient Glycoprotein Syndrome with Hepatic-Intestinal Presentation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altassan, R.; Péanne, R.; Jaeken, J.; Barone, R.; Bidet, M.; Borgel, D.; Brasil, S.; Cassiman, D.; Cechova, A.; Coman, D.; et al. International clinical guidelines for the management of phosphomannomutase 2-congenital disorders of glycosylation: Diagnosis, treatment and follow up. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čechová, A.; Altassan, R.; Borgel, D.; Bruneel, A.; Correia, J.; Girard, M.; Harroche, A.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Mohnike, K.; Pascreau, T.; et al. Consensus guideline for the diagnosis and management of mannose phosphate isomerase-congenital disorder of glycosylation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 671–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, D.J.; Walker-Smith, J.A. Autoimmunity in Diarrhoeal Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1985, 4, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetta, R.; Barzaghi, F.; Roncarolo, M.-G. From IPEX syndrome to FOXP3 mutation: A lesson on immune dysregulation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1417, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano, B.E.; Rosenzweig, S.D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Anderson, V.L.; Darnell, D.N.; Anaya-O’Brien, S.; Hilligoss, D.M.; Malech, H.L.; Gallin, J.I.; Holland, S.M. Gastrointestinal Involvement in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, B.H.; Leto, T.L.; Gallin, J.I.; Malech, H.L.; Holland, S.M. Genetic, biochemical, and clinical features of chronic granuloma-tous disease. Medicine 2000, 79, 170–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.B., Jr. Clinical aspects of chronic granulomatous disease. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2001, 8, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, D.; Wright, V.M.; Shaw, D.G.; Raafat, F. Walker-Smith JA. Chronic granulomatous disease mimicking Crohn’s disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1985, 4, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitomi, H.; Mikami, T.; Takahashi, H. Colitis in chronic granulomatous disease resembling Crohn’s disease: Compara-tive analysis of CD68- positive cells between two disease entities. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 4, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäppi, M.G.; Klein, N.J.; Lindley, K.J.; Rampling, D.; Smith, V.V.; Goldblatt, D.; Milla, P.J. The Nature of Colitis in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 36, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.E.; Khan, A.R.; Heitlinger, L.; Allen, J.E.; Afshani, E. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood with acute ulcerative colitis: A unique association. Pediatr. Pathol. 1987, 7, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oil, C.Y.; Durie, P.R. Cystic fibrosis from the gastroenterologist’s perspective. Nat. Rev. 2016, 13, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Wilschanski, M.; Durie, P.R. Patterns of GI disease in adulthood associated with mutations in the CFTR gene. Gut 2007, 56, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werlin, S.L. Evidence of intestinal inflammation in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Gastrtroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, K.D.; Schiller, L.R. AGA Technical Review on the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Diarrhea☆. Gastroenterol. 1999, 116, 1464–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Perreault, N.; Brestelli, J.E.; Kaestner, K.H. Neurogenin 3 is essential for the proper specification of gastric enteroen-docrine cells and the maintenance of gastric epithelial cell identity. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonhoff, S.E.; Giel-Moloney, M.; Leiter, A.B. Neurogenin 3-expressing progenitor cells in the gastrointestinal tract differen-tiate into both endocrine and non-endocrine cell types. Dev. Biol. 2004, 270, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradwohl, G.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Guillemot, F. Neurogenin3 is required for the development of theour endocrine cell lineages of the pancreas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriati, T.; Mosca, A.; Alterio, T.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Gandullia, P.; Lezo, A.; Lionetti, P.; D’Antiga, L.; Fusaro, F.; Diamanti, A. To Wean or Not to Wean: The Role of Autologous Reconstructive Surgery in the Natural History of Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome on Behalf of Italian Society for Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (SIGENP). Nutrients 2020, 12, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocoshis, S.A.; Merritt, R.J.; Hill, S.; Protheroe, S.; Carter, B.A.; Horslen, S.; Hu, S.; Kaufman, S.S.; Mercer, D.F.; Pakarinen, M.P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Teduglutide in Pediatric Patients With Intestinal Failure due to Short Bowel Syndrome: A 24-Week, Phase III Study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.A.; Cole, C.R. Ultra-short bowel syndrome during infancy: Improving outcomes and novel therapies. Cur. Opin. Ped. 2019, 31, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, S.; Hirano, M. Pathogenesis and treatment of mitochondrial disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 652, 139–170. [Google Scholar]
- Finsterer, J.; Frank, M. Gastrointestinal manifestations of mitochondrial disorders: A systematic review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, I.; Spinazzola, A.; Papadimitriou, A.; Hammans, S.; Steiner, I.; Hahn, C.D.; Connolly, A.M.; Verloes, A.; Guimarães, J.; Maillard, I.; et al. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy: An autosomal recessive disorder due to thymidine phosphorylase mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, L.; Ament, M.; Fleming, C.R. Current use and clinical outcome of home parenteral and enteral nutrition thera-pies in the United States. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, L.; Heaphey, L.; Fleming, C.R.; Lininger, L.; Steiger, E. Four Years of North American Registry Home Parenteral Nutrition Outcome Data and Their Implications for Patient Management. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1991, 15, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beath, S.V.; Gowen, H.; Puntis, J.W.L. Trends in pediatric home parenteral nutrition and implications for service devel-opment. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalzell, A.M. Management of intestinal failure in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antiga, L.; Goulet, O. Intestinal failure in children: The European view. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S. Use of GLP-2 may herald a new era of iproved outcome of short bowel syndrome-associated intestinal failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, B.A.; Cohran, V.C.; Cole, C.R.; Corkins, M.R.; Dimmitt, R.A.; Duggan, C.; Hill, S.; Horslen, S.; Lim, J.D.; Mercer, D.F.; et al. Outcomes from a 12-Week, Open-Label, Multicenter Clinical Trial of Teduglutide in Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 102–111.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Boluda, E.; Redecillas Ferreiro, S.; Manrique Moral, O. Experience with teduglutide in pediatric short bowel syndrome: First real-life data. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).