Moderate Mocha Coffee Consumption Is Associated with Higher Cognitive and Mood Status in a Non-Demented Elderly Population with Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummings, J.L. Frontal-Subcortical Circuits and Human Behavior. Arch. Neurol. 1993, 50, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Bella, R.; Giuffrida, S.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, G.; Spampinato, C.; Giordano, D.; Malaguarnera, G.; Raggi, A.; Pennisi, M. Preserved Transcallosal Inhibition to Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Nondemented Elderly Patients with Leukoaraiosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 351680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizenstein, H.J.; Baskys, A.; Boldrini, M.; Butters, M.A.; Diniz, B.S.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Jellinger, K.A.; Kruglov, L.S.; Meshandin, I.A.; Mijajlovic, M.D.; et al. Vascular Depression Consensus Report—A Critical Update. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, R.; Ferri, R.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Malaguarnera, G.; Spampinato, C.; Giordano, D.; Raggi, A.; Pennisi, G. Motor Cortex Excitability in Vascular Depression. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 82, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concerto, C.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, M.; Giordano, D.; Spampinato, C.; Ricceri, R.; Pennisi, G.; Aguglia, E.; Bella, R. Different Patterns of Cortical Excitability in Major Depression and Vascular Depression: A Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Study. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.D.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Alexopoulos, G.S. The Vascular Depression Hypothesis: Mechanisms Linking Vascular Disease with Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulos, G.S. Mechanisms and Treatment of Late-Life Depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagli, C.; Fisicaro, F.; Vinciguerra, L.; Puglisi, V.; Rodolico, M.S.; Giordano, A.; Ferri, R.; Lanza, G.; Bella, R. Cerebral Hemodynamic Changes to Transcranial Doppler in Asymptomatic Patients with Fabry’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinciguerra, L.; Lanza, G.; Puglisi, V.; Pennisi, M.; Cantone, M.; Bramanti, A.; Pennisi, G.; Bella, R. Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound in Vascular Cognitive Impairment-No Dementia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, V.; Bramanti, A.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Vinciguerra, L.; Pennisi, M.; Bonanno, L.; Pennisi, G.; Bella, R. Impaired Cerebral Haemodynamics in Vascular Depression: Insights From Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, M.D.; Karlawish, J.H.; Arnold, S.E.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Khachaturian, Z.S.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Baumgart, M.; Banerjee, S.; Beck, C.; Blennow, K.; et al. Advancing Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis, Treatment, and Care: Recommendations from the Ware Invitational Summit. Alzheimers Dement. 2012, 8, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantone, M.; Catalano, M.A.; Lanza, G.; La Delfa, G.; Ferri, R.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Pennisi, G.; Bramanti, A. Motor and Perceptual Recovery in Adult Patients with Mild Intellectual Disability. Neural Plast. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Bella, R.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, G.; Ferri, R.; Pennisi, M. Cognitive Impairment and Celiac Disease: Is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation a Trait d’Union between Gut and Brain? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Capurso, C.; D’Introno, A.; Colacicco, A.M.; Santamato, A.; Ranieri, M.; Fiore, P.; Capurso, A.; Panza, F. Lifestyle-Related Factors in Predementia and Dementia Syndromes. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Panza, F.; Frisardi, V.; Seripa, D.; Logroscino, G.; Imbimbo, B.P.; Pilotto, A. Diet and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Factors or Prevention: The Current Evidence. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 677–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Logroscino, G.; Maggi, S.; Santamato, A.; Seripa, D.; Pilotto, A. Current Epidemiological Approaches to the Metabolic-Cognitive Syndrome. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 30 (Suppl. 2), S31–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.; Moll van Charante, E.P.; van Gool, W.A. Vascular Risk Factors as Treatment Target to Prevent Cognitive Decline. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 32, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, G.; Pino, M.; Fisicaro, F.; Vagli, C.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Bellomo, M. Motor Activity and Becker’s Muscular Dystrophy: Lights and Shadows. Phys. Sportsmed. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, G.; Casabona, J.A.; Bellomo, M.; Cantone, M.; Fisicaro, F.; Bella, R.; Pennisi, G.; Bramanti, P.; Pennisi, M.; Bramanti, A. Update on Intensive Motor Training in Spinocerebellar Ataxia: Time to Move a Step Forward? J. Int. Med. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Ferri, R. The Neurophysiology of Hyperarousal in Restless Legs Syndrome: Hints for a Role of Glutamate/GABA. Adv. Pharmacol. 2019, 84, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinciguerra, L.; Lanza, G.; Puglisi, V.; Fisicaro, F.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Cantone, M. Update on the Neurobiology of Vascular Cognitive Impairment: From Lab to Clinic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, F.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Ferri, R.; Pennisi, G.; Nicoletti, A.; Zappia, M.; Bella, R.; Pennisi, M. Clinical and Electrophysiological Hints to TMS in de Novo Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, L.Y.; Marzo, A.; Muñoz-Ruiz, M.; Ikram, M.A.; Kivipelto, M.; Ruefenacht, D.; Venneri, A.; Soininen, H.; Wanke, I.; Ventikos, Y.A.; et al. Modifiable Lifestyle Factors in Dementia: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Observational Cohort Studies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordet, R.; Ihl, R.; Korczyn, A.D.; Lanza, G.; Jansa, J.; Hoerr, R.; Guekht, A. Towards the Concept of Disease-Modifier in Post-Stroke or Vascular Cognitive Impairment: A Consensus Report. BMC Med. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; D’Amico, E.; Fisicaro, F.; Puglisi, V.; Vinciguerra, L.; Bella, R.; Vicari, E.; Malaguarnera, G. Acetyl-L-Carnitine in Dementia and Other Cognitive Disorders: A Critical Update. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantone, M.; Lanza, G.; Fisicaro, F.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Di Pino, G. Evaluation and Treatment of Vascular Cognitive Impairment by Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Calì, F.; Vinci, M.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Tripodi, M.; Spada, R.S.; Cantone, M.; Bella, R.; Mattina, T.; Ferri, R. A Customized Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Panel to Identify Novel Genetic Variants in Dementing Disorders: A Pilot Study. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, e8078103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Musso, S.; Borgione, E.; Scuderi, C.; Ferri, R. Early-Onset Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Dementia in an Adult with MtDNA Mutation 3316G>A. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 968–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, F.; Lanza, G.; Bella, R.; Pennisi, M. “Self-Neuroenhancement”: The Last Frontier of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation? J. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 16, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Centonze, S.S.; Destro, G.; Vella, V.; Bellomo, M.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Ciavardelli, D. Shiatsu as an Adjuvant Therapy for Depression in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pilot Study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 38, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, F.; Lanza, G.; Grasso, A.A.; Pennisi, G.; Bella, R.; Paulus, W.; Pennisi, M. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Stroke Rehabilitation: Review of the Current Evidence and Pitfalls. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, J.; Caraci, F.; Castellano, S.; Currenti, W.; Galvano, F.; Ferri, R.; Grosso, G. Association Between Dietary Flavonoids Intake and Cognitive Function in an Italian Cohort. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Currenti, W.; Angelino, D.; Mena, P.; Castellano, S.; Caraci, F.; Galvano, F.; Del Rio, D.; Ferri, R.; Grosso, G. Diet and Mental Health: Review of the Recent Updates on Molecular Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Malaguarnera, G.; Di Bartolo, G.; Lanza, G.; Bella, R.; Chisari, E.M.; Cauli, O.; Vicari, E.; Malaguarnera, M. Decrease in Serum Vitamin D Level of Older Patients with Fatigue. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Di Bartolo, G.; Malaguarnera, G.; Bella, R.; Lanza, G.; Malaguarnera, M. Vitamin D Serum Levels in Patients with Statin-Induced Musculoskeletal Pain. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 3549402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Ricceri, R.; Ferri, R.; D’Agate, C.C.; Pennisi, G.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Bella, R. Cortical Involvement in Celiac Disease before and after Long-Term Gluten-Free Diet: A Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Barulli, M.R.; Bonfiglio, C.; Guerra, V.; Osella, A.; Seripa, D.; Sabbà, C.; Pilotto, A.; Logroscino, G. Coffee, Tea, and Caffeine Consumption and Prevention of Late-Life Cognitive Decline and Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, M.J. Does Caffeine Intake Enhance Absolute Levels of Cognitive Performance? Psychopharmacology 1993, 110, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson-Kozlow, M.; Kritz-Silverstein, D.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Morton, D. Coffee Consumption and Cognitive Function among Older Adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 156, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, D.M.; Mirzaei, D.F.; Pan, D.A.; Okereke, D.O.I.; Willett, D.W.C.; O’Reilly, D.É.J.; Koenen, D.K.; Ascherio, D.A. Coffee, Caffeine, and Risk of Depression Among Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelber, R.P.; Petrovitch, H.; Masaki, K.H.; Ross, G.W.; White, L.R. Coffee Intake in Midlife and Risk of Dementia and Its Neuropathologic Correlates. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Micek, A.; Castellano, S.; Pajak, A.; Galvano, F. Coffee, Tea, Caffeine and Risk of Depression: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. Coffee and Caffeine Consumption and Depression: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2016, 50, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.D.; Pieper, C.F.; Phillips-Bute, B.G.; Bryant, J.E.; Kuhn, C.M. Caffeine Affects Cardiovascular and Neuroendocrine Activation at Work and Home. Psychosom. Med. 2002, 64, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, M.L.; Niittynen, L.; Korpela, R.; Vapaatalo, H. Coffee, Caffeine and Blood Pressure: A Critical Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgert, R.; Katan, M.B. The Cholesterol-Raising Factor from Coffee Beans. J. R. Soc. Med. 1996, 89, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amicis, A.; Scaccini, C.; Tomassi, G.; Anaclerio, M.; Stornelli, R.; Bernini, A. Italian Style Brewed Coffee: Effect on Serum Cholesterol in Young Men. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 25, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiglia, E.; Bongiovì, S.; Paleari, C.D.; Petucco, S.; Boni, M.; Colangeli, G.; Penzo, M.; Pessina, A.C. Haemodynamic Effects of Coffee and Caffeine in Normal Volunteers: A Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. J. Intern. Med. 1991, 229, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H. The Potential of Caffeine for Functional Modification from Cortical Synapses to Neuron Networks in the Brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2005, 3, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila-Luna, S.; Cabrera-Isidoro, S.; Vila-Luna, L.; Juárez-Díaz, I.; Bata-García, J.L.; Alvarez-Cervera, F.J.; Zapata-Vázquez, R.E.; Arankowsky-Sandoval, G.; Heredia-López, F.; Flores, G.; et al. Chronic Caffeine Consumption Prevents Cognitive Decline from Young to Middle Age in Rats, and Is Associated with Increased Length, Branching, and Spine Density of Basal Dendrites in CA1 Hippocampal Neurons. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanthi, J.R.P.; Dasari, B.; Marwarha, G.; Larson, T.; Chen, X.; Geiger, J.D.; Ghribi, O. Caffeine Protects against Oxidative Stress and Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology in Rabbit Hippocampus Induced by Cholesterol-Enriched Diet. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ghribi, O.; Geiger, J.D. Caffeine Protects against Disruptions of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20 (Suppl. 1), S127–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, L.; Khan, F.; Lam, H. Epidemiologic Evidence of a Relationship between Tea, Coffee, or Caffeine Consumption and Cognitive Decline. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaguchi, H.; Matsuno, A.; Okubo, T.; Hoya, K. Relationship between Silent Brain Infarction and Amount of Daily Coffee Consumption in Middle Age. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Godos, J.; Galvano, F.; Giovannucci, E.L. Coffee, Caffeine, and Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grioni, S.; Agnoli, C.; Sieri, S.; Pala, V.; Ricceri, F.; Masala, G.; Saieva, C.; Panico, S.; Mattiello, A.; Chiodini, P.; et al. Espresso Coffee Consumption and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in a Large Italian Cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”. A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpina, F.; Tagini, S. The Stroop Color and Word Test. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M. A Rating Scale for Depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S. Assessing self-maintenance: Activities of daily living, mobility, and instrumental activities of daily living. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1983, 31, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, A.; Román, G.C.; Esiri, M.; Kettunen, P.; Svensson, J.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Kapaki, E. Update on Vascular Cognitive Impairment Associated with Subcortical Small-Vessel Disease2. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 1417–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokinen, H.; Kalska, H.; Ylikoski, R.; Madureira, S.; Verdelho, A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Visser, M.C.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Longitudinal Cognitive Decline in Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease--the LADIS Study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bella, R.; Pennisi, G.; Cantone, M.; Palermo, F.; Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Zappia, M.; Paolucci, S. Clinical Presentation and Outcome of Geriatric Depression in Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease. Gerontology 2010, 56, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. MR Signal Abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s Dementia and Normal Aging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; L. Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0-8058-0283-2. [Google Scholar]
- McCusker, R.R.; Goldberger, B.A.; Cone, E.J. Caffeine Content of Specialty Coffees. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2003, 27, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, J.; Jia, X.; Kyle, J.A.M.; Gow, A.J.; Brett, C.E.; Starr, J.M.; McNeill, G.; Deary, I.J. Caffeine Consumption and Cognitive Function at Age 70: The Lothian Birth Cohort 1936 Study. Psychosom. Med. 2010, 72, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gelder, B.M.; Buijsse, B.; Tijhuis, M.; Kalmijn, S.; Giampaoli, S.; Nissinen, A.; Kromhout, D. Coffee Consumption Is Inversely Associated with Cognitive Decline in Elderly European Men: The FINE Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, K.; Carrière, I.; de Mendonca, A.; Portet, F.; Dartigues, J.F.; Rouaud, O.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Ancelin, M.L. The Neuroprotective Effects of Caffeine: A Prospective Population Study (the Three City Study). Neurology 2007, 69, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Lunet, N.; Azevedo, A.; de Mendonça, A.; Ritchie, K.; Barros, H. Caffeine Intake Is Associated with a Lower Risk of Cognitive Decline: A Cohort Study from Portugal. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20 (Suppl. 1), S175–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, L.; Biggs, M.L.; O’Meara, E.S.; Longstreth, W.T.; Crane, P.K.; Fitzpatrick, A.L. Gender Differences in Tea, Coffee, and Cognitive Decline in the Elderly: The Cardiovascular Health Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 27, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercambre, M.-N.; Berr, C.; Ritchie, K.; Kang, J.H. Caffeine and Cognitive Decline in Elderly Women at High Vascular Risk. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, M.; Fujii, M.; Takahashi, O.; Kawatsu, A.; Uemura, A.; Niimi, Y. Inverse Relationship between Coffee Consumption and Cerebral Microbleeds in Men, but Not Women. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2196–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.; Montandon, M.-L.; Rodriguez, C.; Herrmann, F.R.; Giannakopoulos, P. Impact of Coffee, Wine, and Chocolate Consumption on Cognitive Outcome and MRI Parameters in Old Age. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boxtel, M.P.J.; Schmitt, J.A.J.; Bosma, H.; Jolles, J. The Effects of Habitual Caffeine Use on Cognitive Change: A Longitudinal Perspective. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitala, V.S.; Kaprio, J.; Koskenvuo, M.; Räihä, I.; Rinne, J.O.; Silventoinen, K. Coffee Drinking in Middle Age Is Not Associated with Cognitive Performance in Old Age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Bättig, K.; Holmén, J.; Nehlig, A.; Zvartau, E.E. Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 83–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kwak, S.M.; Myung, S.-K. Caffeine Intake from Coffee or Tea and Cognitive Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 44, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Costa, J.; Santos, J.; Vaz-Carneiro, A.; Lunet, N. Caffeine Intake and Dementia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20 (Suppl. 1), S187–S204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.A.; Scheltens, P.; Groot, C.; Ossenkoppele, R. Associations Between Caffeine Consumption, Cognitive Decline, and Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.-P.; Wu, Y.-F.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Xia, T.; Ding, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.-M.; Xu, Y. Habitual Coffee Consumption and Risk of Cognitive Decline/Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutrition 2016, 32, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Sun, D.; He, Y. Coffee Intake and the Incident Risk of Cognitive Disorders: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Nine Prospective Cohort Studies. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Park, Y.; Freedman, N.D.; Sinha, R.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Blair, A.; Chen, H. Sweetened Beverages, Coffee, and Tea and Depression Risk among Older US Adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.M.; Abasheva, D.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ruiz-Estigarribia, L.; Martín-Calvo, N.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Toledo, E. Coffee Consumption and the Risk of Depression in a Middle-Aged Cohort: The SUN Project. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Suga, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Sasaki, S. Three-Generation Study of Women on Diets and Health Study Group Intake of Coffee Associated with Decreased Depressive Symptoms among Elderly Japanese Women: A Multi-Center Cross-Sectional Study. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Panza, F.; Imbimbo, B.P.; D’Introno, A.; Galluzzo, L.; Gandin, C.; Misciagna, G.; Guerra, V.; Osella, A.; Baldereschi, M.; et al. Coffee Consumption Habits and the Risk of Mild Cognitive Impairment: The Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 47, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Han, J.W.; Lee, J.R.; Byun, S.; Suh, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.W. Association between Lifetime Coffee Consumption and Late Life Cerebral White Matter Hyperintensities in Cognitively Normal Elderly Individuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Hall, S.M.; Modin, G. Persistent Increase in Caffeine Concentrations in People Who Stop Smoking. BMJ 1989, 298, 1075–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.-C.; Barros, H. Smoking Patterns in a Community Sample of Portuguese Adults, 1999–2000. Prev. Med. 2004, 38, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emma, R.; Caponnetto, P.; Cibella, F.; Caruso, M.; Conte, G.; Benfatto, F.; Ferlito, S.; Gulino, A.; Polosa, R. Short and Long Term Repeatability of Saccharin Transit Time in Current, Former, and Never Smokers. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniaci, A.; Iannella, G.; Cocuzza, S.; Vicini, C.; Magliulo, G.; Ferlito, S.; Cammaroto, G.; Meccariello, G.; De Vito, A.; Nicolai, A.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Biomarker Expression in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
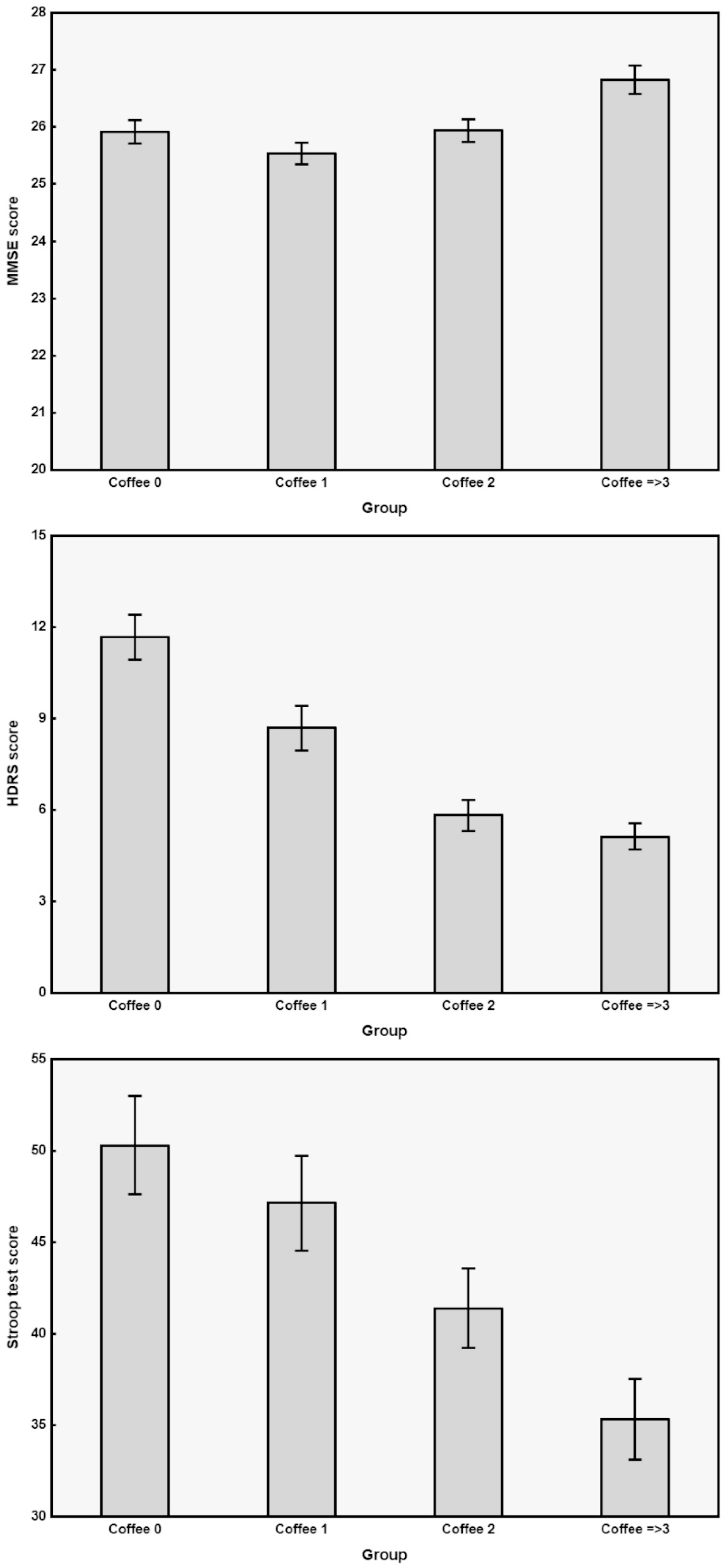
| Coffee 0 cup/day (n = 73) | Coffee 1 cup/day (n = 69) | Coffee 2 cups/day (n = 87) | Coffee ≥ 3 cups/day (n = 71) | ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | F3,296 | p< | |
| Age, years | 73.9 | 6.2 | 72.9 | 5.7 | 73.5 | 6.4 | 70.9 | 5.6 | 3.623 | 0.014 |
| Education, years | 6.5 | 3.7 | 6.9 | 4.0 | 7.5 | 4.0 | 8.2 | 3.9 | 2.635 | 0.05 |
| MMSE | 25.9 | 1.8 | 25.5 | 1.6 | 25.9 | 1.9 | 26.8 | 2.1 | 6.212 | 0.00042 |
| ADL | 5.6 | 0.7 | 5.5 | 0.7 | 5.6 | 0.6 | 5.8 | 0.6 | 2.112 | NS |
| IADL | 7.2 | 1.3 | 6.8 | 1.5 | 7.1 | 1.2 | 7.3 | 1.2 | 1.814 | NS |
| HDRS | 11.7 | 6.4 | 8.7 | 6.0 | 5.8 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 3.6 | 23.790 | 0.000001 |
| Stroop T | 50.3 | 22.9 | 47.1 | 21.6 | 41.4 | 20.4 | 35.3 | 18.6 | 7.182 | 0.00011 |
| Coffee 0 cup/day (n = 73) | Coffee 1 cup/day (n = 69) | Coffee 2 cups/day (n = 87) | Coffee ≥ 3 cups/day (n = 71) | Chi-Square | p< | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male/female | 28/45 | 32/37 | 48/39 | 48/23 | 13.60 | 0.004 |
| Hypertension, yes/no | 60/13 | 50/19 | 70/17 | 59/12 | 3.05 | NS |
| Diabetes, yes/no | 15/58 | 20/49 | 24/63 | 26/45 | 4.62 | NS |
| Hypercholesterolemia, yes/no | 22/51 | 19/50 | 29/58 | 28/43 | 2.54 | NS |
| Coronary artery disease, yes/no | 10/63 | 13/56 | 9/78 | 14/57 | 3.52 | NS |
| Tobacco smoking, yes/no/ex | 7/54/12 | 13/47/9 | 15/57/15 | 26/37/8 | 17.90 | 0.006 |
| Atrial fibrillation, yes/no | 11/62 | 7/62 | 8/79 | 9/62 | 1.56 | NS |
| Neurologic signs, yes/no | 29/44 | 30/39 | 36/51 | 32/39 | 0.49 | NS |
| Family history, yes/no | 8/65 | 13/56 | 8/79 | 8/63 | 3.70 | NS |
| History of depression, yes/no | 15/58 | 17/52 | 29/67 | 16/55 | 2.40 | NS |
| MRI, lacunar/Fazekas 1/2/3 | 13/15/29/16 | 8/22/24/15 | 15/21/32/19 | 12/21/24/14 | 3.81 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fisicaro, F.; Lanza, G.; Pennisi, M.; Vagli, C.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, G.; Ferri, R.; Bella, R. Moderate Mocha Coffee Consumption Is Associated with Higher Cognitive and Mood Status in a Non-Demented Elderly Population with Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020536
Fisicaro F, Lanza G, Pennisi M, Vagli C, Cantone M, Pennisi G, Ferri R, Bella R. Moderate Mocha Coffee Consumption Is Associated with Higher Cognitive and Mood Status in a Non-Demented Elderly Population with Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease. Nutrients. 2021; 13(2):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020536
Chicago/Turabian StyleFisicaro, Francesco, Giuseppe Lanza, Manuela Pennisi, Carla Vagli, Mariagiovanna Cantone, Giovanni Pennisi, Raffaele Ferri, and Rita Bella. 2021. "Moderate Mocha Coffee Consumption Is Associated with Higher Cognitive and Mood Status in a Non-Demented Elderly Population with Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease" Nutrients 13, no. 2: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020536
APA StyleFisicaro, F., Lanza, G., Pennisi, M., Vagli, C., Cantone, M., Pennisi, G., Ferri, R., & Bella, R. (2021). Moderate Mocha Coffee Consumption Is Associated with Higher Cognitive and Mood Status in a Non-Demented Elderly Population with Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease. Nutrients, 13(2), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020536