Lactococcus lactis Strain Plasma Intake Suppresses the Incidence of Dengue Fever-like Symptoms in Healthy Malaysians: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.1.1. Phase 1: Enrollment, Screening/Eligibility Phase
2.1.2. Phase 2: The Randomization and Baseline Visit
2.1.3. Phase 3: The Follow-Up Visit
2.1.4. Phase 4: Final Visit
2.2. Self-Assessment (SA) Booklet
2.3. Study Products
2.4. Blood Collection and Analysis
2.5. Anti-DENV Antibodies (IgM & IgG) and Antigen (NS1) Screening
2.6. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Screening
2.7. DENV Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.8. Definition of Exposure to DENV
- Tested positive for anti-dengue IgM (COI > 1.00) with at least a 4-fold increase in OD reading as compared to the primary sample.
- Tested positive for dengue NS1 antigen (COI > 0.5) with at least a 4-fold increase in OD reading as compared to the primary sample.
- Tested positive for DENV RNA with a Ct-value of less than 40.0 (Ct < 40).
2.9. Statistical Analysis for Outcomes
3. Results
3.1. Rescheduling of Site Visits Due to COVID-19 Pandemic Movement Control Order (MCO)
3.2. Participant Characteristics and Analysis Object
3.3. Number of DENV Exposure and Symptomatic Ratio
3.4. Comparison of Cumulative Symptomatic Days and Severities of Each Clinical Symptom
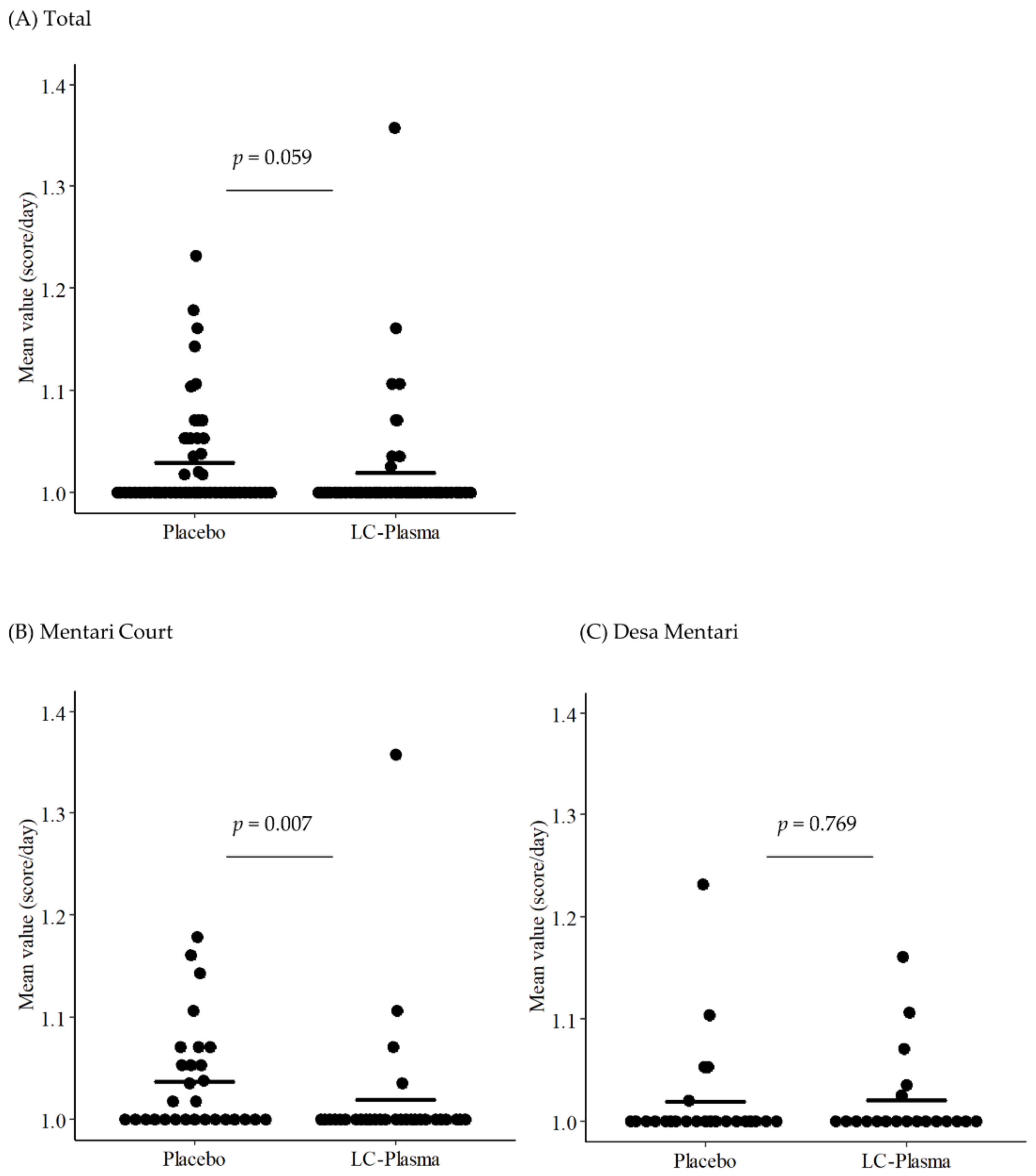
3.5. Subgroup Analysis for DF-like Symptoms Focusing on the Residence
3.6. Number of SARS-CoV-2 Exposed Participants
3.7. Safety Evaluation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chastel, C. Asymptomatic infections in man: A Trojan horse for the introduction and spread of mosquito-borne arboviruses in non-endemic areas? Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2011, 104, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurugama, P.; Garg, P.; Perera, J.; Wijewickrama, A.; Seneviratne, S.L. Dengue viral infections. Indian J. Dermatol. 2010, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Chandra, J.; Aneja, S.; Patwari, A.K.; Dutta, A.K. An epidemic of dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome in children in Delhi. Indian Pediatr. 1998, 35, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sam, S.S.; Omar, S.F.; Teoh, B.T.; Abd-Jamil, J.; AbuBakar, S. Review of Dengue hemorrhagic fever fatal cases seen among adults: A retrospective study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadinegoro, S.R.; Arredondo-Garcia, J.L.; Capeding, M.R.; Deseda, C.; Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Dietze, R.; Muhammad Ismail, H.I.; Reynales, H.; Limkittikul, K.; Rivera-Medina, D.M.; et al. Efficacy and Long-Term Safety of a Dengue Vaccine in Regions of Endemic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Annual Report—Ministry of Health Malaysia 2019. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Penerbitan%20Utama/ANNUAL%20REPORT/LAPORAN%20TAHUNAN%20KKM%202019/mobile/index.html (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Shepard, D.S.; Undurraga, E.A.; Lees, R.S.; Halasa, Y.; Lum, L.C.S.; Ng, C.W. Use of multiple data sources to estimate the economic cost of dengue illness in Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packierisamy, P.R.; Ng, C.W.; Dahlui, M.; Inbaraj, J.; Balan, V.K.; Halasa, Y.A.; Shepard, D.S. Cost of Dengue Vector Control Activities in Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee Han, L.; Vasan, S.; Birgelen, L.; Murtola, T.; Gong, H.; Field, R.W.; Mavalankar, D.V.; Ahmad, N.W.; Hakim, L.S.; Murad, S. Immediate cost of dengue to Malaysia and Thailand: An estimate. Dengue Bull. 2010, 34, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Suaya, J.A.; Shepard, D.S.; Siqueira, J.B.; Martelli, C.T.; Lum, L.C.; Tan, L.H.; Kongsin, S.; Jiamton, S.; Garrido, F.; Montoya, R.; et al. Cost of dengue cases in eight countries in the Americas and Asia: A prospective study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, B.; Assil, S.; Dreux, M. Cell-Cell Sensing of Viral Infection by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10050–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, M. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on diarrheal diseases. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 137S–146S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaiano, D.A. Lactose digestion from yogurt: Mechanism and relevance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1251S–1255S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jounai, K.; Ikado, K.; Sugimura, T.; Ano, Y.; Braun, J.; Fujiwara, D. Spherical lactic acid bacteria activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells immunomodulatory function via TLR9-dependent crosstalk with myeloid dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, T.; Takahashi, H.; Jounai, K.; Ohshio, K.; Kanayama, M.; Tazumi, K.; Tanihata, Y.; Miura, Y.; Fujiwara, D.; Yamamoto, N. Effects of oral intake of plasmacytoid dendritic cells-stimulative lactic acid bacterial strain on pathogenesis of influenza-like illness and immunological response to influenza virus. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.; Chin, W.X.; Han, Q.; Ichiyama, K.; Lee, C.H.; Eyo, Z.W.; Ebina, H.; Takahashi, H.; Takahashi, C.; Tan, B.H.; et al. Characterization of RyDEN (C19orf66) as an Interferon-Stimulated Cellular Inhibitor against Dengue Virus Replication. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shresta, S.; Kyle, J.L.; Snider, H.M.; Basavapatna, M.; Beatty, P.R.; Harris, E. Interferon-dependent immunity is essential for resistance to primary dengue virus infection in mice, whereas T- and B-cell-dependent immunity are less critical. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, R.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamada, S.; Fujii, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Kanauchi, O. Induction of anti-viral genes mediated by humoral factors upon stimulation with Lactococcus lactis strain plasma results in repression of dengue virus replication in vitro. Antiviral Res. 2018, 160, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Tsuji, R.; Sugamata, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Kanauchi, O. Administration of plasmacytoid dendritic cell-stimulative lactic acid bacteria is effective against dengue virus infection in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazni, W.A.; Hoffmann, A.A.; NoorAfizah, A.; Cheong, Y.L.; Mancini, M.V.; Golding, N.; Kamarul, G.M.R.; Arif, M.A.K.; Thohir, H.; NurSyamimi, H.; et al. Establishment of Wolbachia Strain wAlbB in Malaysian Populations of Aedes aegypti for Dengue Control. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 4241–4248.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibata, T.; Kanayama, M.; Haida, M.; Fujimoto, S.; Oroguchi, T.; Sata, K.; Mita, N.; Kutsuzawa, T.; Ikeuchi, M.; Kondo, M. Lactococcus lactis JCM5805 activates anti-viral immunity and reduces symptoms of common cold and influenza in healthy adults in a randomized controlled trial. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SD Biosensor. STANDARD F Dengue NS1 Ag FIA. Available online: https://www.labmark.cz/data/system/attachments/sdbiosensor-flyer-f-dengue-ns1ag.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- SD Biosensor. STANDARD F Dengue IgM/IgG FIA. Available online: https://www.labmark.cz/data/system/attachments/sdbiosensor-insert-f-dengue-igm-igg.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- EUROIMMUN Medizinische Labordiagnostika, AG. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 NCP ELISA (IgM). Available online: https://www.coronavirus-diagnostics.com/documents/Indications/Infections/Coronavirus/EI_2606_D_UK_D.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- EUROIMMUN Medizinische Labordiagnostika, AG. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA (IgG). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137609/download (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- World Health Organization. Dengue: Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Umakanth, M.; Suganthan, N. Unusual Manifestations of Dengue Fever: A Review on Expanded Dengue Syndrome. Cureus 2020, 12, e10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, S.M.; Khoo, E.M.; Ho, B.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Omar, M.; Ayadurai, V.; Mohamed Yusoff, F.; Suli, Z.; Mudin, R.N.; Goh, P.P.; et al. Dengue in Malaysia: Factors Associated with Dengue Mortality from a National Registry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.S.; Tien, C.J.; Lu, M.R. Epidemiological, clinical and climatic characteristics of dengue fever in Kaohsiung City, Taiwan with implication for prevention and control. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Bomar, P.A. Upper Respiratory Tract Infection; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, A.C.; Goldstein, D.R.; Montgomery, R.R. Age-dependent dysregulation of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Ohshio, K.; Fujiwara, D. Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis JCM 5805 activates natural killer cells via dendritic cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jounai, K.; Sugimura, T.; Ohshio, K.; Fujiwara, D. Oral administration of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis JCM5805 enhances lung immune response resulting in protection from murine parainfluenza virus infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz Hernandez, S.I.; Puerta-Guardo, H.; Flores-Aguilar, H.; Gonzalez-Mateos, S.; Lopez-Martinez, I.; Ortiz-Navarrete, V.; Ludert, J.E.; Del Angel, R.M. A strong interferon response correlates with a milder dengue clinical condition. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, J.; Morrison, J.; Laurent-Rolle, M.; Belicha-Villanueva, A.; Plumlee, C.R.; Bernal-Rubio, D.; Williams, K.L.; Harris, E.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Schindler, C.; et al. Mouse STAT2 restricts early dengue virus replication. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, T.; Dutta, S.K.; Mandal, S.; Saha, B.; Tripathi, A. Differential clinical symptoms among acute phase Indian patients revealed significant association with dengue viral load and serum IFN-gamma level. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, A.; Etchart, N.; Rossmann, C.; Ashton, M.; Hou, S.; Gewert, D.; Borrow, P.; Tough, D.F. Cross-priming of CD8+ T cells stimulated by virus-induced type I interferon. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrack, P.; Kappler, J.; Mitchell, T. Type I interferons keep activated T cells alive. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upasani, V.; Scagnolari, C.; Frasca, F.; Smith, N.; Bondet, V.; Vanderlinden, A.; Lay, S.; Auerswald, H.; Heng, S.; Laurent, D.; et al. Decreased Type I Interferon Production by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Contributes to Severe Dengue. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Jounai, K.; Fujii, T.; Fujiwara, D. Preventive Effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis JCM 5805 Yogurt Intake on Influenza Infection among Schoolchildren. Health 2017, 9, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komano, Y.; Shimada, K.; Naito, H.; Fukao, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Fujii, T.; Kokubo, T.; Daida, H. Efficacy of heat-killed Lactococcus lactis JCM 5805 on immunity and fatigue during consecutive high intensity exercise in male athletes: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Aziz, F. The Investigation of the Implications of Squatter Relocations in High-Risk Neighbourhoods in Malaysia. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Leh, O.L.H.; Rosli, N.N.F.M.; Marhalim, F.A.; Musthafa, S.N.A.M. Social Impact of Foreign Immigrants in Affordable Housing Area. Case Study: Mentari Court, Selangor, Malaysia. Plan. Malays. 2017, 15, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week2/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1305 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week9/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1345. (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week8/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1338 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week7/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1329 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week6/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1321 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week5/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1312 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Press Statement of the Director-General of Health Malaysia. Current Situation of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika in Malaysia (Week4/2020). Available online: https://www.moh.gov.my/index.php/database_stores/attach_download/337/1309 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Undurraga, E.A.; Halasa, Y.A.; Shepard, D.S. Use of expansion factors to estimate the burden of dengue in Southeast Asia: A systematic analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, Y.; Kanayama, M.; Yanai, S.; Nozawa, H.; Kanauchi, O.; Suzuki, S. Safety evaluation of excessive intake of Lactococcus lactis Subsp. lactis JCM 5805: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar]
- Kirin Holdings Company. Kirin Launched the iMUSE Product for Medical Distributor. Available online: https://www.kirin.co.jp/company/news/2017/1219_03.html (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Tsuji, R.; Yazawa, K.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kanauchi, O. The Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Lactococcus lactis Strain Plasma on Skin Microbiome and Skin Conditions in Healthy Subjects-A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Placebo | LC-Plasma | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | MC: 29, DM: 24 | MC: 30, DM: 20 | ||
| Gender | Male: 16, Female: 37 | Male: 11, Female: 39 | ||
| (Unit) | p-value | |||
| Age | year | 37.69 ± 14.33 | 36.12 ± 13.10 | 0.673 |
| Height | cm | 157.72 ± 8.15 | 155.64 ± 9.68 | 0.179 |
| Weight | kg | 71.28 ± 16.67 | 68.11 ± 17.23 | 0.150 |
| BP-Diastole | mmHg | 125.54 ± 13.69 | 125.81 ± 12.40 | 0.983 |
| BP-Systole | mmHg | 79.36 ± 7.99 | 78.38 ± 9.25 | 0.414 |
| Pulse | bpm | 82.90 ± 13.09 | 81.74 ± 12.08 | 0.431 |
| Exposed | Not Exposed | p-Value 1 | Symptomatic | Asymptomatic | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | 5 | 48 | 0.797 2 | 2 | 3 | 0.635 2 |
| LC-Plasma | 4 | 46 | 1 | 3 |
| Symptoms | Cumulative Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| without Symptoms | with Symptoms | p-Value | ||
| Fever | Placebo | 2837 | 64 | 0.001 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2678 | 28 | ||
| Headache | Placebo | 2706 | 195 | 0.000 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2633 | 72 | ||
| Muscle pain | Placebo | 2792 | 109 | 0.005 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2640 | 66 | ||
| Joint pain | Placebo | 2770 | 131 | 0.000 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2645 | 61 | ||
| Pain behind eyes | Placebo | 2853 | 48 | 0.000 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2691 | 15 | ||
| Sore throat | Placebo | 2761 | 140 | 0.000 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2643 | 63 | ||
| Cough | Placebo | 2746 | 154 | 0.028 * |
| LC-Plasma | 2596 | 110 | ||
| Runny nose | Placebo | 2711 | 190 | 0.000 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2628 | 78 | ||
| Sneezing | Placebo | 2738 | 162 | 0.008 ** |
| LC-Plasma | 2596 | 110 | ||
| Vomit | Placebo | 2887 | 14 | 0.055 + |
| LC-Plasma | 2701 | 5 | ||
| Diarrhea | Placebo | 2867 | 34 | 0.133 |
| LC-Plasma | 2685 | 21 | ||
| Mentari Court | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo Group | LC-Plasma Group | p-Value | |
| Fever | 1.037 ± 0.052 | 1.019 ± 0.068 | 0.007 ** |
| Headache | 1.108 ± 0.158 | 1.034 ± 0.076 | 0.027 * |
| Muscle pain | 1.038 ± 0.105 | 1.016 ± 0.053 | 0.218 |
| Joint pain | 1.050 ± 0.140 | 1.013 ± 0.050 | 0.028 * |
| Pain behind eyes | 1.022 ± 0.071 | 1.007 ± 0.028 | 0.146 |
| Desa Mentari | |||
| Fever | 1.019 ± 0.052 | 1.020 ± 0.044 | 0.769 |
| Headache | 1.044 ± 0.110 | 1.046 ± 0.086 | 0.535 |
| Muscle pain | 1.056 ± 0.207 | 1.070 ± 0.291 | 0.894 |
| Joint pain | 1.064 ± 0.214 | 1.069 ± 0.258 | 0.595 |
| Pain behind eyes | 1.016 ± 0.057 | 1.008 ± 0.029 | 1.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khor, C.-S.; Tsuji, R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Nor’e, S.-S.; Sahimin, N.; Azman, A.-S.; Tiong, V.; Hasandarvish, P.; Teoh, B.-T.; Soh, Y.-H.; et al. Lactococcus lactis Strain Plasma Intake Suppresses the Incidence of Dengue Fever-like Symptoms in Healthy Malaysians: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124507
Khor C-S, Tsuji R, Lee H-Y, Nor’e S-S, Sahimin N, Azman A-S, Tiong V, Hasandarvish P, Teoh B-T, Soh Y-H, et al. Lactococcus lactis Strain Plasma Intake Suppresses the Incidence of Dengue Fever-like Symptoms in Healthy Malaysians: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124507
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhor, Chee-Sieng, Ryohei Tsuji, Hai-Yen Lee, Siti-Sarah Nor’e, Norhidayu Sahimin, Adzzie-Shazleen Azman, Vunjia Tiong, Pouya Hasandarvish, Boon-Teong Teoh, Yih-Harng Soh, and et al. 2021. "Lactococcus lactis Strain Plasma Intake Suppresses the Incidence of Dengue Fever-like Symptoms in Healthy Malaysians: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124507
APA StyleKhor, C.-S., Tsuji, R., Lee, H.-Y., Nor’e, S.-S., Sahimin, N., Azman, A.-S., Tiong, V., Hasandarvish, P., Teoh, B.-T., Soh, Y.-H., Chai, J.-H., Kokubo, T., Kanauchi, O., Yamamoto, N., & AbuBakar, S. (2021). Lactococcus lactis Strain Plasma Intake Suppresses the Incidence of Dengue Fever-like Symptoms in Healthy Malaysians: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 13(12), 4507. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124507







