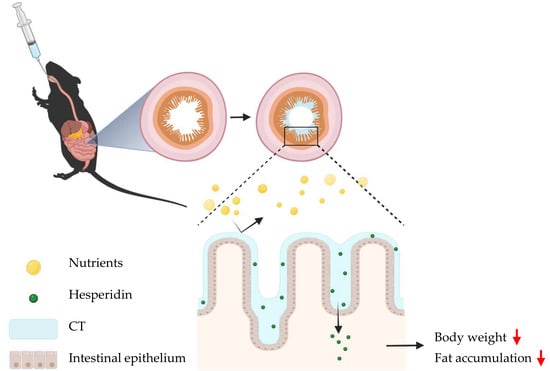
Thiolated Chitosan as an Intestinal Absorption Carrier with Hesperidin Encapsulation for Obesity Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Chitosan-TGA (CT)
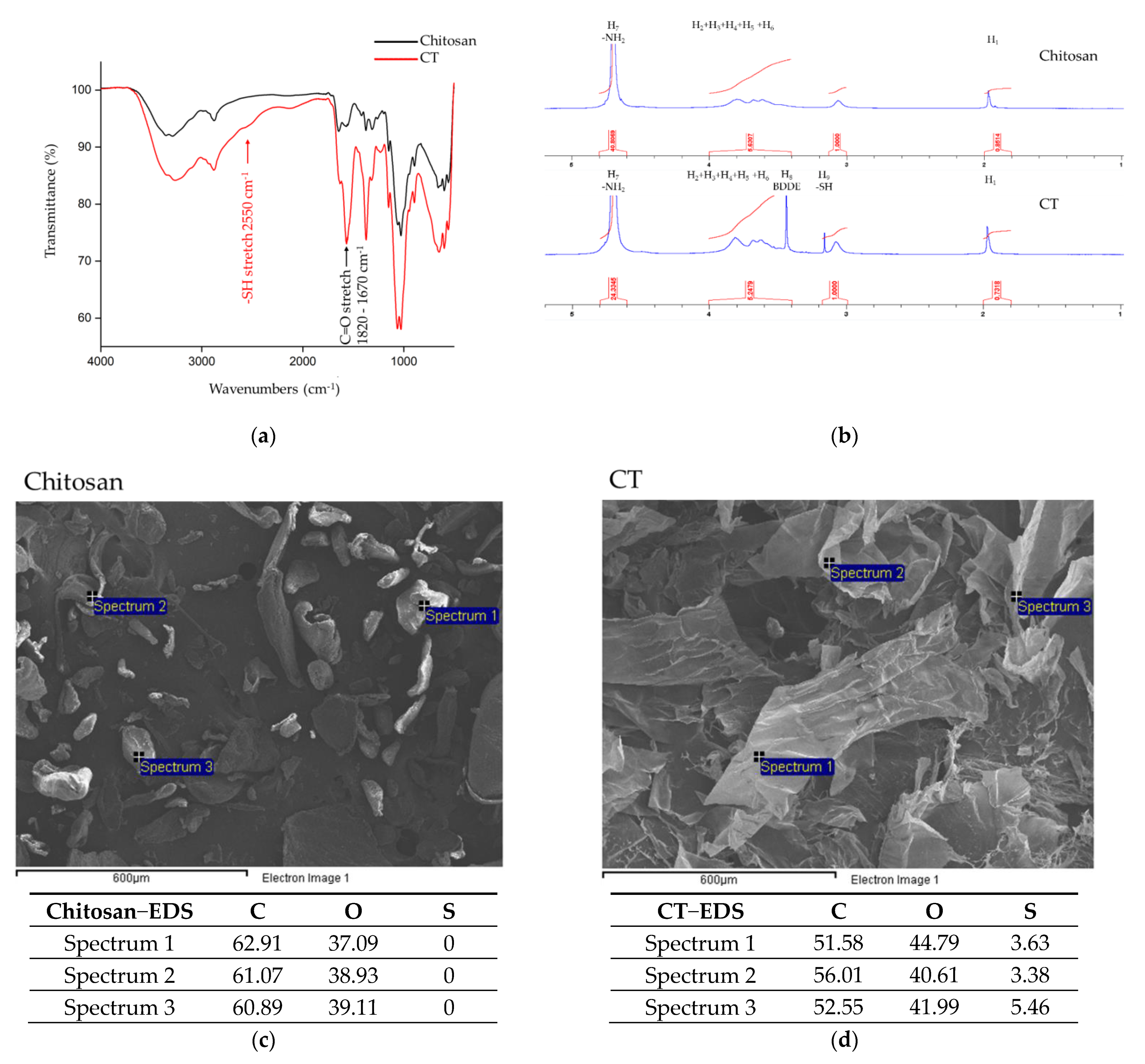
2.2. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
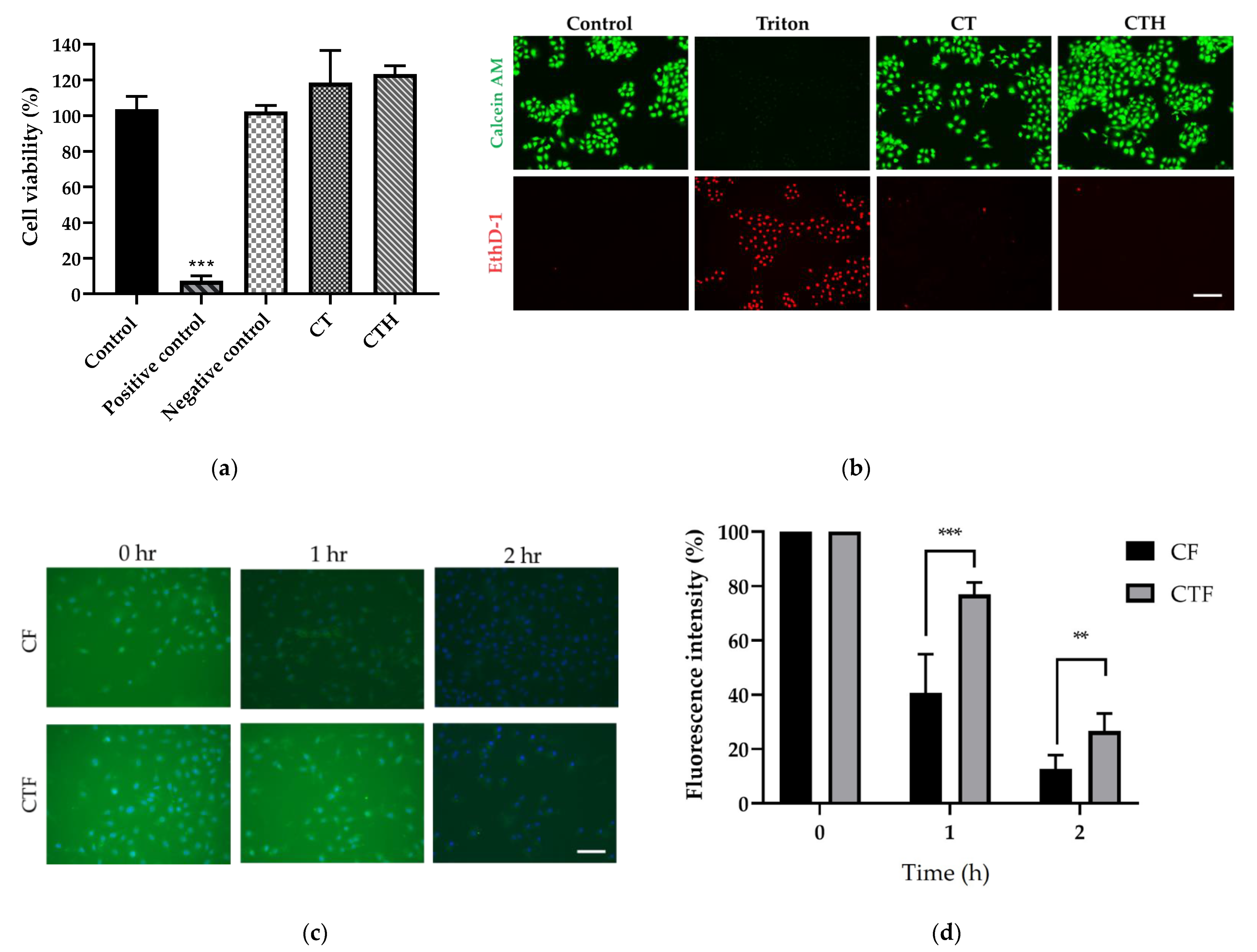
2.4. Cytotoxicity of CT
2.5. In Vitro Mucus Adhesion Test
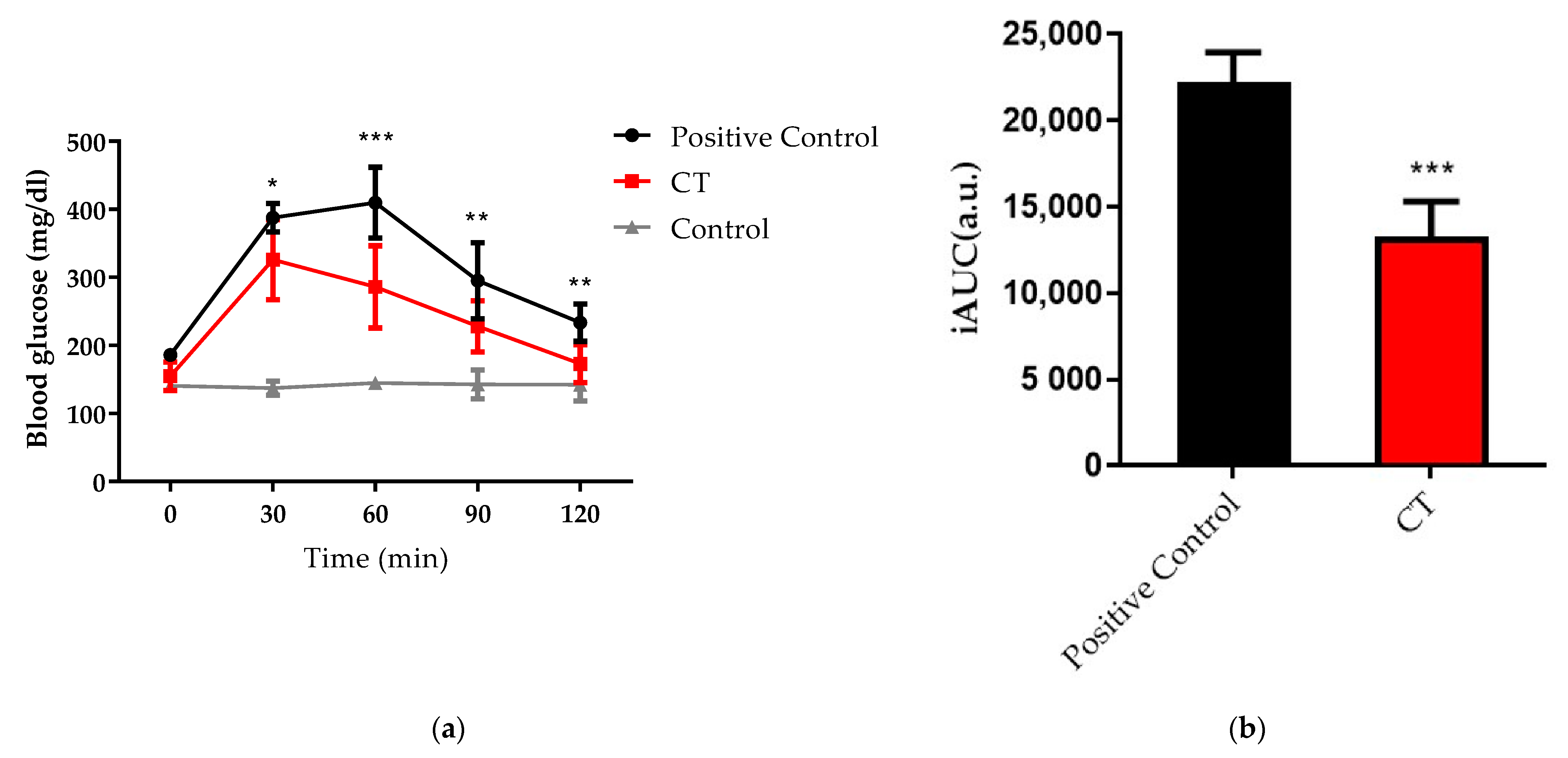
2.6. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) and Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test (IPGTT)
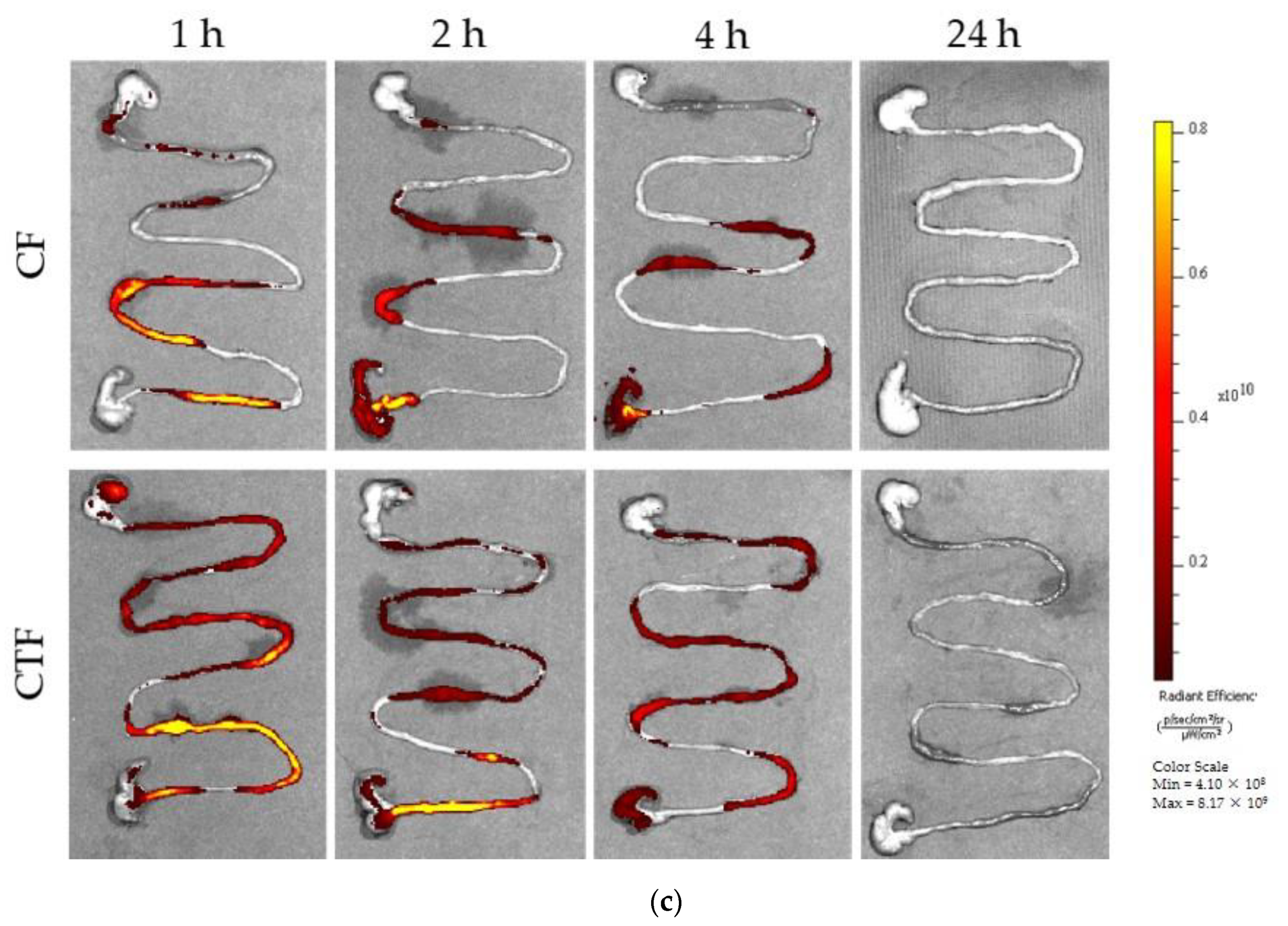
2.7. In Vivo Adhesion Test of CT
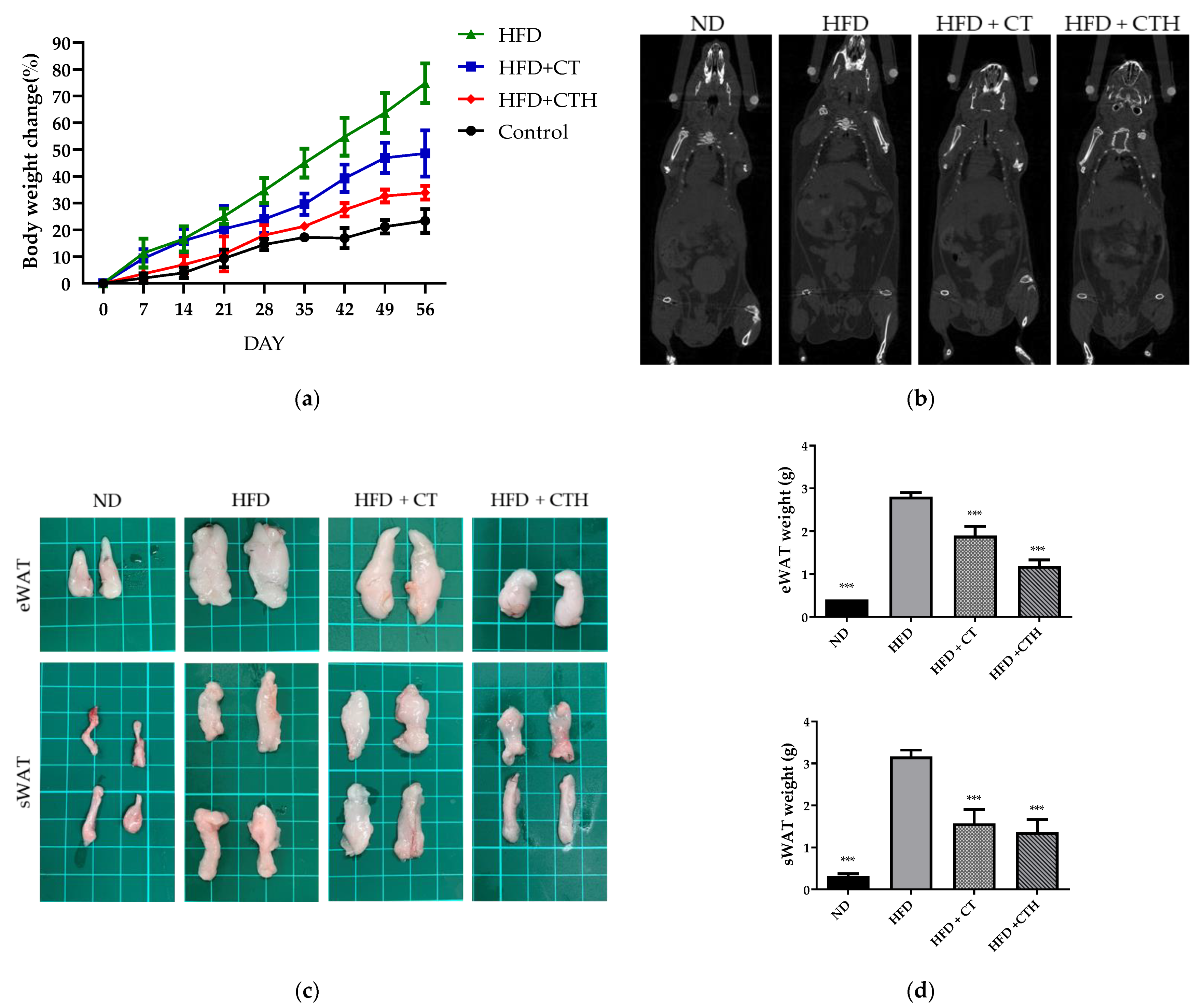
2.8. In Vivo Study
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Material Molecular Structure Analysis
3.2. Cytotoxicity and Mucus Adhesion Test of CT In Vitro
3.3. Functional Barrier Test and Mucosal Adhesion In Vivo
3.4. CT as a Drug Release Hydrogel with a Long-Term Effect in an HFD Model
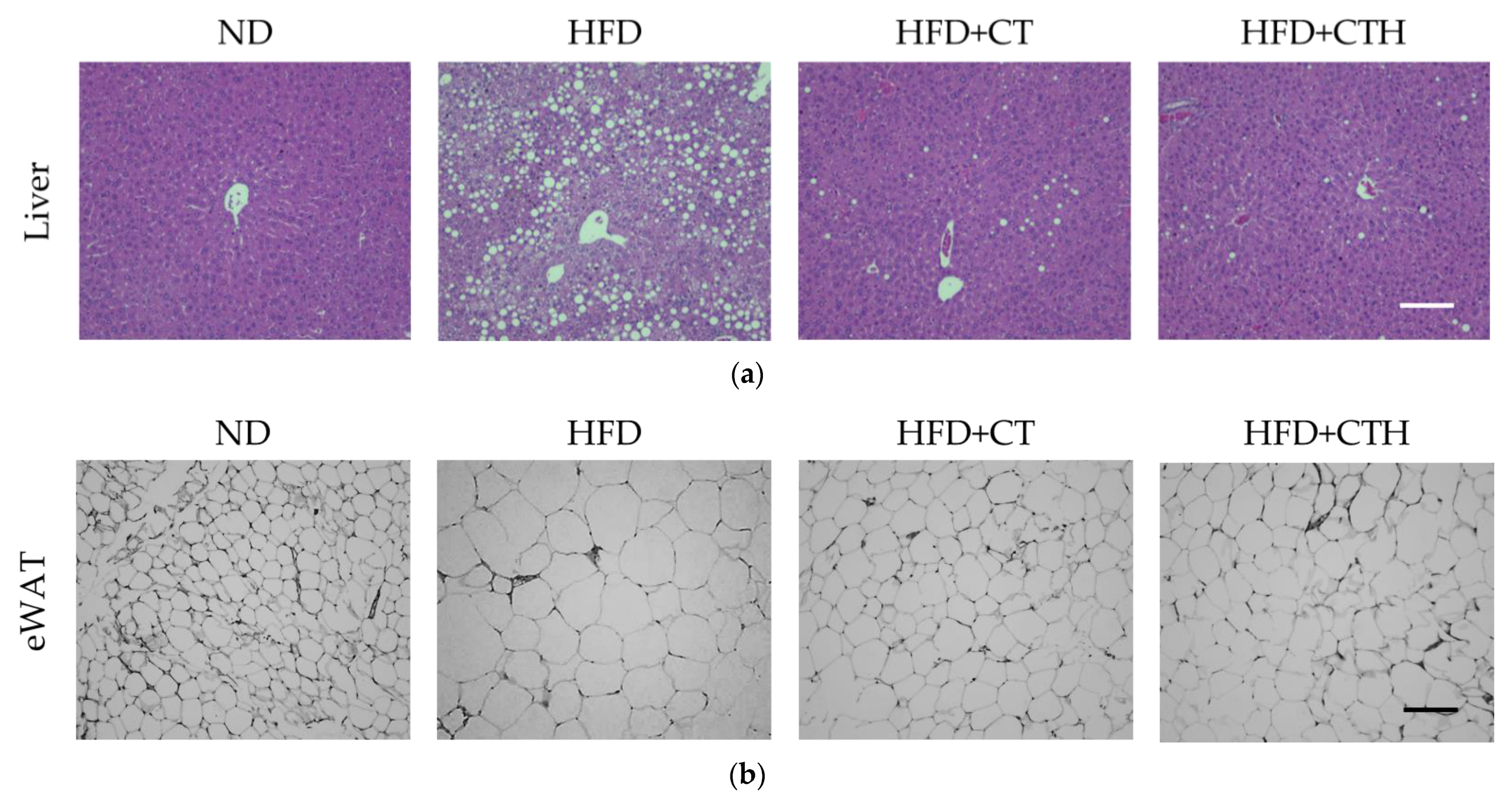
3.5. The Result of H&E Staining
3.6. Serum Biochemical Analysis and Complete Blood Count
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, S.Z.; Lu, W.; Zong, X.F.; Ruan, H.Y.; Liu, Y. Obesity and hypertension. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoner, L.; Cornwall, J. Did the American Medical Association make the correct decision classifying obesity as a disease? Australas. Med. J. 2014, 7, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.-S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, E.G. Obesity: Etiologic and pathophysiological analysis. Endocrinol. Y Nutr. (Engl. Ed. ) 2013, 60, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Angulo, M.; Butler, M.; Cataletto, M. Prader-Willi syndrome: A review of clinical, genetic, and endocrine findings. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bray, G.A. Epidemiology, risks and pathogenesis of obesity. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanneganti, T.-D.; Dixit, V.D. Immunological complications of obesity. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Himpens, J.; Dobbeleir, J.; Peeters, G. Long-term results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Ikramuddin, S.; Gourash, W.; Ramanathan, R.; Luketich, J. Outcomes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Ann. Surg. 2000, 232, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, R.; Rijs, C.S.; Bouvy, N.D.; Hameeteman, W.; Koek, G.H.; Janssen, I.M.; Greve, J.-W.M. A multicenter, randomized efficacy study of the EndoBarrier Gastrointestinal Liner for presurgical weight loss prior to bariatric surgery. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Hakim, D.; Mason, J.; Hakim, N. The duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve (EndoBarrier Gastrointestinal Liner) for weight loss and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, P.M.; Ramacciotti, T.; Farey, J.E.; Lord, R.V. Safety and effectiveness of an endoscopically placed duodenal-jejunal bypass device (EndoBarrier®): Outcomes in 114 patients. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 3306–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri-Khoulenjani, S.; Taghizadeh, S.; Mirzadeh, H. An investigation on the short-term biodegradability of chitosan with various molecular weights and degrees of deacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-h.; Whu, S.W.; Tsai, C.-L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-W.; Hsieh, K.-H. Chitosan as scaffold materials: Effects of molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. J. Polym. Res. 2004, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jull, A.B.; Mhurchu, C.N.; Bennett, D.A.; Dunshea-Mooij, C.A.; Rodgers, A. Chitosan for overweight or obesity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 3, CD003892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, V.M.; Walker, G.F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated polymers: Evidence for the formation of disulphide bonds with mucus glycoproteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiomers: A new generation of mucoadhesive polymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Garg, S.; Zaneveld, L.; Singla, A. Chemistry and pharmacology of the citrus bioflavonoid hesperidin. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Xu, L.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B. Metabolism study of hesperetin and hesperidin in rats by UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS n. Xenobiotica 2020, 50, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Queiroz, M.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the use of chitosan contribute to oxalate kidney stone formation? Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Miyake, S.; Yano, M.; Ueki, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Akazawa, S.; Tominaga, Y. Glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin sensitivity in nonobese and obese Japanese subjects. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.S.; Key, T.J.; Norat, T.; Scoccianti, C.; Cecchini, M.; Berrino, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Espina, C.; Leitzmann, M.; Powers, H. European code against cancer 4th edition: Obesity, body fatness and cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, S34–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marmot, M.; Atinmo, T.; Byers, T.; Chen, J.; Hirohata, T.; Jackson, A.; James, W.; Kolonel, L.; Kumanyika, S.; Leitzmann, C. Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective; World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.C.; McPherson, K.; Marsh, T.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Brown, M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet 2011, 378, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Intestinal redox biology and oxidative stress. Proc. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Ran, Q.; Lou, G.; Peng, C.; Gan, Q.; Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Yao, R.; Huang, Q. Hesperidin: A therapeutic agent for obesity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Kandhare, A.D.; Kandhare, A.A.; Bodhankar, S.L. Hesperidin ameliorates bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of TGF-beta1/Smad3/AMPK and IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB pathways. EXCLI J. 2019, 18, 723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diepvens, K.; Westerterp, K.R.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Obesity and thermogenesis related to the consumption of caffeine, ephedrine, capsaicin, and green tea. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Phys. 2007, 292, R77–R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| ND | HFD | HFD + CT | HFD + CTH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC (mg/dL) | 82.41 | 1.46 *** | 149.63 *** | 14.31 *** |
| TG (mg/dL) | 6.73 | 121.83 * | 1163.57 * | 105.3 7.55 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 74.52 | 14.89 *** | 1234.61 *** | 12.59 *** |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 8.93 | 15.20 *** | 13.9.91 ** | 13.29 ** |
| AST (U/L) | 108.1 26.14 | 286.3 91.52 *** | 153.4 51.6 ### | 88.24 28.7 ### |
| ALT (U/L) | 35.62 6.37 | 40.63 8.70 | 37.64 8.26 | 33.73 11.73 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 20.86 3.91 | 19.48 2.61 | 18.57 | 17.33 |
| Crea (mg/dL) | 0.25 0.05 | 0.2.05 | 0.2.03 | 0.23 0.05 |
| ND | HFD | HFD + CT | HFD + CTH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (M/μL) | 10.25 ± 0.62 | 9.975 ± 0.261 | 10.71 ± 0.213 | 10.48 ± 0.376 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 14.57 ± 0.85 | 14.25 ± 0.212 | 15.41 ± 0.3586 | 15.10 ± 0.916 |
| HCT (%) | 55.71 ± 3.75 | 53.05 ± 1.061 | 53.62 ± 1.45 | 54.50 ± 3.830 |
| MCV (fL) | 52.98 ± 1.033 | 53.20 ± 0.282 | 50.06 ± 1.276 | 51.93 ± 1.790 |
| MCH (pg) | 14.62 ± 0.25 | 14.30 ± 0.141 | 14.39 ± 0.209 | 14.40 ± 0.360 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 27.61 ± 0.516 | 26.90 ± 0.141 | 28.77 ± 0.9447 | 27.70 ± 0.264 |
| RET (K/μL) | 429.4 ± 106.8 | 514.8 ± 18.24 | 490.3 ± 79.54 | 502.8 ± 113.9 |
| PLT (K/μL) | 1124 ± 259.0 | 802.0 ± 114.6 | 1258 ± 140.30 | 928.7 ± 328.7 |
| WBC (K/μL) | 4.631 ± 2.186 | 3.650 ± 0.480 | 6.193 ± 1.229 | 2.547 ± 0.140 |
| NEUT (K/μL) | 1.181 ± 1.015 | 0.755 ± 0.304 | 1.324 ± 0.57 | 0.450 ± 0.155 |
| LYMPH (K/μL) | 3.263 ± 1.568 | 2.570 ± 0.08485 | 7.523 ± 2.474 | 1.887 ± 0.2228 |
| MONO (K/μL) | 0.1589 ± 0.1776 | 0.190 ± 0.084 | 0.257 ± 0.150 | 0.1300 ± 0.079 |
| EO (K/μL) | 0.026 ± 0.018 | 0.1267 ± 0.006 | 0.233 ± | 0.076 ± 0.035 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.-C.; Ho, Y.-Y.; Tang, R.-C.; Ke, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-N.; Yang, I.-H.; Lin, F.-H. Thiolated Chitosan as an Intestinal Absorption Carrier with Hesperidin Encapsulation for Obesity Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124405
Chen T-C, Ho Y-Y, Tang R-C, Ke Y-C, Lin J-N, Yang I-H, Lin F-H. Thiolated Chitosan as an Intestinal Absorption Carrier with Hesperidin Encapsulation for Obesity Treatment. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124405
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tzu-Chien, Yu-Yu Ho, Rui-Chian Tang, Yong-Chen Ke, Jhih-Ni Lin, I-Hsuan Yang, and Feng-Huei Lin. 2021. "Thiolated Chitosan as an Intestinal Absorption Carrier with Hesperidin Encapsulation for Obesity Treatment" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124405
APA StyleChen, T.-C., Ho, Y.-Y., Tang, R.-C., Ke, Y.-C., Lin, J.-N., Yang, I.-H., & Lin, F.-H. (2021). Thiolated Chitosan as an Intestinal Absorption Carrier with Hesperidin Encapsulation for Obesity Treatment. Nutrients, 13(12), 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124405