Effect on an Oral Nutritional Supplement with β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and Vitamin D on Morphofunctional Aspects, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Malnourished Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Oral Nutritional Supplements
2.3. Dietary-Intake Evaluation and Clinical Data
2.4. Body-Composition Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Nutritional Status
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Compliance and Nutrient Intake
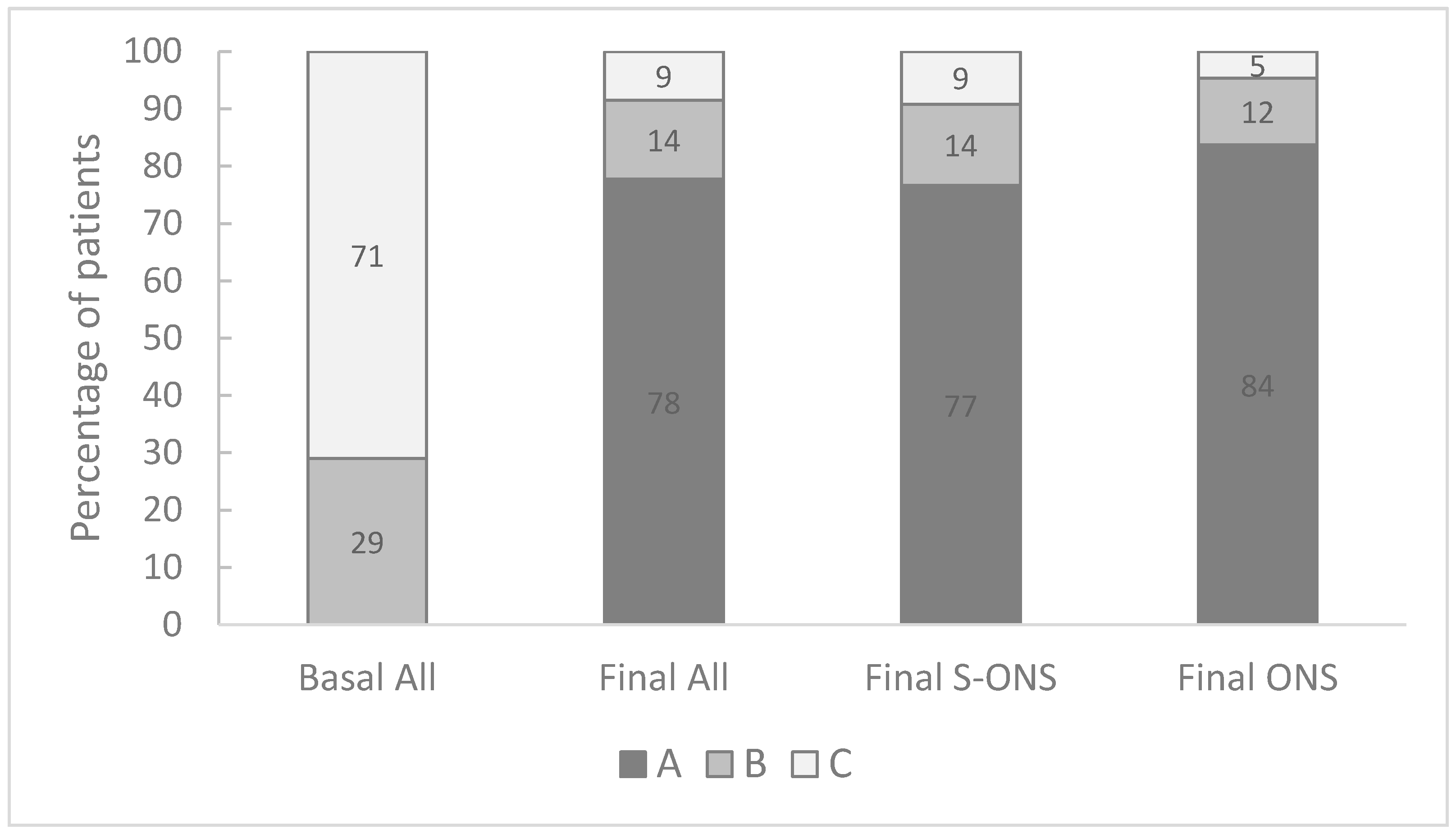
3.3. Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation
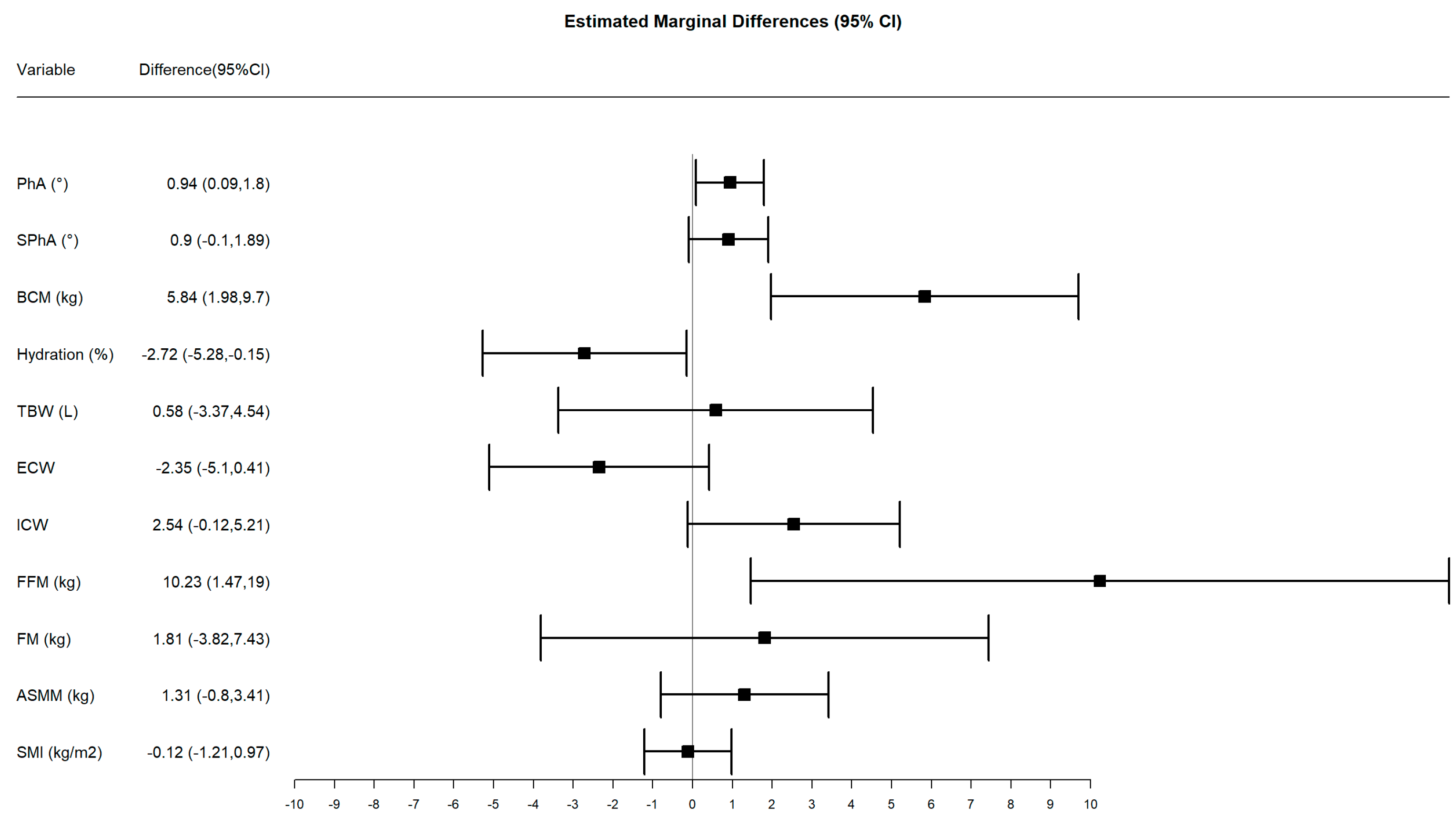
3.4. Subsample Analysis by Phase Angle
3.5. Efficacy of the Specialized Oral Nutritional Supplement with HMB on Oncology Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norman, K.; Pichard, C.; Lochs, H.; Pirlich, M. Prognostic impact of disease-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Camprubi-Robles, M.; Bear, D.E.; Cederholm, T.; Malafarina, V.; Welch, A.A.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Muscle loss: The new malnutrition challenge in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pourhassan, M.; Rommersbach, N.; Lueg, G.; Klimek, C.; Schnatmann, M.; Liermann, D.; Janssen, G.; Wirth, R. The Impact of Malnutrition on Acute Muscle Wasting in Frail Older Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, N.E.P.; Ashurst, I.; Ballesteros, M.D.; Bear, D.E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Genton, L.; Landi, F.; Laviano, A.; Norman, K.; Prado, C.M. The Underappreciated Role of Low Muscle Mass in the Management of Malnutrition. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cederholm, T.; Bosaeus, I.; Barazzoni, R.; Bauer, J.; Van Gossum, A.; Klek, S.; Muscaritoli, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Ockenga, J.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for malnutrition—An ESPEN Consensus Statement. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souza, N.C.; Avesani, C.M.; Prado, C.M.; Martucci, R.B.; Rodrigues, V.D.; de Pinho, N.B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Gonzalez, M.C. Phase angle as a marker for muscle abnormalities and function in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4799–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Almeida, J.M.; Garcia Garcia, C.; Vegas Aguilar, I.M.; Bellido Castaneda, V.; Bellido Guerrero, D. Morphofunctional assessment of patient s nutritional status: A global approach. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiles, J.M.; Campos, N.; Lopez-Pedrosa, J.M.; Rueda, R.; Rodriguez-Manas, L. Skeletal Muscle Regulates Metabolism via Interorgan Crosstalk: Roles in Health and Disease. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caillet, P.; Liuu, E.; Raynaud Simon, A.; Bonnefoy, M.; Guerin, O.; Berrut, G.; Lesourd, B.; Jeandel, C.; Ferry, M.; Rolland, Y.; et al. Association between cachexia, chemotherapy and outcomes in older cancer patients: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebuterne, X.; Lemarie, E.; Michallet, M.; de Montreuil, C.B.; Schneider, S.M.; Goldwasser, F. Prevalence of malnutrition and current use of nutrition support in patients with cancer. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2014, 38, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, A.M.; Power, D.G.; Daly, L.; Cushen, S.J.; Ni Bhuachalla, E.; Prado, C.M. Cancer-associated malnutrition, cachexia and sarcopenia: The skeleton in the hospital closet 40 years later. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pressoir, M.; Desne, S.; Berchery, D.; Rossignol, G.; Poiree, B.; Meslier, M.; Traversier, S.; Vittot, M.; Simon, M.; Gekiere, J.P.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors and clinical implications of malnutrition in French Comprehensive Cancer Centres. Br. J. Cancer. 2010, 102, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prado, C.M.; Cushen, S.J.; Orsso, C.E.; Ryan, A.M. Sarcopenia and cachexia in the era of obesity: Clinical and nutritional impact. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreyev, H.J.; Norman, A.R.; Oates, J.; Cunningham, D. Why do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies? Eur. J. Cancer 1998, 34, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Fehr, R.; Baechli, V.; Geiser, M.; Deiss, M.; Gomes, F.; Kutz, A.; Tribolet, P.; Bregenzer, T.; Braun, N.; et al. Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk: A randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, N.E.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznaric, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hutterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diet Calculator. Available online: https://calcdieta.ienva.org/tu_menu.php (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Garcia-Almeida, J.M.; Bellido-Guerrero, D.; Talluri, A.; Lukaski, H.; Tinahones, F.J. Phase angle and standardized phase angle from bioelectrical impedance measurements as a prognostic factor for mortality at 90 days in patients with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez Torralvo, F.J.; Porras, N.; Abuin Fernandez, J.; Garcia Torres, F.; Tapia, M.J.; Lima, F.; Soriguer, F.; Gonzalo, M.; Rojo Martinez, G.; Olveira, G. Normative reference values for hand grip dynamometry in Spain. Association with lean mass. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Laviano, A.; Gillis, C.; Sung, A.D.; Gardner, M.; Yalcin, S.; Dixon, S.; Newman, S.M.; Bastasch, M.D.; Sauer, A.C.; et al. Examining guidelines and new evidence in oncology nutrition: A position paper on gaps and opportunities in multimodal approaches to improve patient care. Support Care Cancer 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Dutt, A.; Hemraj, S.; Bhat, S.; Manipadybhima, B. Phase Angle Measurement in Healthy Human Subjects through Bio-Impedance Analysis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 15, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Vega Diaz, N.; Talluri, A.; Nescolarde, L. Classification of Hydration in Clinical Conditions: Indirect and Direct Approaches Using Bioimpedance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garlini, L.M.; Alves, F.D.; Ceretta, L.B.; Perry, I.S.; Souza, G.C.; Clausell, N.O. Phase angle and mortality: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapel, S.N.; Looijaard, W.; Dekker, I.M.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle at admission as a predictor of 90-day mortality in intensive care patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewoude, M.F.; Alish, C.J.; Sauer, A.C.; Hegazi, R.A. Malnutrition-sarcopenia syndrome: Is this the future of nutrition screening and assessment for older adults? J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 651570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, A.; Karimi, E.; Vingrys, K.; Shirani, F. Is phase angle a valuable prognostic tool in cancer patients’ survival? A systematic review and meta-analysis of available literature. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3182–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.W.; Hong, N.; Kim, C.O.; Kim, H.C.; Youm, Y.; Choi, J.; Rhee, Y. The diagnostic value of phase angle, an integrative bioelectrical marker, for identifying individuals with dysmobility syndrome: The Korean Urban-Rural Elderly study. Osteoporos Int. 2021, 32, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, N.P.; Gomes, T.L.N.; Barreto, C.S.; Borges, T.C.; Soares, J.D.P.; Pichard, C.; Laviano, A.; Pimentel, G.D. Low phase angle is associated with the risk for sarcopenia in unselected patients with cancer: Effects of hydration. Nutrition 2021, 84, 111122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, G.; Madeddu, C.; Maccio, A.; Gramignano, G.; Lusso, M.R.; Massa, E.; Astara, G.; Serpe, R. Cancer-related anorexia/cachexia syndrome and oxidative stress: An innovative approach beyond current treatment. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Maccio, A.; Madeddu, C.; Gramignano, G.; Mulas, C.; Floris, C.; Sanna, E.; Cau, M.C.; Panzone, F.; Mantovani, G. A randomized phase III clinical trial of a combined treatment for cachexia in patients with gynecological cancers: Evaluating the impact on metabolic and inflammatory profiles and quality of life. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargetzi, L.; Brack, C.; Herrmann, J.; Bargetzi, A.; Hersberger, L.; Bargetzi, M.; Kaegi-Braun, N.; Tribolet, P.; Gomes, F.; Hoess, C.; et al. Nutritional support during the hospital stay reduces mortality in patients with different types of cancers: Secondary analysis of a prospective randomized trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracos, V.; Kazemi-Bajestani, S.M. Clinical outcomes related to muscle mass in humans with cancer and catabolic illnesses. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Birdsell, L.; Macdonald, N.; Reiman, T.; Clandinin, M.T.; McCargar, L.J.; Murphy, R.; Ghosh, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: Skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odelli, C.; Burgess, D.; Bateman, L.; Hughes, A.; Ackland, S.; Gillies, J.; Collins, C.E. Nutrition support improves patient outcomes, treatment tolerance and admission characteristics in oesophageal cancer. Clin. Oncol. R Coll Radiol 2005, 17, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paccagnella, A.; Morello, M.; Da Mosto, M.C.; Baruffi, C.; Marcon, M.L.; Gava, A.; Baggio, V.; Lamon, S.; Babare, R.; Rosti, G.; et al. Early nutritional intervention improves treatment tolerance and outcomes in head and neck cancer patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Support Care Cancer 2010, 18, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, H.; Yano, M.; Yasuda, T.; Hamano, R.; Yamasaki, M.; Hou, E.; Motoori, M.; Shiraishi, O.; Tanaka, K.; Mori, M.; et al. Randomized study of clinical effect of enteral nutrition support during neoadjuvant chemotherapy on chemotherapy-related toxicity in patients with esophageal cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, N.; Montoya, J.E.; Luna, H.G.; Amparo, J.R.; Cristal-Luna, G. Quality of life and nutritional status among cancer patients on chemotherapy. Oman Med. J. 2013, 28, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Lopez, L.; Blanco, B.; Colato, C.A.; Kelly, O.J.; Sanz, R.; AdNut, G. AdNut study: Effectiveness of a high calorie and protein oral nutritional supplement with beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate in an older malnourished population in usual clinical practice. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritch, C.R.; Cookson, M.S.; Clark, P.E.; Chang, S.S.; Fakhoury, K.; Ralls, V.; Thu, M.H.; Penson, D.F.; Smith, J.A., Jr.; Silver, H.J. Perioperative Oral Nutrition Supplementation Reduces Prevalence of Sarcopenia following Radical Cystectomy: Results of a Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Urol. 2019, 201, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrao, G.; Cantarutti, A. Building reliable evidence from real-world data: Needs, methods, cautiousness and recommendations. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 53, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall (N = 283) | S-ONS N = 240 | ONS N = 43 | p-Value (between Groups) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.9 (14.2) | 59.0 (14.6) | 62.7 (13.8) | 0.131 |
| Gender N (%) | 0.107 | |||
| Male | 149 (53%) | 121 (50.4) | 28 (65.1) | |
| Female | 134 (47%) | 119 (49.6) | 15 (34.9) | |
| Admission | 0.304 | |||
| Oncology surgery | 179 (63%) | 155 (64.6) | 24 (55.8) | |
| General surgery | 44 (16%) | 34 (14.2) | 10 (23.3) | |
| Others | 60 (21%) | 51 (21.2) | 9 (20.9) | |
| Anthropometrics | ||||
| Basal weight (kg) | 63.1 (12.9) | 63.2 (12.9) | 62.6 (13.3) | 0.770 |
| Basal BMI (kg/m2) | 23.2 (4.4) | 23.2 (4.5) | 23.1 (4.3) | 0.827 |
| Biceps fold (mm) | 10.4 (4.8) | 10.7 (5.0) | 9.0 (2.6) | 0.026 |
| Arm circumference (cm) | 25.5 (3.9) | 25.7 (3.9) | 24.1 (3.5) | 0.011 |
| Handgrip strength | ||||
| Dynamometry (kg) | 18.7 (13.0) | 18.3 (13.0) | 20.4 (12.6) | 0.333 |
| Body composition | ||||
| Fat mass (kg) | 15.3 (7.7) | 15.5 (7.9) | 14.5 (6.5) | 0.438 |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 47.9 (9.1) | 47.9 (9.1) | 48.1 (9.3) | 0.859 |
| Total body water (kg) | 35.1 (6.6) | 35.1 (6.6) | 35.1 (6.8) | 0.950 |
| Nutritional status | ||||
| PG-SGA | 0.704 | |||
| At risk of malnutrition | 82 (29.0) | 68 (28.3) | 14 (32.6) | |
| Malnutrition | 201 (71.0) | 172 (71.7) | 29 (67.4) | |
| SEDOM-SENPE Calorie malnutrition Protein malnutrition Protein calorie malnutrition | 0.074 | |||
| 20 (7.1) | 20 (8.3) | |||
| 16 (5.7) | 15 (6.2) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| 247 (87.3) | 205 (85.4) | 42 (97.7) | ||
| Biochemistry | ||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.9 (0.7) | 2.9 (0.6) | 2.9 (0.6) | 0.895 |
| Prealbumin (mg/dL) | 19.2 (6.5) | 18.9 (6.4) | 20.7 (6.8) | 0.088 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 32.2 (51.0) | 32.6 (50.9 | 30.2 (51.7) | 0.772 |
| CRP/Prealbumin | 0.24 (0.50) | 0.25 (0.52) | 0.18 (0.33) | 0.395 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 150.1 (41.3) | 151.1 (40.7) | 144.5 (44.5) | 0.335 |
| Lymphocytes (mm3 × 10−3) | 1.5 (1.0) | 1.5 (1.1) | 1.4 (0.5) | 0.346 |
| S-ONS N = 240 | ONS N = 43 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal | Final | Basal | Final | |
| Anthropometrics | ||||
| Body weight (kg) | 63.2 (12.9) | 67.2 (13.5) * | 62.6 (13.3) | 66.2 (14.6) * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.2 (4.5) | 24.7 (4.8) * | 23.1 (4.3) | 24.4 (4.8) * |
| Biceps fold (mm) | 10.7 (5.0) # | 12.2 (5.3) * | 9.0 (2.6) | 10.4 (3.6) * |
| Arm circumference (cm) | 25.7 (3.9) # | 27.5 (4.1) *# | 24.1 (3.5) | 25.7 (4.3) * |
| Handgrip strength | ||||
| Dynamometry (kg) | 18.3 (13.0) | 25.2 (14.4) * | 20.4 (12.6) | 24.9 (14.7) * |
| Body composition | ||||
| Fat mass (kg) | 15.5 (7.9) | 18.1 (9.0) * | 14.5 (6.5) | 17.0 (8.4) * |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 47.9 (9.1) | 49.1 (9.0) * | 48.1 (9.3) | 49.0 (8.8) |
| Total body water (kg) | 35.1 (6.6) | 35.9 (6.5) * | 35.1 (6.8) | 36.0 (6.6) * |
| Biochemistry | ||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.9 (0.7) | 3.8 (0.5) * | 2.9 (0.6) | 3.6 (0.4) * |
| Prealbumin (mg/dL) | 18.9 (6.4) | 24.7 (6.7) * | 20.7 (6.8) | 24.4 (7.1) * |
| CRP (mg/L) | 32.6 (50.9) | 10.8 (34.0) * | 30.2 (51.7) | 9.3 (29.9) * |
| CRP/Prealbumin | 0.25 (0.52) | 0.08 (0.40) * | 0.18 (0.33) | 0.15 (0.82) |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 151.1 (40.7) | 178.7 (48.4) * | 144.5 (44.5) | 165.1 (36.9) * |
| Lymphocytes (mm3 × 10−3) | 1.5 (1.1) | 1.9 (0.9) * | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.8 (0.8) * |
| S-ONS N = 31 | ONS N = 12 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal | Final | Basal | Final | |
| Anthropometrics | ||||
| Body weight (kg) | 60.5 (10.8) | 63.9 (11.5) * | 58.9 (11.7) | 60.5 (12.5) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.0 (3.2) | 23.2 (3.5) * | 22.2 (2.9) | 22.8 (3.3) |
| Biceps fold (mm) | 9.0 (3.2) | 10.3 (3.6) * | 8.1 (1.5) | 9.1 (2.0) * |
| Arm circumference (cm) | 23.7 (2.6) | 25.2 (2.8) * | 22.9 (2.6) | 23.9 (3.2) * |
| Handgrip strength | ||||
| Dynamometry (kg) | 24.7 (11.3) | 30.0 (11.0) * | 18.6 (12.7) | 23.2 (14.7) * |
| Body composition by phase angle | ||||
| PhA (°) | 5.2 (1.1) | 6.0 (1.1) * | 4.9 (1.0) | 5.2 (1.0) |
| SPhA (°) | −0.9 (1.1) | −0.1 (0.9) * | 0.2 (1.7) | 0.6 (1.7) |
| BCM (kg) | 24.2 (6.7) | 26.8 (5.9) *# | 22.1 (5.2) | 22.5 (3.7) |
| Nutritional status (mg/m/24 h) | 728.5 (200.8) | 807.3 (180.7) * | 687.5 (145.4) | 717.5 (126.9) |
| Hydration (%) | 74.8 (3.3) | 72.9 (1.3) * | 75.5 (4.4) | 74.8 (4.3) |
| TBW (L) | 36.6 (6.6) | 36.5 (6.6) | 35.4 (8.6) | 36.2 (7.8) |
| ECW (L) | 18.0 (3.2) | 16.7 (3.1) * | 19.0 (5.4) | 18.4 (5.6) |
| ICW (L) | 18.3 (4.7) | 19.8 (4.4) * | 17.3 (3.4) | 17.8 (3.1) |
| FFM (kg) | 49.0 (8.8) # | 49.5 (9.5) # | 36.1 (17.7) | 41.0 (15.7) * |
| FM (kg) | 11.4 (5.5) # | 13.1 (6.5) | 9.0 (6.9) | 12.1 (7.0) |
| ASMM (kg) | 18.3 (4.2) | 18.7 (4.0) * | 17.3 (3.7) | 17.5 (3.9) |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 8.7 (1.7) | 8.5 (1.7) | 8.8 (1.6) | 8.6 (1.8) |
| Biochemistry | ||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.2 (0.6) | 3.9 (0.6) * | 3.1 (0.4) | 3.6 (0.4) |
| Prealbumin (mg/dL) | 19.4 (5.5) | 24.9 (7.0) * | 18.8 (4.7) | 21.8 (5.7) |
| CRP (mg/L) | 11.2 (17.2) | 6.6 (19.2) | 20.8 (41.0) | 6.2 (5.6) |
| CRP/Prealbumin | 0.07 (0.14) | 0.06 (0.24) | 0.13 (0.27) | 0.03 (0.04) |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 155.5 (39.4) | 178.9 (42.0) * | 163.6 (46.0) | 178.4 (41.4) |
| Lymphocytes (mm3 × 10−3) | 1.6 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.4) * | 2.0 (0.6) | 1.9 (1.0) * |
| Basal | Final | |
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometrics | ||
| Body weight (kg) | 63.1 (12.4) | 66.2 (12.4) * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.3 (4.3) | 24.5 (4.5) * |
| Biceps fold (mm) | 10.9 (5.2) | 12.2 (5.4) * |
| Arm circumference (cm) | 25.5 (3.8) | 27.1 (3.9) * |
| Handgrip strength | ||
| Dynamometry (kg) | 18.9 (12.9) | 25.8 (14.4) * |
| Body composition | ||
| Fat mass (kg) | 15.6 (7.8) | 17.6 (8.3) * |
| Fat-Free mass (kg) | 47.7 (8.9) | 48.7 (8.6) * |
| Corporal water (kg) | 34.9 (6.5) | 35.6 (6.3) * |
| Biochemistry | ||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.0 (0.7) | 3.8 (0.5) * |
| Prealbumin (mg/dL) | 18.3 (5.9) | 24.0 (7.1) * |
| CRP (mg/L) | 31.7 (51.9) | 13.9 (41.9) * |
| CRP/Prealbumin | 0.27 (0.59) | 0.12 (0.49) * |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 157.0 (39.2) | 181.6 (43.7) * |
| Lymphocytes (mm3 × 10−3) | 1.5 (1.2) | 1.9 (1.0) * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Ramirez, M.; Camprubi-Robles, M.; Rueda, R.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Garcia-Almeida, J.M. Effect on an Oral Nutritional Supplement with β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and Vitamin D on Morphofunctional Aspects, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Malnourished Patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124355
Cornejo-Pareja I, Ramirez M, Camprubi-Robles M, Rueda R, Vegas-Aguilar IM, Garcia-Almeida JM. Effect on an Oral Nutritional Supplement with β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and Vitamin D on Morphofunctional Aspects, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Malnourished Patients. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124355
Chicago/Turabian StyleCornejo-Pareja, Isabel, Maria Ramirez, Maria Camprubi-Robles, Ricardo Rueda, Isabel Maria Vegas-Aguilar, and Jose Manuel Garcia-Almeida. 2021. "Effect on an Oral Nutritional Supplement with β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and Vitamin D on Morphofunctional Aspects, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Malnourished Patients" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124355
APA StyleCornejo-Pareja, I., Ramirez, M., Camprubi-Robles, M., Rueda, R., Vegas-Aguilar, I. M., & Garcia-Almeida, J. M. (2021). Effect on an Oral Nutritional Supplement with β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate and Vitamin D on Morphofunctional Aspects, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Malnourished Patients. Nutrients, 13(12), 4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124355






