Salicylic Acid and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genetic Variants for Salicylic Acid
2.2. Genetic Variants for CRC Incidence
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
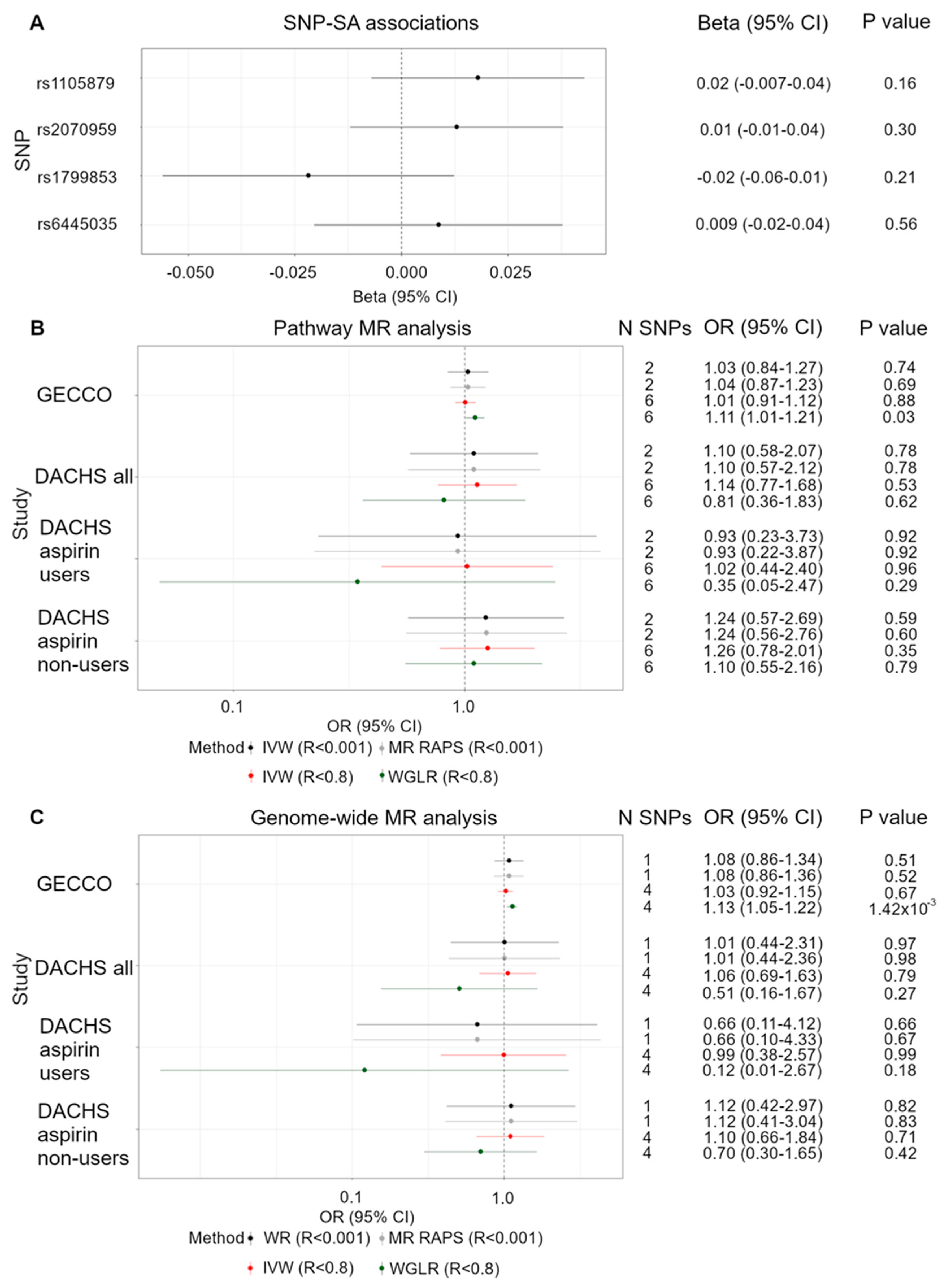
3.1. Functional SNPs and CRC Risk
3.2. Pathway SNPs and CRC Risk
3.3. Genome-Wide Significant SNPs and CRC Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowel Cancer Statistics|Cancer Research, UK. Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/bowel-cancer#heading-Zero (accessed on 13 April 2018).
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Research, UK. Bowel Cancer Incidence Trends over Time. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/bowel-cancer/incidence#heading-Two (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Anderson, W.F.; Miller, K.D.; Ma, J.; Rosenberg, P.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Incidence Patterns in the United States, 1974–2013. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, S.; Gibson, P.R.; Barrett, J.S.; Muir, J.G. Naturally occurring dietary salicylates: A closer look at common Australian foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 57, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.; Baxter, G.; Thies, F.; Kyle, J.; Duthie, G. A systematic review of salicylates in foods: Estimated daily intake of a Scottish population. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, S7–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadafranca, A.; Bertoli, S.; Fiorillo, G.; Testolin, G.; Battezzati, A. Circulating salicylic acid is related to fruit and vegetable consumption in healthy subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, D.; Lau, R.; Chan, D.S.; Vieira, R.; Greenwood, D.C.; Kampman, E.; Norat, T. Nonlinear Reduction in Risk for Colorectal Cancer by Fruit and Vegetable Intake Based on Meta-analysis of Prospective Studies. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Chan, D.S.M.; Lau, R.; Vieira, R.; Greenwood, D.C.; Kampman, E.; Norat, T. Dietary fibre, whole grains, and risk of colorectal cancer: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ 2011, 343, d6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatham, M.H.; Cole, C.; Scullion, P.; Wilkie, R.; Westwood, N.J.; Stark, L.A.; Hay, R.T. A Proteomic Approach to Analyze the Aspirin-mediated Lysine Acetylome. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.K. Aspirin and salicylate: An old remedy with a new twist. Circulation 2000, 102, 2022–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, J.R.; Srivastava, R.; Baxter, G.J.; Graham, A.B.; Lawrence, J.R. Salicylic acid content of spices and its implications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, S.; Chivukula, R.S.V.; Alfonso, L.F.; Moridani, M.; Hagen, F.K.; Bhat, G.J. Aspirin acetylates multiple cellular proteins in HCT-116 colon cancer cells: Identification of novel targets. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rang, H.; Dale, M.M. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology, 7th ed.; Elsevier Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, Scotland, 2012; 113p. [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Cook, N.R.; Gaziano, J.M.; Price, J.F.; Belch, J.J.; Roncaglioni, M.C.; Morimoto, T.; Mehta, Z. Effects of aspirin on risks of vascular events and cancer according to bodyweight and dose: Analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2018, 392, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agundez, J.; Martinez, C.; Perez-Sala, D.; Carballo, M.; Torres, M.; Garcia-Martin, E. Pharmacogenomics in Aspirin Intolerance. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, D.A.; Chan, A.T. Aspirin in the Prevention of Colorectal Neoplasia. Annu. Rev. Med. 2021, 72, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.-M.; Zhang, S.M.; Moorthy, M.V.; Buring, J.E. Alternate-Day, Low-Dose Aspirin and Cancer Risk: Long-Term Observational Follow-up of a Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Yang, T.; Gan, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Gong, Y.; Lu, Z. Associations between aspirin use and the risk of cancers: A meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Wilson, M.; Elwin, C.-E.; Norrving, B.; Algra, A.; Warlow, C.P.; Meade, T.W. Long-term effect of aspirin on colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: 20-year follow-up of five randomised trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Belch, J.J.; Ogawa, H.; Warlow, C.P.; Meade, T.W. Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk of death due to cancer: Analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needs, C.J.; Brooks, P.P.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of the Salicylates. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1985, 10, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, B.K.; Waltner-Law, M.E.; Entingh, A.J.; Chytil, A.; Aakre, M.E.; Nørgaard, P.; Moses, H.L. Salicylate-induced Growth Arrest Is Associated with Inhibition of p70s6k and Down-regulation of c-Myc, Cyclin D1, Cyclin A, and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38261–38267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, G.M.; Johnson, A.S.; Partington, M.; Burn, J.; Wilson, R.; Arthur, H.M. Therapeutic levels of aspirin and salicylate directly inhibit a model of angiogenesis through a Cox- independent mechanism. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathi, S.; Jutooru, I.; Chadalapaka, G.; Nair, V.; Lee, S.O.; Safe, S. Aspirin Inhibits Colon Cancer Cell and Tumor Growth and Downregulates Specificity Protein (Sp) Transcription Factors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Ebrahim, S. “Mendelian randomization”: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hemani, G. Mendelian randomization: Genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Timpson, N.; Smith, G.D. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Ebrahim, S. What can Mendelian randomisation tell us about modifiable behavioural and environmental exposures? Br. Med. J. 2005, 330, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, D.; Molokhia, M.; Smeeth, L.; DeStavola, B.L.; Whittaker, J.; Leon, D. Limits to Causal Inference based on Mendelian Randomization: A Comparison with Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.A.; Thompson, I.; Tangen, C.M.; Lucia, M.S.; Goodman, P.; Minasian, L.M.; Ford, L.G.; Parnes, H.L.; Gaziano, J.M.; Karp, D.D.; et al. Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: Updated results of the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarmolinsky, J.; Bonilla, C.; Haycock, P.C.; Langdon, R.J.Q.; Lotta, L.A.; Langenberg, C.; Relton, C.L.; Lewis, S.J.; Evans, D.M.; Smith, G.D.; et al. Circulating Selenium and Prostate Cancer Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, N.; Oakes, S.; Luben, R.; Khaw, K.T.; Bingham, S.; Welch, A.; Wareham, N. EPIC-Norfolk: Study design and characteristics of the cohort. European Prospective Investigation of Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80 (Suppl. 1), 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Thompson, S.G.; Kaptoge, S.; Moore, C.; Walker, M.; Armitage, J.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Roberts, D.J.; Danesh, J.; Donovan, J.; et al. Efficiency and safety of varying the frequency of whole blood donation (INTERVAL): A randomised trial of 45,000 donors. Lancet 2017, 390, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.-R.; Tucker, G.J.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.K.; Vilhjalmsson, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Salem, R.; Chasman, D.I.; Ridker, P.M.; Neale, B.M.; Berger, B.; et al. Efficient Bayesian mixed-model analysis increases association power in large cohorts. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, C.; Li, Y.; Abecasis, G.R. METAL: Fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2190–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiger, D.; Stock, J.H. Instrumental Variables Regression with Weak Instruments Author. Econometrica 1997, 65, 557–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mRnd: Power Calculations for Mendelian Randomization. Available online: http://cnsgenomics.com/shiny/mRnd/ (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Huyghe, J.R.; Bien, S.A.; Harrison, T.A.; Kang, H.M.; Chen, S.; Schmit, S.L.; Conti, D.V.; Qu, C.; Jeon, J.; Edlund, C.K.; et al. Discovery of common and rare genetic risk variants for colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, F.; Schmit, S.L.; Jiao, S.; Edlund, C.K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Hsu, L.; Huang, S.-C.; Fischer, C.P.; Harju, J.F.; et al. Genome-wide association study of colorectal cancer identifies six new susceptibility loci. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, H.; Chang-Claude, J.; Seiler, C.M.; Rickert, A.; Hoffmeister, M. Protection from Colorectal Cancer After Colonoscopy: A Population-Based, Case-Control Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 154, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, H.; Chang–Claude, J.; Jansen, L.; Knebel, P.; Stock, C.; Hoffmeister, M. Reduced Risk of Colorectal Cancer Up to 10 Years After Screening, Surveillance, or Diagnostic Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitay, E.L.; Carr, P.; Jansen, L.; Walter, V.; Roth, W.; Herpel, E.; Kloor, M.; Bläker, H.; Chang-Claude, J.; Brenner, H.; et al. Association of Aspirin and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs with Colorectal Cancer Risk by Molecular Subtypes. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 111, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian Randomization Analysis with Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Hemani, G.; Bowden, J.; Small, D.S. Statistical inference in two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization using robust adjusted profile score. Ann. Stat. 2020, 48, 1742–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slob, E.A.; Burgess, S. A comparison of robust Mendelian randomization methods using summary data. Genet Epidemiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Smith, G.D.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Smith, G.D.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Smith, G.D.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.F.; Del Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Dudbridge, F.; Thompson, S.G. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: Comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat. Med. 2015, 35, 1880–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Marathe, G.; Hartiala, J.; Hazen, S.L.; Allayee, H.; Tang, W.H.W.; McIntyre, T.M. Aspirin Hydrolysis in Plasma Is a Variable Function of Butyrylcholinesterase and Platelet-activating Factor Acetylhydrolase 1b2 (PAFAH1b2). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11940–11948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, M.; Marrone, A.; Potter, C.; Owens, I.S. Genetic polymorphism in the human UGT1A6 (planar phenol) UDP-glucuronosyltransferase: Pharmacological implications. Pharmacogenetics 1997, 7, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, S.; Zalatoris, J.J.; Blanchard, R.L. Human UGT1A6 pharmacogenetics: Identification of a novel SNP, characterization of allele frequencies and functional analysis of recombinant allozymes in human liver tissue and in cultured cells. Pharmacogenetics 2004, 14, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespi, C.L.; Miller, V.P. The R144C change in the CYP2C9*2 allele alters interaction of the cytochrome P450 with NADPH:cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. Pharmacogenetics 1997, 7, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Tilling, K.; Davey Smith, G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007081. [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel, P.T. The heterogeneity statistic I2 can be biased in small meta-analyses. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2015, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, J.R.; Lawrence, J.R. Salicylic acid: A link between aspirin, diet and the prevention of colorectal cancer. QJM Int. J. Med. 2001, 94, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachineni, R.; Ai, G.; Kumar, D.R.; Sadhu, S.S.; Tummala, H.; Bhat, G.J. Cyclin A2 and CDK2 as Novel Targets of Aspirin and Salicylic acid: A Potential Role in Cancer Prevention. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, N.A.; Didelez, V. Epidemiology, genetic epidemiology and Mendelian randomisation: More need than ever to attend to detail. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 139, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoore, R.V.; Vaidyanathan, S. Towards quantitative mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in microbial and mammalian systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.L.; Ahsan, H.; VanderWeele, T.J. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 40, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
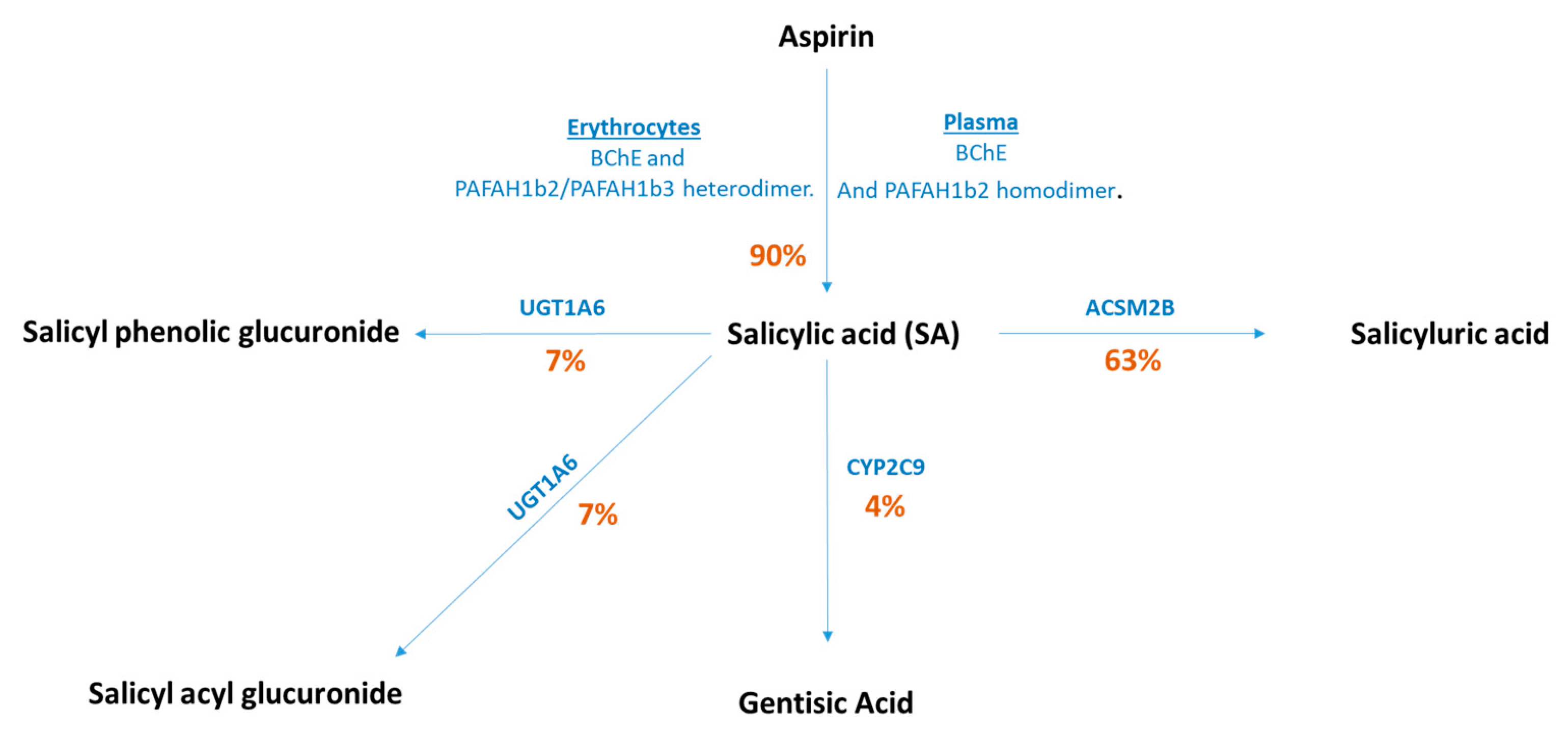

| SNP Set | Study | Outcome Sample Size | Percentage Cases (%) | N SNPs | LD R2 | Variance Explained R2 (%) | F Statistics | OR Detected at 80% Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decreased Risk | Increased Risk | ||||||||
| Pathway SNPs | GECCO | 120,328 | 45.85 55,168/120,328) | 2 | 0.001 | 0.025 | 1.74 | 0.90 | 1.11 |
| DACHS | 7851 | 56.17 | 2 | 0.68 | 1.51 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin users | 1589 | (4410/7851) | 2 | 0.43 | 2.38 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin non-users | 5660 | 50.98 | 2 | 0.64 | 1.64 | ||||
| GECCO | 120,328 | (810/1589) | 6 | 0.8 | 0.092 | 2.16 | 0.95 | 1.06 | |
| DACHS | 7851 | 59.01 | 6 | 0.81 | 1.24 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin users | 1589 | (3340/5660) | 6 | 0.63 | 1.58 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin non-users | 5660 | 45.85 (55,168/120,328) | 6 | 0.78 | 1.30 | ||||
| Genome-wide SNPs | GECCO | 120,328 | 45.85 55,168/120,328) | 2 | 0.001 | 0.053 | 7.44 | 0.93 | 1.07 |
| DACHS | 7851 | 56.17 | 2 | 0.76 | 1.32 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin users | 1589 | (4410/7851) | 2 | 0.55 | 1.83 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin non-users | 5660 | 50.98 | 2 | 0.73 | 1.42 | ||||
| GECCO | 120,328 | (810/1589) | 6 | 0.8 | 0.090 | 3.18 | 0.95 | 1.06 | |
| DACHS | 7851 | 59.01 | 6 | 0.81 | 1.24 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin users | 1589 | (3340/5660) | 6 | 0.63 | 1.59 | ||||
| DACHS aspirin non-users | 5660 | 45.85 (55,168/120,328) | 6 | 0.78 | 1.30 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nounu, A.; Richmond, R.C.; Stewart, I.D.; Surendran, P.; Wareham, N.J.; Butterworth, A.; Weinstein, S.J.; Albanes, D.; Baron, J.A.; Hopper, J.L.; et al. Salicylic Acid and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114164
Nounu A, Richmond RC, Stewart ID, Surendran P, Wareham NJ, Butterworth A, Weinstein SJ, Albanes D, Baron JA, Hopper JL, et al. Salicylic Acid and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114164
Chicago/Turabian StyleNounu, Aayah, Rebecca C. Richmond, Isobel D. Stewart, Praveen Surendran, Nicholas J. Wareham, Adam Butterworth, Stephanie J. Weinstein, Demetrius Albanes, John A. Baron, John L. Hopper, and et al. 2021. "Salicylic Acid and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114164
APA StyleNounu, A., Richmond, R. C., Stewart, I. D., Surendran, P., Wareham, N. J., Butterworth, A., Weinstein, S. J., Albanes, D., Baron, J. A., Hopper, J. L., Figueiredo, J. C., Newcomb, P. A., Lindor, N. M., Casey, G., Platz, E. A., Marchand, L. L., Ulrich, C. M., Li, C. I., van Dujinhoven, F. J. B., ... Relton, C. L. (2021). Salicylic Acid and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients, 13(11), 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114164








