Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Glucose, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism and L-Theanine in the Metabolism-Regulatory Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate
Abstract
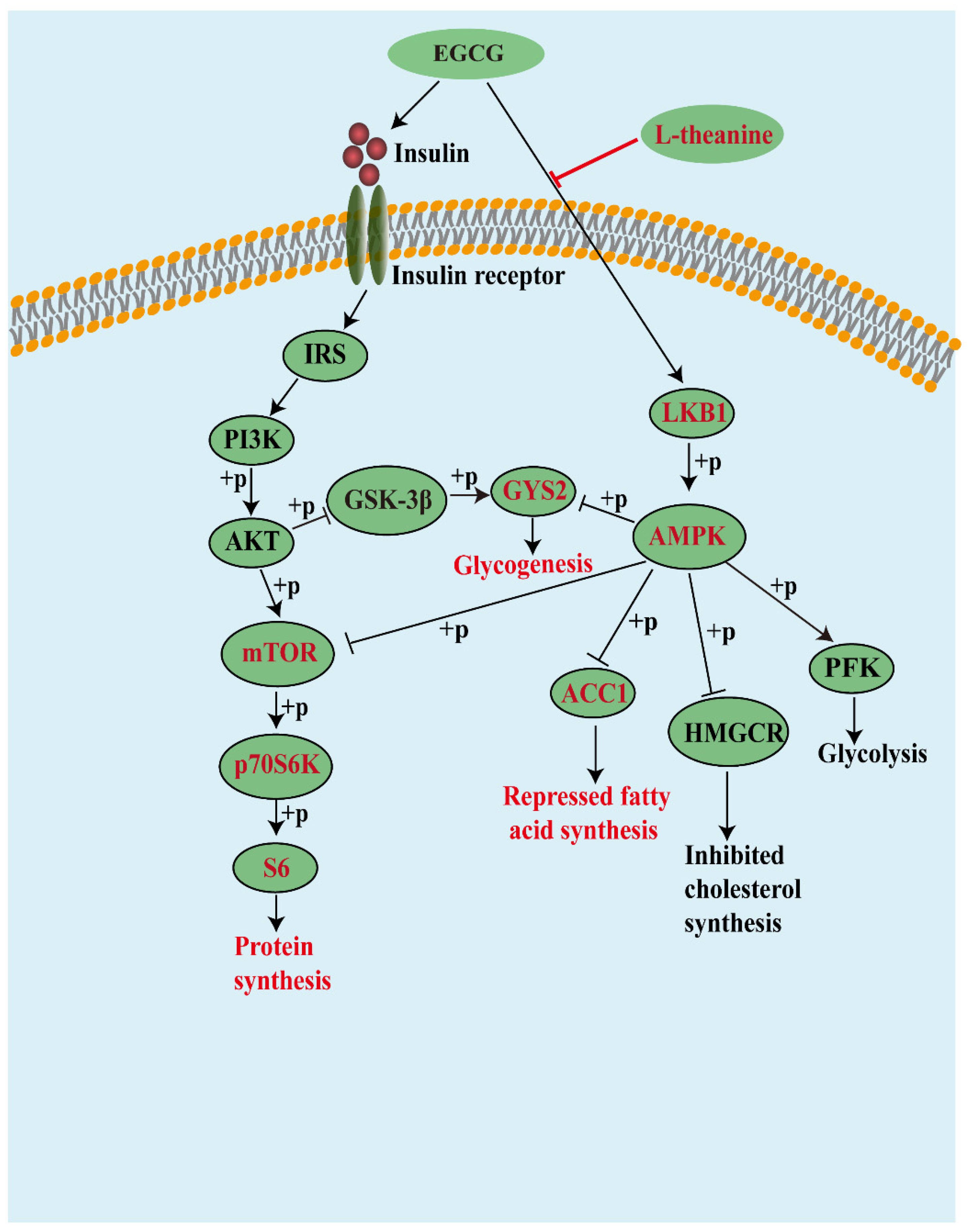
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Liver Histological Analysis
2.5. Serum Biochemical Indexes and Enzyme Activity Measurement
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Neither EGCG Nor EGCG+LTA Was Toxic to Rats
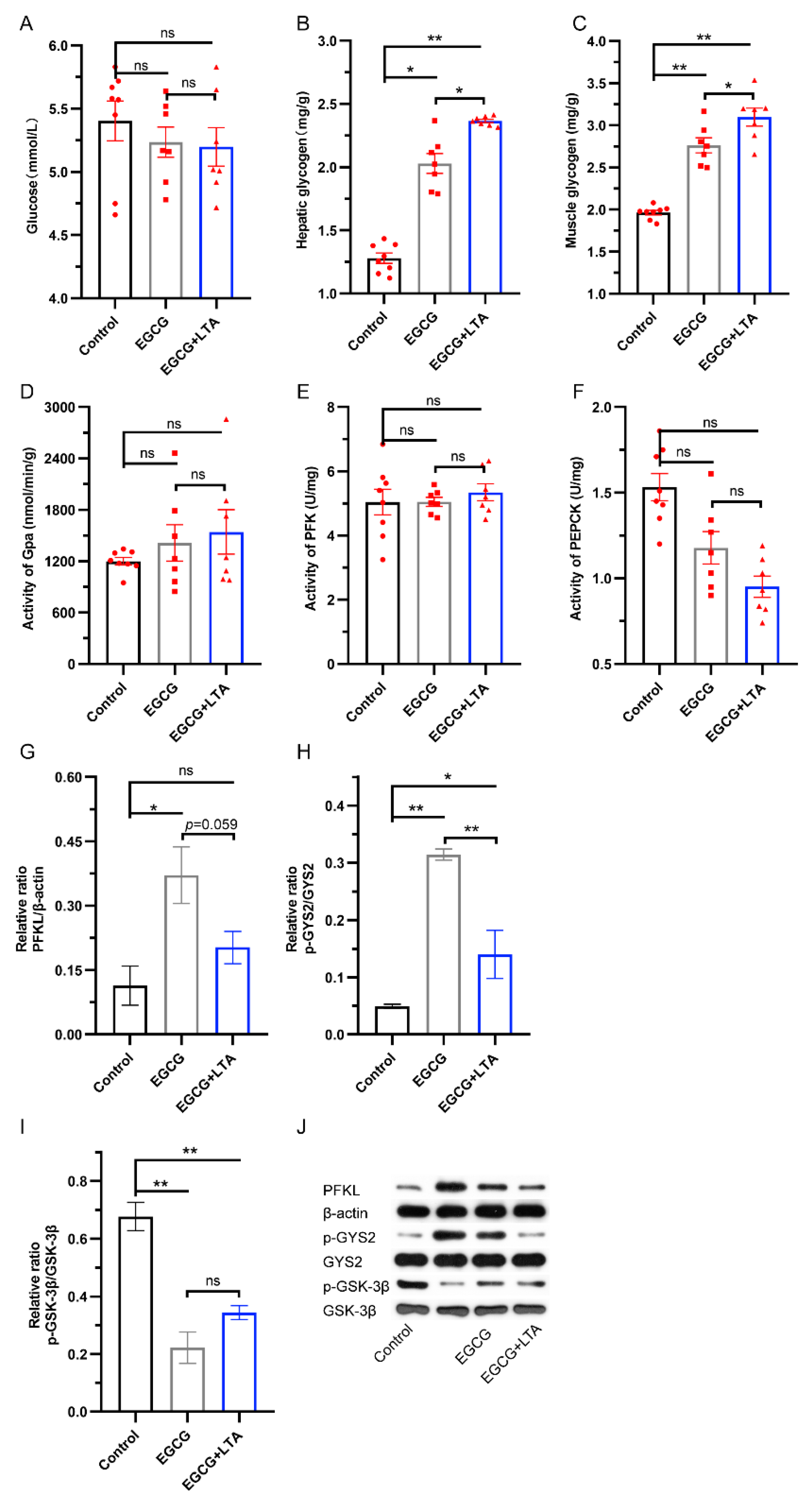
3.2. LTA Cooperated with EGCG to Promote Glycogen Synthesis
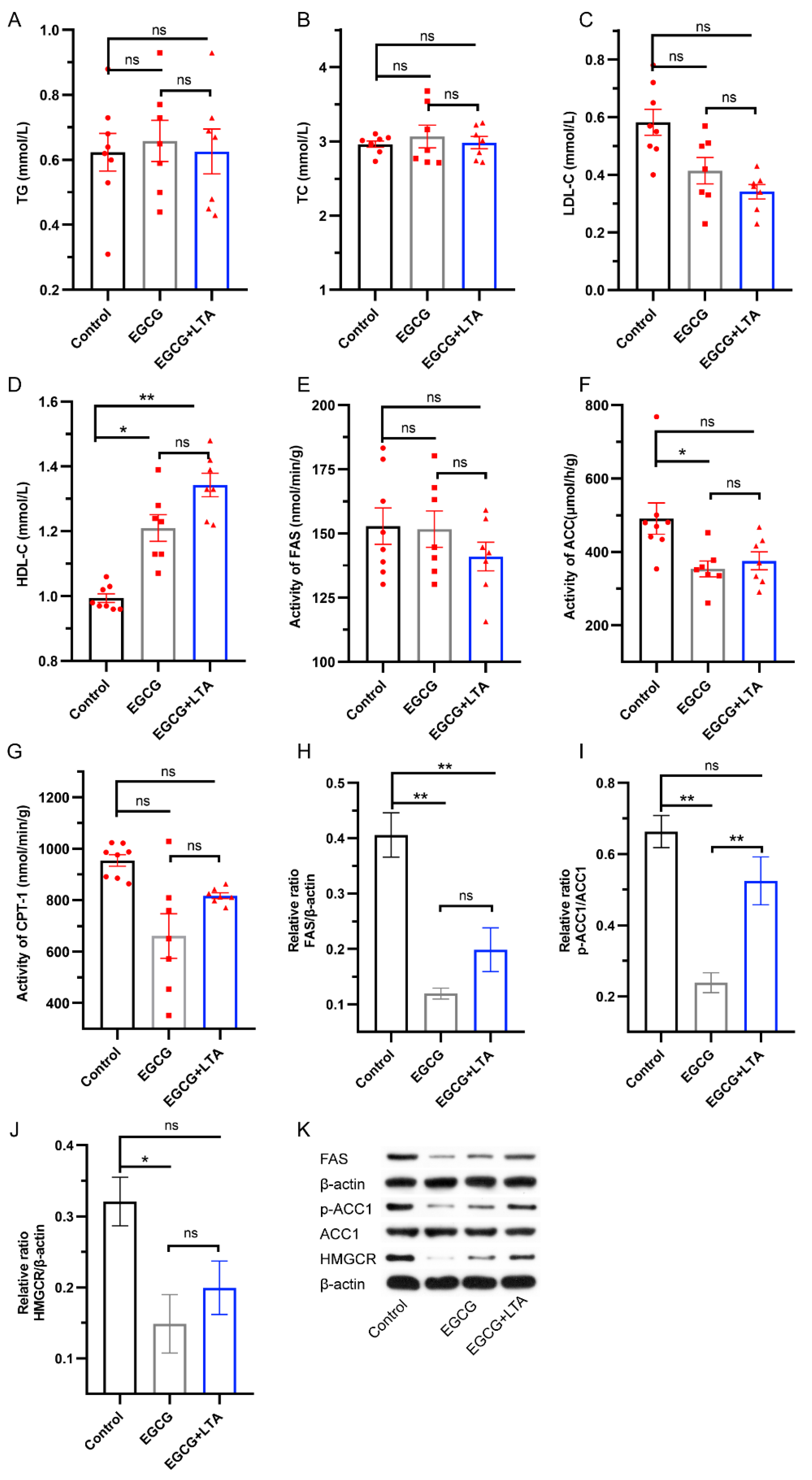
3.3. EGCG and LTA Co-Administration Affected Lipid Synthesis Less Significantly Than EGCG Alone
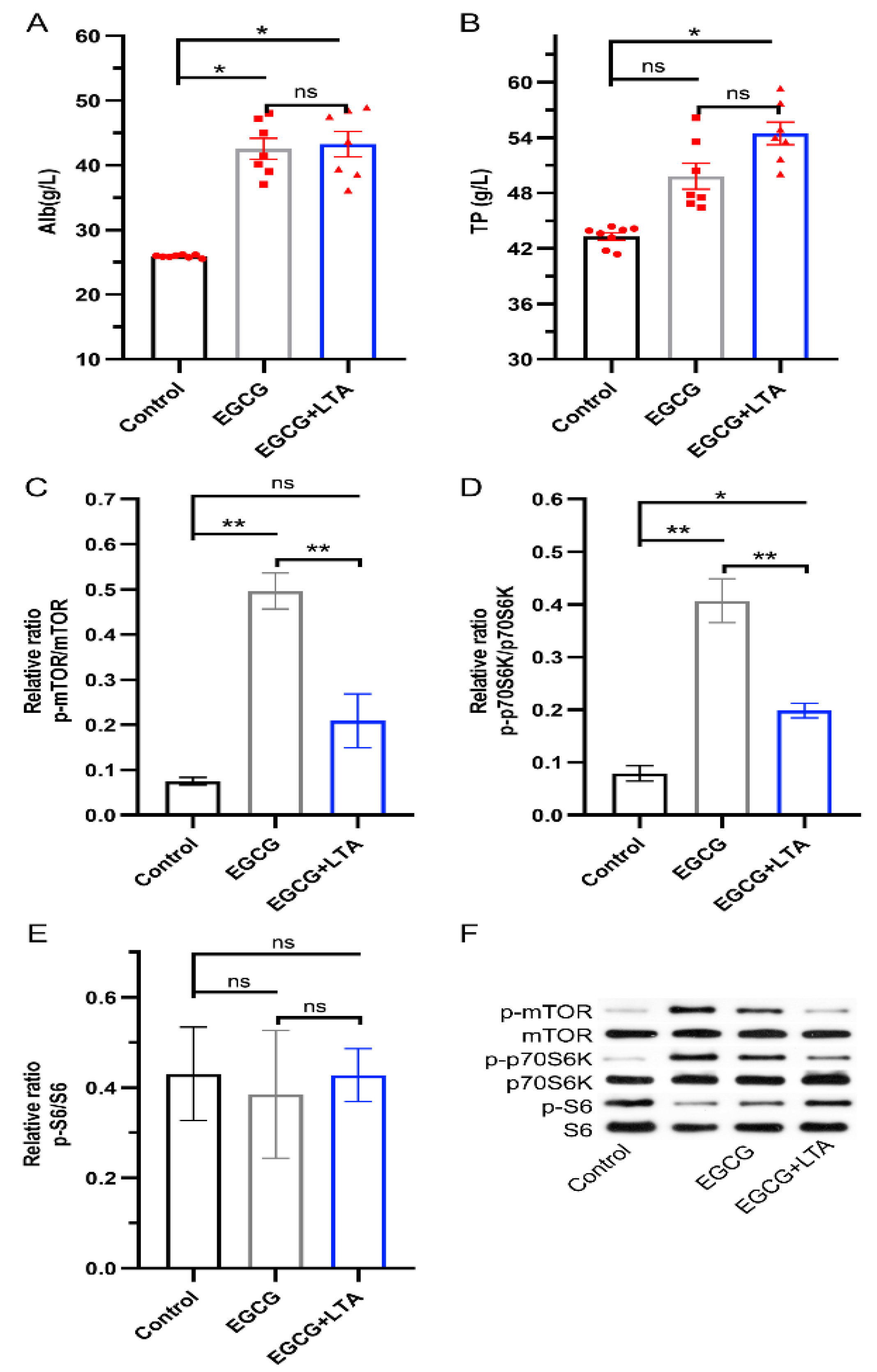
3.4. Protein Synthesis Promoted by EGCG Was Weakened by LTA
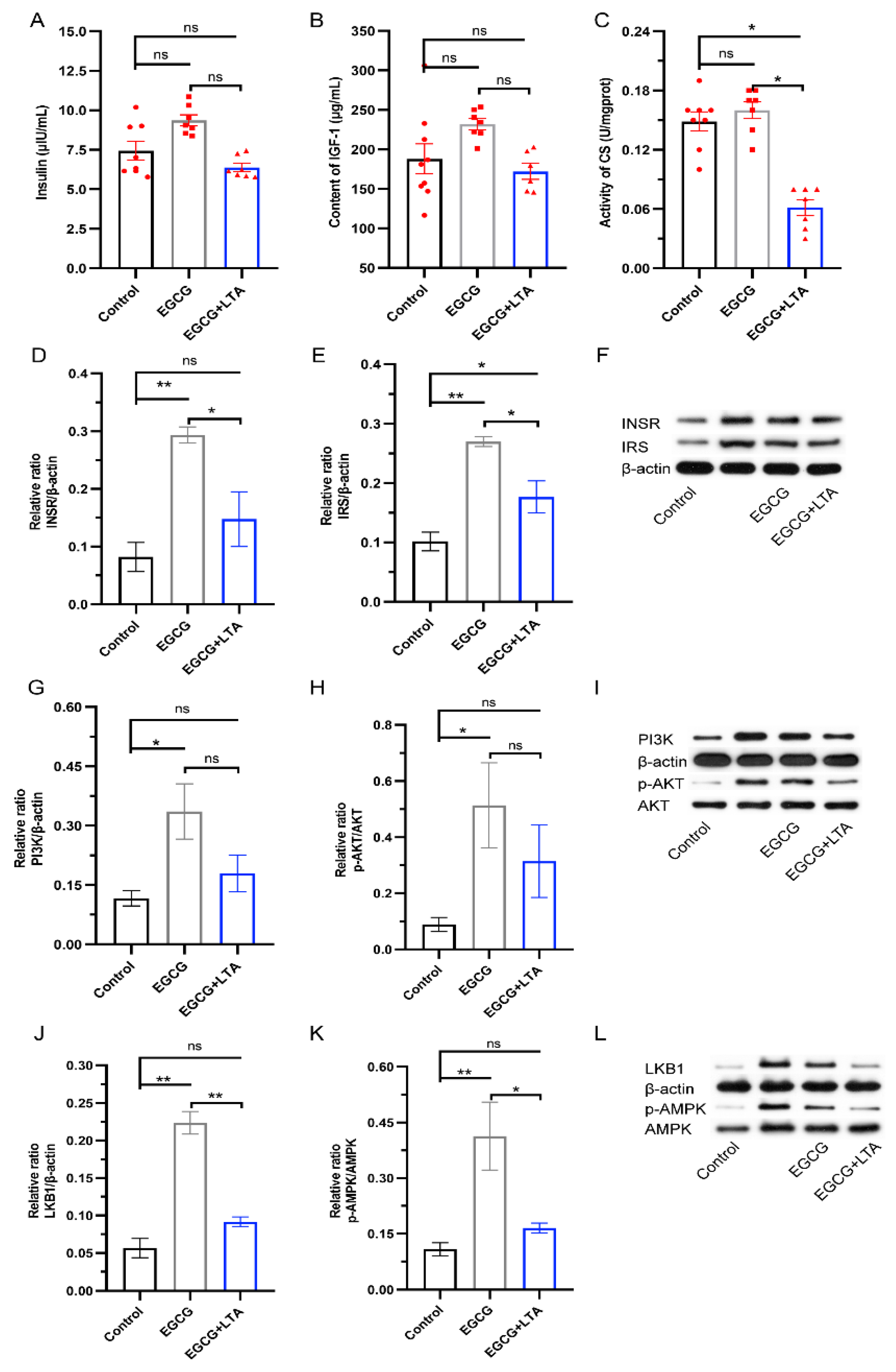
3.5. AMPK Signals Played an Important Role in the Metabolism-Regulatory Effects of EGCG and EGCG+LTA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarris, J.; Byrne, G.J.; Cribb, L.; Oliver, G.; Murphy, J.; Macdonald, P.; Nazareth, S.; Karamacoska, D.; Galea, S.; Short, A.; et al. L-theanine in the adjunctive treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 110, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Lin, L.; Liu, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Gong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, W. L-Theanine affects intestinal mucosal immunity by regulating short-chain fatty acid metabolism under dietary fiber feeding. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8369–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.H.; Lin, L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, A.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.L.; Deng, Y.L.; Xiao, W.J. Immune-modulatory effects and mechanism of action of L-theanine on ETEC-induced immune-stressed mice via nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidese, S.; Ogawa, S.; Ota, M.; Ishida, I.; Yasukawa, Z.; Ozeki, M.; Kunugi, H. Effects of L-Theanine Administration on Stress-Related Symptoms and Cognitive Functions in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turkozu, D.; Sanlier, N. L-theanine, unique amino acid of tea, and its metabolism, health effects, and safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Tong, H.; Tang, S.; Tan, Z.; Han, X.; Zhou, C. L-Theanine Administration Modulates the Absorption of Dietary Nutrients and Expression of Transporters and Receptors in the Intestinal Mucosa of Rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9747256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.D.; Sayama, K.; Okubo, T.; Juneja, L.R.; Oguni, I. Anti-obesity effects of three major components of green tea, catechins, caffeine and theanine, in mice, In vivo. In Vivo 2004, 18, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.Q.; Yuan, D.Y.; Lin, L.; Gong, Z.H.; Song, H.B.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.B.; Xiao, W.J. The Effect of EGCG on the Regulation of L-Theanine on Free Amino Acids in Serum and Intestine of Mice. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, A.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, W.; Gong, Z. l-Theanine regulates glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism via insulin and AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yan, W. Lipophilization of EGCG and effects on antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Z.; Yayla, M.; Cinar, I.; Atila, N.E.; Ozmen, S.; Bayraktutan, Z.; Bilici, D. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) exert therapeutic effect on acute inflammatory otitis media in rats. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 124, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, A.; Naponelli, V.; Rizzi, F.; Bettuzzi, S. Molecular Targets of Epigallocatechin-Gallate (EGCG): A Special Focus on Signal Transduction and Cancer. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eng, Q.Y.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Ramamurthy, S. Molecular understanding of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrawarti, L.; Agrawal, R.; Dang, S.; Gupta, S.; Gabrani, R. Therapeutic effects of EGCG: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gao, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Sheng, J. EGCG Reduces Obesity and White Adipose Tissue Gain Partly Through AMPK Activation in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.J.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, L.; Sun, Y.L.; Qu, X. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhance glycogen synthesis and inhibit lipogenesis in hepatocytes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 920128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, T.; Misawa, K.; Haramizu, S.; Hase, T. Catechin-induced activation of the LKB1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, P.; He, B.; Wu, N.; Han, P. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) attenuates FFAs-induced peripheral insulin resistance through AMPK pathway and insulin signaling pathway in vivo. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2011, 93, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camfield, D.A.; Stough, C.; Farrimond, J.; Scholey, A.B. Acute effects of tea constituents L-theanine, caffeine, and epigallocatechin gallate on cognitive function and mood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, M.Z.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wen, B.B.; An, H.M.; Ou, X.C.; Xiong, Y.F.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Huang, J.A. Coadministration of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and caffeine in low dose ameliorates obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lin, L.; Deng, Y.; Cai, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, W.; Xiong, S.; Chen, D. l-Theanine prevents ETEC-induced liver damage by reducing intrinsic apoptotic response and inhibiting ERK1/2 and JNK1/2 signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wan, X.; Yang, C.S.; Zhang, J. Green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate triggered hepatotoxicity in mice: Responses of major antioxidant enzymes and the Nrf2 rescue pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 283, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, M.; Ren, Z.; Meydani, M.; Shang, F.; Smith, D.; Meydani, S.N.; Wu, D. Dietary supplementation with high dose of epigallocatechin-3-gallate promotes inflammatory response in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Schmitz, H.J.; Baumgart, A.; Guedon, D.; Netsch, M.I.; Kreuter, M.H.; Schmidlin, C.B.; Schrenk, D. Toxicity of green tea extracts and their constituents in rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oketch-Rabah, H.A.; Roe, A.L.; Rider, C.V.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Giancaspro, G.I.; Navarro, V.; Paine, M.F.; Betz, J.M.; Marles, R.J.; Casper, S.; et al. United States Pharmacopeia (USP) comprehensive review of the hepatotoxicity of green tea extracts. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbrucker, R.A.; Edwards, J.A.; Wolz, E.; Davidovich, A.; Bausch, J. Safety studies on epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) preparations. Part 2: Dermal, acute and short-term toxicity studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.P.; Lin, J.K. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and rutin suppress the glucotoxicity through activating IRS2 and AMPK signaling in rat pancreatic beta cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9817–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R. Insulin signaling in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambandam, N.; Lopaschuk, G.D. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) control of fatty acid and glucose metabolism in the ischemic heart. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, S.; Cittadini, A.; Sabatini, D.; Merola, B.; Colao, A.; Biondi, B.; Longobardi, S.; Lombardi, G.; Sacca, L. Growth hormone and heart performance. A novel mechanism of cardiac wall stress regulation in humans. Eur. Heart J. 1997, 18, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsin, A.S.; Bertrand, L.; Rider, M.H.; Deprez, J.; Beauloye, C.; Vincent, M.F.; Van den Berghe, G.; Carling, D.; Hue, L. Phosphorylation and activation of heart PFK-2 by AMPK has a role in the stimulation of glycolysis during ischaemia. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, R.R., 3rd; Bergeron, R.; Shulman, G.I.; Young, L.H. Translocation of myocardial GLUT-4 and increased glucose uptake through activation of AMPK by AICAR. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, H643–H649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, H.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; Clanachan, A.S. Alteration of glycogen and glucose metabolism in ischaemic and post-ischaemic working rat hearts by adenosine A1 receptor stimulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Doble, B.W.; MacAulay, K.; Sinclair, E.M.; Drucker, D.J.; Woodgett, J.R. Tissue-specific role of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in glucose homeostasis and insulin action. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 6314–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roach, P.J.; Depaoli-Roach, A.A.; Hurley, T.D.; Tagliabracci, V.S. Glycogen and its metabolism: Some new developments and old themes. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 763–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flannery, C.A.; Choe, G.H.; Cooke, K.M.; Fleming, A.G.; Radford, C.C.; Kodaman, P.H.; Jurczak, M.J.; Kibbey, R.G.; Taylor, H.S. Insulin Regulates Glycogen Synthesis in Human Endometrial Glands Through Increased GYS2. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2018, 103, 2843–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultot, L.; Guigas, B.; Von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, A.; Maisin, L.; Vertommen, D.; Hussain, N.; Beullens, M.; Guinovart, J.J.; Foretz, M.; Viollet, B.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylates and inactivates liver glycogen synthase. Biochem. J. 2012, 443, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, T.; Singh, A.K.; Haratipour, P.; Sah, A.N.; Pandey, A.K.; Naseri, R.; Juyal, V.; Farzaei, M.H. Targeting AMPK signaling pathway by natural products for treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 17212–17231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Qi, G.; Liu, X. EGCG stimulates the recruitment of brite adipocytes, suppresses adipogenesis and counteracts TNF-alpha-triggered insulin resistance in adipocytes. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3374–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Chiu, J.P.; Hsu, C.H. Therapeutic effect of high-dose green tea extract on weight reduction: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Li, H.; Tang, J.J.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.K.; Shi, X.J.; Cui, H.W.; Tang, J.; et al. Discovery of a potent HMG-CoA reductase degrader that eliminates statin-induced reductase accumulation and lowers cholesterol. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Xu, M. YAP Inhibition by Nuciferine via AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Ji, J.; Yan, X.H. Cross-talk between AMPK and mTOR in regulating energy balance. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Manning, B.D. A complex interplay between Akt, TSC2 and the two mTOR complexes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, M.S. The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Insulin Signaling. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Kim, J.; Guan, K.L. AMPK and mTOR in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, G.C.; Reis, B.F. Simultaneous photometric determination of albumin and total protein in animal blood plasma employing a multicommutated flow system to carried out on line dilution and reagents solutions handling. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2004, 60, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raederstorff, D.G.; Schlachter, M.F.; Elste, V.; Weber, P. Effect of EGCG on lipid absorption and plasma lipid levels in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2003, 14, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, A.; Yuan, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, W.; Gong, Z. Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Glucose, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism and L-Theanine in the Metabolism-Regulatory Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114120
Lin L, Zeng L, Liu A, Yuan D, Peng Y, Zhang S, Li Y, Chen J, Xiao W, Gong Z. Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Glucose, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism and L-Theanine in the Metabolism-Regulatory Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ling, Li Zeng, An Liu, Dongyin Yuan, Yingqi Peng, Sheng Zhang, Yinhua Li, Jinhua Chen, Wenjun Xiao, and Zhihua Gong. 2021. "Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Glucose, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism and L-Theanine in the Metabolism-Regulatory Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114120
APA StyleLin, L., Zeng, L., Liu, A., Yuan, D., Peng, Y., Zhang, S., Li, Y., Chen, J., Xiao, W., & Gong, Z. (2021). Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate in Glucose, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism and L-Theanine in the Metabolism-Regulatory Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate. Nutrients, 13(11), 4120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114120






