Abstract
Higher serum phosphorus has detrimental health effects. Even high-normal rage sP is associated with worse outcomes. The relationship of serum phosphorus with prognostic markers in heart failure remains unclear. We investigated the association of serum phosphorus with heart failure prognostic factors and risk of mortality related to serum phosphorus. In 1029 stable heart failure patients, we investigated the distribution of markers of more advanced heart failure stage across quintiles of serum phosphorus and estimated the relative risk of mortality in comparison to reference. Higher serum phosphorus levels sP were associated with markers of a worse outcome. The best survival was observed in low-normal serum levels. The unadjusted hazard ratio for mortality increased toward higher phosphorus quintiles but not to lower levels of sP. The correction for age, sex, BMI, percent weight loss, inflammation, kidney function, and LVEF did not modify the risk profile substantially. The adjustment for NYHA, natriuretic peptides, serum sodium, and treatment characteristics broke down the risk relationship completely. A higher serum phosphorus is associated with markers of a more risky profile of heart failure. Elevated serum levels of phosphorus sP does not provide independent prognostic information beyond the strongest markers of the severity of the syndrome. The potential involvement of higher serum phosphorus as a mediator in the pathophysiology of heart failure warrants further study.
1. Introduction
Phosphorus is a key nutrient for living organisms. The element is important for energy production, proper function of nucleic acids and enzymes, cell proliferation and signaling, and as a component of the skeleton [1,2]. The exit from physiological range leads to detrimental health consequences. For example, low serum phosphorus (sP) is a known risk factor for development of heart failure (HF) and aggravates clinical profile of existing HF [3]; in patients with septic shock, reduced sP increases their morbidity and mortality [4]. Elevated sP is known to initiate cardiovascular remodeling and clinical events in renal patients [5,6]. However, in non-renal populations, even high-normal sP has been associated with accelerated atherosclerosis [7] and excessive morbidity and mortality [8,9,10].
HF has reached an epidemic proportion worldwide [11]. It is characterized by multiple endocrine abnormalities, malnutrition, and altered kidney function [12], all of which are associated with changes of phosphorus metabolism and alteration of serum levels.
Although numerous studies showed the association of high normal sP and worse outcome in general population and various diseases [8,9], very little is known about such an association among HF patients [13,14,15]. It is unclear why sP is elevated in high proportion among HF patients even with preserved kidney function and whether these elevated levels are associated with a poor outcome independently of known markers of HF severity.
We attempted to determine the association of sP with markers of HF severity as well as with intensity of HF therapy. Finally, we investigated whether sP was associated with all-cause mortality independently from these variables.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Group
We analyzed patients included in the Prospective Registry of Heart Failure conducted in our department since 2003. We selected patients with reduced left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF ≤ 40%), diagnosed according to the current European Society of Cardiology criteria as having HF, with age > 18 years, and duration of signs and symptoms of more than 6 months [16]. They had received optimal therapy for at least 1 month. All inclusion patients had no signs or symptoms of volume overload. Patients who received glucocorticosteroids, bisphosphonates, vitamin D formulations, or calcium- or phosphorus-containing salts and those who had an active infection, liver disease with enzymes exceeding 4 times the upper reference limit, active bleeding, known neoplasm or granulomatous disease, and patients with a history of any surgery reducing gut absorption capacity were excluded from the study.
Study criteria were fulfilled in 1029 registry participants, and their data were included in the final analysis.
Based on the medical history, we established the date of HF onset with a one-month precision and calculated the duration of HF symptoms. Using medical records, we determined the highest body weight within a year before the development of HF, taken as the pre-HF body weight. When multiple measurements were available in individual patients, the mean value was taken as pre-HF body weight.
Comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia, were recognized based on medical history, current therapy, or laboratory values of respective variables. A history of smoking was defined as current or previous use of tobacco products.
Blood samples were drawn in a standardized fashion, between 8 and 10 am, after at least 8 h of fasting and after 30 min of rest in a supine position in a quiet, environmentally controlled room. Blood was immediately centrifuged at 4 °C and stored at –75 °C for further analysis. All procedures were in accordance with Helsinki Declaration, and the protocol was approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Medical University of Silesia. All patients expressed their informed, written consent.
2.2. Measurements
Body mass and height were measured on the day of blood sampling (index date) using a certified scale (B150L, Redwag, Zawiercie, Poland). Body mass indexes (BMI) were calculated for pre-HF and index date weight and are shown as pre-HF BMI and indexBMI, respectively. We calculated weight loss during HF based on formula shown below:
Weight loss [%] = 100 × [(pre-HF BMI − indexBMI)/pre-HF BMI]
We used Sonos-5000 Hewlett-Packard Ultrasound Scanner (Hewlett-Packard, Andover, MA, USA) to measure LVEF from the apical four-chamber view and calculated it with the formulation:
LVEF = [(end-diastolic volume − end-systolic volume)/end-diastolic volume] × 100
Commercially available reagents (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) allowed measurements of serum creatinine, N-terminal brain-type natriuretic pro peptide (NTproBNP), high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), serum sodium, albumin, phosphorus, and calcium. We calculated GFR using the known MDRD formulation:
eGFRMDRD = 186 × plasma creatinine [mg/dL] − 1.154 × age [years] − 0.203 × 0.742 (if female).
For serum albumin <40 g/L, we corrected calcium using the formulation:
Corrected calcium [mmol/L] = total calcium + 0.02 × (40 − plasma albumin [g/L]).
We did not measure ionized calcium.
2.3. Statistics
Continuous variables are presented as means and standard deviations, categorical as percentages. For parameters with a skewed distribution, medians and interquartile ranges (IQR) are given. To correct non-normal distribution of variables in calculations, we used log10 transformed values (in tables shown before transformation). The study cohort was divided into sP quintiles, and a comparison of parameters between quintiles was carried out using Kruskal–Wallis or chi-square tests, where appropriate. For each quintile, we calculated the crude all-cause mortality rate based on 18-month follow-up. Data on mortality were obtained from the National Database on Inhabitants. We constructed Kaplan–Meier cumulative survival curves and compared the survival of phosphorus quintiles using log-rank test. Cox proportional hazard model was used to estimate the risk of death by taking quintile with the lowest mortality as a reference. In each quintile, we calculated relative hazard (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) in unadjusted, minimally adjusted, and fully adjusted models. The adjustment parameters were based on the significant differences between the quintiles and on clinical reasoning. Finally, we applied cubic spline modelling to estimate the association between sP and the risk of all-cause mortality in either unadjusted or adjusted models. The significance level was set at 0.05 (two-tailed), and all calculations were performed using packages of “Statistica” v.10.0 and “R” version 3.1.0 (2014).
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics
In groups with higher sP, there were more women. Patients were younger, and they lost more weight in a shorter duration of HF, resulting in lower indexBMI. Their LVEF was lower and their NYHA class higher. They also had worse kidney function and higher NTproBNP, hsCRP, and calcium but lower serum sodium. Patients with higher sP received lower doses of ACEI/ARB but higher aldosterone antagonists and loop diuretics. They were also treated more frequently with digoxin. The comorbidity profile did not differ between the quintiles of SP. Detailed characteristics of patients included in the study and comparison of patients in quintiles of sP are shown in Table 1. In general, patients in ascending quintiles of sP had a more advanced clinical and laboratory profile of HF, and their treatment was less intense.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the study cohort. Data are presented as mean ± SD, median value with quartile range, or as percentages.
Among patients in the bottom quintile of sP, hypophosphatemia with levels below 0.81 mmol/L was observed in 57 (28.3%) patients, while in the top quintile of sP, hyperphosphatemia with levels exceeding 1.40 mmol/L was recognized in 108 (52.4%) patients.
The clinical and laboratory characteristics of the hypophosphatemic patients and the remaining low normal patients of quintile 1 were not different, with the exception of lower NTproBNP: 869 (972) pg/mL versus 1203 (1813) pg/mL, p < 0.001; and lower serum calcium: 2.31 ± 0.16 mmol/L versus 2.37 ± 0.14 mmol/L, p < 0.001 in patients with hypophosphatemia (not shown in Table 1).
Patients with hyperphosphatemia compared to high-normal patients in quintile 5 had more advanced NYHA class: (I < 1%, II—24%, III—55%, IV—21%) versus (I—1%, II—39%, III—50%, IV—10%), p = 0.009, higher serum calcium: 2.47 ± 0.16 versus 2.43 ± 0.18, p = 0.04, and lower eGFRMDRD: 64 (47) mL/min × 1.73 m2 versus 79 (42) mL/min × 1.73 m2, p = 0.008.
3.2. Unadjusted and Adjusted Risk of All-Cause Mortality
During 18 months of follow-up, 185 patients (18%) died. The crude mortality rate was the lowest in quintile 2 and increased in both extremes of sP. The difference in mortality between quintiles was significant (Table 1).
The cumulative probability of death represented by the Kaplan–Meier curves also showed significant differences between the sP quintiles (p = 0.02) (Figure 1).
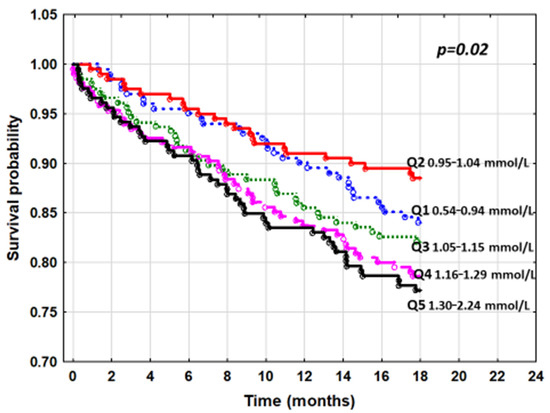
Figure 1.
The cumulative survival curves by Kaplan–Meier for quintiles of serum phosphorus and all-cause mortality.
The cumulative survival of patients with hypophosphatemia and patients with low-normal sP from quintile 1 was similar (log-rank p = 0.32) (Figure 2).
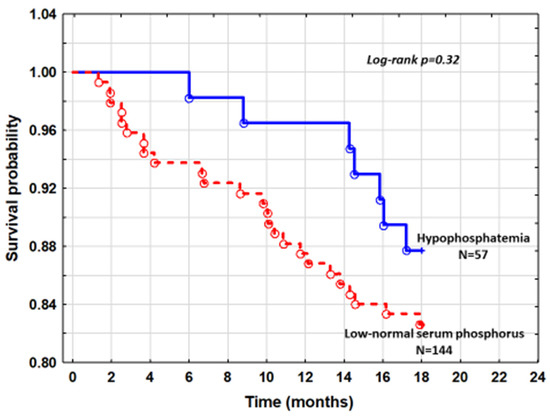
Figure 2.
The cumulative survival curves comparing patients with hypophosphatemia and low normal serum phosphorus.
Mortality in patients with hyperphosphatemia and patients with high-normal phosphorus from quintile 5 was also comparable (log-rank p = 0.58) (Figure 3).
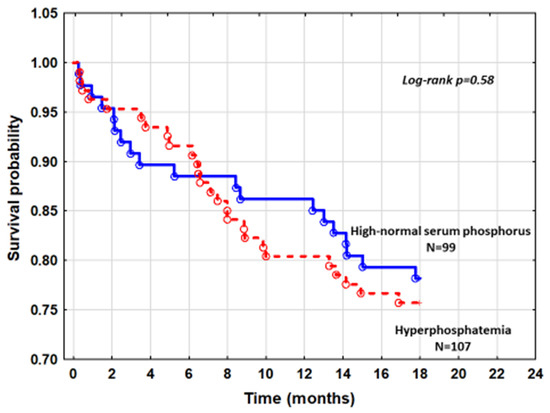
Figure 3.
The cumulative survival curves comparing patients with hyperphosphatemia and patients with high-normal SP.
An unadjusted Cox analysis with quintile 2 as a reference showed increasing risk of mortality toward quintiles with higher sP (p = 0.03 for trend). Hazard ratio peaked in quintile 5, reaching a value of 2.15; (95% CI: 1.35–3.53, p = 0.003) (Table 2). The risk of death in a group with the lowest sP was not different from the reference. The cubic-spline modelling of an unadjusted relation between sP and mortality is presented in Figure 4.

Table 2.
The risk of all-cause mortality related to increasing levels of sP in unadjusted model and in models adjusted for various clinical and laboratory variables.
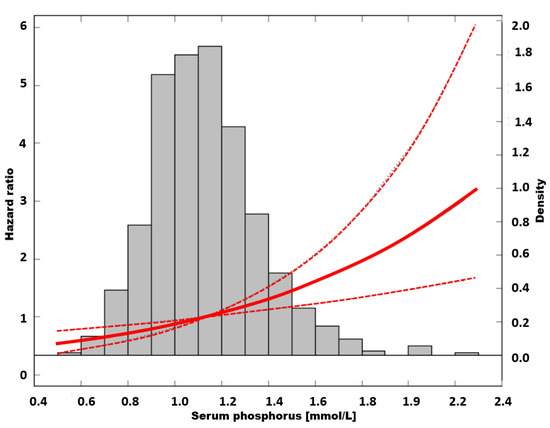
Figure 4.
The risk of all-cause mortality in unadjusted model.
By fitting serum calcium into the unadjusted model, we tried to disclose the possible interaction of serum calcium and phosphorus as risk factors for mortality. The adjustment has changed the risk marginally in the lowest sP; however, the risk of death was increasingly attenuated in each incremental quintile of sP. The greatest reduction in the hazard ratio was observed in the top quintile. Despite HR attenuation, the risk in patients in two upper quintiles of sP remained significantly higher compared to the reference (Table 2, model 1).
In the next step, we examined the influence of sex, age, BMI, weight loss, hsCRP, eGFRMDRD, and LVEF but not calcium on the association between sP and mortality. The analysis showed a slight reduction in risk attributable to higher sP. However, the HR of patients in the two upper quintiles of sP still remained significantly elevated (Table 2, model 2).
As variation in treatment and differences in functional status, serum sodium and NTproBNP could potentially be linked to a worse prognosis; the association between sP and mortality was further adjusted for these variables. When we added the use of ACEI/ARB, beta-blockers, loop diuretics, and digoxin as categorial variable and a percentage of recommended doses of ACEI/ARB, aldosterone antagonists, and the dose of loop diuretics as continuous variables as well as NYHA class, serum sodium, and NTproBNP levels, the association of mortality with increasing quintiles of sP was no longer significant (Table 2, model 3).
In Figure 5, the fully adjusted relation between sP and mortality is presented as a cubic spline model.
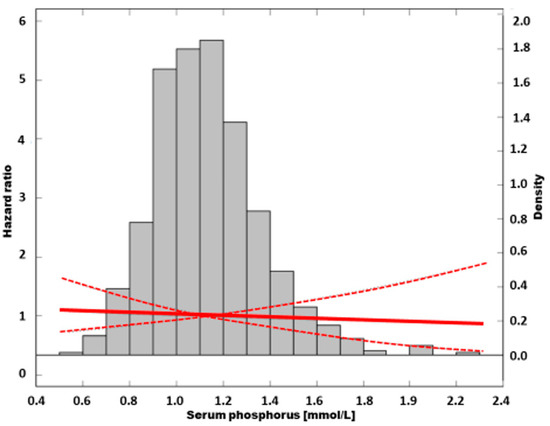
Figure 5.
The association of all-cause mortality risk and serum phosphorus in fully adjusted model.
Our final analysis was designed to identify the risk attributable to sP taken as a continuous variable together with all potential confounders, such as age, sex, BMI, weight loss, hsCRP, eGFRMDRD, serum calcium, LVEF, serum sodium, NTproBNP, the use of beta-blockers and digoxin, loop diuretic dose, and the percentage of the recommended dose of ACEI/ARB and aldosterone antagonist administered to patients. In this final model, the only significant independent predictors of mortality were NYHA class (HR = 1.92; 95%CI: 1.42–2.59, p < 0.001), NTproBNP (1.08; 95%CI: 1.04–1.13, per 1000 pg/mL increase, p < 0.001), serum calcium (HR = 1.24; 95%CI: 1.02–1.51 per 0.2 mmol/L increase, p = 0.02), and loop diuretic dose (HR = 1.12; 95%CI: 1.02–1.24, per 40 mg of furosemide equivalent increase, p = 0.02). Serum phosphorus was not a significant predictor. The relationship between sP and mortality after full adjustment is shown on Figure 6.
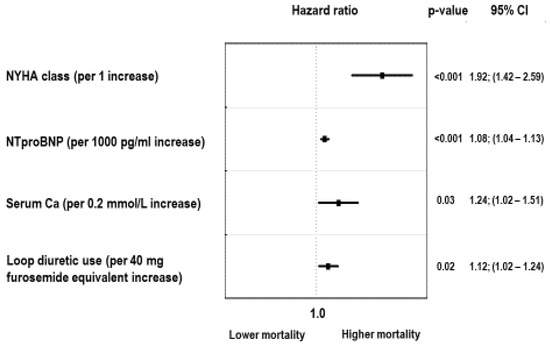
Figure 6.
Independent predictors of all-cause mortality in fully adjusted model.
As there was no difference in mortality between patients with hypophosphatemia and those with low-normal sP of quintile 1 in Kaplan–Meier analysis (Figure 2), we constructed Cox proportional hazard model to estimate the risk of hypophosphatemia after accounting for factors that were different between these subgroups. After adjusting for NTproBNP and serum calcium, the hazard ratio for mortality was HR = 0.78; 95%CI: 0.34–1.82, p = 0.58. Comparison of hypophosphatemic patients with all patients with normal sP did not significantly change the results.
Similar analysis was performed in patients with hyperphosphatemia as compared to those with high-normal sP from quintile 5 (Figure 3). Adjusting for differences in NYHA class, serum calcium, and eGFRMDRD that exist between these subgroups in the Cox model did not reveal a higher risk in death of hyperphosphatemic patients with HR = 1.04, 95%CI: 0.58–1.88, p = 0.88. The inclusion of all patients with normal phosphorus compared to hyperphosphatemic patients did not modify the risk profile.
4. Discussion
The link between altered phosphorus metabolism and prognosis in HF has been debated [13,14,15,17,18]. There is a significant heterogeneity between studies with respect to patient clinical characteristics [13,14,17], kidney function [15,18], duration of follow-up [19,20], and the study outcome [15,17]. In addition, important confounders were taken into account only in the small amount of studies [15,18]. Some studies did not account for standard prognostic factors in HF [17] or only made minimal adjustments [18]. As a result, the conclusions of these studies are inconsistent.
Our study reports all-cause mortality in a relatively large cohort of optimally treated HF with reduced ejection fraction. We found the lowest death rates in a range of sP between 0.95 and 1.04 mmol/L. There was a gradual increase in mortality in the ascending quintiles of sP but not at the lowest levels. In the bottom and top quintiles of phosphorus, there were subgroups with hypophosphatemia and hyperphosphatemia, respectively. Apart from sP, in these subgroups, important HF severity markers were different in comparison to patients with normal sP. Despite these differences, the prognosis for these patients was similar.
Many markers of more severe HF aggregated in groups of higher sP, while therapy modifying prognosis was less intensive in these patients. Younger patients and women were more frequent among those with higher sP. This distribution probably represents the effect of splitting into quintiles of phosphorus because higher levels occur naturally in younger people and in women [19]. However, since these characteristics also affect the prognosis, they were included in the analysis as potential covariates.
In the multivariable analysis, we found a significant association between higher sP and all-cause mortality that was independent of age, sex, BMI, eGFRMDRD, inflammation, LVEF, and weight loss. However, when we considered differences in therapy, NYHA class, and neuroactivation markers, such as serum sodium and NTproBNP, this association disappeared.
In one investigation that included a population similar to ours, the association of sP with the composite of death and heart transplantation was independent of NYHA class and natriuretic peptides [14]. This discrepancy may be explained by differences in clinical outcome because in this study, up to 24% of the composite end point was driven by heart transplantation alone [14]. Another reason for the inconsistent result may come from the stratification by gender used in the study mentioned above but not in ours.
In a much smaller study by Plischke, with a twice-longer follow-up [15], sP significantly predicted the composite of death or cardiac hospitalization [15]. Again, difference in length of follow-up and study outcome may explain the observed discrepancy.
The key questions when studying the prognostic role of phosphorus in HF are the reasons for the elevation of phosphorus in more severe HF and why sP correlates with numerous markers of a poor prognosis.
Many authors argue that reduced kidney perfusion in HF alters the renal excretory potential, leading to phosphorus accumulation [20]. Poor heart function and impaired kidney filtration are both recognized as reasons for poor clinical outcomes in HF [21]. In this interpretation, higher sP would be secondary event in response to the underlying cardio-renal interaction.
Our data challenged this interpretation. Among patients with reduced eGFRMDRD (<60 mL/min × 1.73 m2) and with preserved eGFRMDRD (≥60 mL/min × 1.73 m2), there was a huge overlap of sP. Hypophosphatemia was present in patients with low kidney function, while hyperphosphatemia was seen in normal eGFRMDRD (Figure 7).
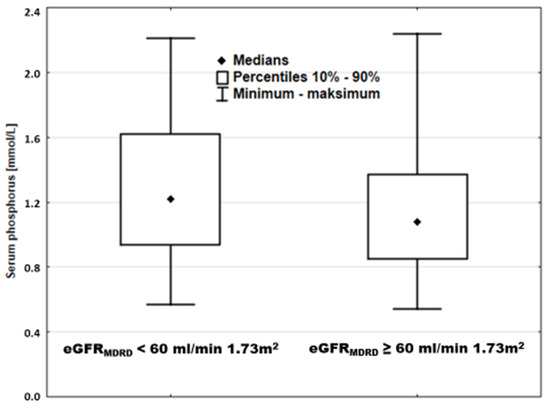
Figure 7.
Serum phosphorus in patients stratified according to kidney function.
Similar overlap was also observed when the entire cohort was divided by median sP (Figure 8).
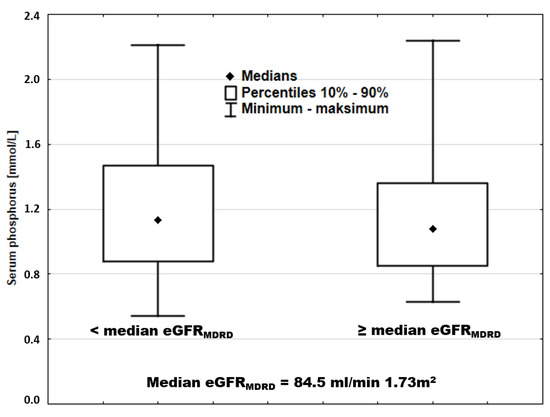
Figure 8.
Serum phosphorus in patients stratified according to eGFRMDRD.
Additionally, in multivariable analysis, the increase in the risk in the ascending quintiles of sP was independent of both LVEF and eGFRMDRD, suggesting the contribution of other mechanisms.
Among potential mechanisms, one may point to hypoxia and energetic insufficiency at the cellular level. Intracellular phosphorus transport is coupled with energy-consuming sodium pumping in the opposite direction, which gives a primary force to intracellular phosphorus transport [22]. Low serum sodium may inhibit intracellular transport, suggesting that sP elevation may be a secondary event. Low serum sodium and elevated natriuretic peptide both reflect disturbed neurohormonal regulation and, according to current understanding, represent central pathways in HF pathophysiology [23]. Previously, we showed that among the significant sP predictors in HF, the strength of associations between mortality and NTproBNP, serum sodium, and degree of catabolism was similar to that of eGFRMDRD [24]. These observations suggest high complexity of processes underlying sP increase in more ill patients with HF. Based on this, we believe that the correlation between higher sP and markers of more severe HF may stem from common pathophysiological pathways, in which cardio-renal interaction is only one piece of the puzzle. Therefore, a higher sP may be a downstream event of the key pathophysiological pathways in HF.
This hypothesis was further supported by the observation of less intensive pharmacotherapy in patients with higher SP and also by the fact that the association between sP and mortality was broken down by accounting for differences in pharmacotherapy. At a more advanced stage of HF, there is a limited use of ACEI/ARBs due to intolerance but more frequent application and use of higher doses of loop diuretics and aldosterone antagonists [25]. We previously showed that in patients with less intensive treatment and worse clinical response to therapy, hyperphosphatemia occurred more frequently [26].
Another important question is whether, for whatever reason, increased sP poses an additional cardiovascular risk in HF beyond that related to known pathways.
Most animal experiments support the direct role of excessive sP on the cardiovascular system. They showed decreased vascular nitric oxide bioavailability, up-regulation of angiotensin converting enzyme expression, and induction of vascular calcifications in animals exposed to higher sP [27,28]. In a study of uremic rats, high phosphorus diet-induced hyperphosphatemia was shown as a direct stimulator of systemic inflammation, malnutrition with body wasting, and vascular calcification [29].
In our study, the association between mortality and a higher sP remained significant after adjustment for systemic inflammation, BMI, and degree of weight loss. This observation is in agreement with the animal experiment cited above and suggests that elevated sP might be, at least in part, an upstream event for inflammation and weight loss, all known risk factors for mortality in HF [30].
In in-vivo experiments of humans, endothelial dysfunction appeared after exposure to a diet rich in phosphorus, leading to elevation of sP [31]. Not only that, but cellular experiment clearly demonstrated induction by phosphorus of apoptosis within cardiomyocytes in culture [32]. Furthermore, calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells was recognized in patients with elevated phosphorus and calcium [33,34]. In a very recent study in humans with HF with reduced ejection fraction, the higher propensity for calcification as estimated by function T-50 test was associated with worse outcome in patients with ischemic etiology [35].
It is worth noting that when we account for different serum calcium levels in the multivariate analysis, we found a preferential reduction of risk in higher quintiles of phosphorus. When we compared the hazard ratios for mortality in unadjusted and calcium-only adjusted models, the risk reduction in the later model was 1% in quintile 1, while 3% and 15% in quintiles 4 and 5, respectively. This observation may suggest a complex interaction between calcium/phosphorus abnormalities and mortality, especially in higher sP groups. Indeed, a previous study showed a significant prediction of total mortality in HF by calcium phosphorus product and serum calcium but not by sP alone [13]. Our final result of multivariable prediction of mortality was in agreement with this observation. This analysis showed that apart from NTproBNP, NYHA class, and loop diuretic dose, serum calcium but not phosphorus remained significantly associated with the outcome.
In addition to the direct effect related to phosphorus, typical hormonal adaptations to phosphorus loading, such as higher parathyroid hormone, fibroblast growth factor 23, and lower 1.25-dihydroxy vitamin D [2], all were suggested to increase cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [18,36,37]. Unfortunately, serum levels of calciotropic and phosphaturic hormones were not available in our study, and we were unable to perform a more in-depth analysis.
5. Conclusions
Serum phosphorus is associated with numerous HF prognostic markers. Elevated sP does not provide independent prognostic information beyond already known markers of syndrome severity. The potential involvement of elevated serum phosphorus as a mediator in important pathways of HF pathophysiology warrants further study.
6. Strengths and Limitations
Our study shows the association of high-normal and elevated sP with numerous prognostic HF risk markers in a large homogenous cohort of HF patients with reduced ejection fraction. The lack of dietetic data precluded analysis of nutritional impact on SP. The use of stepwise adjustment for potential confounders pointed out hypothetical mechanisms that lead to elevation of sP in HF. However, the cross-sectional design did not allow analysis of causality.
The lack of measurement of calciotropic and phosphaturic hormones prevents a more in-depth understanding of observed associations.
6.1. Clinical Perspectives
In everyday clinical practice in patients with HF, elevated SP cannot be treated as a signature of poor kidney function. It does not have an independent prognostic power, but it may be implicated as a mediator in some aspects of HF pathophysiology.
6.2. Translational Look
Future studies should address in more detail the reasons for the elevation of serum phosphorus in CHF as well as the potential direct phosphorus toxicity in cardiovascular system and indirect effects of calciotropic and phosphaturic hormones. The question of potential clinical benefits of interventions that modify phosphorus and/or phosphaturic hormones warrants further studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R. and R.P.; methodology, R.P., P.R., N.J.; formal analysis, R.P. and M.-B.J.; investigation, M.A.; data acquisition, N.J., H.B., G.M.; resources, B.M., G.-G.A. and D.S., writing—original draft preparation, R.P. and P.R.; writing—review and editing, M.-B.J. supervision, R.P. and M.-B.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Part of the research has received funding from the National Center for Research & Development under the framework of the STRATEGMED project. Grant number: STRATEGMED1/233221/3/NCBR/2014 was acknowledged to Silesian Centre for Heart Diseases on 20 October 2014.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was reviewed and accepted by the Ethical Committee of Medical University of Silesia in Katowice (NN-6501-12/I/04).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
Robert Partyka, Alina Mroczek, Sylwia Duda, Jolanta Malinowska-Borowska, Marta Buczkowska, Jacek Niedziela, Bartosz Hudzik, Mariusz Gąsior, and Piotr Rozentryt declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| CHF | chronic heart failure |
| eGFRMDRD | estimated glomerular filtration rate calculated with the use of Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula |
| hsCRP | high-sensitive C-reactive protein |
| LVEF | left ventricular ejection fraction |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal Prohormone of Brain Natriuretic Peptide |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| SICA | Studies on Comorbidities Aggravating Heart Failure |
| SP | serum phosphorus |
References
- Bergwitz, C.; Jüppner, H. Regulation of Phosphate Homeostasis by PTH, Vitamin D, and FGF23. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lederer, E. Regulation of serum phosphate. J. Physiol. 2014, 592 Pt 18, 3985–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyoshi, N.; Nogi, M.; Ando, A.; Watanabe, H.; Umekawa, S. Hypophosphatemia-induced Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 352, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Harbi, S.A.; Al-Dorzi, H.M.; Al Meshari, A.M.; Tamim, H.; Abdukahil, S.A.I.; Sadat, M.; Arabi, Y. Association between phosphate disturbances and mortality among critically ill patients with sepsis or septic shock. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, W.G.; Goldin, J.; Kuizon, B.D.; Yoon, C.; Gales, B.; Sider, D.; Wang, Y.; Chung, J.; Emerick, A.; Greaser, L.; et al. Coronary-Artery Calcification in Young Adults with End-Stage Renal Disease Who Are Undergoing Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, G.A.; Klassen, P.S.; Lazarus, J.M.; Ofsthun, N.; Lowrie, E.G.; Chertow, G.M. Mineral Metabolism, Mortality, and Morbidity in Maintenance Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, R.N.; Collins, A.J.; Herzog, C.A.; Ishani, A.; Kalra, P.A. Serum Phosphorus Levels Associate with Coronary Atherosclerosis in Young Adults. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonelli, M.; Sacks, F.; Pfeffer, M.; Gao, Z.; Curhan, G.; Cholesterol, F.T. Recurrent Events Trial Investigators. Relation Between Serum Phosphate Level and Cardiovascular Event Rate in People With Coronary Disease. Circulation 2005, 112, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhingra, R.; Sullivan, L.M.; Fox, C.S.; Wang, T.J.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Gaziano, J.M.; Vasan, R.S. Relations of Serum Phosphorus and Calcium Levels to the Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease in the Community. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, W.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Serum phosphorus, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in the general population: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 461, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Anker, S.D.; AlHabib, K.F.; Cowie, M.R.; Force, T.L.; Hu, S.; Jaarsma, T.; Krum, H.; Rastogi, V.; Rohde, L.E.; et al. Heart failure: Preventing disease and death worldwide. ESC Heart Fail. 2014, 1, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.; Abdelhamid, M.; Ibrahim, B.; Elshazly, A.; Aboleineen, M.W.; Sobhy, H.; Nasr, G.; Elmesseiry, F.; Abdelmoniem, A.; Ashmawy, M.; et al. Clinical characteristics and management of hospitalized and ambulatory patients with heart failure–results from ESC heart failure long-term registry–Egyptian cohort. ESC Heart Fail. 2015, 2, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubbon, R.; Thomas, C.; Drozd, M.; Gierula, J.; Jamil, H.; Byrom, R.; Barth, J.; Kearney, M.; Witte, K.A. Calcium, phosphate and calcium phosphate product are markers of outcome in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Nephrol. 2015, 28, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ess, M.; Heitmair-Wietzorrek, K.; Frick, M.; Umlauf, N.; Ulmer, H.; Poelzl, G. Serum Phosphate and Long-Term Outcome among Patients with Stable Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2013, 19, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plischke, M.; Neuhold, S.; Adlbrecht, C.; Bielesz, B.; Shayganfar, S.; Bieglmayer, C.; Szekeres, T.; Hörl, W.H.; Strunk, G.; Vavken, P.; et al. Inorganic phosphate and FGF-23 predict outcome in stable systolic heart failure. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittermann, A.; Fuchs, U.; Kuhn, J.; Dreier, J.; Schulz, U.; Gummert, J.F.; Börgermann, J. Parameters of Mineral Metabolism predict Midterm Clinical Outcome in End-Stage Heart Failure Patients. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2011, 45, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruson, D.; Lepoutre, T.; Ketelslegers, J.M.; Cumps, J.; Ahn, S.A.; Rousseau, M.F. C-terminal FGF23 is a strong predictor of survival in systolic heart failure. Peptides 2012, 37, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, L.; Schmid, C. Effects of Age, Sex, and Estrogen on Serum Phosphorus: Role for Growth Hormone and Klotho? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charytan, D.M.; Fishbane, S.; Malyszko, J.; McCullough, P.A.; Goldsmith, D. Cardiorenal Syndrome and the Role of the Bone-Mineral Axis and Anemia. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hillege, H.L.; Girbes, A.R.J.; de Kam, P.J.; Boomsma, F.; de Zeeuw, D.; Charlesworth, A.; Hampton, J.R.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Renal Function, Neurohormonal Activation, and Survival in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. Circulation 2000, 102, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morth, J.P.; Pedersen, B.P.; Buch-Pedersen, M.J.; Andersen, J.P.; Vilsen, B.; Palmgren, M.G.; Nissen, P. A structural overview of the plasma membrane Na+,K+-ATPase and H+-ATPase ion pumps. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 12, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floras, J.S. Sympathetic Nervous System Activation in Human Heart Failure: Clinical Implications of an Updated Model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozentryt, P.; Niedziela, J.T.; Hudzik, B.; Lekston, A.; Doehner, W.; Jankowska, E.A.; Nowak, J.; von Haehling, S.; Partyka, R.; Rywik, T.; et al. Higher serum phosphorus is associated with catabolic/anabolic imbalance in heart failure. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, G.C.; Kittleson, M.M.; Patel, P.C.; Cowger, J.A.; Patel, C.B.; Mountis, M.M.; Johnson, F.L.; Guglin, M.E.; Rame, J.E.; Teuteberg, J.J.; et al. INTERMACS (Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support) Profiling Identifies Ambulatory Patients at High Risk on Medical Therapy After Hospitalizations for Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e003032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozentryt, P.; Nowak, J.; Niedziela, J.; Hudzik, B.; Doehner, W.; Jankowska, E.A.; von Haehling, S.; Partyka, R.; Kawecka, E.; Myrda, K.; et al. Serum phosphorus level is related to degree of clinical response to up-titration of heart failure pharmacotherapy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 177, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eräranta, A.; Törmänen, S.; Kööbi, P.; Vehmas, T.I.; Lakkisto, P.; Tikkanen, I.; Moilanen, E.; Niemelä, O.; Mustonen, J.; Pörsti, I. Phosphate Binding Reduces Aortic Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Enhances Nitric Oxide Bioactivity in Experimental Renal Insufficiency. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, M.; Razzaque, M.S. Dietary and genetic evidence for phosphate toxicity accelerating mammalian aging. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3562–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, S.; Tokumoto, M.; Tatsumoto, N.; Taniguchi, M.; Noguchi, H.; Nakano, T.; Masutani, K.; Ooboshi, H.; Tsuruya, K.; Kitazono, T. Phosphate overload directly induces systemic inflammation and malnutrition as well as vascular calcification in uremia. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F1418–F1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Negassa, A.; Coats, A.J.; Afzal, R.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Cohn, J.N.; Yusuf, S. Prognostic importance of weight loss in chronic heart failure and the effect of treatment with angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors: An observational study. Lancet 2003, 361, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, E.; Taketani, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Harada, N.; Isshiki, M.; Sato, M.; Nashiki, K.; Amo, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Higashi, Y.; et al. Dietary Phosphorus Acutely Impairs Endothelial Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.L.; Lin, K.H.; Tamilselvi, S.; Chen, W.K.; Shen, C.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Day, C.H.; Wu, H.C.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Huang, C.Y. Elevated Phosphate Levels Trigger Autophagy-Mediated Cellular Apoptosis in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts. Cardiorenal Med. 2018, 8, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, J.L.; Joannides, A.J.; Skepper, J.N.; McNair, R.; Schurgers, L.J.; Proudfoot, D.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Undergo Vesicle-Mediated Calcification in Response to Changes in Extracellular Calcium and Phosphate Concentrations: A Potential Mechanism for Accelerated Vascular Calcification in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scialla, J.J.; Lau, W.L.; Reilly, M.P.; Isakova, T.; Yang, H.-Y.; Crouthamel, M.H.; Chavkin, N.W.; Rahman, M.; Wahl, P.; Amaral, A.P.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is not associated with and does not induce arterial calcification. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bojic, M.; Koller, L.; Cejka, D.; Niessner, A.; Bielesz, B. Propensity for Calcification in Serum Associates with 2-Year Cardiovascular Mortality in Ischemic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Front Med. 2021, 8, 672348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilz, S.; Marz, W.; Wellnitz, B.; Seelhorst, U.; Fahrleitner-Pammer, A.; Dimai, H.P.; Boehm, B.O.; Dobnig, H. Association of vitamin D deficiency with heart failure and sudden cardiac death in a large cross-sectional study of patients referred for coronary angiography. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3927–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilz, S.; Tomaschitz, A.; Drechsler, C.; Ritz, E.; Boehm, B.O.; Grammer, T.B.; Marz, W. Parathyroid hormone level is associated with mortality and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).