Regulatory Framework of Fortified Foods and Dietary Supplements for Athletes: An Interpretive Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Topic “Foodstuffs for Particular Nutritional Uses”
3.2. Regulation of the Marketing and Labelling of Fortified Foods and Supplements
- (a)
- Name of the food
- (b)
- List of ingredients
- (c)
- Quantity of certain ingredients or category of ingredients
- (d)
- Presence of substances or products causing allergies or intolerances
- (e)
- Weight or net volume
- (f)
- Minimum durability date, ‘use by’ date and date of freezing
- (g)
- Special storage conditions and/or conditions of use
- (h)
- Name and address of manufacturer
- (i)
- Country of origin or place or provenance
- (j)
- Instructions for use where it would be difficult to make an appropriate use
- (k)
- Nutritional information
- (a)
- The names of the categories of nutrients or substances that characterize the product or an indication of the nature of those nutrients or substances
- (b)
- The portion of the product recommended for daily consumption
- (c)
- A warning not to exceed the stated recommended daily dose
- (d)
- A statement about that food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a varied diet
- (e)
- A warning about that the products should be stored out of the reach of young children
3.3. Use of Substances as Ingredients in Food Fortification
- (a)
- Fatty acids
- (b)
- Amino acids (and their salts of Na, K, Ca, Mg and HCl) and other nitrogenous compounds
- (c)
- Dipeptides and peptides
- (d)
- Coenzymes
- (e)
- Flavonoids, carotenoids
- (f)
- Nucleotides
- (g)
- Polysaccharides and oligosaccharides
- (h)
- Other substances
3.4. Nutritional Claims and/or Health Properties Associated with a Nutrient, an Ingredient or Any Other Substance
- (a)
- A statement indicating the importance of a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
- (b)
- The quantity of the food and pattern of consumption required to obtain the claimed beneficial effect.
- (c)
- Where appropriate, a statement addressed to persons who should avoid using the food.
- (d)
- An appropriate warning for products that are likely to present a health risk if consumed to excess.
4. An Interpretive Approach to the Legislative Framework
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, R.; Gavin-Smith, B.; Ferraboschi, C.; Kraemer, K. Food fortification: The advantages, disadvantages and lessons from sight and life programs. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis Taylor, C. Regulatory frameworks for functional foods and dietary supplements. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, F.; Sumbal, S. Physical performance and functional food. J. Hum. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 7, 1128. [Google Scholar]
- Garthe, I.; Maughan, R.J. Athletes and supplements: Prevalence and perspectives. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and athletic performance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Burke, L.M.; Dvorak, J.; Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Peeling, P.; Philips, S.M.; Rawson, E.S.; Walsh, N.P.; Garthe, I.; Geyer, H.; et al. IOC consensus statement: Dietary supplements and the high-performance athlete. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J. Quality assurance issues in the use of dietary supplements, with special reference to protein supplements. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1843S–1847S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Directive 89/398/EEC of the Council of 3 May 1989 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to foodstuffs intended for particular nutritional uses. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 1989, L186.
- Directive 2009/39/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 May 2009 on foodstuffs intended for particular nutritional uses. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, L124, 21–29.
- Regulation (EU) 609/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 June 2013 on food intended for infants and young children, food for special medical purposes, and total diet replacement for weight control and repealing Council Directive 92/52/EEC, Commission Directives 96/8/EC, 1999/21/EC, 2006/125/EC and 2006/141/EC, Directive 2009/39/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulations (EC) No 41/2009 and (EC) No 953/2009. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L181, 35.
- Regulation (EU) 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the provision of food information to consumers, amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L304, 29.
- Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 10 June 2002 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to food supplements. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2002, L183, 51–57.
- United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Codex Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling (CAC/GL 2-1985); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EC) 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on the addition of vitamins and minerals and of certain other substances to foods. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L404, 26–38.
- Commission Regulation (EC) 1170/2009 of 30 November 2009 amending Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of Council and Regulation (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the lists of vitamin and minerals and their forms that can be added to foods, including food supplements. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, L314, 36.
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/403 of 11 March 2015 amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards Ephedra species and Yohimbe (Pausinystalia yohimbe (K. Schum) Pierre ex Beille). Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, L67, 4–5.
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/650 of 24 April 2019 amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards Yohimbe (Pausinystalia yohimbe (K. Schum) Pierre ex Beille). Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, L110, 21–22.
- Royal Decree 130/2018, of March 16, which modifies Royal Decree 1487/2009, of September 26, relating to food supplements. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, L404.
- Regulation (EC) 764/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 9 July 2008 laying down procedures relating to the application of certain national technical rules to products lawfully marketed in another Member State and repealing Decision No 3052/95/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L218, 21–29.
- Regulation (EC) 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L404, 9–25.
- United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO). Codex Guidelines for Use of Nutrition and Health Claims (CAC/GL 23-1997); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
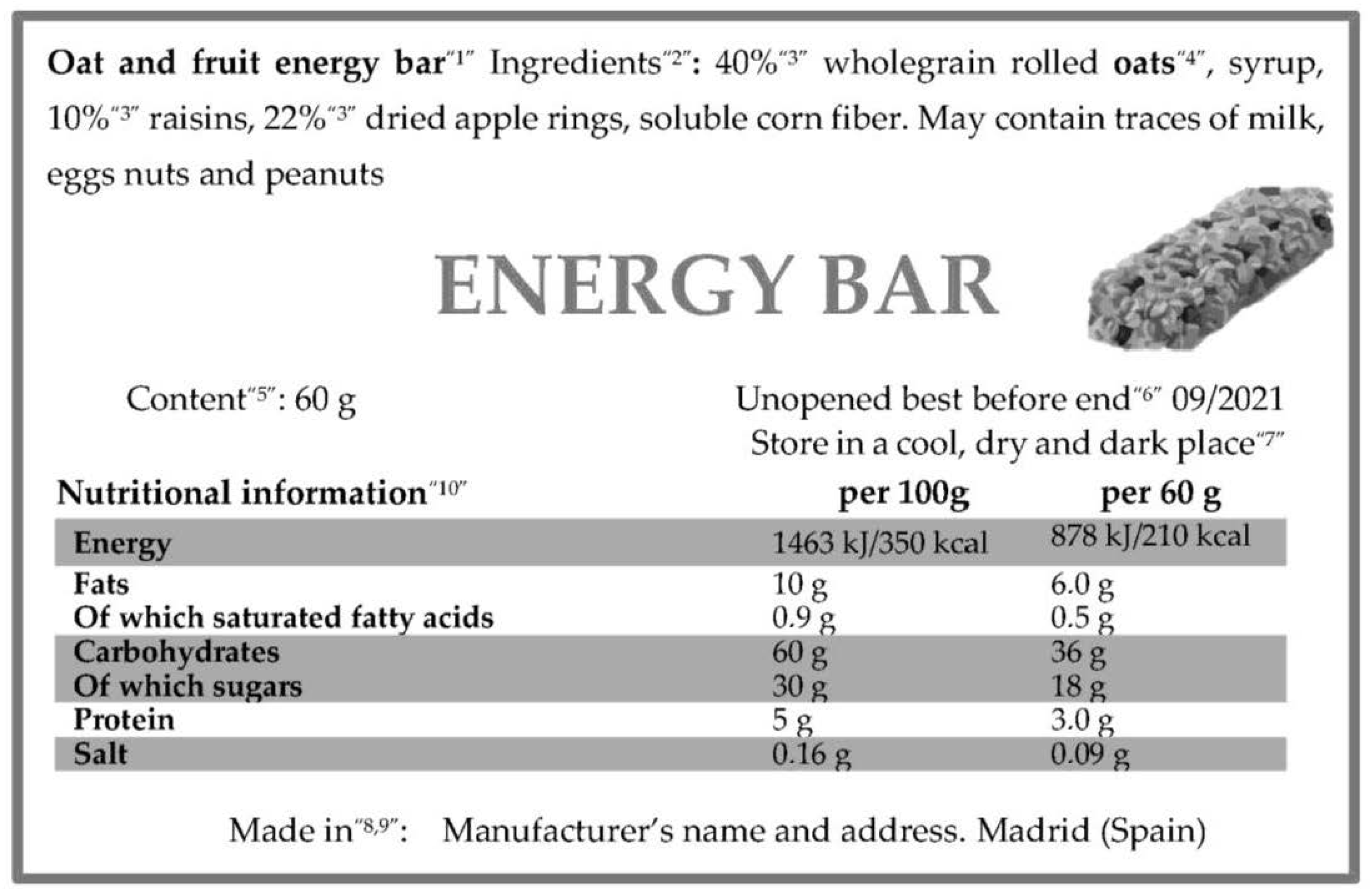




| Mention | Particular Requirements |
|---|---|
| Foodstuff designation | If the product has a legal name, it must be used in the label. In its absence, the customary name or a descriptive name of the food can replace it. It may not be replaced by trademark, brand name or fancy name. |
| Ingredients list | The list of ingredients must be preceded by a heading with the word «ingredients». The list must include the ingredients in descending order of weight, including flavourings, food additives and food enzymes, and any constituent of a compound ingredient, used in the manufacture or preparation of a food and still present in the finished product. |
| Quantity indication of certain ingredients or category of ingredients | The indication of the quantity of an ingredient or category of ingredients used in the manufacture or preparation of a food shall be required where the ingredient or category of ingredients appears in the name of the food or is usually associated with that name by the consumer; or when this ingredient is emphasized on the labelling in words, pictures or graphics; or when is essential to characterize a food and to distinguish it from products with which it might be confused because of its name or appearance. |
| Substances causing allergies or intolerances | Must be indicated in the list of ingredients with a clear reference to the name of the substance or product emphasized through a typeset that clearly distinguishes it from the rest of the ingredients, for example by means of the font, style or background color. In the absence of a list of ingredients, the indication of the particulars referred shall comprise the word ‘contains’ followed by the name of the substance or products. |
| Net quantity | It must be expressed using liters, centiliters, milliliters, kilograms or grams. These expressions could be changed in order to ensure a better understanding by the consumer of the food information on the labelling. |
| Minimum durability date, ‘use by’ date and date of freezing | In the case of foods which, from a microbiological point of view, are highly perishable and are therefore likely after a short period to constitute an immediate danger to human health, the date of minimum durability shall be replaced by the ‘use by’ date. |
| Storage conditions or conditions of use | This information must be included when foods require special storage conditions and/or conditions of use. It could refer to appropriate storage or use of the food after opening the package, the storage conditions and/or time limit for consumption. |
| Manufacturer’s name and address | The company name and the address must be indicated. |
| Country of origin or place of provenance | Indication of the country of origin or place of provenance shall be mandatory to food business operators whenever its absence might to mislead consumers as to the true country of origin or place of provenance of that product, in particular if the information accompanying the food or the label as a whole would otherwise imply that the food has a different country of origin or place of provenance. Also, where the country of origin or the place of provenance of a food is given and it is not the same as that of its primary ingredient, the country of origin or place of provenance of the primary ingredient shall also be given; or (b) the country of origin or place of provenance of the primary ingredient shall be indicated as being different to that of the food. |
| Instructions for use | This information must be indicated to enable appropriate use to be made of the food, if it is necessary. |
| Nutritional information | The mandatory nutrition for sport foods must include the following: energy value and the amounts of fat, saturates, carbohydrate, sugars, protein and salt. Where appropriate, a statement indicating that the salt content is exclusively due to the presence of naturally occurring sodium may appear in close proximity to the nutrition declaration. The content of the mandatory nutrition declaration may be supplemented with an indication of the amounts of one or more of the following: monounsaturated fats; polyunsaturated fats; polyols; starch; fiber; any of the vitamins or minerals listed in the Regulation, present in significant amounts and expressed as a percentage of the maximum daily intakes set out in this Regulation. This information must be expressed per 100 g or per 100 mL. In addition, to the form of expression per 100 g or per 100 mL, the nutritional information may be expressed per portion or per consumption unit when it is easily recognizable by the consumer (for example per energy bar) or when portion size is referred in the label. In these cases, the information “per portion or per consumption unit” alone is permitted, however, the energy value shall be expressed per 100 g or 100 mL. |
| Nutrient/Substance | Declaration |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Carbohydrates contribute to the recovery of normal muscle function (contraction) after highly intensive and/or long-lasting physical exercise leading to muscle fatigue and the depletion of glycogen stores in skeletal muscle. |
| Creatine | Daily consumption of creatine can reinforce the effect of resistance training on muscle strength in adults over 55 years of age. |
| Creatine improves physical performance in successive sets of short, high-intensity exercise. | |
| Vitamin C | Vitamin C contributes to maintain the normal function of the immune system during and after intense physical exercise. |
| Carbohydrate-based electrolyte solutions | The carbohydrate-based electrolyte solutions improve water absorption during exercise. It helps to maintain the resistance level in exercises that require prolonged resistance. |
| The carbohydrate-based electrolyte solution improves water absorption during exercise. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menal-Puey, S.; Marques-Lopes, I. Regulatory Framework of Fortified Foods and Dietary Supplements for Athletes: An Interpretive Approach. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113858
Menal-Puey S, Marques-Lopes I. Regulatory Framework of Fortified Foods and Dietary Supplements for Athletes: An Interpretive Approach. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113858
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenal-Puey, Susana, and Iva Marques-Lopes. 2021. "Regulatory Framework of Fortified Foods and Dietary Supplements for Athletes: An Interpretive Approach" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113858
APA StyleMenal-Puey, S., & Marques-Lopes, I. (2021). Regulatory Framework of Fortified Foods and Dietary Supplements for Athletes: An Interpretive Approach. Nutrients, 13(11), 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113858







