Anemia of School-Age Children in Primary Schools in Southern China Should Be Paid More Attention despite the Significant Improvement at National Level: Based on Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance Data (2016–2017)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
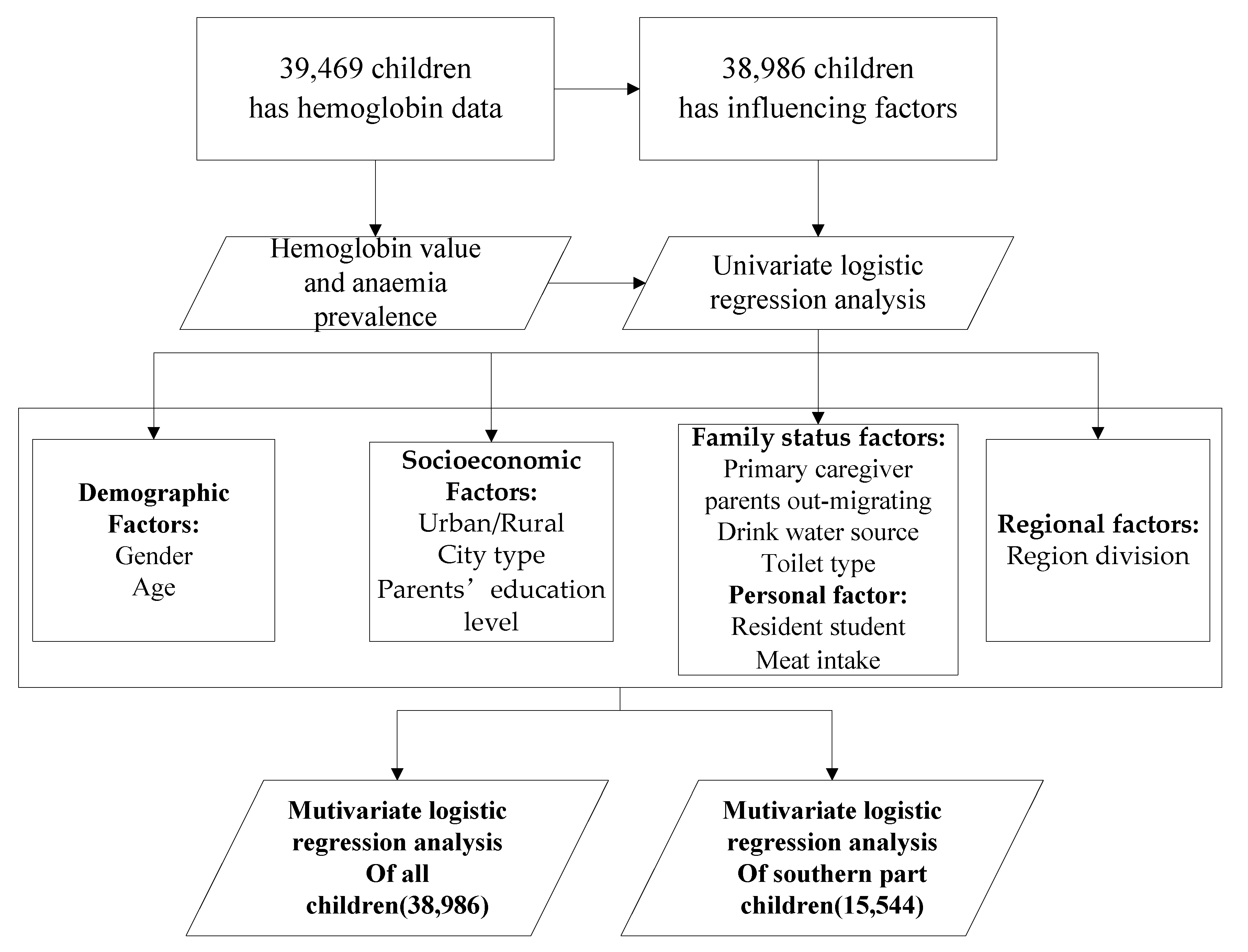
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Hemoglobin and Anemia Status
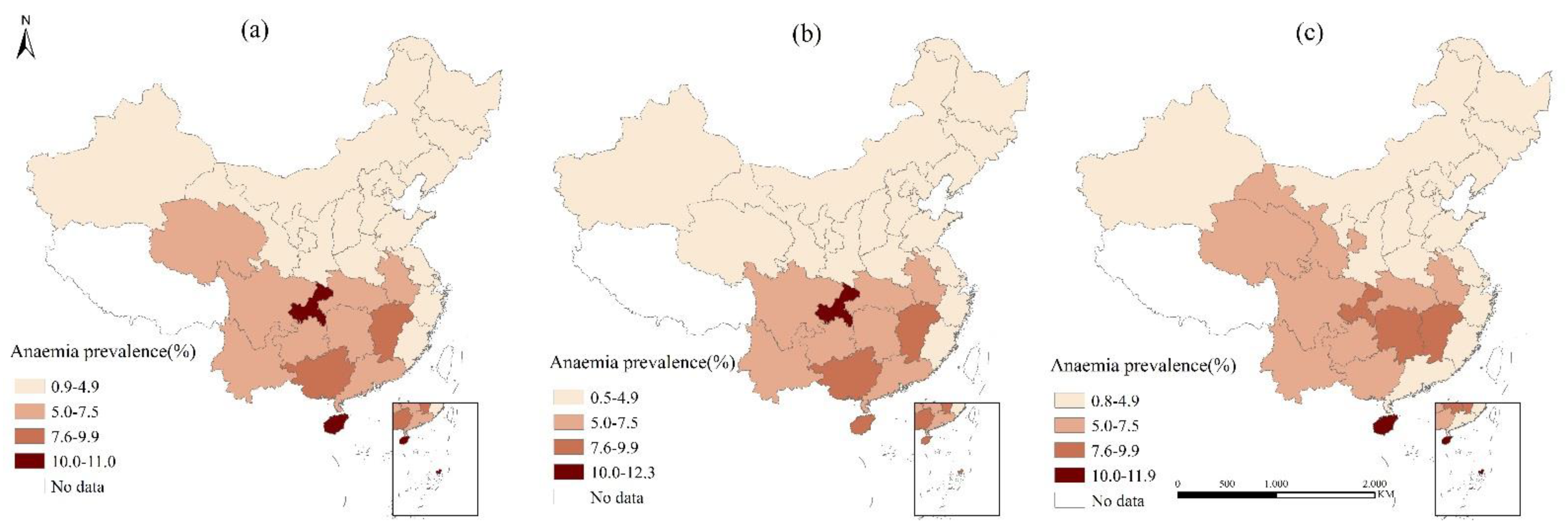
3.2. Regional Disparity of Anemia
3.3. Influencing Factors of SAC Anemia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Characteristic | All Children | South | The Others | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | Anemia% | OR (95%CI) | % | Anemia% | OR (95%CI) | % | Anemia% | OR (95%CI) | |
| Total | 4.37 | 6.95 | 3.08(2.78–3.42) | 2.37 | 1.00(ref) | ||||
| Gender | |||||||||
| Boy | 49.80 | 3.95 | 1.00(ref) | 49.85 | 6.61 | 1.00(ref) | 49.77 | 2.19 | 1.00(ref) |
| Girl | 50.20 | 4.44 | 1.13(1.02–1.25) * | 50.15 | 7.30 | 1.11(0.98–1.26) | 50.23 | 2.55 | 1.17(0.99–1.39) |
| Child’s age(in year) | |||||||||
| 6 | 10.07 | 6.78 | 1.00(ref) | 10.45 | 10.15 | 1.00(ref) | 9.81 | 4.39 | 1.00(ref) |
| 7 | 17.68 | 5.56 | 0.81(0.69–0.95) * | 17.70 | 9.70 | 0.95(0.78–1.17) | 17.67 | 2.80 | 0.63(0.48–0.82) * |
| 8 | 18.54 | 4.76 | 0.69(0.58–0.81) * | 18.74 | 7.72 | 0.74(0.60–0.91) * | 18.41 | 2.76 | 0.62(0.47–0.81) * |
| 9 | 18.47 | 3.44 | 0.49(0.41–0.59) * | 18.03 | 6.21 | 0.59(0.47–0.73) * | 18.76 | 1.68 | 0.37(0.28–0.51) * |
| 10 | 17.89 | 3.13 | 0.44(0.37–0.53) * | 17.75 | 5.07 | 0.47(0.37–0.60) * | 17.98 | 1.85 | 0.41(0.30–0.55) * |
| 11 | 17.36 | 2.62 | 0.37(0.30–0.45) * | 17.33 | 4.08 | 0.38(0.29–0.48) * | 17.38 | 1.64 | 0.36(0.27–0.50) * |
| Resident student | |||||||||
| Yes | 12.82 | 5.07 | 1.27(1.10–1.45) * | 18.89 | 6.90 | 0.99(0.84–1.16) | 8.84 | 2.51 | 1.07(0.80–1.43) |
| No | 87.18 | 4.05 | 1.00(ref) | 81.11 | 6.97 | 1.00(ref) | 91.16 | 2.36 | 1.00(ref) |
| Meat intake | |||||||||
| <3 times/week | 51.42 | 4.72 | 1.30(1.18–1.44) * | 57.64 | 7.47 | 1.21(1.06–1.37) * | 47.28 | 2.49 | 1.10(0.93–1.30) |
| ≥3 times/week | 48.58 | 3.67 | 1.00(ref) | 42.36 | 6.28 | 1.00(ref) | 52.72 | 2.27 | 1.00(ref) |
| City type | |||||||||
| BC | 11.79 | 2.75 | 1.00(ref) | 10.01 | 5.21 | 1.00(ref) | 12.97 | 1.49 | 1.00(ref) |
| SMC | 35.63 | 3.16 | 1.15(0.94–1.41) | 26.16 | 6.47 | 1.26(0.97–1.63) | 41.95 | 1.78 | 1.20(0.86–1.67) |
| OC | 36.48 | 5.25 | 1.96(1.62–2.37) * | 41.60 | 7.76 | 1.53(1.20–1.95) * | 33.05 | 3.14 | 2.15(1.56–2.96) * |
| PC | 16.10 | 5.21 | 1.94(1.58–2.40) * | 22.22 | 6.80 | 1.33(1.02–1.72) * | 12.02 | 3.25 | 2.22(1.55–3.19) * |
| Father’s education level | |||||||||
| junior middle school and below | 64.94 | 4.78 | 1.58(1.41–1.76) * | 71.87 | 7.48 | 1.37(1.18–1.59) * | 60.33 | 2.64 | 1.39(1.16–1.66) * |
| senior high school/technical secondary school and above | 35.06 | 3.09 | 1.00(ref) | 28.13 | 5.58 | 1.00(ref) | 39.67 | 1.92 | 1.00(ref) |
| Mother’s educational level | |||||||||
| junior middle school and below | 68.04 | 4.79 | 1.67(1.48–1.88) * | 75.75 | 7.40 | 1.36(1.16–1.59) * | 62.91 | 2.69 | 1.53(1.27–1.85) * |
| senior high school/technical secondary school and above | 31.96 | 2.92 | 1.00(ref) | 24.25 | 5.55 | 1.00(ref) | 37.09 | 1.78 | 1.00(ref) |
| Primary caregiver | |||||||||
| Mother | 70.88 | 3.74 | 1.00(ref) | 60.26 | 6.63 | 1.00(ref) | 77.93 | 2.26 | 1.00(ref) |
| Father | 5.43 | 3.88 | 1.04(0.82–1.30) | 6.11 | 6.22 | 0.93(0.71–1.23) | 4.98 | 1.97 | 0.87(0.57–1.33) |
| Grand parents | 22.07 | 5.76 | 1.57(1.41–1.75) * | 31.11 | 7.80 | 1.19(1.04–1.36) * | 16.07 | 3.13 | 1.40(1.14–1.72) * |
| Other relatives | 1.62 | 3.96 | 1.06(0.71–1.59) | 2.52 | 6.12 | 0.92(0.60–1.40) | 1.02 | 0.42 | 0.18(0.03–1.29) |
| Father out-migrating | |||||||||
| Yes | 31.27 | 5.35 | 1.48(1.34–1.64) * | 40.76 | 7.43 | 1.14(1.01–1.29) * | 24.95 | 3.09 | 1.45(1.21–1.74) * |
| No | 68.73 | 3.67 | 1.00(ref) | 59.24 | 6.59 | 1.00(ref) | 75.05 | 2.14 | 1.00(ref) |
| Mother out-migrating | |||||||||
| Yes | 16.40 | 6.09 | 1.64(1.45–1.84) * | 26.19 | 7.79 | 1.18(1.03–1.36) * | 9.94 | 3.13 | 1.35(1.05–1.74) * |
| No | 83.600 | 3.81 | 1.00(ref) | 73.81 | 6.64 | 1.00(ref) | 90.06 | 2.28 | 1.00(ref) |
| Sources of drinking water | |||||||||
| Safe | 95.08 | 4.11 | 1.00(ref) | 93.67 | 6.82 | 1.00(ref) | 96.02 | 2.35 | 1.00(ref) |
| Not safe | 4.92 | 5.94 | 1.48(1.21–1.80) * | 6.33 | 8.80 | 1.32(1.05–1.66) * | 3.98 | 2.92 | 1.25(0.84–1.85) |
| Toilet type | |||||||||
| Sanitary toilet | 72.18 | 4.06 | 1.00(ref) | 74.23 | 6.91 | 1.00(ref) | 70.83 | 2.07 | 1.00(ref) |
| Non-Sanitary toilet | 27.82 | 4.57 | 1.13(1.02–1.26) * | 25.77 | 7.09 | 1.03(0.89–1.18) | 29.17 | 3.09 | 1.51(1.27–1.79) * |
References
- Kassebaum, N.J. The Global Burden of Anemia. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 247–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benoist, B.D.; Cogswell, M.; Egli, I.; Mclean, E. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia 1993-2005. Geneva World Health Organ. 2008 2008, 2, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.D.; Brownlie, I.V.; Thomas. Iron Deficiency and Reduced Work Capacity: A Critical Review of the Research to Determine a Causal Relationship. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 676S–690S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grantham-McGregor, S.; Ani, C. A review of studies on the effect of iron deficiency on cognitive development in children. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 649S–668S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.A.; Finucane, M.M.; De-Regil, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Flaxman, S.R.; Branca, F.; PeñA-Rosas, J.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Ezzati, M. Global, regional, and national trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995–2011: A systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e16–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, Q.Q.; Chen, B.W.; Yin, D.L.; Xiao, F.; Li, R.L.; Yin, T.; Yang, H.M.; Zheng, X.G.; Wang, L.H. Prevalence of Anemia and its Risk Factors among Children under 36 Months Old in China. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2016, 63, fmw049. [Google Scholar]
- Balarajan, Y.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Ozaltin, E.; Shankar, A.H.; Subramanian, S.V. Anaemia in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2011, 378, 2123–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Agardh, A. National Trends in Hemoglobin Concentration and Prevalence of Anemia among Chinese School-Aged Children, 1995-2010. J. Pediatr. 2017, 183, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Mao, D.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Piao, J.; Yang, L.; et al. Prevalence of Anemia in Chinese Children and Adolescents and Its Associated Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Miller, G.; Yu, E.; Sharbono, B.; Medina, A.; Rozelle, S. Anaemia among students of rural China’s elementary schools: Prevalence and correlates in Ningxia and Qinghai’s poor counties. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2011, 29, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, P.; Ma, J.; Song, Y. Prevalence of Anemia and its Associated Factors among Chinese 9-, 12-, and 14-Year-Old Children: Results from 2014 Chinese National Survey on Students Constitution and Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, P.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Cao, W.; Gan, Q.; Pan, H.; Xu, J. Anemia status and related factors among left-behind children in poverty-sticken rural areas in China, 2016. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, R.H.; Xia, S.C.; Huang, L.C.; Fang, Y.Q.; Meng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhou, B.; Ding, G.Q. The Rural-Urban Difference in BMI and Anemia among Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.H. Profiles of anemia among school-aged children categorized by body mass index and waist circumference in Shandong, China. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y. Modern Children and Adolescent Health; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of disease control and Prevention. Report on Chinese Residents’ Chronic Diseases and Nutrition; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Gao, X.; Tang, W.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Cai, W. Food insecurity and malnutrition in Chinese elementary school students. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.Y.; Hu, P.J.; Luo, D.M.; Dong, B.; Ma, Y.; Dai, J.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Lau, P.W.C. Reducing Anemia Among School-Aged Children in China by Eliminating the Geographic Disparity and Ameliorating Stunting: Evidence From a National Survey. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Yan, X.; Hu, P.; Zhang, J.; Lei, Y.; Song, Y.; Ma, J. Subnational disparity of anemia among Chinese Han students aged 7–14 years in 2014. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2019, 40, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Fang, H.; Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Ju, L.; et al. China Nutrition and Health Surveys (1982-2017). China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 3. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Bo, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhou, C.; Lao, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D. Regional Differences in the Prevalence of Anaemia and Associated Risk Factors among Infants Aged 0–23 Months in China: China Nutrition and Health Surveillance. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Addo, O.Y.; De la Cruz-Gongora, V.; Ashour, F.A.; Ziegler, T.R.; Suchdev, P.S. Determinants of Anemia among School-Aged Children in Mexico, the United States and Colombia. Nutrients 2016, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Bulliyya, G. Magnitude of Anemia and Hematological Predictors among Children under 12 Years in Odisha, India. Anemia 2016, 2016, 1729147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mesfin, F.; Berhane, Y.; Worku, A. Anemia among Primary School Children in Eastern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assefa, S.; Mossie, A.; Hamza, L. Prevalence and severity of anemia among school children in Jimma Town, Southwest Ethiopia. BMC Hematol. 2014, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- China, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China. Net Enrolment Ratio of School-Age Children in Primary Schools. Available online: http://www.moe.gov.cn/s78/A03/moe_560/2020/quanguo/202108/t20210831_556355.html (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y. Comprehensive Report on Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance 2010–2013; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Xu, R.; Ma, J.; Yan, X.; Hu, P.; Song, Y.; Jan, C.; Raat, H.; Patton, G.C. The associations of economic growth and anaemia for school-aged children in China. Matern. Child Nutr. 2020, 16, e12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China, Ministry of Education of the people’s Republic of China. The inform of the State Council on the Nutrition Improvement Program for Rural Compulsory Education Students. Available online: http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xwfb/s6052/moe_838/201110/t20111026_125887.html (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Yiwen, R.; Dingwen, L.; Weiwen, Z.; Zhenzhu, T.; Yuemei, L.; Xiaopeng, L.; Qiulan, Q.; Wutao, L.; Meng, L. Analysis of anemia among students in rural areas of Guangxi in 2012 and 2019. J. Appl. Prev. Med. 2021, 27, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of anemia status of students in the rural nutrition improvement program area of Henan,2012-2019. Mod. Prev. Med. 2021, 48, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. Study on the Changes of Anemia Status and Related Factors in Rural Students in the Implementation Area of the “Nutrition Improvement Plan for Rural Students” from 2012 to 2014. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, China.
- Xu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Qiu, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L. Analysis on disease burden and health equity of iron-deficiency anemia among children and adolescents in China. Chin. J. Women Child Health Res. 2021, 32, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gayawan, E.; Arogundade, E.D.; Adebayo, S.B. Possible determinants and spatial patterns of anaemia among young children in Nigeria: A Bayesian semi-parametric modelling. Int. Health 2014, 6, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Liao, Q.K. Prevalence of iron deficiency in children aged 7 months to 7 years in China. Chin. J. Pediatr. 2004, 42, 6. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristic | N(%) | Hb(g/L) | Anemia Prevalence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X ± SD | % | 95%CI | ||
| Total | 39,469(100%) | 133.18 ± 10.84 | 4.37 | 3.22–5.52 |
| Boy | 19,647(49.8%) | 133.52 ± 10.90 * | 4.24 * | 2.94–5.55 |
| Girl | 19,822(50.2%) | 132.84 ± 10.77 * | 4.52 * | 3.44–5.59 |
| Child’s age (in years) | ||||
| 6 | 3937(10.0%) | 129.51 ± 10.73 | 5.71 | 4.20–7.22 |
| 7 | 6916(17.5%) | 130.75 ± 10.63 | 5.33 | 4.02–6.65 |
| 8 | 7250(18.4%) | 132.49 ± 10.82 | 4.35 | 3.46–5.24 |
| 9 | 7240(18.3%) | 133.60 ± 10.31 | 4.21 | 2.71–5.70 |
| 10 | 7004(17.7%) | 134.65 ± 10.56 | 4.01 | 1.62–6.39 |
| 11 | 7122(18.0%) | 136.40 ± 10.71 | 3.25 | 1.48–5.01 |
| Urban/Rural | ||||
| Urban | 18,649(47.2%) | 134.03 ± 10.51 * | 3.50 * | 1.13–5.87 |
| Rural | 20,820(52.8%) | 132.42 ± 11.08 * | 4.99 * | 3.96–6.02 |
| Influencing Factors | Reference | All Children | Children in Southern Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | p | OR(95%CI) | p | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Girl | Boy | 1.14(1.03–1.26) | 0.01 | NS | NS |
| Age | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 0.82(0.69–0.96) | 0.02 | 0.95(0.77–1.17) | 0.63 |
| 8 | 6 | 0.67(0.56–0.79) | <0.01 | 0.72(0.58–0.89) | <0.01 |
| 9 | 6 | 0.49(0.41–0.59) | <0.01 | 0.58(0.46–0.72) | <0.01 |
| 10 | 6 | 0.43(0.36–0.52) | <0.01 | 0.44(0.35–0.56) | <0.01 |
| 11 | 6 | 0.37(0.30–0.45) | <0.01 | 0.35(0.27–0.45) | <0.01 |
| City Type | |||||
| SMC | BC | 1.09(0.88–1.34) | 0.42 | NS | NS |
| OC | BC | 1.39(1.12–1.71) | <0.01 | NS | NS |
| PC | BC | 1.25(1.00–1.57) | 0.05 | NS | NS |
| Zone | |||||
| South area | The other area | 2.83(2.54–3.16) | <0.01 | NA | NA |
| Mother’s education | |||||
| Low | High | 1.23(1.04–1.45) | 0.01 | 1.24(1.01–1.52) | 0.04 |
| Father’s education | |||||
| Low | High | 1.18(1.00–1.37) | 0.04 | 1.27(1.05–1.54) | 0.01 |
| Meat type | |||||
| <3 times/week | ≥3 times/week | 1.12(1.00–1.25) | 0.04 | 1.18(1.04–1.35) | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, L.; Ren, H. Anemia of School-Age Children in Primary Schools in Southern China Should Be Paid More Attention despite the Significant Improvement at National Level: Based on Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance Data (2016–2017). Nutrients 2021, 13, 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113705
Li S, Cheng X, Zhao L, Ren H. Anemia of School-Age Children in Primary Schools in Southern China Should Be Paid More Attention despite the Significant Improvement at National Level: Based on Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance Data (2016–2017). Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113705
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shujuan, Xue Cheng, Liyun Zhao, and Hongyan Ren. 2021. "Anemia of School-Age Children in Primary Schools in Southern China Should Be Paid More Attention despite the Significant Improvement at National Level: Based on Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance Data (2016–2017)" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113705
APA StyleLi, S., Cheng, X., Zhao, L., & Ren, H. (2021). Anemia of School-Age Children in Primary Schools in Southern China Should Be Paid More Attention despite the Significant Improvement at National Level: Based on Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance Data (2016–2017). Nutrients, 13(11), 3705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113705







