Mother’s Milk Microbiome Shaping Fecal and Skin Microbiota in Infants with Food Allergy and Atopic Dermatitis: A Pilot Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Metagenomic Analysis
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses
2.5. Additional Information
3. Results
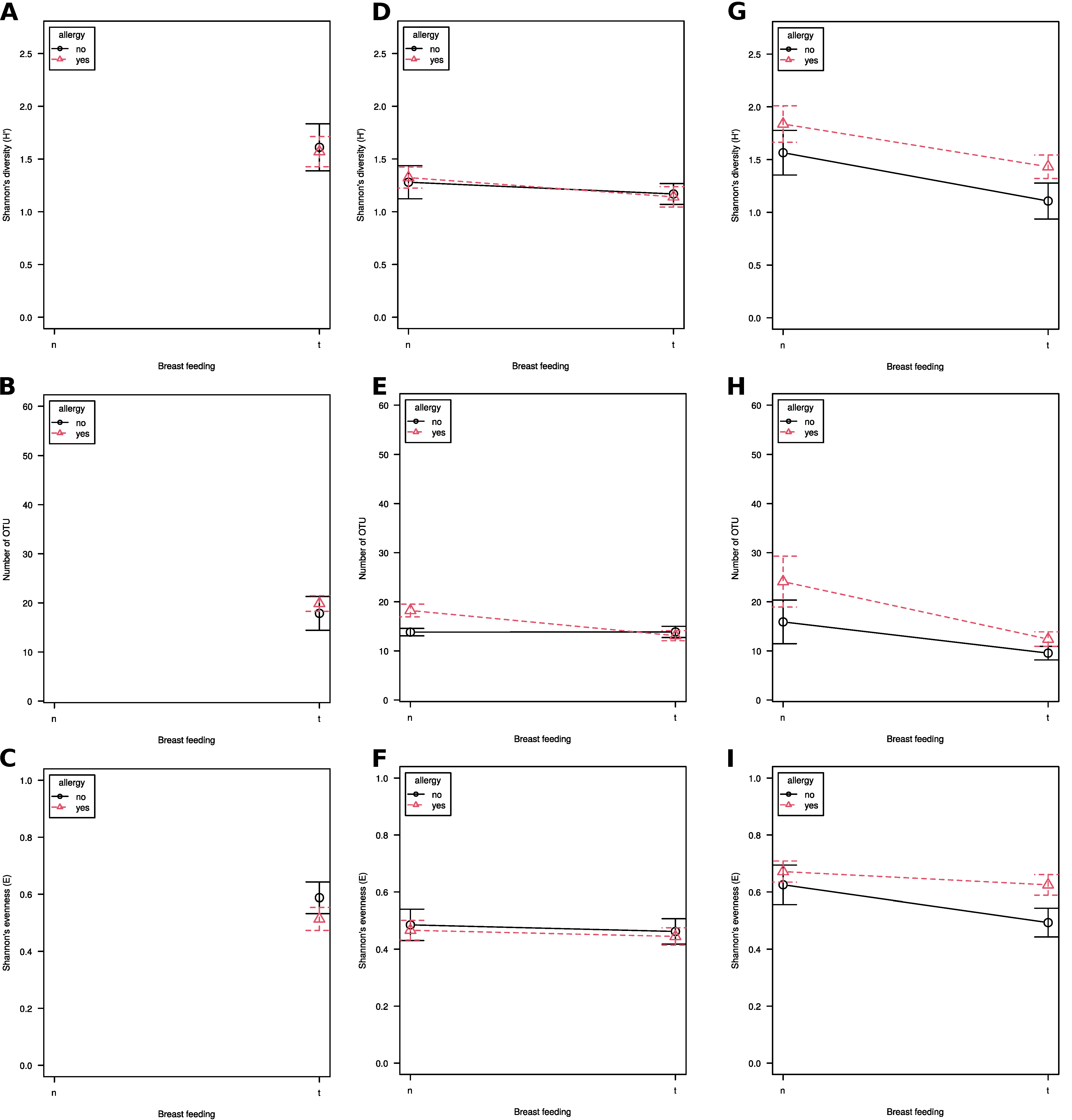
3.1. Alpha Diversity
3.2. Beta-Diversity
3.3. Taxonomic Composition
3.4. Significant Differences in Taxa Abundance
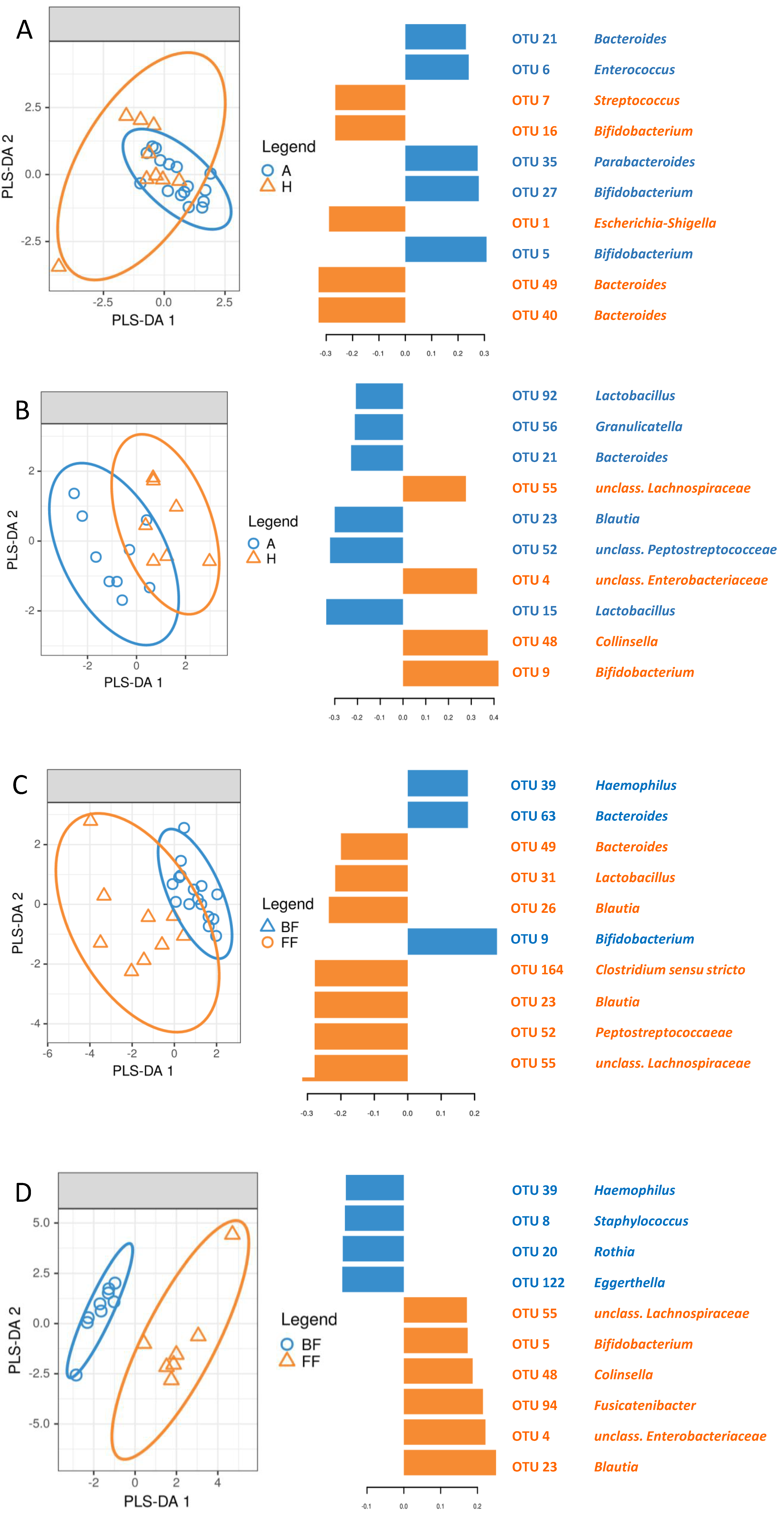
3.5. Identification of Signature Taxa (sPLS-DA)
3.6. Co-Occurrence of Bacteria in Milk and Feces as Well as Milk and Skin Depending on Allergic Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younge, N.E.; Araújo-Pérez, F.; Brandon, D.; Seed, P.C. Early-life skin microbiota in hospitalized preterm and full-term infants. Microbiome 2018, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Bender, J.M.; Yang, S.; Rollie, A.; Adisetiyo, H.; Zabih, S.; Lincez, P.J.; Bittinger, K.; et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 71, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, B.; Peura, S.; Hammar, U.; Vicenzi, S.; Hedman, A.; Almqvist, C.; Andolf, E.; Pershagen, G.; Dicksved, J.; Bertilsson, S.; et al. Oral Microbiota Development in Early Childhood. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penders, J.; Gerhold, K.; Stobberingh, E.E.; Thijs, C.; Zimmermann, K.; Lau, S.; Hamelmann, E. Establishment of the intestinal microbiota and its role for atopic dermatitis in early childhood. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, N.T.; Li, F.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Tun, H.M.; Brown, B.P.; Pannaraj, P.S.; Bender, M.; Azad, M.B.; Thompson, A.L.; Weiss, S.T.; et al. Meta-analysis of effects of exclusive breastfeeding on infant gut microbiota across populations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpela, K.; Salonen, A.; Hickman, B.; Kunz, C.; Sprenger, N.; Kukkonen, K.; Savilahti, E.; Kuitunen, M.; de Vos, W.M. Fucosylated oligosaccharides in mother's milk alleviate the effects of caesarean birth on infant gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sitarik, A.R.; Bobbitt, K.R.; Havstad, S.L.; Fujimura, K.E.; Levin, A.M.; Zoratti, E.M.; Kim, H.; Woodcroft, K.; Wegienka, G.; Ownby, D.R.; et al. Breast Milk Transforming Growth Factor beta Is Associated With Neonatal Gut Microbial Composition. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, e60–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Cervantes, K.; García-González, I.; Villalobos-Flores, L.E.; Hernández-Quiroz, F.; Piña-Escobedo, A.; Hoyo-Vadillo, C.; Rangel-Calvillo, M.N.; García-Mena, J. Human milk microbiota associated with early colonization of the neonatal gut in Mexican newborns. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wopereis, H.; Sim, K.; Shaw, A.; Warner, J.O.; Knol, J.; Kroll, J.S. Intestinal microbiota in infants at high risk for allergy: Effects of prebiotics and role in eczema development. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savage, J.H.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Sordillo, J.E.; Lange, N.E.; Zhou, Y.; O’Connor, G.T.; Sandel, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; Zeiger, R.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Diet during Pregnancy and Infancy and the Infant Intestinal Microbiome. J. Pediatr. 2018, 203, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Curley, D.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; O’Shea, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. The Composition of Human Milk and Infant Faecal Microbiota over the First Three Months of Life: A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, H.; Zhuo, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, D. Comparison of gut microbiota in exclusively breast-fed and formula-fed babies: A study of 91 term infants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, C.C.; Tavalire, H.F.; Neiderhiser, J.M.; Bohannan, B.; Leve, L.D. History of breastfeeding but not mode of delivery shapes the gut microbiome in childhood. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Andersson, A.F.; Björkstén, B.; Engstrand, L.; Jenmalm, M.C. Low diversity of the gut microbiota in infants with atopic eczema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sordillo, J.E.; Zhou, Y.; McGeachie, M.J.; Ziniti, J.; Lange, N.; Laranjo, N.; Savage, J.R.; Carey, V.; O’Connor, G.; Sandel, M.; et al. Factors influencing the infant gut microbiome at age 3–6 months: Findings from the ethnically diverse Vitamin D Antenatal Asthma Reduction Trial (VDAART). Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madan, J.C.; Hoen, A.G.; Lundgren, S.N.; Farzan, S.F.; Cottingham, K.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Li, H.; Moore, J.H.; Karagas, M.R. Association of Cesarean Delivery and Formula Supplementation With the Intestinal Microbiome of 6-Week-Old Infants. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazzo, G.; van Best, N.; Bervoets, L.; Dapaah, I.O.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Hornef, M.W.; GI-MDH consortium; Lau, S.; Hamelmann, E.; Penders, J. Development of the Microbiota and Associations With Birth Mode, Diet, and Atopic Disorders in a Longitudinal Analysis of Stool Samples, Collected From Infancy Through Early Childhood. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, M.; Alba, C.; Proctocolitis Study Group of Cam Public Health Area; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, L. Microbiological and Immunological Markers in Milk and Infant Feces for Common Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benítez-Páez, A.; Olivares, M.; Szajewska, H.; Pieścik-Lech, M.; Polanco, I.; Castillejo, G.; Nuñez, M.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Koletzko, S.; et al. Breast-Milk Microbiota Linked to Celiac Disease Development in Children: A Pilot Study From the PreventCD Cohort. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, S.L.; Lohmann, P.; Preidis, G.A.; Gordon, P.S.; O’Donnell, A.; Hagan, J.; Venkatachalam, A.; Balderas, M.; Luna, R.A.; Hair, A.B. Improved feeding tolerance and growth are linked to increased gut microbial community diversity in very-low-birth-weight infants fed mother's own milk compared with donor breast milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotterud, C.L.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Simpson, M.R.; Rudi, K.; Storrø, O.; Johnsen, R.; Øien, T. Does Maternal Perinatal Probiotic Supplementation Alter the Intestinal Microbiota of Mother and Child? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeorg, H.; Metsvaht, T.; Eelmäe, I.; Merila, M.; Treumuth, S.; Huik, K.; Jürna-Ellam, M.; Ilmoja, M.L.; Lutsar, I. The role of breast milk in the colonization of neonatal gut and skin with coagulase-negative staphylococci. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.E.; Samuel, B.S.; Houghteling, P.; Shan, G.; Ausubel, F.M.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Walker, W.A. Influence of maternal breast milk ingestion on acquisition of the intestinal microbiome in preterm infants. Microbiome 2016, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, S.; Song, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lv, N.; Xue, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Zhu, B.; Ma, J. et a. The Perturbation of Infant Gut Microbiota Caused by Cesarean Delivery Is Partially Restored by Exclusive Breastfeeding. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 26, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbes, J.D.; Azad, M.B.; Vehling, L.; Tun, H.M.; Konya, T.B.; Guttman, D.S.; Field, C.J.; Lefebvre, D.; Sears, M.R.; Becker, A.B.; et al. Canadian Healthy Infant Longitudinal Development (CHILD) Study Investigators Association of Exposure to Formula in the Hospital and Subsequent Infant Feeding Practices With Gut Microbiota and Risk of Overweight in the First Year of Life. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, e181161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzidic, M.; Mira, A.; Artacho, A.; Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Collado, M.C. Allergy development is associated with consumption of breastmilk with a reduced microbial richness in the first month of life. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, K.; Won, K.; Suh, D.I.; Kim, K.W.; Sheen, J.H.; Ahn, K.; et al. Perturbations of gut microbiome genes in infants with atopic dermatitis according to feeding type. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łoś-Rycharska, E.; Gołębiewski, M.; Sikora, M.; Grzybowski, T.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Popielarz, M.; Gawryjołek, J.; Krogulska, A. A Combined Analysis of Gut and Skin Microbiota in Infants with Food Allergy and Atopic Dermatitis: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiem, D.; Gołębiewski, M.; Hulisz, P.; Piernik, A.; Hrynkiewicz, K. How does salinity shape bacterial and fungal microbiomes of Alnus glutinosa Roots? Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DA-DA2: High resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project:improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, M.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J. et a. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ. Microbiol 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package v.2.5-6. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Chen, J. GUniFrac: Generalized UniFrac Distances. R Package v.1.1. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=GUniFrac (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Chen, J.; Bittinger, K.; Charlson, E.S.; Hoffmann, C.; Lewis, J.; Wu, G.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Associating microbiome composition with environmental covariates using generilized UniFrac distances. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheneman, L.; Evans, J.; Foster, J.A. Clearcut: A fast implementation of relaxed neighbor joining. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2823–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lê Cao, K.A.; Boitard, S.; Besse, P. Sparse PLS discriminant analysis: Biologically relevant feature selection and graphical displays for multiclass problems. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.-A. mixOmics: An R package for 'omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saitoh, S.; Noda, S.; Aiba, Y.; Takagi, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Benno, Y.; Koga, Y. Bacteroides ovatus as the Predominant Commensal Intestinal Microbe Causing a Systemic Antibody Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eribe, E.R.K.; Paster, B.J.; Caugant, D.A.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Stromberg, V.K.; Lacy, G.H.; Olsen, I. Genetic diversity of Leptotrichia and description of Leptotrichia goodfellowii sp. nov., Leptotrichia hofstadii sp. nov., Leptotrichia shahii sp. nov. and Leptotrichia wadei sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, D.C. The normal human microflora composition. In The Regulatory and Protective Role of the Normal Microflora; Grubb, R., Midvedt, M., Norin, E., Eds.; Stockton Press: London, UK, 1989; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chua, H.-H.; Chou, H.-C.; Tung, Y.-L.; Chiang, B.-L.; Liao, C.-C.; Liu, H.-H.; Ni, Y.-H. Intestinal dysbiosis featuring abundance of Ruminococcus gnavus associates with allergic diseases in infants. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compared Groups | Material | Bacterial Taxa | Incidence | q |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breastfed: allergic vs healthy | milk | OTU3 (Pseudomonas peli) OTU40 (Bacteroides ovatus) OTU93 (Leptotrichia wadei) | healthy only healthy only healthy > allergic | 0.03 0.03 0.04 |
| feces | OTU30 (Serratia marcescens) OTU68 (Lactococcus lactis) OTU35 (Parabacteroides) | healthy only healthy only allergic only | 0.03 0.03 0.04 | |
| skin | - | |||
| Allergic: breastfed vs formula-fed | feces | Blautia Eschericha-Shigella OTU1 (Escherichia-Shigella) OTU52 (Peptostreptococcaceae) OTU55 (Lachnospiraceae) | formula-fed > breastfed | 0.025 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.02 |
| skin | Enterobacteriales Pseudomonadales Enterobacteriaceae Moraxellaceae | formula-fed > breastfed | 0.02 0.049 0.02 0.04 | |
| Healthy: breastfed vs formula-fed | feces | OTU23 Blautia | formula-fed > breastfed | 0.04 |
| skin | Bacteroidales | formula-fed > breastfed | 0.02 |
| Allergic Group | Healthy Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU | rho | q | OTU | rho | q | ||
| 2 | Steptococcus | 0.44 | 0.02 | 5 | Bifidobacterium longum | 0.64 | 0.02 |
| 20 | Rothia mucillaginosa | 0.46 | 0.02 | 10 | Acinetobacter johnsoni | 0.65 | 0.02 |
| 21 | Bacteroides | 0.37 | 0.05 | 16 | Bifidobacterium scardivii | 0.74 | 0.004 |
| 27 | Bifidobacterium bifidum | 0.46 | 0.02 | 25 | Acinetobacter | 0.61 | 0.03 |
| 31 | Lactobacillus gasseri | 0.48 | 0.008 | 30 | Serratia marcescens | 0.61 | 0.03 |
| 48 | Colinsella aerofaciens | 0.53 | 0.003 | 32 | Haemophilus haemolyticus | 0.61 | 0.03 |
| 62 | Agrobacterium fabrum | 0.42 | 0.02 | 89 | Streptococcus anginosus | 1 | 0 |
| 81 | Atopobium parvulum | 0.62 | 0.0001 | ||||
| 89 | Streptococcus anginosus | 0.49 | 0.07 | ||||
| 95 | Lactobacillus oris | 0.53 | 0.003 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gołębiewski, M.; Łoś-Rycharska, E.; Sikora, M.; Grzybowski, T.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Krogulska, A. Mother’s Milk Microbiome Shaping Fecal and Skin Microbiota in Infants with Food Allergy and Atopic Dermatitis: A Pilot Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103600
Gołębiewski M, Łoś-Rycharska E, Sikora M, Grzybowski T, Gorzkiewicz M, Krogulska A. Mother’s Milk Microbiome Shaping Fecal and Skin Microbiota in Infants with Food Allergy and Atopic Dermatitis: A Pilot Analysis. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103600
Chicago/Turabian StyleGołębiewski, Marcin, Ewa Łoś-Rycharska, Marcin Sikora, Tomasz Grzybowski, Marta Gorzkiewicz, and Aneta Krogulska. 2021. "Mother’s Milk Microbiome Shaping Fecal and Skin Microbiota in Infants with Food Allergy and Atopic Dermatitis: A Pilot Analysis" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103600
APA StyleGołębiewski, M., Łoś-Rycharska, E., Sikora, M., Grzybowski, T., Gorzkiewicz, M., & Krogulska, A. (2021). Mother’s Milk Microbiome Shaping Fecal and Skin Microbiota in Infants with Food Allergy and Atopic Dermatitis: A Pilot Analysis. Nutrients, 13(10), 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103600






