The Intake of a Cafeteria Diet in Nursing Rats Alters the Breast Milk Concentration of Proteins Important for the Development of Offspring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
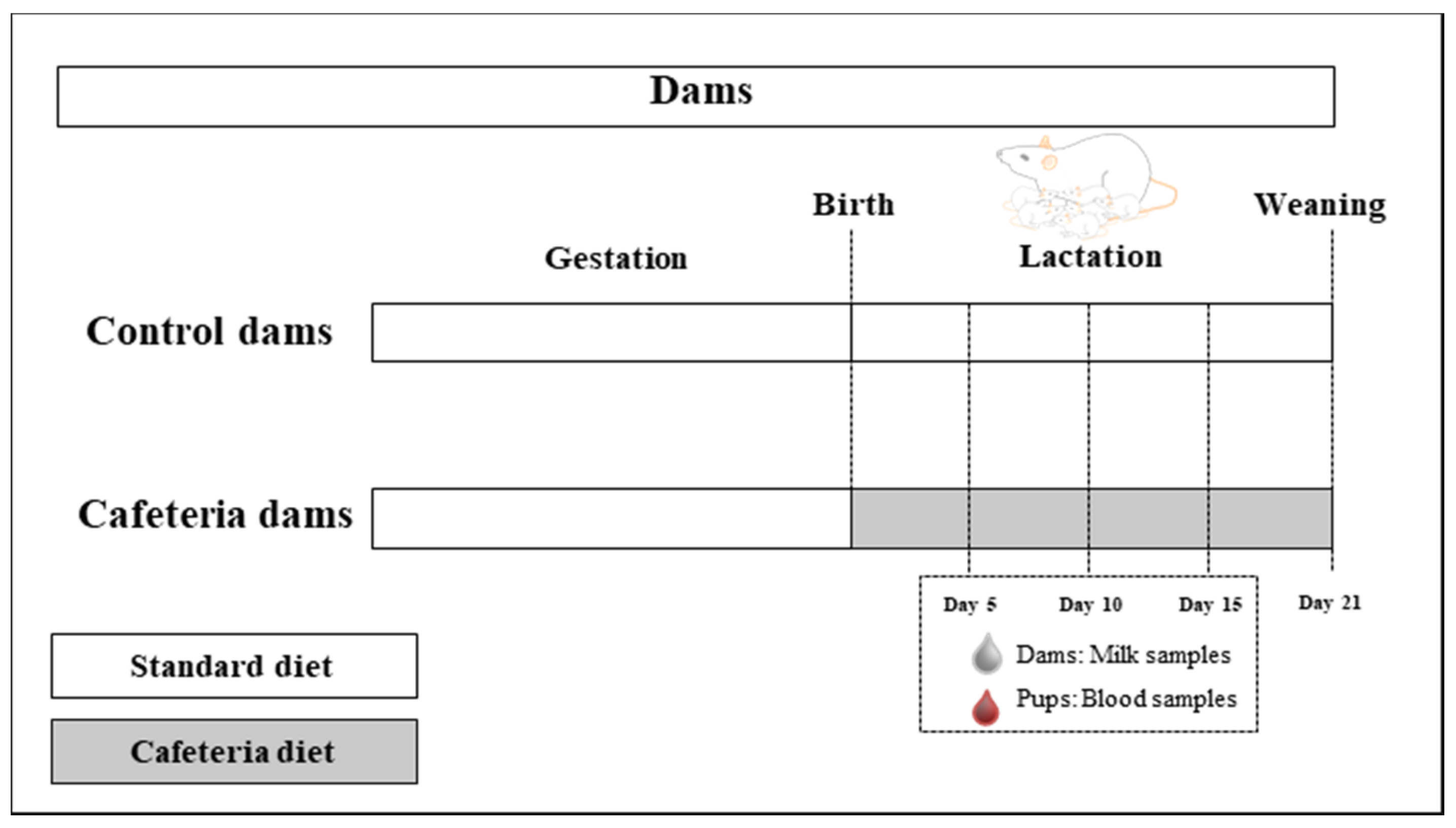
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. One-Dimensional SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.4. Staining and Quantification
2.5. Digestion of Bands and Identification of the Peptides and Proteins
2.6. Quantification of Milk and Plasma Specific Proteins
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. SDS-PAGE Separation, MALDI-TOF MS and MASCOT Protein Identification
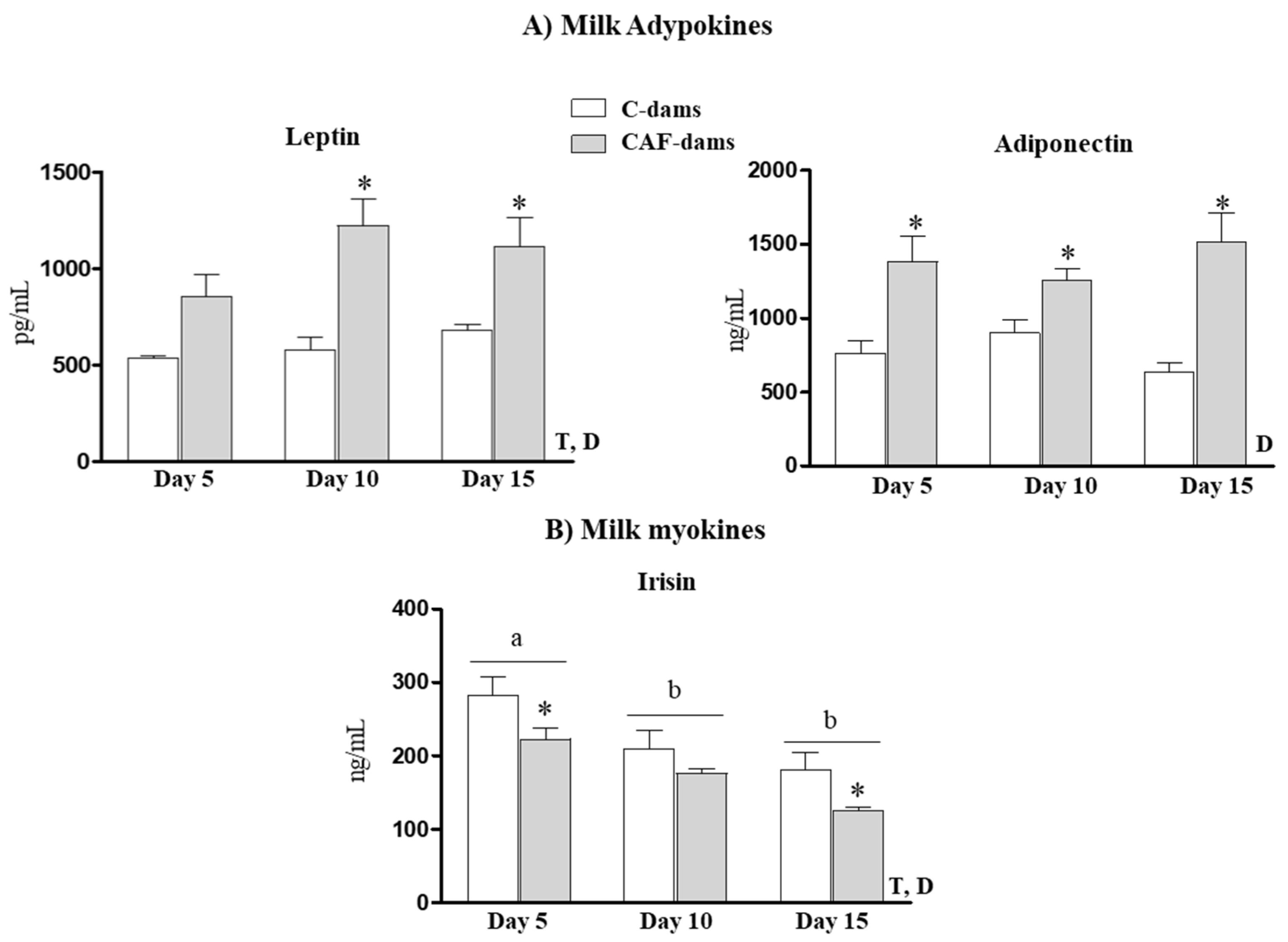
3.2. Leptin, Adiponectin, Irisin Levels During Lactation
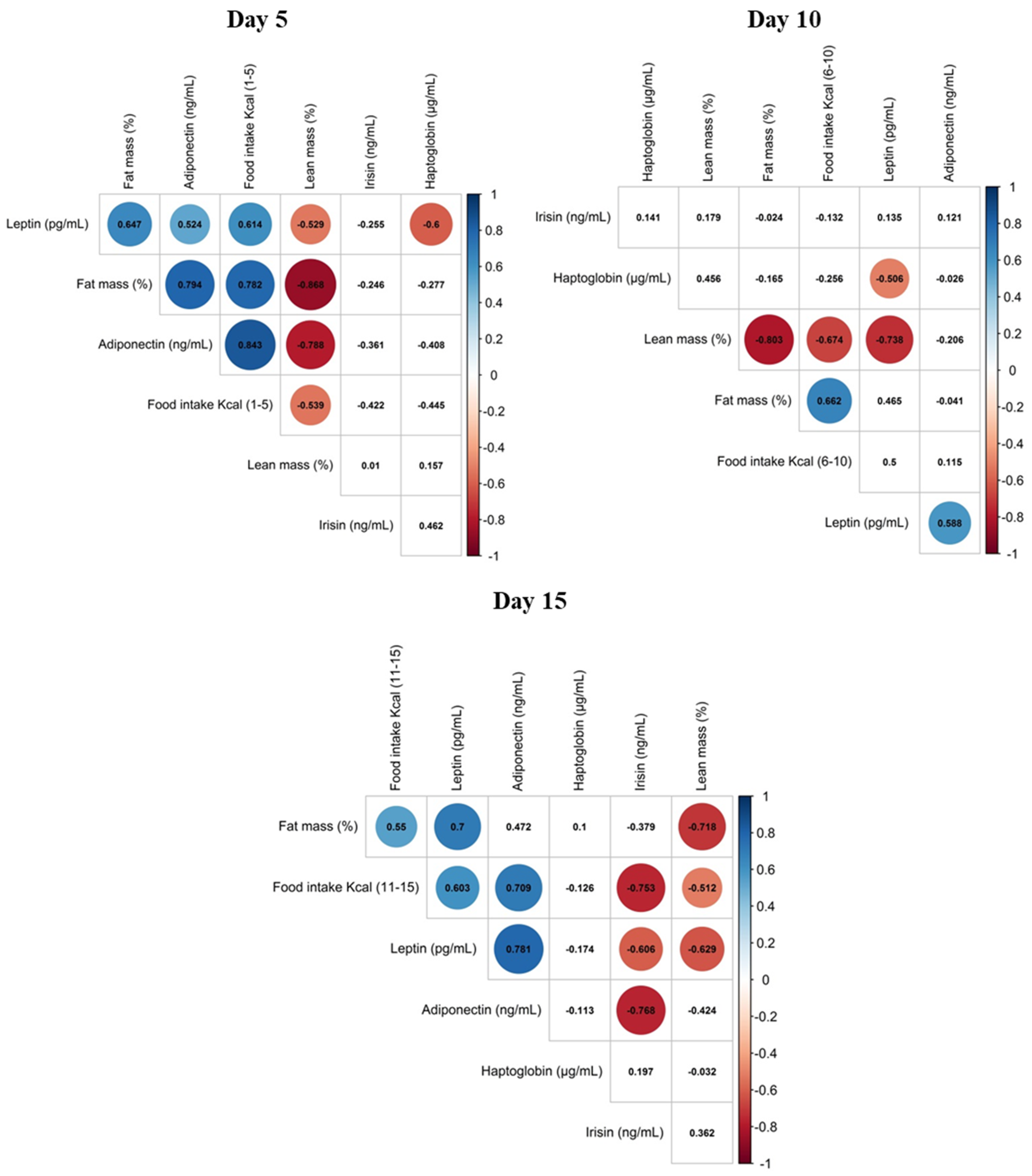
3.3. Correlation of Maternal Phenotypic Traits and the Levels of Selected Proteins in Maternal Milk
3.4. Leptin, Haptoglobin and Irisin Plasma Levels in Offspring During Lactation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive proteins in breast milk. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2013, 49 (Suppl. S1), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.S.; Witherly, S.A.; Clark, D.A. Casein: A Milk Protein with Diverse Biologic Consequences. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1990, 195, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, I.; Chronopoulou, R. Milk Peptides and Immune Response in the Neonate. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 606, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petermann, K.; Vordenbäumen, S.; Maas, R.; Braukmann, A.; Bleck, E.; Saenger, T.; Schneider, M.; Jose, J. Autoantibodies to αS1-Casein Are Induced by Breast-Feeding. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Lien, E.L. Nutritional and Physiologic Significance of α-Lactalbumin in Infants. Nutr. Rev. 2003, 61, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartol, F.F.; Wiley, A.A.; Miller, D.J.; Silva, A.J.; Roberts, K.E.; Davolt, M.L.P.; Chen, J.C.; Frankshun, A.-L.; Camp, M.E.; Rahman, K.M.; et al. Lactation Biology Symposium: Lactocrine signaling and developmental programming. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. Milk’s Role as an Epigenetic Regulator in Health and Disease. Diseases 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, O.; Sánchez, J.; Palou, A.; Picó, C. A Physiological Role of Breast Milk Leptin in Body Weight Control in Developing Infants. Obes. Silver Spring 2006, 14, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, F.K.; Onal, E.E.; Aral, Y.Z.; Adam, B.; Dilmen, U.; Ardiçolu, Y. Breast milk leptin: Its relationship to maternal and infant adiposity. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 21, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Woo, J.G.; Geraghty, S.R.; Altaye, M.; Davidson, B.S.; Banach, W.; Dolan, L.M.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Morrow, A.L. Adiponectin is present in human milk and is associated with maternal factors. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T. Copeptin, adropin and irisin concentrations in breast milk and plasma of healthy women and those with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 2013, 47, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palou, M.; Picó, C.; Palou, A. Leptin as a breast milk component for the prevention of obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 875–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesur, G.; Ozguner, F.; Yilmaz, N.; Dundar, B. The relationship between ghrelin and adiponectin levels in breast milk and infant serum and growth of infants during early postnatal life. J. Physiol. Sci. 2012, 62, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyermann, M.; Brenner, H.; Rothenbacher, D. Adipokines in Human Milk and Risk of Overweight in Early Childhood: A prospective cohort study. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.G.; Guerrero, M.L.; Guo, F.; Martin, L.J.; Davidson, B.S.; Ortega, H.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Morrow, A.L. Human Milk Adiponectin Affects Infant Weight Trajectory During the Second Year of Life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mól, N.; Zasada, M.; Tomasik, P.; Klimasz, K.; Kwinta, P. Evaluation of irisin and visfatin levels in very low birth weight preterm newborns compared to full term newborns—A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briana, D.D.; Boutsikou, M.; Boutsikou, T.; Marmarinos, A.; Gourgiotis, D.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A. Novel bioactive substances in human colostrum: Could they play a role in postnatal adaptation? J. Matern. Neonat. Med. 2016, 30, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomar, C.A.; van Nes, R.; Sánchez, J.; Picó, C.; Keijer, J.; Palou, A. Maternal consumption of a cafeteria diet during lactation in rats leads the offspring to a thin-outside-fat-inside phenotype. Int. J. Obes. Lond. 2017, 41, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyne, A.; Kiesselbach, C.; Sahún, I.; McDonald, J.; Gaiffi, M.; Dierssen, M.; Wolffgramm, J. An animal model of compulsive food-taking behaviour. Addict. Biol. 2009, 14, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, C.; Pons, A.; Gianotti, M.; Palou, A. Sustained changes in blood alpha amino nitrogen compartmentation during recovery from cafeteria feeding in rats. Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim. Biophys. 1991, 99, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, A.; McMullen, S.; Langley-Evans, S.C. Glucose intolerance associated with early-life exposure to maternal cafeteria feeding is dependent upon post-weaning diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 107, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampey, B.P.; Vanhoose, A.M.; Winfield, H.M.; Freemerman, A.J.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Fueger, P.T.; Newgard, C.B.; Makowski, L. Cafeteria Diet Is a Robust Model of Human Metabolic Syndrome With Liver and Adipose Inflammation: Comparison to High-Fat Diet. Obes. Silver Spring 2011, 19, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-Gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, R.C.; Singh, A.; Pezeshki, A.; Nibber, T.; Chelikani, P.K. Whey Protein Components—Lactalbumin and Lactoferrin—Improve Energy Balance and Metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobryszycka, W. Biological functions of haptoglobin—New pieces to an old puzzle. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1997, 35, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Schaer, D.J.; Vinchi, F.; Ingoglia, G.; Tolosano, E.; Buehler, P.W. Haptoglobin, hemopexin, and related defense pathways-basic science, clinical perspectives, and drug development. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, M.; Barone, I.; Scabia, G.; Santini, F. The Multifaceted Haptoglobin in the Context of Adipose Tissue and Metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Bahouth, S.W.; Madan, A.K. Haptoglobin release by human adipose tissue in primary culture. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.; Agnew, K.; Van Schothorst, E.M.; Keijer, J.; Klaus, S. Short-Term, high fat feeding-induced changes in white adipose tissue gene expression are highly predictive for long-term changes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, I.; Thanislass, J.; Veerapandyan, A.; Badami, S.; Antony, P.X. Characterization of Haptoglobin Isotype in Milk of Mastitis-Affected Cows. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, C.; Bertacca, A.; Novelli, S.E.; Görgün, C.Z.; Ciccarone, A.; Giordano, A.; Xu, H.; Soukas, A.; Costa, M.; Gandini, D.; et al. Obesity modulates the expression of haptoglobin in the white adipose tissue via TNFα. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001, 190, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, D.A.; George, B.; Williams, M.; Whitaker, K.; Allison, D.B.; Teague, A.; Demerath, E.W. Associations between human breast milk hormones and adipocytokines and infant growth and body composition in the first 6 months of life. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doneray, H.; Orbak, Z.; Yildiz, L. The relationship between breast milk leptin and neonatal weight gain. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.; Hechler, C.; Gebauer, C.; Kiess, W.; Kratzsch, J. Leptin in Maternal Serum and Breast Milk: Association With Infants’ Body Weight Gain in a Longitudinal Study Over 6 Months of Lactation. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, C.; Palou, M.; Priego, T.; Sánchez, J.; Palou, A. Metabolic programming of obesity by energy restriction during the perinatal period: Different outcomes depending on gender and period, type and severity of restriction. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Newburg, D.S. Human Milk Glycoproteins Protect Infants Against Human Pathogens. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, J.W.; Dodds, E.D.; Barboza, M.; McJimpsey, E.L.; Seipert, R.R.; Francis, J.; An, H.J.; Freeman, S.; German, J.B.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycoprotein Expression in Human Milk during Lactation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6440–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, K.; Marth, J.D. Glycosylation in Cellular Mechanisms of Health and Disease. Cell 2006, 126, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Benetti, S.; Liguori, S.A.; Sorrenti, M.; Cordero Di Montezemolo, L. Advances on human milk hormones and protection against obesity. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2013, 59, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Schöndorf, T.; Maiworm, A.; Emmison, N.; Forst, T.; Pfützner, A. Biological background and role of adiponectin as marker for insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk. Clin. Lab. 2005, 51, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Newburg, D.S.; Woo, J.G.; Morrow, A.L. Characteristics and Potential Functions of Human Milk Adiponectin. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, S41–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, S.; Schmid, D.; Zang, K.; Much, D.; Knoeferl, B.; Kratzsch, J.; Amann-Gassner, U.; Bader, B.L.; Hauner, H. Breast milk leptin and adiponectin in relation to infant body composition up to 2 years. Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Du, Y.; Schwaid, A.G.; Asterholm, I.W.; Scherer, P.E.; Saghatelian, A.; Wan, Y. Maternal adiponectin controls milk composition to prevent neonatal inflammation. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, H.; Pomar, C.A.; Palou, A.; Picó, C.; Sánchez, J. Offspring predisposition to obesity due to maternal-diet-induced obesity in rats is preventable by dietary normalization before mating. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pomar, C.A.; Sánchez, J.; Palou, A. The Intake of a Cafeteria Diet in Nursing Rats Alters the Breast Milk Concentration of Proteins Important for the Development of Offspring. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082470
Pomar CA, Sánchez J, Palou A. The Intake of a Cafeteria Diet in Nursing Rats Alters the Breast Milk Concentration of Proteins Important for the Development of Offspring. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082470
Chicago/Turabian StylePomar, Catalina Amadora, Juana Sánchez, and Andreu Palou. 2020. "The Intake of a Cafeteria Diet in Nursing Rats Alters the Breast Milk Concentration of Proteins Important for the Development of Offspring" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082470
APA StylePomar, C. A., Sánchez, J., & Palou, A. (2020). The Intake of a Cafeteria Diet in Nursing Rats Alters the Breast Milk Concentration of Proteins Important for the Development of Offspring. Nutrients, 12(8), 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082470







