The Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Physical Capacity among Active College-Aged Males
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
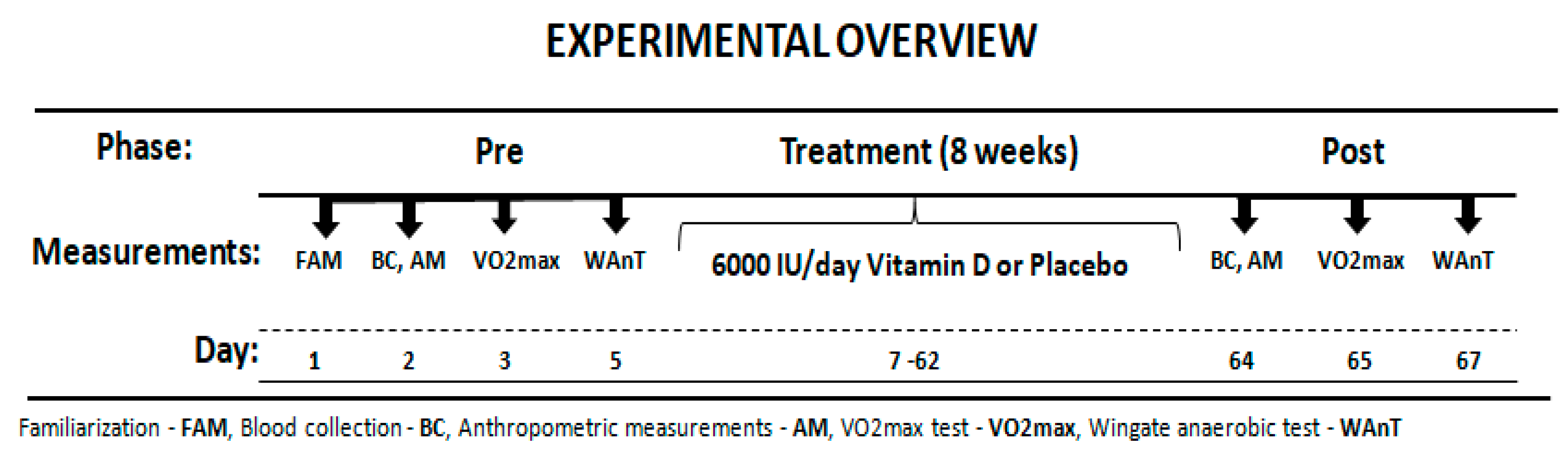
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Supplementation
2.4. Maximal Oxygen Uptake-O2max Test
2.5. Anaerobic Capacity Measurement—Wingate Anaerobic Test
2.6. Vitamin D Determination
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
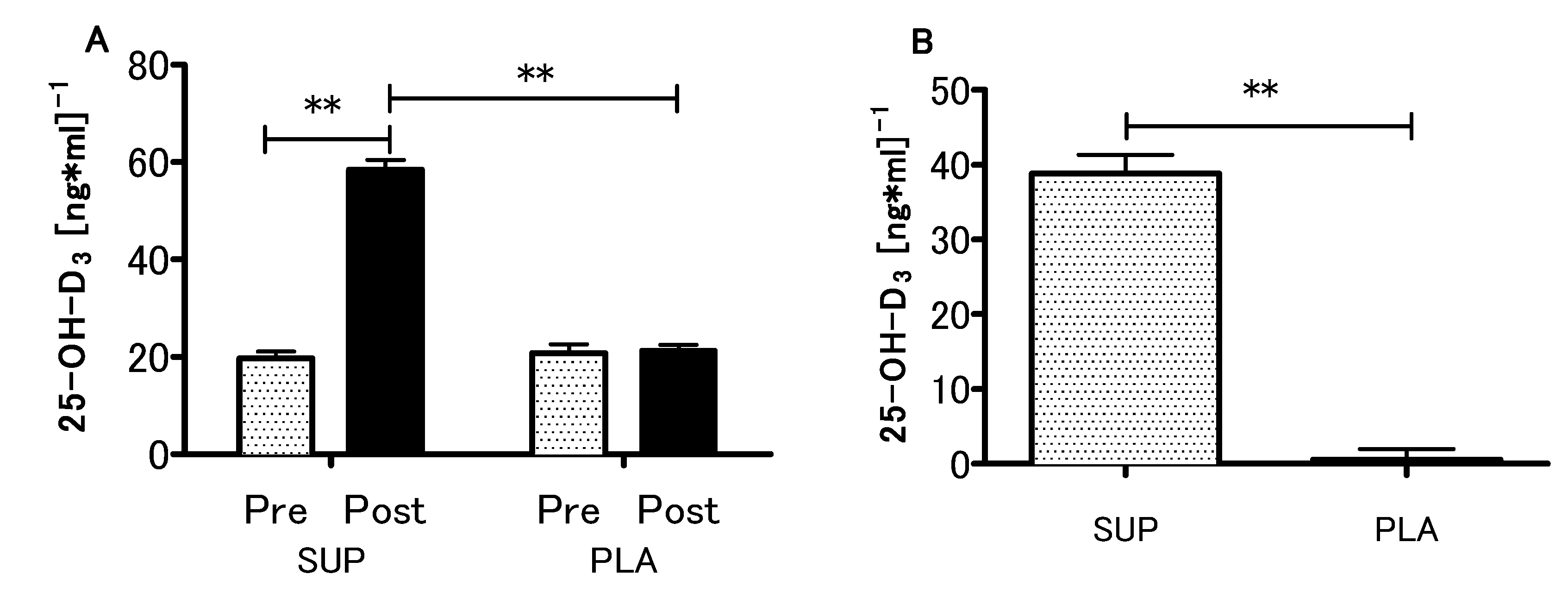
3.2. Vitamin D Status
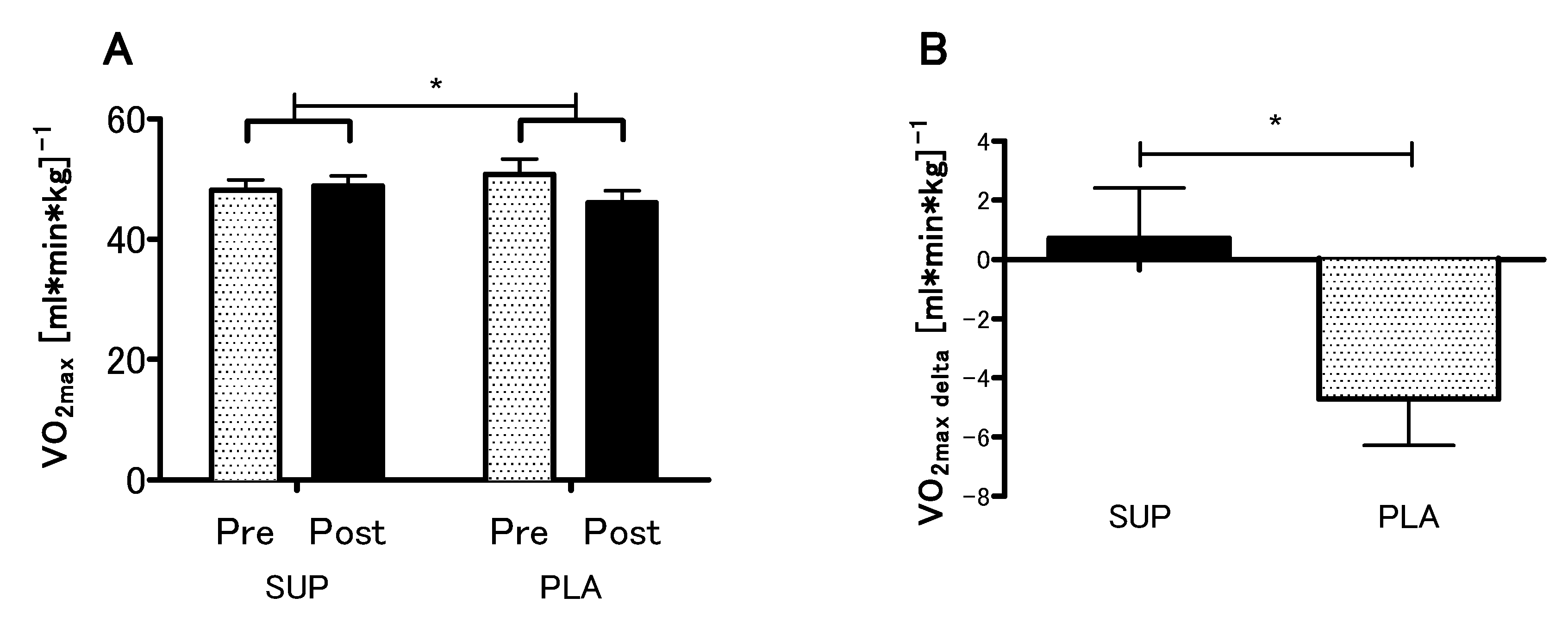
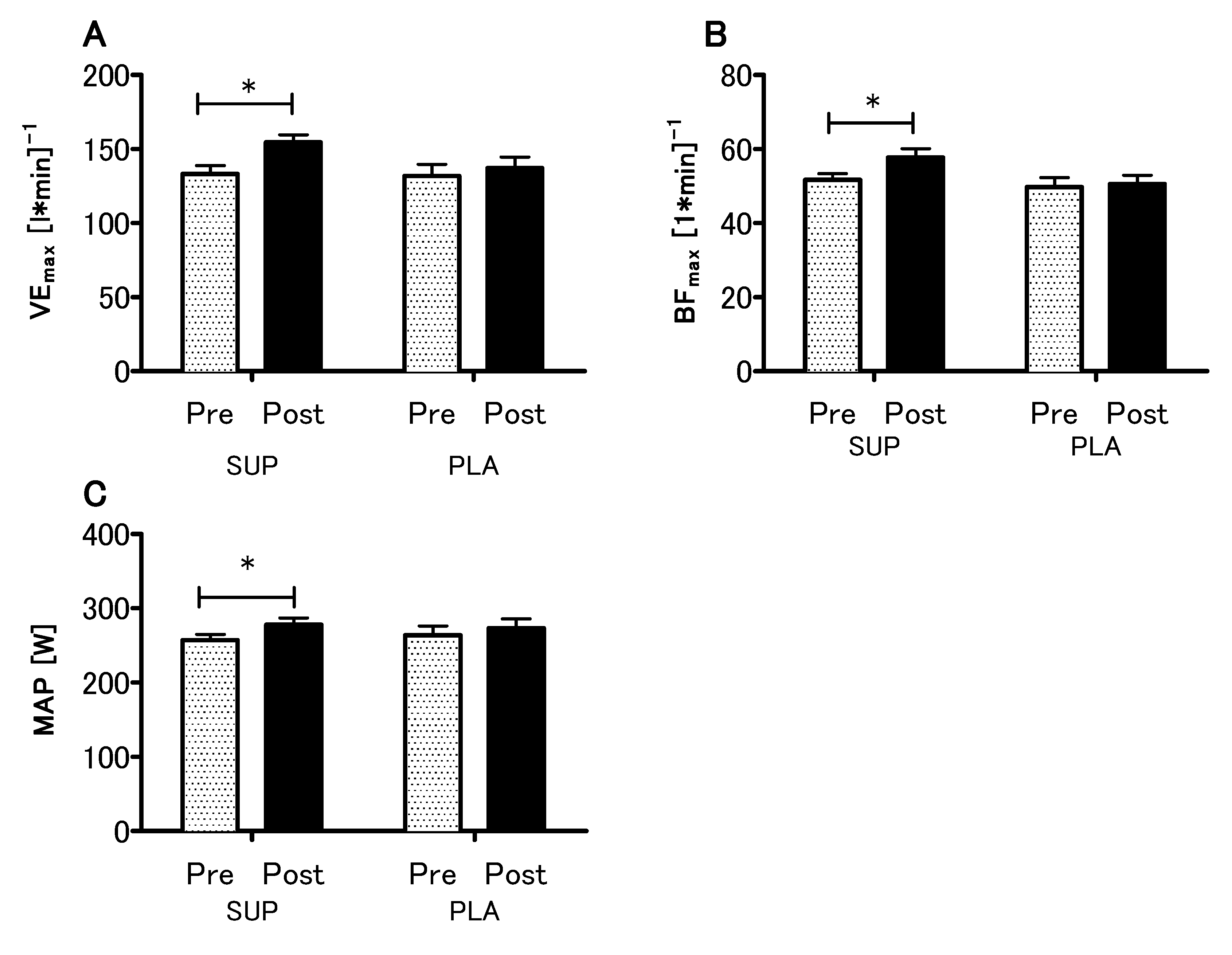
3.3. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Aerobic Capacity
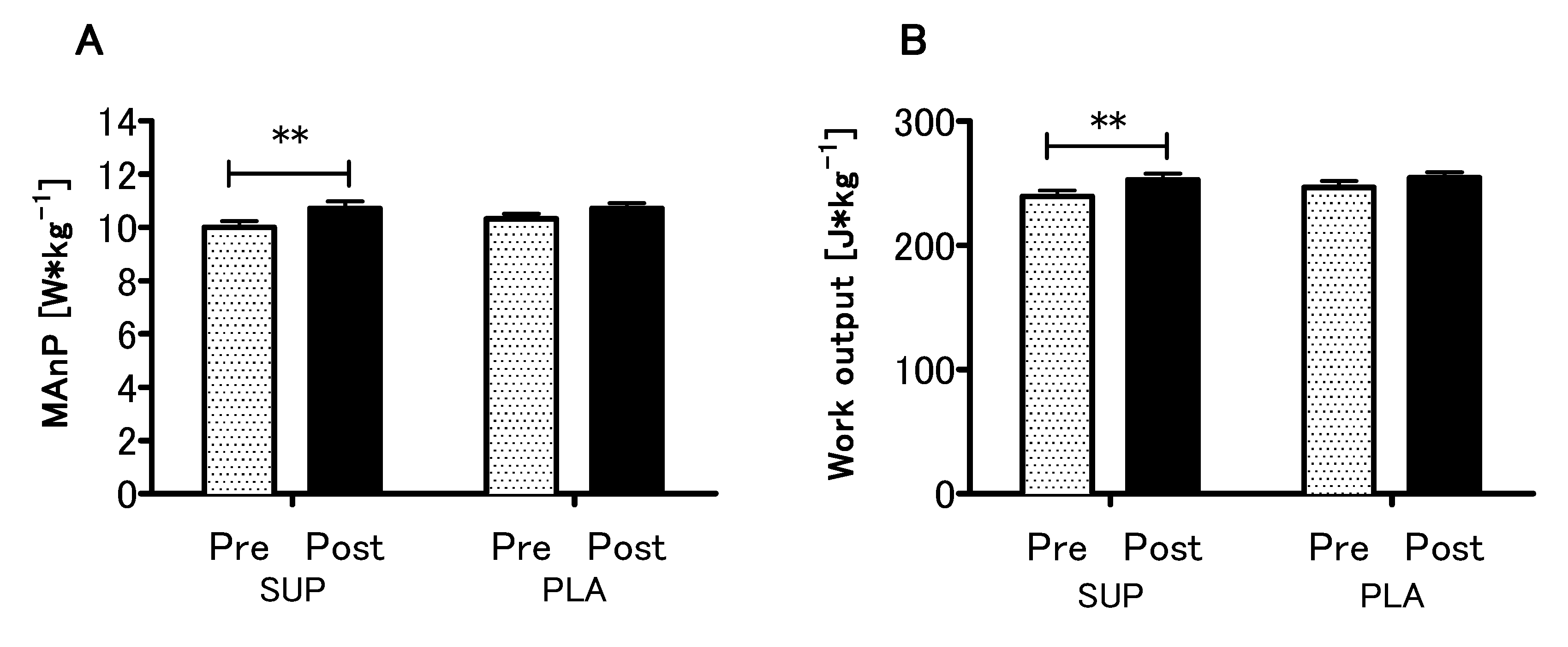
3.4. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Anaerobic Capacity
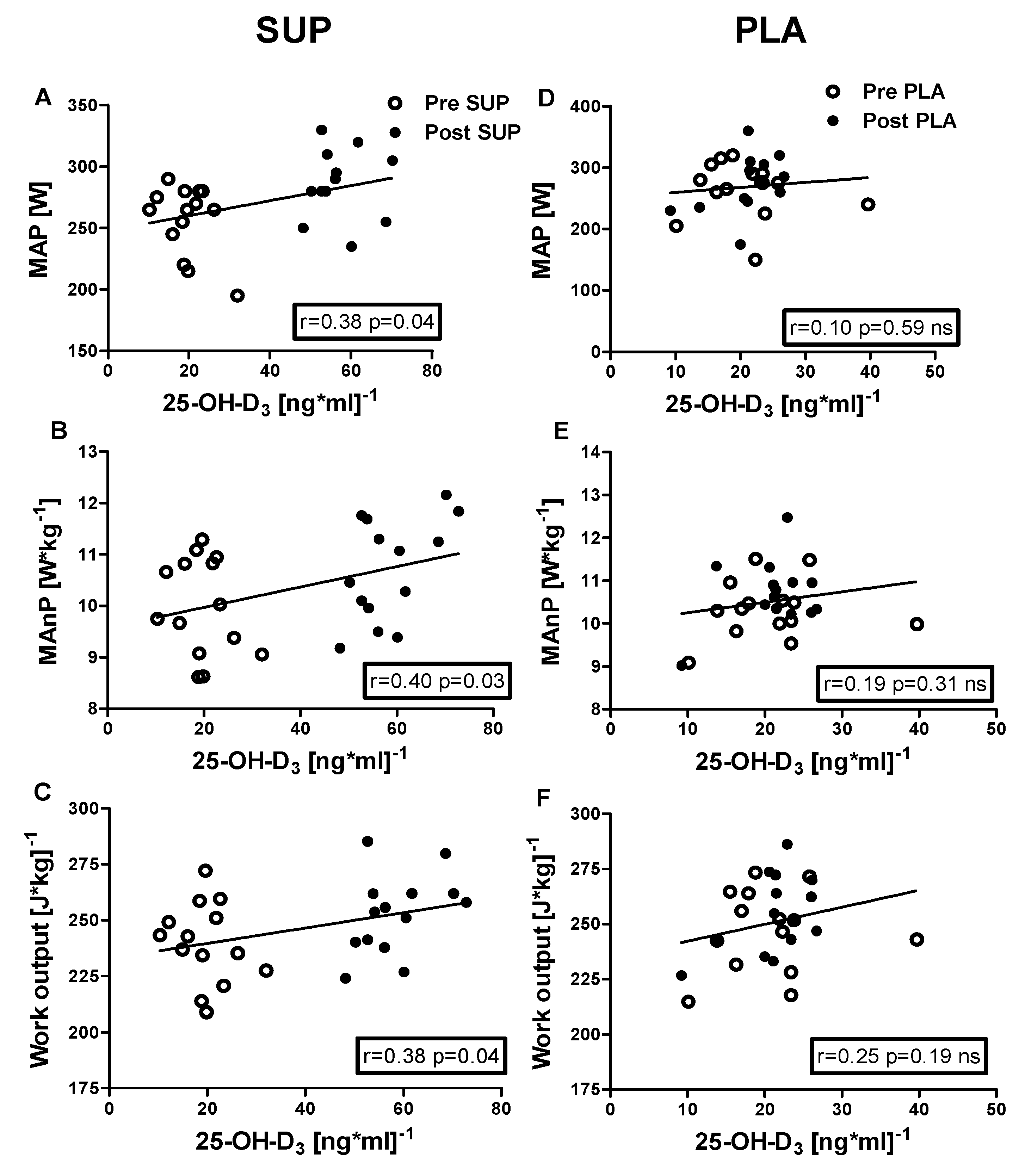
3.5. Correlation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radak, Z. The Physiology of Physical Training, 1st ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2018; 280p. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore, J.H.; Costill, D.L.; Kenney, W.L. Physiology of Sport and Exercise, 5th ed.; Human Kinetics: Leeds, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, D.J.; Allison, R.; Close, G.L. Vitamin D and the Athlete: Current Perspectives and New Challenges. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogan, D.; Pritchett, K. Vitamin D and the athlete: Risks, recommendations, and benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpowitz, D.; Gilchrest, B.A. The vitamin D questions: How much do you need and how should you get it? J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pludowski, P.; Holick, M.F.; Grant, W.B.; Konstantynowicz, J.; Mascarenhas, M.R.; Haq, A.; Povoroznyuk, V.; Balatska, N.; Barbosa, A.P.; Karonova, T.; et al. Vitamin D supplementation guidelines. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.J.; Close, G.L.; Farooq, A.; Riding, N.R.; Salah, O.; Hamilton, B.; Wilson, M.G. Severely vitamin D-deficient athletes present smaller hearts than sufficient athletes. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forney, L.A.; Earnest, C.P.; Henagan, T.M.; Johnson, L.E.; Castleberry, T.J.; Stewart, L.K. Vitamin D status, body composition, and fitness measures in college-aged students. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.S.; Peterson, B.J.; Warpeha, J.M.; Wilson, P.B.; Rhodes, G.S.; Ingraham, S.J. Vitamin D status and V[combining dot above]O2peak during a skate treadmill graded exercise test in competitive ice hockey players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3200–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, R.; Prins, H.J.; Boersma, W.G.; Daniels, J.M.; den Heijer, M.; Lips, P.; de Jongh, R.T. Effects of daily vitamin D supplementation on respiratory muscle strength and physical performance in vitamin D-deficient COPD patients: A pilot trial. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zosky, G.R.; Berry, L.J.; Elliot, J.G.; James, A.L.; Gorman, S.; Hart, P.H. Vitamin D deficiency causes deficits in lung function and alters lung structure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, P.N.; Scragg, R. Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d and pulmonary function in the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Chest 2005, 128, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illi, S.K.; Held, U.; Frank, I.; Spengler, C.M. Effect of respiratory muscle training on exercise performance in healthy individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzik, K.P.; Kaczor, J.J. Mechanisms of vitamin D on skeletal muscle function: Oxidative stress, energy metabolism and anabolic state. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, S.; Sykes, J.; Rigby, M.; Hess, B. A review and clinical summary of vitamin D in regard to bone health and athletic performance. Physician Sportsmed. 2015, 43, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B. Vitamin d and athletic performance: The potential role of muscle. Asian J. Sports Med. 2011, 2, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, C.M.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Hamrick, M.W.; Holick, M.F.; Gunton, J.E. The roles of vitamin D in skeletal muscle: Form, function, and metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 33–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, Z.C.; Craig, T.A.; Folmes, C.D.; Wang, X.; Lanza, I.R.; Schaible, N.S.; Salisbury, J.L.; Nair, K.S.; Terzic, A.; Sieck, G.C.; et al. 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Regulates Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption and Dynamics in Human Skeletal Muscle Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1514–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Ball, S.; Cheetham, T. Improving the vitamin D status of vitamin D deficient adults is associated with improved mitochondrial oxidative function in skeletal muscle. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E509–E513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundourakis, N.E.; Avgoustinaki, P.D.; Malliaraki, N.; Margioris, A.N. Muscular effects of vitamin D in young athletes and non-athletes and in the elderly. Hormones 2016, 15, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Sakuma, M.; Endo, N. The impact of exercise and vitamin D supplementation on physical function in community-dwelling elderly individuals: A randomized trial. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, C.M. Vitamin D and muscle function in the elderly: The elixir of youth? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagatsuma, A.; Sakuma, K. Vitamin D signaling in myogenesis: Potential for treatment of sarcopenia. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 121254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.K.; Cesari, M.; Ferrucci, L.; Cherubini, A.; Maggio, D.; Bartali, B.; Johnson, M.A.; Schwartz, G.G.; Kritchevsky, S.B. Association between vitamin D status and physical performance: The InCHIANTI study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med Sci. 2007, 62, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardestani, A.; Parker, B.; Mathur, S.; Clarkson, P.; Pescatello, L.S.; Hoffman, H.J.; Polk, D.M.; Thompson, P.D. Relation of vitamin D level to maximal oxygen uptake in adults. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, A.; Zagrodna, A.; Dziubek, W.; Pietraszewski, B.; Ochmann, B.; Slowinska-Lisowska, M. 25(OH)D3 Levels Relative to Muscle Strength and Maximum Oxygen Uptake in Athletes. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 50, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowry, D.A.; Costello, M.M.; Heelan, K.A. Association among cardiorespiratory fitness, body fat, and bone marker measurements in healthy young females. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2009, 109, 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Farrokhyar, F.; Sivakumar, G.; Savage, K.; Koziarz, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Ayeni, O.R.; Peterson, D.; Bhandari, M. Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations and Physical Performance in Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2323–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujach, S.; Olek, R.A.; Byun, K.; Suwabe, K.; Sitek, E.J.; Ziemann, E.; Laskowski, R.; Soya, H. Acute Sprint Interval Exercise Increases Both Cognitive Functions and Peripheral Neurotrophic Factors in Humans: The Possible Involvement of Lactate. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwabe, K.; Hyodo, K.; Byun, K.; Ochi, G.; Fukuie, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kato, M.; Yassa, M.A.; Soya, H. Aerobic fitness associates with mnemonic discrimination as a mediator of physical activity effects: Evidence for memory flexibility in young adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, E.; Grzywacz, T.; Luszczyk, M.; Laskowski, R.; Olek, R.A.; Gibson, A.L. Aerobic and anaerobic changes with high-intensity interval training in active college-aged men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olek, R.A.; Kujach, S.; Ziemann, E.; Ziolkowski, W.; Waz, P.; Laskowski, R. Adaptive Changes After 2 Weeks of 10-s Sprint Interval Training With Various Recovery Times. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enko, D.; Kriegshauser, G.; Stolba, R.; Worf, E.; Halwachs-Baumann, G. Method evaluation study of a new generation of vitamin D assays. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Close, G.L.; Leckey, J.; Patterson, M.; Bradley, W.; Owens, D.J.; Fraser, W.D.; Morton, J.P. The effects of vitamin D(3) supplementation on serum total 25[OH]D concentration and physical performance: A randomised dose-response study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannell, J.J.; Hollis, B.W.; Sorenson, M.B.; Taft, T.N.; Anderson, J.J. Athletic performance and vitamin D. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, L.; Stokes, K.A.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Moore, D.R.; Baker, S.K.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J.; Phillips, S.M. Two weeks of reduced activity decreases leg lean mass and induces “anabolic resistance” of myofibrillar protein synthesis in healthy elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, B.T.; Snijders, T.; Senden, J.M.; Ottenbros, C.L.; Gijsen, A.P.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J. Disuse impairs the muscle protein synthetic response to protein ingestion in healthy men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4872–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikssen, J.; Rodahl, K. Seasonal variation in work performance and heart rate response to exercise. A study of 1,835 middle-aged men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1979, 42, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.; Raschka, C. Circannual period of physical performance analysed by means of standard cosinor analysis: A case report. Rom. J. Physiol. Physiol. Sci. 2000, 37, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Svedenhag, J.; Sjodin, B. Physiological characteristics of elite male runners in and off-season. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1985, 10, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, S.M.; Parker, B.A.; Capizzi, J.A.; Grimaldi, A.S.; Clarkson, P.M.; Moeckel-Cole, S.; Keadle, J.; Chipkin, S.; Pescatello, L.S.; Simpson, K.; et al. Changes in Vitamin D are Not Associated with Changes in Cardiorespiratory Fitness. Clin. Med. Res. 2013, 2, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.S.; McClung, J.P.; Kohen, T.; Lieberman, H.R. Vitamin d and physical performance. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B. Vitamin D and human skeletal muscle. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszewska, M.; Kamboj, M.; Patel, D.R. Vitamin D, muscle function, and exercise performance. Pediatric Clin. N. Am. 2010, 57, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Quan, M.; Cao, Z.B. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on upper and lower limb muscle strength and muscle power in athletes: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dietrich, T.; Orav, E.J.; Hu, F.B.; Zhang, Y.; Karlson, E.W.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with better lower-extremity function in both active and inactive persons aged > or =60 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A. Relevance of vitamin D in muscle health. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2012, 13, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhesi, J.K.; Jackson, S.H.; Bearne, L.M.; Moniz, C.; Hurley, M.V.; Swift, C.G.; Allain, T.J. Vitamin D supplementation improves neuromuscular function in older people who fall. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koundourakis, N.E.; Androulakis, N.E.; Malliaraki, N.; Margioris, A.N. Vitamin D and exercise performance in professional soccer players. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Close, G.L.; Russell, J.; Cobley, J.N.; Owens, D.J.; Wilson, G.; Gregson, W.; Fraser, W.D.; Morton, J.P. Assessment of vitamin D concentration in non-supplemented professional athletes and healthy adults during the winter months in the UK: Implications for skeletal muscle function. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Malloy, P.J.; Feldman, D. Identification of a functional vitamin D response element in the human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 promoter. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyscin, J.W.; Jaroslawski, J.; Sobolewski, P.S. A mathematical model for seasonal variability of vitamin D due to solar radiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2011, 105, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. The vitamin D deficiency pandemic and consequences for nonskeletal health: Mechanisms of action. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemant, J.; Le, H.T.; Maria, A.; Allemandou, A.; Peres, G.; Guillemant, S. Wintertime vitamin D deficiency in male adolescents: Effect on parathyroid function and response to vitamin D3 supplements. Osteoporos. Int. 2001, 12, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, P.T.; Shaikh, U. The effects of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency on the endocrine and paracrine systems. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2007, 9, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.R.; Kline, L.; Holick, M.F. Influence of season and latitude on the cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D3: Exposure to winter sunlight in Boston and Edmonton will not promote vitamin D3 synthesis in human skin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 67, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrzebska, M.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Michalczyk, M.; Radziminski, L.; Stepien, P.; Jastrzebska, J.; Wakuluk, D.; Suarez, A.D.; Lopez Sanchez, G.F.; Cieszczyk, P.; et al. Can Supplementation of Vitamin D Improve Aerobic Capacity in Well Trained Youth Soccer Players? J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 61, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, K.D.; Dowling, K.G.; Skrabakova, Z.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Valtuena, J.; De Henauw, S.; Moreno, L.; Damsgaard, C.T.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Molgaard, C.; et al. Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: Pandemic? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | SUP (n = 14) | PLA (n = 14) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |
| Age (y) | 21.7 ± 1.8 | 22.0 ± 1.8 | 20.5 ± 1.4 | 20.7 ± 1.1 |
| Height (cm) | 180.3 ± 7.4 | 180.3 ± 7.4 | 183.2 ± 7.1 | 183.3 ± 7.4 |
| Weight (kg) | 76.7 ± 9.0 | 77.1 ± 8.6 | 75.9 ± 7.0 | 75.5 ± 7.1 |
| Fat (%) | 14.4 ± 4.4 | 14.7 ± 4.4 | 13.0 ± 2.7 | 12.8 ± 3.2 |
| Fat (kg) | 11.3 ± 4.3 | 11.6 ± 4.2 | 9.9 ± 2.9 | 9.8 ± 3.3 |
| FFM (kg) | 65.3 ± 5.8 | 65.5 ± 5.8 | 65.9 ± 4.8 | 65.7 ± 4.7 |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 23.6 ± 3.1 | 23.8 ± 2.8 | 22.6 ± 1.9 | 22.4 ± 1.9 |
| TBW (kg) | 47.8 ± 5.8 | 47.9 ± 4.2 | 48.3 ± 3.5 | 48.1 ± 3.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kujach, S.; Lyzwinski, D.; Chroboczek, M.; Bialowas, D.; Antosiewicz, J.; Laskowski, R. The Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Physical Capacity among Active College-Aged Males. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071936
Kujach S, Lyzwinski D, Chroboczek M, Bialowas D, Antosiewicz J, Laskowski R. The Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Physical Capacity among Active College-Aged Males. Nutrients. 2020; 12(7):1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071936
Chicago/Turabian StyleKujach, Sylwester, Dariusz Lyzwinski, Maciej Chroboczek, Dawid Bialowas, Jedrzej Antosiewicz, and Radoslaw Laskowski. 2020. "The Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Physical Capacity among Active College-Aged Males" Nutrients 12, no. 7: 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071936
APA StyleKujach, S., Lyzwinski, D., Chroboczek, M., Bialowas, D., Antosiewicz, J., & Laskowski, R. (2020). The Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Physical Capacity among Active College-Aged Males. Nutrients, 12(7), 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071936






