Improvement in Healthy Meal Index, Lunch Quality, and Diversity Scores Following an Integrated Nutritional Intervention in a Communal Dining Room: The NEKST Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
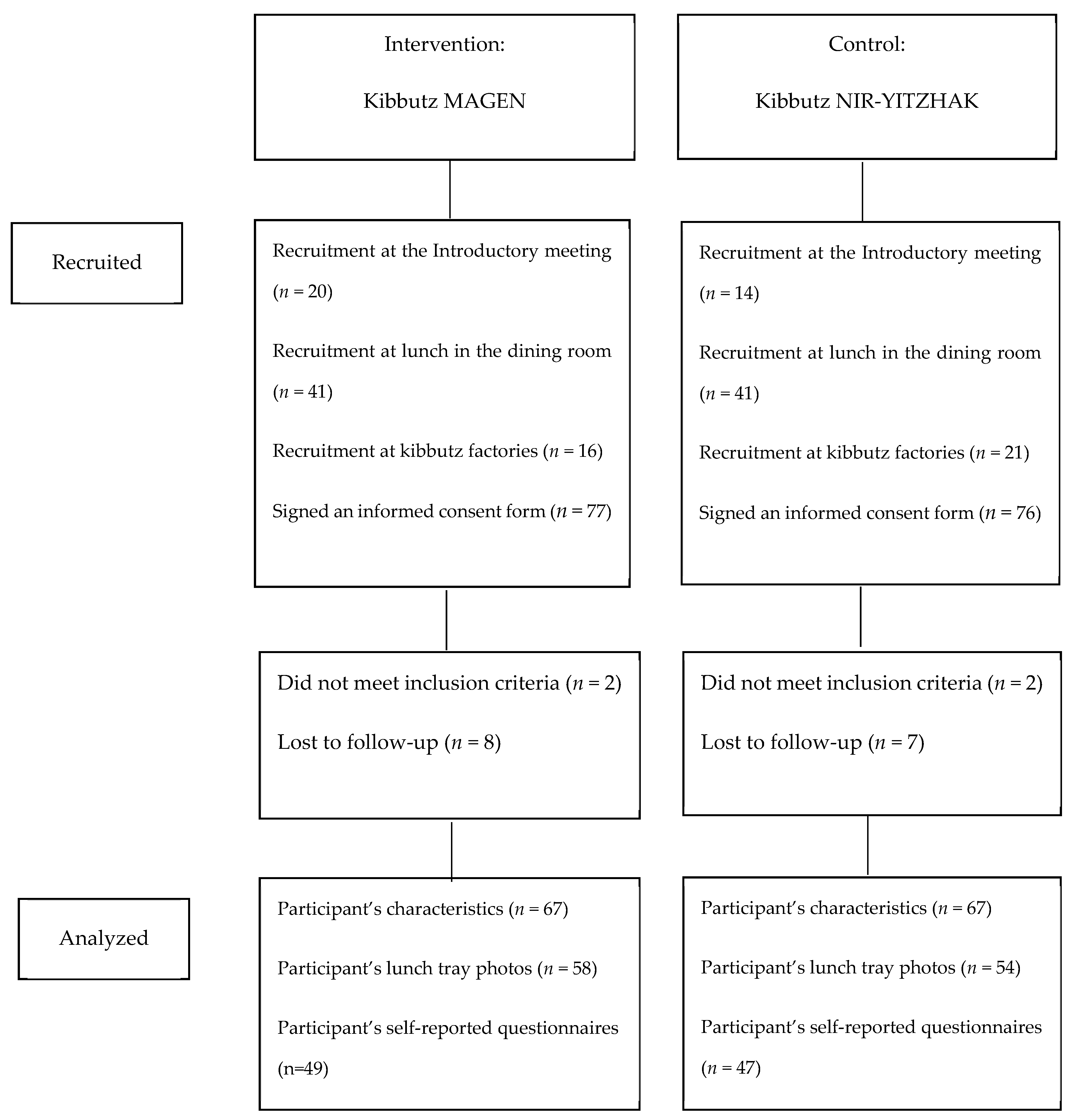
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Procedure
2.2. Study Population
2.3. The Intervention Program
2.4. Study Measures
2.4.1. Simple Healthy Meal Index
2.4.2. Lunch Quality Score
2.4.3. Lunch Diversity Score
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Change in the Simple Healthy Meal Index Following the Intervention
3.2. Change in Lunch Quality Score Following the Intervention
3.3. Change in Lunch Diversity Score Following the Intervention
3.4. Self-Reported Daily Consumption of Fruits and Vegetables
3.5. The Preferred Choice for Something Sweet
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankovic, N.; Geelen, A.; Streppel, M.T.; De Groot, L.C.; Orfanos, P.; Hooven, E.H.V.D.; Pikhart, H.; Boffetta, P.; Trichopoulou, A.; Bobak, M.; et al. Adherence to a Healthy Diet According to the World Health Organization Guidelines and All-Cause Mortality in Elderly Adults From Europe and the United States. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Bogensberger, B.; Hoffmann, G. Diet Quality as Assessed by the Healthy Eating Index, Alternate Healthy Eating Index, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Score, and Health Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 74–100.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millen, B.E.; Abrams, S.; Adams-Campbell, L.; Anderson, C.A.; Brenna, J.T.; Campbell, W.W.; Clinton, S.; Hu, F.; Nelson, M.; Neuhouser, M.L.; et al. The 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee Scientific Report: Development and Major Conclusions. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeing, H.; Bechthold, A.; Bub, A.; Ellinger, S.; Haller, D.; Kroke, A.; Leschik-Bonnet, E.; Müller, M.J.; Oberritter, H.; Schulze, M.B.; et al. Critical review: Vegetables and fruit in the prevention of chronic diseases. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 637–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, D.; Giovannucci, E.; Boffetta, P.; Fadnes, L.T.; Keum, N.; Norat, T.; Greenwood, D.C.; Riboli, E.; Vatten, L.J.; Tonstad, S. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality-a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1029–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruel, M.T. Operationalizing Dietary Diversity: A Review of Measurement Issues and Research Priorities. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3911S–3926S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Healthy settings. Available online: https://www.who.int/healthy_settings/en/. (accessed on 26 January 2019).
- Dooris, M. Healthy settings: Challenges to generating evidence of effectiveness. Health Promot. Int. 2005, 21, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanos, P.; Naska, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Grioni, S.; Boer, J.M.A.; Van Bakel, M.M.E.; Ericson, U.; Rohrmann, S.; Boeing, H.; Rodríguez, L.; et al. Eating out of home: Energy, macro- and micronutrient intakes in 10 European countries. The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, S239–S262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, N.A.; McCarthy, S.N.; Burke, S.J.; Gibney, M.J. The temporal pattern of the contribution of fat to energy and of food groups to fat at various eating locations: Implications for developing food-based dietary guidelines. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, A.K.; Graubard, B.I. Eating out in America, 1987–2000: Trends and nutritional correlates. Prev. Med. 2004, 38, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, C.; Nago, E.; Verstraeten, R.; Roberfroid, D.; Van Camp, J.; Kolsteren, P. Eating out of home and its association with dietary intake: A systematic review of the evidence. Obes. Rev. 2011, 13, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanz, K.; Mullis, R.M. Environmental Interventions to Promote Healthy Eating: A Review of Models, Programs, and Evidence. Health Educ. Q. 1988, 15, 395–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J. Impact of nutrition environmental interventions on point-of-purchase behavior in adults: A review. Prev. Med. 2004, 39, 108–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, C.; Naska, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Engeset, D.; Fairgrieve, A.; Marques, H. Ávila; Kolsteren, P. Essential actions for caterers to promote healthy eating out among European consumers: Results from a participatory stakeholder analysis in the HECTOR project. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, C.; Jewell, J.; Allen, K. A food policy package for healthy diets and the prevention of obesity and diet-related non-communicable diseases: The NOURISHING framework. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, R.W.; Raether, C.; Baxter, J.; French, S.A. An Environmental Intervention to Increase Fruit and Salad Purchases in a Cafeteria. Prev. Med. 1994, 23, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, T.; Van Der Horst, K.; Siegrist, M. Improvement of meal composition by vegetable variety. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, C.M.; Lahti-Koski, M.; Puukka, P.; Kinnunen, M.; Jallinoja, P.; Absetz, P. Effects of a healthy food supply intervention in a military setting: Positive changes in cereal, fat and sugar containing foods. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geaney, F.; Harrington, J.; Fitzgerald, A.; Perry, I.J. The impact of a workplace catering initiative on dietary intakes of salt and other nutrients: A pilot study. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighton, F.; Polic, G.; Strobel, P.; Perez, D.; Martinez, C.; Vásquez, L.; Castillo, O.; Villarroel, L.; Echeverría, G.; Urquiaga, I.; et al. Health impact of Mediterranean diets in food at work. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belanger, M.B.A.; Kwon, J. Effectiveness of Healthy Menu Changes in a Nontrainee Military Dining Facility. Mil. Med. 2016, 181, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, T.; Collins, C.; Rollo, M.; McCaffrey, T.A.; De Vlieger, N.; Van Der Bend, D.; Truby, H.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Nudging consumers towards healthier choices: A systematic review of positional influences on food choice. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olstad, D.L.; Vermeer, J.; McCargar, L.J.; Prowse, R.J.; Raine, K.D. Using traffic light labels to improve food selection in recreation and sport facility eating environments. Appetite 2015, 91, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, L.; Gelsomin, E.; Levy, D.E.; Riis, J.; Barraclough, S.; Thorndike, A.N. A traffic light food labeling intervention increases consumer awareness of health and healthy choices at the point-of-purchase. Prev. Med. 2013, 57, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyth, E.L.; Steenhuis, I.; Heymans, M.W.; Roodenburg, A.J.C.; Brug, J.; Seidell, J.C. Influence of Placement of a Nutrition Logo on Cafeteria Menu Items on Lunchtime Food Choices at Dutch Work Sites. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliemann, D.; McKinley, M.C.; Woodside, J.V. The Impact of a Policy-Based Multicomponent Nutrition Pilot Intervention on Young Adult Employee’s Diet and Health Outcomes. Am. J. Health Promot. 2018, 33, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, M.; Bianchi, M.A.; Rapetti, V.; Pepe, J.M.; Giacco, A.; Giacco, R.; Riccardi, G. A nutritional intervention programme at a worksite canteen to promote a healthful lifestyle inspired by the traditional Mediterranean diet. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 69, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geaney, F.; Kelly, C.; Di Marrazzo, J.S.; Harrington, J.M.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Greiner, B.; Perry, I.J.; Fiztgerald, A.P. The effect of complex workplace dietary interventions on employees’ dietary intakes, nutrition knowledge and health status: A cluster controlled trial. Prev. Med. 2016, 89, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, R.E.; Bukhari, A.S.; Champagne, C.M.; McGraw, S.M.; Hatch, A.; Montain, S.J. Performance Nutrition Dining Facility Intervention Improves Special Operations Soldiers’ Diet Quality and Meal Satisfaction. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2018, 50, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombie, A.P.; Funderburk, L.K.; Smith, T.J.; McGraw, S.M.; Walker, L.A.; Champagne, C.M.; Allen, H.R.; Margolis, L.; McClung, H.L.; Young, A.J. Effects of Modified Foodservice Practices in Military Dining Facilities on Ad Libitum Nutritional Intake of US Army Soldiers. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorndike, A.N.; Sonnenberg, L.; Riis, J.; Barraclough, S.; Levy, U.E. A 2-Phase Labeling and Choice Architecture Intervention to Improve Healthy Food and Beverage Choices. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, A.D.; Beck, A.; Leedo, E.; Andersen, E.; Christensen, T.; Mejborn, H.; Thorsen, A.; Tetens, I. Effectiveness of offering healthy labelled meals in improving the nutritional quality of lunch meals eaten in a worksite canteen. Appetite 2014, 75, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, A.D.; Thorsen, A.V.; Sommer, H.M.; Fagt, S.; Trolle, E.; Biltoft-Jensen, A.P.; Tetens, I. Improving the diet of employees at blue-collar worksites: Results from the ‘Food at Work’ intervention study. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandoni, D.; Sarno, F.; Jaime, P.C. Impact of an intervention on the availability and consumption of fruits and vegetables in the workplace. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 14, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenhuis, I.; Van Assema, P.; Van Breukelen, G.J.; Glanz, K.; Kok, G.; De Vries, H. The impact of educational and environmental interventions in Dutch worksite cafeterias. Health Promot. Int. 2004, 19, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackison, D.; Mooney, J.; MacLeod, M.; Anderson, A.S. Lessons learnt from a feasibility study on price incentivised healthy eating promotions in workplace catering establishments. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 29, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, J. The Communal Experience of the Kibbutz; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Israeli Ministry of Health. Report of the regulation committee for healthy nutrition. Available online: https://www.health.gov.il/publicationsfiles/healthydietcommittee_recommendation.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2018).
- Martin, C.K.; Han, H.; Coulon, S.M.; Allen, H.R.; Champagne, C.M.; Anton, S.D. A novel method to remotely measure food intake of free-living individuals in real time: The remote food photography method. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 101, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, N.A.; Allen, H.; Martin, P.D.; Alfonso, A.J.; Gerald, B.; Hunt, A. Comparison of digital photography to weighed and visual estimation of portion sizes. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodenburg, A.J.C.; Schlatmann, A.; Dötsch-Klerk, M.; Daamen, R.; Dong, J.; Guarro, M.; Stergiou, M.; Sayed, N.; Ronoh, E.; Jansen, L.; et al. Potential Effects of Nutrient Profiles on Nutrient Intakes in the Netherlands, Greece, Spain, USA, Israel, China and South-Africa. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israeli Ministry of Health. Dietary-guidelines. Available online: https://www.health.gov.il/PublicationsFiles/dietary-guidelines.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Lassen, A.D.; Biltoft-Jensen, A.P.; Hansen, G.L.; Hels, O.; Tetens, I. Development and validation of a new simple Healthy Meal Index for canteen meals. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman-Shriqui, V.; Fraser, D.; Friger, M.; Geva, D.; Bilenko, N.; Vardi, H.; Elhadad, N.; Mor, K.; Feine, Z.; Shahar, D.R. Effect of a School-Based Intervention on Nutritional Knowledge and Habits of Low-Socioeconomic School Children in Israel: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrition 2016, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elinder, L.S.; Brunosson, A.; Bergström, H.; Hagströmer, M.; Patterson, E. Validation of personal digital photography to assess dietary quality among people with intellectual disabilities. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2011, 56, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naimark, J.S.; Madar, Z.; Shahar, D.R.; Pojednic, R.; Janwantanakul, P. The Impact of a Web-Based App (eBalance) in Promoting Healthy Lifestyles: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2015, 17, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmenter, K.; Wardle, J. Development of a general nutrition knowledge questionnaire for adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, C.; Verstraeten, R.; De Meulenaer, B.; Menten, J.; Huybregts, L.; Van Camp, J.; Roberfroid, M.; Kolsteren, P. Availability of free fruits and vegetables at canteen lunch improves lunch and daily nutritional profiles: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duyn, M.A.S.; Pivonka, E. Overview of the Health Benefits of Fruit and Vegetable Consumption for the Dietetics Professional. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2000, 100, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nutrient Profiling. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/profiling/en/ (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Schulze, M.B.; A Martinez-Gonzalez, M.; Fung, T.T.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Forouhi, N.G. Food based dietary patterns and chronic disease prevention. BMJ 2018, 361, k2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
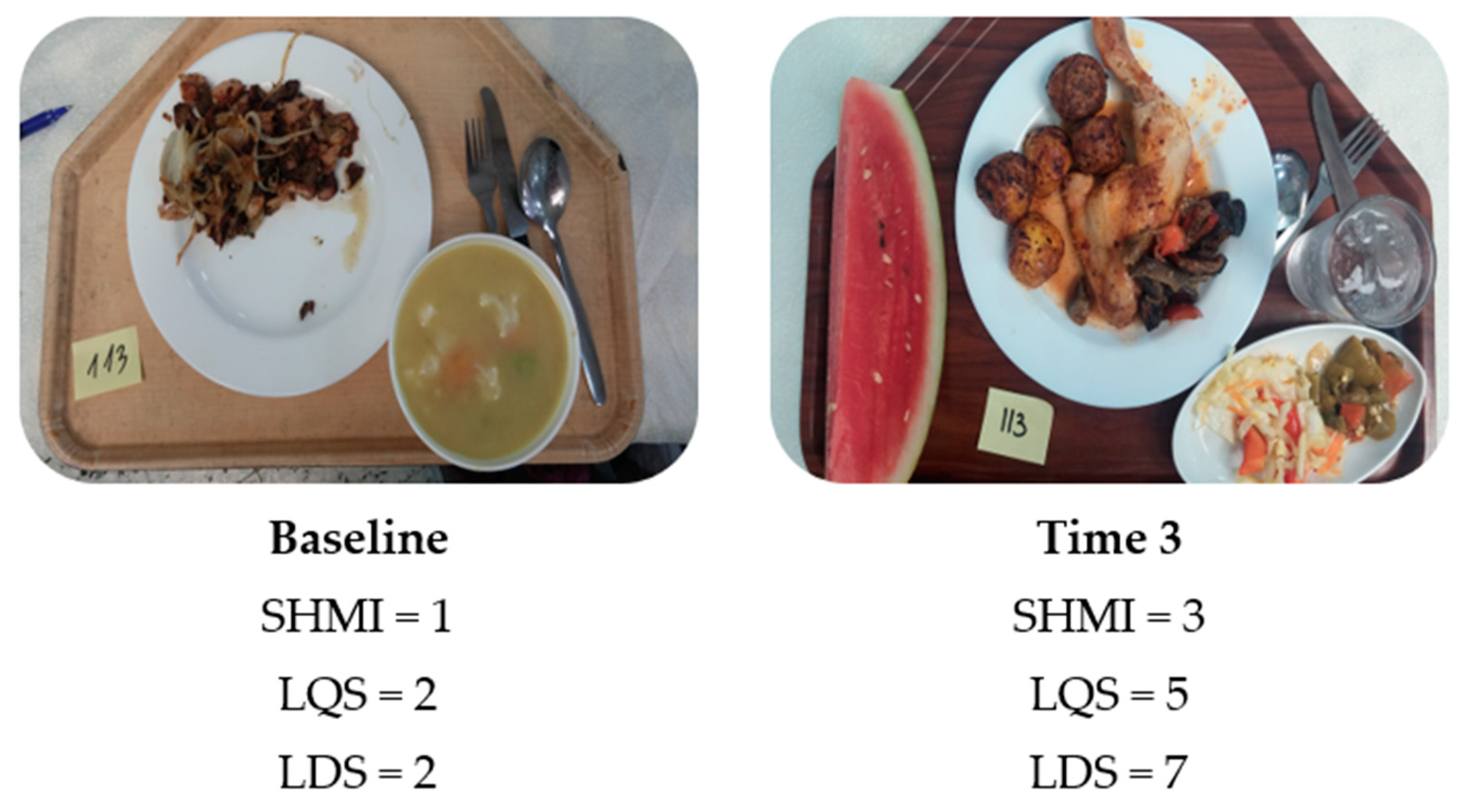

| Intervention Group (Magen) | Control Group (Nir Yitzhak) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 58 | 54 | |
| Age (years) a | 56.8 ± 15.5 (59, 32–83) | 61.5 ± 14.9 (60, 30–87) | 0.232 b |
| Gender—male c | 31 (53.4%) | 30 (55.6%) | 0.823 d |
| Live in the kibbutz | 50 (87.7%) | 41 (77.4%) | 0.151 d |
| Educational level b Academic education | 33 (61.6%) | 21 (38.9%) | 0.057 d |
| Nutritional & physical activity knowledge score a, e | 22.9 ± 4.6 (24, 10.5–30) | 22.0 ± 4.6 (21.5, 11–31) | 0.207 b |
| BMI (kg/m2) a | 28.7 ± 4.9 (28, 21–43) | 27.8 ± 4.9 (27, 19–39) | 0.355 b |
| Performance of physical activity c, e | 43 (79.6%) | 42 (87.5%) | 0.287 d |
| Lunch Score Followed by Its Components | Intervention Group (Magen), n = 58 | Control Group (Nir Yitzhak), n = 54 | p-Value between Groups c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Change a | p-Value b | Mean Change a | p-Value b | ||
| SHMI | 0.51 ± 0.88 | <0.001 d | 0.04 ± 0.76 | 0.734 d | 0.003 e |
| Fruits and vegetables | 0.26 ± 0.54 | <0.001 | 0.04 ± 0.32 | 0.468 | 0.018 |
| Fat | 0.12 ± 0.49 | 0.145 | 0.07 ± 0.28 | 0.061 | 0.275 |
| Whole grain and potatoes | 0.13 ± 0.58 | 0.206 | −0.07 ± 0.64 | 0.379 | 0.116 |
| LQS | 0.27 ± 1.01 | 0.045 d | −0.15 ± 1.00 | 0.283 d | 0.029 e |
| Main dish (rich in protein) | 0.01 ± 0.41 | 0.832 | −0.10 ± 0.36 | 0.051 | 0.171 |
| Carbohydrate side dish | 0.02 ± 0.39 | 0.828 | −0.17 ± 0.37 | 0.002 | 0.022 |
| Vegetables | 0.19 ± 0.45 | 0.004 | 0.08 ± 0.31 | 0.091 | 0.058 |
| Pulses | −0.03 ± 0.17 | 0.220 | 0.11 ± 0.27 | 0.010 | 0.001 |
| Other side dishes | −0.09 ± 0.36 | 0.040 | 0.04 ± 0.28 | 0.247 | 0.023 |
| Deserts | 0.28 ± 0.49 | <0.001 | 0.02 ± 0.14 | 0.317 | <0.001 |
| Drinks | −0.03 ± 0.38 | 0.681 | −0.10 ± 0.30 | 0.019 | 0.236 |
| LDS | 0.95 ± 1.30 | <0.001 d | 0.13 ± 1.27 | 0.464 d | 0.001 e |
| Protein | 0.01 ± 0.22 | 0.841 | 0.01 ± 0.24 | 0.844 | 0.981 |
| Carbohydrate | −0.06 ± 0.36 | 0.169 | −0.03 ± 0.36 | 0.348 | 0.682 |
| Vegetables | 0.80 ± 1.40 | <0.001 d | 0.19 ± 1.24 | 0.269 d | 0.015 e |
| Fruit | 0.20 ± 0.36 | <0.001 | −0.03 ± 0.20 | 0.244 | <0.001 |
| (a): Determinants of change in simple healthy meal index. | |||
| β | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Study group (intervention vs. control) | 0.26 | 0.12–0.76 | 0.015 |
| Nutritional & physical activity knowledge score | −0.24 | −0.08–(−0.01) | 0.016 |
| Education (academic vs. other) | 0.08 | −0.20–0.46 | 0.447 |
| n | 100 | ||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.091 | ||
| (b): Determinants of change in lunch quality score. | |||
| β | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Study group (intervention vs. control) | 0.23 | 0.06–0.83 | 0.024 |
| Live in the kibbutz (yes vs. no) | −0.22 | −1.20–(−0.09) | 0.024 |
| Nutritional & physical activity knowledge score | −0.21 | −0.09–(−0.003) | 0.036 |
| Education (academic vs. other) | −0.06 | −0.50–0.28 | 0.584 |
| n | 98 | ||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.120 | ||
| (c): Determinants of change in lunch diversity score. | |||
| β | β | p-Value | |
| Study group (intervention vs. control) | 0.34 | 0.41–1.39 | <0.001 |
| Education (academic vs. other) | −0.16 | −0.90–0.07 | 0.094 |
| n | 112 | ||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.101 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katz-Shufan, O.; Simon-Tuval, T.; Sabag, L.; R. Shahar, D. Improvement in Healthy Meal Index, Lunch Quality, and Diversity Scores Following an Integrated Nutritional Intervention in a Communal Dining Room: The NEKST Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061741
Katz-Shufan O, Simon-Tuval T, Sabag L, R. Shahar D. Improvement in Healthy Meal Index, Lunch Quality, and Diversity Scores Following an Integrated Nutritional Intervention in a Communal Dining Room: The NEKST Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(6):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061741
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatz-Shufan, Ofira, Tzahit Simon-Tuval, Liron Sabag, and Danit R. Shahar. 2020. "Improvement in Healthy Meal Index, Lunch Quality, and Diversity Scores Following an Integrated Nutritional Intervention in a Communal Dining Room: The NEKST Study" Nutrients 12, no. 6: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061741
APA StyleKatz-Shufan, O., Simon-Tuval, T., Sabag, L., & R. Shahar, D. (2020). Improvement in Healthy Meal Index, Lunch Quality, and Diversity Scores Following an Integrated Nutritional Intervention in a Communal Dining Room: The NEKST Study. Nutrients, 12(6), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061741





