Fetal Head Growth during Early to Mid-Gestation Associated with Weight Gain in Mothers with Hyperemesis Gravidarum: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Limitations
4.2. Interpretation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fairweather, D.V. Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1968, 102, 135–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Källén, B. Hyperemesis during pregnancy and delivery outcome: A registry study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1987, 26, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T.R.; Piwko, C.; Koren, G. Prevalence of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy in the USA: A meta analysis. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 20, e163–e170. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, K.; Ushioda, N.; Nagamatsu, M.; Kimura, T. Hyperemesis Gravidarum in Eastern Asian Population. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2007, 64, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy: ACOG practice bulletin No. 52. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 94, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailit, J.L. Hyperemesis gravidarium: Epidemiologic findings from a large cohort. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 193, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, H. The effect of hyperemesis gravidarum on prenatal adaptation and quality of life: A prospective case-control study. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejzo, M.; Myhre, R.; Colodro-Conde, L.; MacGibbon, K.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Reddy, M.P.L.; Pajukanta, P.; Nyholt, D.R.; Wright, M.J.; Martin, N.G.; et al. Genetic analysis of hyperemesis gravidarum reveals association with intracellular calcium release channel (RYR2). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 439, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejzo, M.; 23andMe Research Team; Sazonova, O.V.; Sathirapongsasuti, J.F.; Hallgrímsdóttir, I.B.; Vacic, V.; MacGibbon, K.; Schoenberg, F.P.; Mancuso, N.; Slamon, D.J.; et al. Placenta and appetite genes GDF15 and IGFBP7 are associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejzo, M.; Trovik, J.; Grooten, I.J.; Sridharan, K.; Roseboom, T.J.; Vikanes, Å.; Painter, R.C.; Mullin, P.M. Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and hyperemesis gravidarum. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Golding, J.; Kuh, D.; Wadsworth, M.E. Growth in utero, blood pressure in childhood and adult life, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. BMJ 1989, 298, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooten, I.J.; Painter, R.; Pontesilli, M.; Van Der Post, J.; Mol, B.; Van Eijsden, M.; Vrijkotte, T.; Roseboom, T. Weight loss in pregnancy and cardiometabolic profile in childhood: Findings from a longitudinal birth cohort. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2014, 122, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyavoo, A.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Hofman, P.L.; Biggs, J.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Cormack, B.; Stone, P.; Cutfield, W.S. Severe Hyperemesis Gravidarum Is Associated with Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in the Offspring in Childhood. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3263–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fejzo, M.; Magtira, A.; Schoenberg, F.P.; MacGibbon, K.; Mullin, P.M. Neurodevelopmental delay in children exposed in utero to hyperemesis gravidarum. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2015, 189, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, P.M.; Bray, A.; Schoenberg, F.; MacGibbon, K.; Romero, R.; Goodwin, T.M.; Fejzo, M. Prenatal exposure to hyperemesis gravidarum linked to increased risk of psychological and behavioral disorders in adulthood. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2011, 2, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, T.M.; Montoro, M.; Mestman, J.H.; Pekary, A.E.; Hershman, J.M. The role of gonadotropin in transient hyperthyroidism of hyperemesis gravidarum. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.J.; Godfrey, K.M.; Osmond, C.; Bull, A. The relation of fetal length, ponderal index and head circumference to blood pressure and the risk of hypertension in adult life. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 1992, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, S.; Johns, A.M.; Albert, P.S.; Kim, S.; Grantz, K.L. Longitudinal changes in gestational weight gain and the association with intrauterine fetal growth. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2015, 190, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, M.J.; Uthlaut, A.B.; Nijland, M.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Hess, B.W.; Ford, S. Upregulation of growth signaling and nutrient transporters in cotyledons of early to mid-gestational nutrient restricted ewes. Placenta 2011, 32, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, A.G.; Guedj, F.; Sverdlov, D.; Pennings, J.L.A.; Bianchi, D.W. Significant Effects of Maternal Diet During Pregnancy on the Murine Fetal Brain Transcriptome and Offspring Behavior. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikke, G.G.; Grooten, I.J.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; van Eijsden, M.; Roseboom, T.J.; Painter, R.C. Vitamin B12 and folate status in early pregnancy and cardiometabolic risk factors in the offspring at age 5-6 years: Findings from the ABCD multi-ethnic birth cohort. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 123, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadić, A.S.; Predojević, M. Fetal neurophysiology according to gestational age. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 17, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocka, M.; Beres, A.M. From fetus to older age: A review of brain metabolic changes across the lifespan. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 46, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, J.C.; Justulin, L.A.; Lacorte, L.M.; Sarobo, C.; Boer, P.A.; Scarano, W.R.; Felisbino, S.L. Implications of intrauterine protein malnutrition on prostate growth, maturation and aging. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombelli, K.T.; Santos, S.A.; Camargo, A.C.L.; Constantino, F.B.; Barquilha, C.N.; Rinaldi, J.C.; Felisbino, S.L.; Justulin, L.A. Impairment of microvascular angiogenesis is associated with delay in prostatic development in rat offspring of maternal protein malnutrition. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 246, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
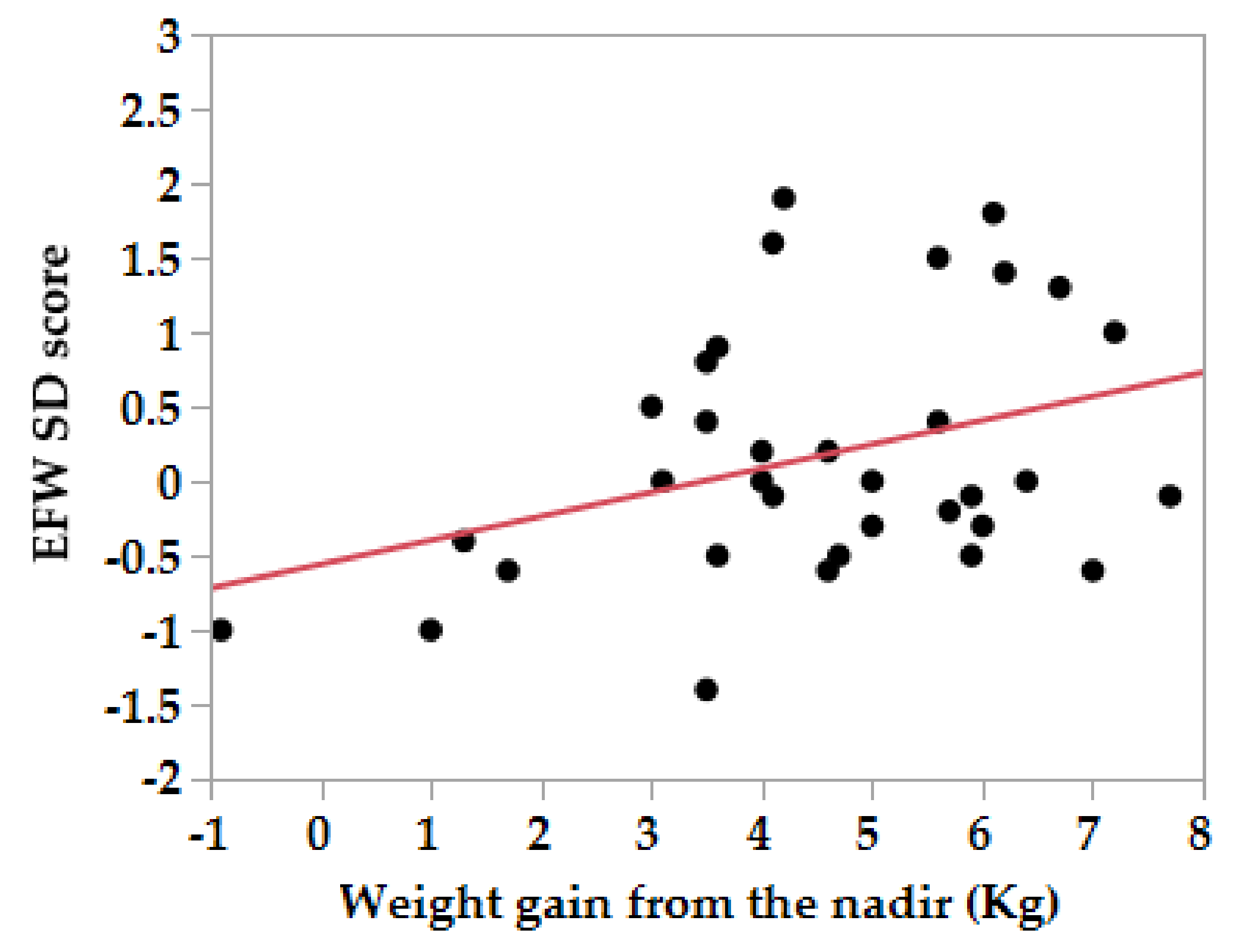
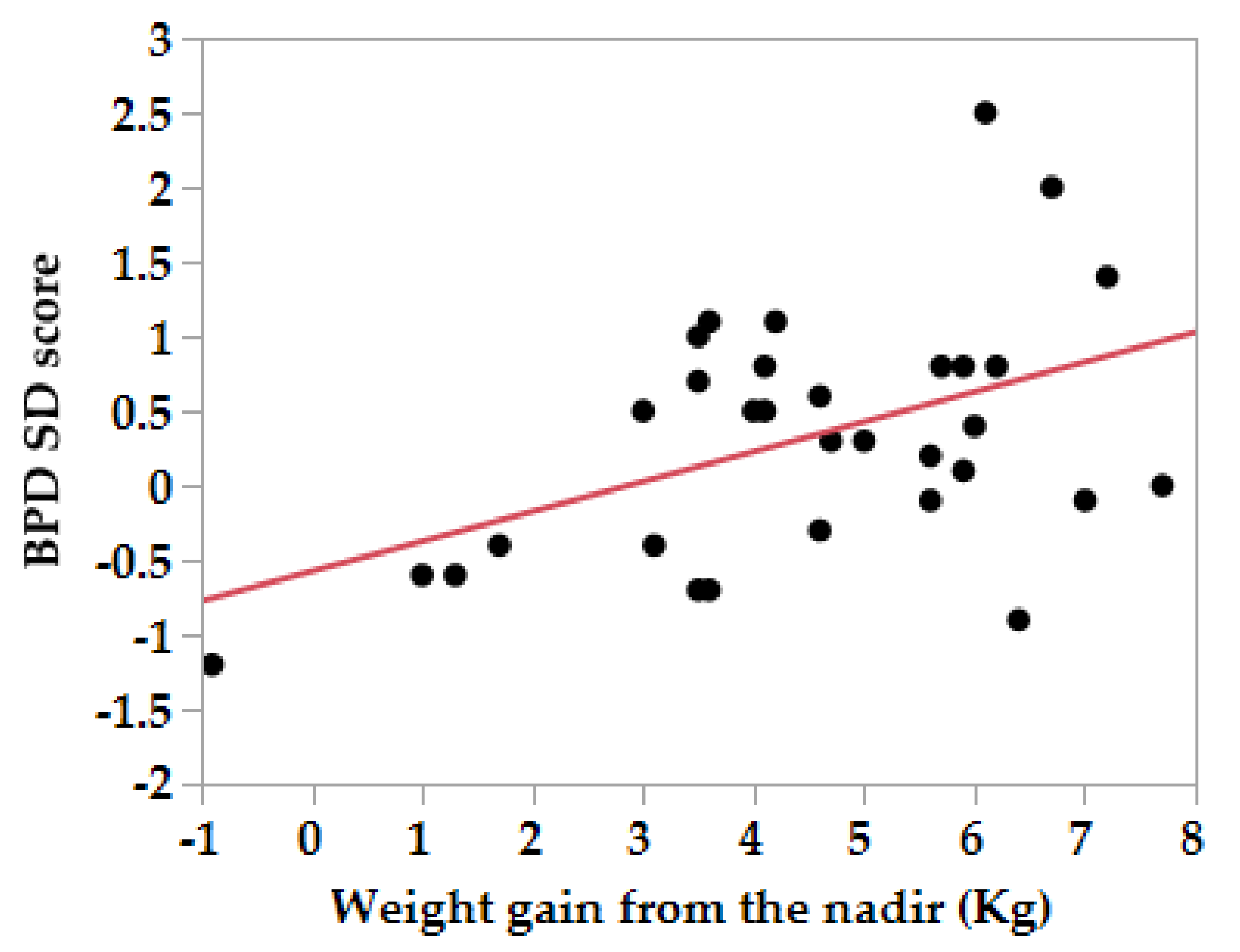
| Group | HG (n = 34) | Control (n = 69) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Japanese 33, Burmese 1 | Japanese 69 | 0.716 |
| Smoking before pregnancy | 1 | 0 | 0.716 |
| Smoking during pregnancy | 0 | 0 | |
| Maternal age (years old) | 33.0 ± 5.0 (23–42) | 33.0 ± 4.0 (23–41) | 0.88 |
| Parity | 0.50 ± 0.70 (0–3) | 0.60 ± 0.80 (0–3) | 0.94 |
| Pre-gestational BMI (Kg/m2) | 21.0 ± 3.4 (15.8–34) | 21.0 ± 3.7 (16–32) | 0.71 |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks) | 39.0 ± 1.1 (37–41) | 39.0 ± 1.0 (37–41) | 0.13 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3148.9 ± 348.0 (2536–3948) | 3070.9 ± 316.0 (2592–4440) | 0.98 |
| Sex ratio (male/female) | 1:1 | 1:1 | 0.61 |
| Placenta weight (g) | 569.9 ± 103.1 (410–820) | 582.0 ± 107 (205–1544) | 0.71 |
| Weight ratio of fetus to placenta | 0.18 ± 0.030 (0.13–0.26) | 0.1 9 ± 0.030 (0.11–0.52) | 0.73 |
| Weight gain at 20 weeks of gestation | −0.29 ± 2.8 (−6.9–−4.7) | 3.2 ± 2.5 (−4.8–9.0) | 0.0001 |
| Net weight gain (Kg) | 8.7 ± 3.5 (0–15.6) | 10.0 ± 3.3 (3.3–19.4) | 0.011 |
| Weight gain from the nadir (Kg) | 15.0 ± 4.9 (6–25.6) |
| Group | HG (n = 34) |
|---|---|
| Onset of HG (gestational age in weeks) | 9.0 ± 2.0 (6–15) |
| Weight loss (Kg) | 6.3 ± 2.8 (0–14) |
| Weight loss ratio (%) | 8.5 ± 3.8 (4.0–18.2) |
| Duration of admission (days) | 27.0 ± 18.0 (8–90) |
| Fetal Growth Parameters | Gestational Age (Weeks) | HG (n = 34) | Control (n = 69) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.33 ± 0.8 | 0.09 ± 0.69 | 0.12 | |
| BPD (SD score) | 30 | 0.26 ± 1.1 | 0.35 ± 0.82 | 0.63 |
| 36 | 0.17 ± 0.89 | 0.33 ± 0.74 | 0.35 | |
| 20 | 0.33 ± 1.1 | 0.47 ± 0.96 | 0.53 | |
| AC (SD score) | 30 | 0.15 ± 1.1 | 0.32 ± 0.97 | 0.44 |
| 36 | 0.22 ± 0.67 | 0.40 ± 0.86 | 0.30 | |
| 20 | −0.24 ± 0.7 | −0.02 ± 0.8 | 0.17 | |
| FL (SD score) | 30 | −0.11 ± 0.84 | −0.003 ± 0.86 | 0.55 |
| 36 | −0.2 ± 0.91 | −0.045 ± 1.1 | 0.48 | |
| 20 | 0.17 ± 0.85 | 0.10 ± 0.69 | 0.67 | |
| EFW (SD score) | 30 | 0.09 ± 0.86 | 0.05 ± 0.75 | 0.79 |
| 36 | −0.19 ± 0.75 | −0.16 ± 0.73 | 0.81 |
| HG Group Weight Gain (n = 34) | Control Group Weight Gain (n = 69) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GW | Correlation Coefficient = r (p Value) | Nadir 20 Weeks | Pre-Gest 20 Weeks | 20–30 Weeks | 30–36 Weeks | Pre-Gest 20 Weeks | 20–30 Weeks | 30–36 Weeks |
| 20 | BPD | 0.47 (0.0048) | 0.38 (0.02) | 0.037 (0.76) | ||||
| AC | 0.18 (0.30) | 0.17 (0.42) | 0.024 (0.85) | |||||
| FL | 0.23 (0.18) | 0.26 (0.12) | 0.128 (0.88) | |||||
| EFW | 0.36 (0.037) | 0.03 (0.86) | 0.026 (0.83) | |||||
| 30 | BPD | 0.04 (0.98) | 0.23 (0.06) | |||||
| AC | 0.10 (0.58) | 0.006 (0.96) | ||||||
| FL | 0.18 (0.31) | 0.21 (0.82) | ||||||
| EFW | 0.049 (0.79) | 0.18 (0.15) | ||||||
| 36 | BPD | 0.07 (0.70) | 0.049 (0.68) | |||||
| AC | 0.25 (0.17) | 0.34 (0.0045) | ||||||
| FL | 0.08 (0.67) | 0.13 (0.0045) | ||||||
| EFW | 0.06 (0.75) | 0.27 (0.027) | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muraoka, M.; Takagi, K.; Ueno, M.; Morita, Y.; Nagano, H. Fetal Head Growth during Early to Mid-Gestation Associated with Weight Gain in Mothers with Hyperemesis Gravidarum: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061664
Muraoka M, Takagi K, Ueno M, Morita Y, Nagano H. Fetal Head Growth during Early to Mid-Gestation Associated with Weight Gain in Mothers with Hyperemesis Gravidarum: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(6):1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061664
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuraoka, Mitsue, Koichiro Takagi, Mariko Ueno, Yoshihiro Morita, and Hiroaki Nagano. 2020. "Fetal Head Growth during Early to Mid-Gestation Associated with Weight Gain in Mothers with Hyperemesis Gravidarum: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Nutrients 12, no. 6: 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061664
APA StyleMuraoka, M., Takagi, K., Ueno, M., Morita, Y., & Nagano, H. (2020). Fetal Head Growth during Early to Mid-Gestation Associated with Weight Gain in Mothers with Hyperemesis Gravidarum: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 12(6), 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061664




