Sex Differences and Commonalities in the Impact of a Palatable Meal on Thalamic and Insular Connectivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design and Procedure
2.3. Intervention: Probe Meal
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.4.1. Assessment of Subjective Responses
2.4.2. Neuroimaging
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Perception Measurements
2.5.2. Brain Connectivity
2.5.3. Correlation of Brain Connectivity and Sensations
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
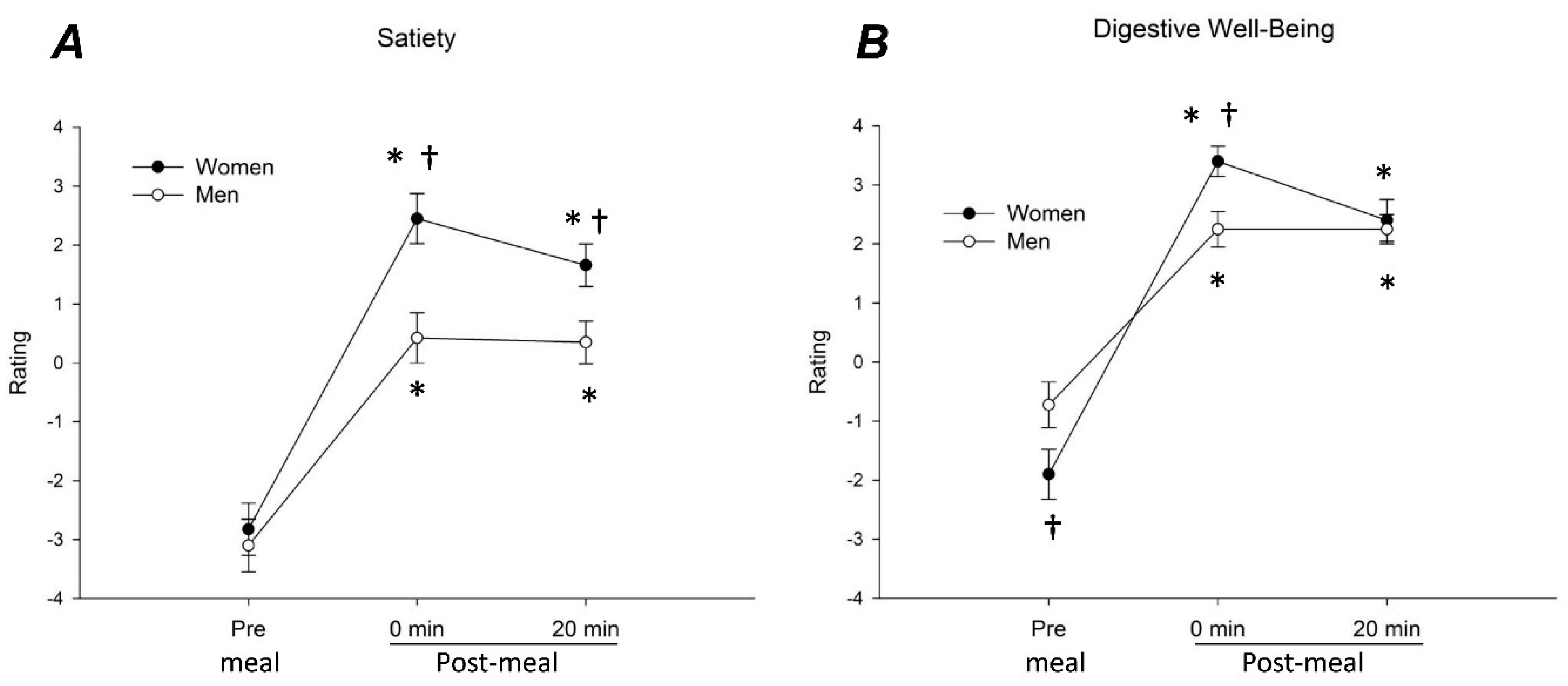
3.2. Meal-Related Sensations
3.3. Brain Imaging
3.3.1. Anterior Insular Connectivity
3.3.2. Thalamic Connectivity
3.3.3. Correlations between Brain Activity and Sensations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Livovsky, D.M.; Pribic, T.; Azpiroz, F. Food, eating, and the gastrointestinal tract. Nutrients 2020, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pribic, T.; Hernandez, L.; Nieto, A.; Malagelada, C.; Accarino, A.; Azpiroz, F. Effects of meal palatability on postprandial sensations. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 30, e13248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanarajah, S.E.; Backes, H.; DiFeliceantonio, A.G.; Albus, K.; Cremer, A.L.; Hanssen, R.; Lippert, R.N.; Cornely, O.A.; Small, D.M.; Brüning, J.C.; et al. Food intake recruits orosensory and post-ingestive dopaminergic circuits to affect eating desire in humans. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.; Kullmann, S.; Veit, R. Food related processes in the insular cortex. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Osadchiy, V.; Mayer, E. Brain–gut–microbiome interactions in obesity and food addiction. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Pribic, T.; Kilpatrick, L.; Ciccantelli, B.; Malagelada, C.; Accarino, A.; Rovira, A.; Pareto, D.; Mayer, E.; Azpiroz, F. Brain networks associated with cognitive and hedonic responses to a meal. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrroy, H.; Pribic, T.; Galan, C.; Nieto, A.; Amigó, N.; Accarino, A.; Correig, X.; Azpiroz, F. Meal enjoyment and tolerance in women and men. Nutrients 2019, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrroy, H.; Borghi, G.; Pribic, T.; Galan, C.; Nieto, A.; Amigó, N.; Accarino, A.; Correig, X.; Azpiroz, F. Biological response to meal ingestion: Gender differences. Nutrients 2019, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masihy, M.; Monrroy, H.; Borghi, G.; Pribic, T.; Galan, C.; Nieto, A.; Accarino, A.; Azpiroz, F. Influence of eating schedule on the postprandial response: Gender differences. Nutrients 2019, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, J.A. Applying the new SABV (sex as a biological variable) policy to research and clinical care. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 187, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigrok, A.N.V.; Salimi-Khorshidi, G.; Lai, M.-C.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Lombardo, M.V.; Tait, R.J.; Suckling, J. A meta-analysis of sex differences in human brain structure. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 39, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, P.M.; Rieken, N.S.; Ogren, J.A.; Macey, K.E.; Kumar, R.; Harper, R.M. Sex differences in insular cortex gyri responses to a brief static handgrip challenge. Boil. Sex Differ. 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A.; Labus, J.S.; Bhatt, R.R.; Ju, T.; Love, A.; Bal, A.; Tillisch, K.; Naliboff, B.; SanMiguel, C.P.; et al. Sex commonalities and differences in obesity-related alterations in intrinsic brain activity and connectivity. Obesity 2017, 26, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucyi, A.; Hodaie, M.; Davis, K.D. Lateralization in intrinsic functional connectivity of the temporoparietal junction with salience- and attention-related brain networks. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 108, 3382–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Nan, H.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yan, L.-F.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.-Y.; et al. Gender differences in functional connectivities between insular subdivisions and selective pain-related brain structures. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, L.; Green, E.; Murphy, C. Males and females show differential brain activation to taste when hungry and sated in gustatory and reward areas. Appetite 2011, 57, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornier, M.-A.; Salzberg, A.K.; Endly, D.C.; Bessesen, D.H.; Tregellas, J.R. Sex-based differences in the behavioral and neuronal responses to food. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 99, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.M.; Loughead, J.; Bakizada, Z.M.; Hopkins, C.; Geliebter, A.; Gur, R.C.; Wadden, T.A. Sex/gender differences in neural correlates of food stimuli: A systematic review of functional neuroimaging studies. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, E.-M.; Rehme, A.K.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Fink, G.R.; Grefkes, C. Functional resting-state connectivity of the human motor network: Differences between right- and left-handers. NeuroImage 2015, 109, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manichanh, C.; Eck, A.; Varela, E.; Roca, J.; Clemente, J.C.; González, A.; Knights, D.; Knight, R.; Estrella, S.; Hernandez, C.; et al. Anal gas evacuation and colonic microbiota in patients with flatulence: Effect of diet. Gut 2013, 63, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, E.; Barba, E.; Huaman, J.W.; Cisternas, D.; Accarino, A.; Soldevilla, A.; Malagelada, J.-R.; Azpiroz, F. Mechanisms of postprandial abdominal bloating and distension in functional dyspepsia. Gut 2013, 63, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, E.; Burri, E.; Accarino, A.; Cisternas, D.; Quiroga, S.; Monclus, E.; Navazo, I.; Malagelada, J.; Azpiroz, F. Abdomino-thoracic mechanisms of functional abdominal distension and correction by biofeedback. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccantelli, B.; Pribic, T.; Malagelada, C.; Accarino, A.; Azpiroz, F. Relation between cognitive and hedonic responses to a meal. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pribic, T.; Nieto, A.; Hernandez, L.; Malagelada, C.; Accarino, A.; Azpiroz, F. Appetite influences the responses to meal ingestion. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, D.M.; Smith, S.M.; Beckmann, C.F. Advances and pitfalls in the analysis and interpretation of resting-state FMRI data. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destrieux, C.; Fischl, B.; Dale, A.; Halgren, E. Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.A. Frequency distribution of the values of the correlation coefficient in samples from an indefinitely large population. Biometrika 1915, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.R.; Bookstein, F.; Haxby, J.; Grady, C. Spatial pattern analysis of functional brain images using partial least squares. NeuroImage 1996, 3, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.R.; Lobaugh, N.J. Partial least squares analysis of neuroimaging data: Applications and advances. NeuroImage 2004, 23, S250–S263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, P.; De Graaf, K.; Stafleu, A.; Van Osch, M.J.; Nievelstein, R.A.J.; Van Der Grond, J. Effect of satiety on brain activation during chocolate tasting in men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Naliboff, B.D.; Craig, A.B. Neuroimaging of the Brain-Gut Axis: From Basic Understanding to Treatment of Functional GI Disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1925–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbetta, M.; Shulman, G.L. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahnt, T.; Tobler, P.N.; Hayashi, M.J.; Tanabe, H.C.; Yoshida, Y.; Carlson, S.; Sadato, N.; Kanai, R.; Walsh, V. Salience signals in the right temporoparietal junction facilitate value-based decisions. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoettinger, E.; Aichhorn, M.; Anderson, B.; Danckert, J. The neural systems for perceptual updating. Neuropsychology 2018, 112, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, J.A.; Kerr, K.L.; Ingeholm, J.E.; Burrows, K.; Bodurka, J.; Simmons, W. A common gustatory and interoceptive representation in the human mid-insula. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, F.; Zilles, K.; Fox, P.T.; Laird, A.R.; Eickhoff, S.B. A link between the systems: Functional differentiation and integration within the human insula revealed by meta-analysis. Anat. Embryol. 2010, 214, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, W.; Rapuano, K.M.; Kallman, S.J.; Ingeholm, J.E.; Miller, B.; Gotts, S.J.; Avery, J.A.; Hall, K.D.; Martin, A. Category-specific integration of homeostatic signals in caudal but not rostral human insula. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1551–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D.M. Taste representation in the human insula. Anat. Embryol. 2010, 214, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuizen, M.; Albrecht, J.; Zelano, C.; Boesveldt, S.; Breslin, P.; Lundström, J.N. Identification of human gustatory cortex by activation likelihood estimation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Seed Region | X | Y | Z | BSR | Num. | Pre-1 rz | Pre-2 rz | Post rz | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | mm | mm | voxels | F | M | F | M | F | M | ||
| Left anterior insula | |||||||||||
| L precentral, postcentral | −60 | 8 | 28 | 6.75 | 8808 | 0.20 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| R insula | 40 | −32 | 18 | 6.72 | 6054 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.56 | 0.18 | 0.30 |
| Bilat precuneus | 4 | −54 | 10 | 6.16 | 4470 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.07 |
| Bilat medial superior frontal | 2 | 56 | 16 | 5.63 | 2180 | 0.19 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| R precentral, postcentral | 32 | −20 | 50 | 5.62 | 1223 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| L SMA | −12 | 0 | 70 | 5.19 | 420 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.39 | 0.16 | 0.19 |
| L superior frontal | −16 | 28 | 46 | 5.18 | 368 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.18 | −0.08 | 0.14 |
| Bilat paracentral lobule | −4 | −24 | 68 | 4.74 | 549 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.12 |
| Right anterior insula | |||||||||||
| L insula, Bilat postcentral, precentral, paracentral lobule, inferior frontal, SMA | −36 | −26 | 22 | 7.46 | 30687 | 0.16 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.08 | 0.28 |
| Bilat lingual | 12 | −44 | −8 | 6.54 | 4286 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.30 | −0.08 | 0.10 |
| Bilat medial superior frontal | 2 | 66 | 18 | 5.88 | 4002 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.06 |
| R inferior frontal | 26 | 24 | −2 | 5.51 | 910 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.43 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| L precuneus | −16 | −76 | 38 | 4.52 | 150 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.27 | 0.46 | 0.24 | 0.30 |
| R calcarine | 8 | −98 | −8 | 4.48 | 193 | −0.08 | 0.15 | −0.17 | 0.17 | −0.10 | 0.05 |
| Left thalamus | |||||||||||
| R superior parietal, angular | 28 | −68 | 54 | 6.44 | 1463 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.32 |
| R fusiform | 38 | −40 | −18 | 6.40 | 1366 | −0.08 | 0.05 | −0.14 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.12 |
| R medial superior frontal | 14 | 62 | 30 | 6.39 | 637 | 0.06 | 0.30 | −0.01 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.37 |
| R mid frontal | 40 | 52 | −4 | 6.35 | 2734 | −0.02 | 0.12 | −0.09 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.25 |
| L fusiform | −46 | −54 | −14 | 6.34 | 1165 | −0.07 | 0.12 | −0.09 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.25 |
| R putamen, insula | 36 | 0 | −2 | 6.31 | 2286 | 0.01 | 0.18 | −0.12 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.28 |
| L putamen, insula | −38 | −6 | −2 | 5.96 | 2890 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.41 |
| L inferior frontal | −44 | 28 | 0 | 5.73 | 910 | 0.05 | 0.17 | −0.07 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.34 |
| L mid occipital | −32 | −88 | 16 | 5.54 | 1739 | −0.02 | 0.10 | −0.15 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.24 |
| R superior frontal | 16 | 38 | 50 | 5.52 | 582 | 0.08 | 0.17 | −0.06 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.29 |
| L superior frontal | −18 | 32 | 56 | 5.22 | 154 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.38 |
| R medial OFC | 6 | 56 | −4 | 5.11 | 480 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.35 |
| L calcarine | −8 | −58 | 8 | 5.05 | 772 | 0.03 | 0.17 | −0.01 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.33 |
| L inferior parietal | −28 | −46 | 40 | 4.38 | 150 | 0.00 | 0.12 | −0.08 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.17 |
| Right thalamus | |||||||||||
| R putamen, R insula | 34 | 2 | −2 | 6.75 | 4820 | 0.09 | 0.22 | −0.07 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.33 |
| R fusiform | 40 | −50 | −18 | 5.78 | 861 | −0.12 | −0.04 | −0.15 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.20 |
| R superior parietal | 28 | −68 | 54 | 5.58 | 494 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.34 |
| L anterior insula, inferior frontal gyrus | −46 | 16 | −2 | 5.51 | 917 | 0.01 | 0.16 | −0.01 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.26 |
| R mid occipital gyrus | 36 | −84 | 24 | 5.38 | 212 | −0.05 | 0.11 | −0.15 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
| L fusiform gyrus | −48 | −54 | −14 | 5.27 | 261 | −0.01 | 0.16 | −0.06 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.21 |
| L posterior insula | −36 | −6 | 0 | 5.20 | 1498 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.39 |
| R mid frontal gyrus | 22 | 44 | 28 | 5.07 | 609 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.28 |
| Bilat SMA | 2 | 26 | 58 | 5.00 | 307 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.31 |
| R medial OFC | 6 | 54 | −2 | 4.87 | 280 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.30 |
| L angular gyrus | −40 | −54 | 24 | 4.84 | 368 | −0.05 | 0.11 | −0.11 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.14 |
| L mid occipital | −28 | −88 | 16 | 4.55 | 296 | −0.06 | 0.07 | −0.12 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
| L cerebellum | −18 | −74 | −28 | 4.41 | 435 | 0.19 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.42 |
| Region | X mm | Y mm | Z mm | BSR | Size Voxels | Well-Being r | Satiety r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEMALES | |||||||
| Left thalamus | |||||||
| R mid-temporal | 64 | −46 | −4 | 7.25 | 391 | 0.74 | 0.53 |
| R fusiform gyrus | 40 | −42 | −22 | 5.45 | 217 | 0.69 | 0.69 |
| L pINS | −32 | −32 | 16 | 4.70 | 254 | 0.61 | 0.38 |
| Right thalamus | |||||||
| L pINS | −36 | −26 | 10 | 6.45 | 291 | 0.70 | 0.33 |
| R midINS | 40 | −4 | −14 | 6.15 | 177 | 0.60 | 0.44 |
| R fusiform gyrus | 28 | −40 | −12 | 4.96 | 171 | 0.50 | 0.54 |
| MALES | |||||||
| Left anterior insula | |||||||
| L TPJ | −44 | −44 | 22 | 5.38 | 191 | −0.72 | −0.56 |
| Right anterior insula | |||||||
| R inferior frontal | 42 | 16 | 22 | 5.43 | 288 | 0.69 | 0.40 |
| L precentral | −32 | −6 | 50 | 5.04 | 427 | 0.65 | 0.46 |
| R midfrontal | 36 | 10 | 46 | −4.87 | 288 | 0.57 | 0.53 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kilpatrick, L.; Pribic, T.; Ciccantelli, B.; Malagelada, C.; Livovsky, D.M.; Accarino, A.; Pareto, D.; Azpiroz, F.; Mayer, E.A. Sex Differences and Commonalities in the Impact of a Palatable Meal on Thalamic and Insular Connectivity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061627
Kilpatrick L, Pribic T, Ciccantelli B, Malagelada C, Livovsky DM, Accarino A, Pareto D, Azpiroz F, Mayer EA. Sex Differences and Commonalities in the Impact of a Palatable Meal on Thalamic and Insular Connectivity. Nutrients. 2020; 12(6):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061627
Chicago/Turabian StyleKilpatrick, Lisa, Teodora Pribic, Barbara Ciccantelli, Carolina Malagelada, Dan M. Livovsky, Anna Accarino, Deborah Pareto, Fernando Azpiroz, and Emeran A. Mayer. 2020. "Sex Differences and Commonalities in the Impact of a Palatable Meal on Thalamic and Insular Connectivity" Nutrients 12, no. 6: 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061627
APA StyleKilpatrick, L., Pribic, T., Ciccantelli, B., Malagelada, C., Livovsky, D. M., Accarino, A., Pareto, D., Azpiroz, F., & Mayer, E. A. (2020). Sex Differences and Commonalities in the Impact of a Palatable Meal on Thalamic and Insular Connectivity. Nutrients, 12(6), 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061627





