Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Data
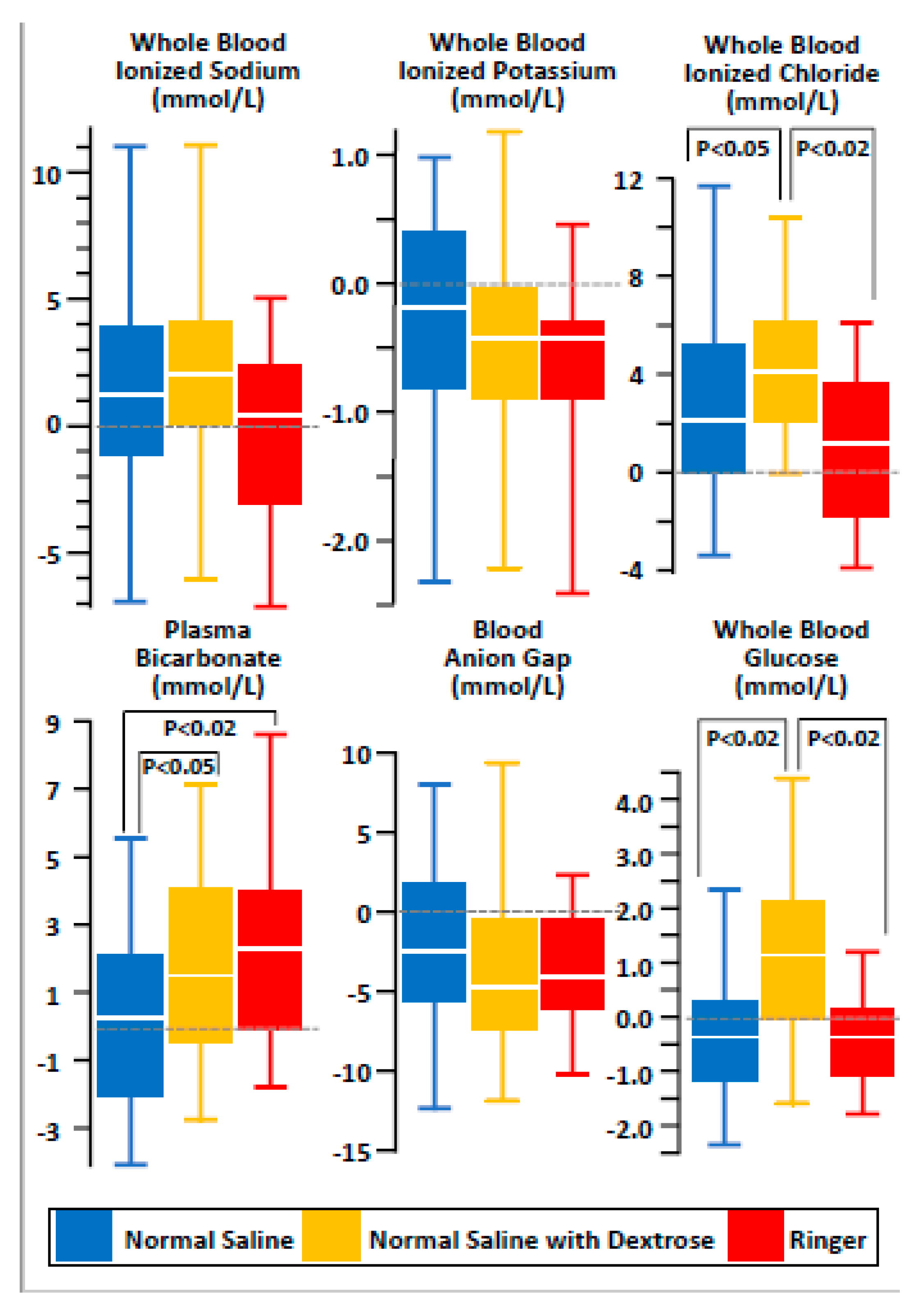
3.2. Effects of Maintenance Fluid Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moritz, M.L.; Ayus, J.C. Maintenance Intravenous Fluids in Acutely Ill Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santi, M.; Lava, S.A.G.; Camozzi, P.; Giannini, O.; Milani, G.P.; Simonetti, G.D.; Fossali, E.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Faré, P.B. The great fluid debate: Saline or so-called "balanced" salt solutions? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2015, 41, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semler, M.W.; Kellum, J.A. Balanced Crystalloid Solutions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, L.G.; Neuspiel, D.R.; Foster, B.A.; Leu, M.G.; Garber, M.D.; Austin, K.; Basu, R.K.; Conway, E.E.; Fehr, J.J.; Hawkins, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Maintenance Intravenous Fluids in Children. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20183083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, A.; Ashkenazi, S.; Gendrel, M.; Vecchio, A.L.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition/European Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in Children in Europe. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canziani, B.C.; Uestuener, P.; Fossali, E.; Lava, S.A.G.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Clinical Practice: Nausea and vomiting in acute gastroenteritis: Physiopathology and management. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 177, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, M.B.; Milani, G.P.; Bernardi, S.; Odone, L.; Rocchi, A.; D’Angelo, E.A.; Alberzoni, M.; Agostoni, C.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Fossali, E.F. Hyponatremia in infants with community-acquired infections on hospital admission. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.R.; Losek, J.D. Rehydration: Role for early use of intravenous dextrose. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2009, 25, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.A.; Waltzman, M.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Bachur, R. Value of Point-of-care Ketones in Assessing Dehydration and Acidosis in Children with Gastroenteritis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2013, 20, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severs, D.; Hoorn, E.J.; Rookmaaker, M.B. A critical appraisal of intravenous fluids: From the physiological basis to clinical evidence. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 30, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, M.L. Why 0.9% saline is isotonic: Understanding the aqueous phase of plasma and the difference between osmolarity and osmolality. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 34, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, R.W.; Covington, A.K.; Fogh-Andersen, N.; Külpmann, W.R.; Lewenstam, A.; Maas, A.H.; Muller-Plathe, O.; Sachs, C.; Siggaard-Andersen, O.; Vankessel, A.L.; et al. Recommendations for Measurement of and Conventions for Reporting Sodium and Potassium by Ion-Selective Electrodes in Undiluted Serum, Plasma or Whole Blood. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavagno, C.; Milani, G.P.; Uestuener, P.; Simonetti, G.D.; Casaulta, C.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Fare, P.B.; Lava, S.A.G. Hyponatremia in children with acute respiratory infections: A reappraisal. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 92, 430–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampmeier, T.G.; Rehberg, S.; Ertmer, C. Evolution of fluid therapy. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterns, R.H.; Silver, S. Salt and water: Read the package insert. QJM Int. J. Med. 2003, 96, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| All Cases | Normal Saline | Dextrose-Supplemented Saline | Lactated Ringer Solution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 134 | 56 | 48 | 30 |
| Gender (females:males) | 56:78 | 19:37 | 29:19 * | 8:22 |
| Age, years | 2.4 (1.2–5.1) | 3.6 ◆ (1.3–7.7) | 2.2 (1.6–4.6) | 1.8 (1.0–2.7) |
| Whole blood concentration | ||||
| Ionized sodium, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 134 (131–137) | 135 (133–137) | 133 (130–136) | 135 (131–138) |
| 4–6 h later | 135 (133–138) | 136 (133–138) | 135 (133–138) | 135 (133–137) |
| Ionized potassium, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 4.2 (3.8–4.6) | 4.3 (3.8–4.9) | 4.2 (3.9–4.5) | 4.2 (3.5–4.5) |
| 4–6 h later | 3.8 (3.4–4.2) | 4.0 (3.4–4.4) | 3.8 (3.5–4.1) | 3.7 (3.2–4.0) |
| Ionized chloride, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 104 (102–107) | 104 (102–107) | 103 (100–104) | 108 ✙ (104–111) |
| 4–6 h later | 107 (104–110) | 107 (103–109) | 107 (105–109) | 107 (105–113) |
| L-lactate ≥2.5 mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4–6 h later | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 4.4 (3.7–5.6) | 4.9 (4.3–6.4) | 3.6 ▪ (3.2–4.3) | 4.4 (3.9–6.8) |
| 4–6 h later | 4.6 (3.9–5.7) | 4.6 (3.8–5.7) | 5.3 ▪ (4.3–6.6) | 4.3 (3.7–4.8) |
| Plasma bicarbonate, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 17.1 (14.7–20.2) | 19.9 (15.9–22.3) | 16.1 (14.7–18.6) | 15.2 ✙ (13.7–17.7) |
| 4–6 h later | 19.0 (16.0–21.6) | 19.3 (16.0–22.5) | 19.1 (16.2–21.3) | 18.5 (15.6–20.3) |
| Blood, anion gap, mmol/L | ||||
| At baseline | 12 (9–16) | 10 (8–14) | 14 ☩ (11–17) | 12 (9–15) |
| 4–6 h later | 9 (6–12) | 9 (7–12) | 9 (7–11) | 7 (4–12) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricciuti, A.; Milani, G.P.; Tarantino, S.; Ghilardi, R.; Lava, S.A.G.; Alberzoni, M.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Agostoni, C. Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449
Ricciuti A, Milani GP, Tarantino S, Ghilardi R, Lava SAG, Alberzoni M, Bianchetti MG, Agostoni C. Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicciuti, Alessandra, Gregorio P. Milani, Silvia Tarantino, Roberta Ghilardi, Sebastiano A.G. Lava, Marco Alberzoni, Mario G. Bianchetti, and Carlo Agostoni. 2020. "Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449
APA StyleRicciuti, A., Milani, G. P., Tarantino, S., Ghilardi, R., Lava, S. A. G., Alberzoni, M., Bianchetti, M. G., & Agostoni, C. (2020). Maintenance Fluid Therapy with Saline, Dextrose-Supplemented Saline or Lactated Ringer in Childhood: Short-Term Metabolic Effects. Nutrients, 12(5), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051449








