Topical Application of A New Herbal Complex, NI-01, Ameliorates House Dust Mite-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Preparation of NI-01 Water Extract
2.4. Preparations of Sample and Standard Solutions
2.5. Apparatus and Conditions
2.6. Validation of Analytical Procedures
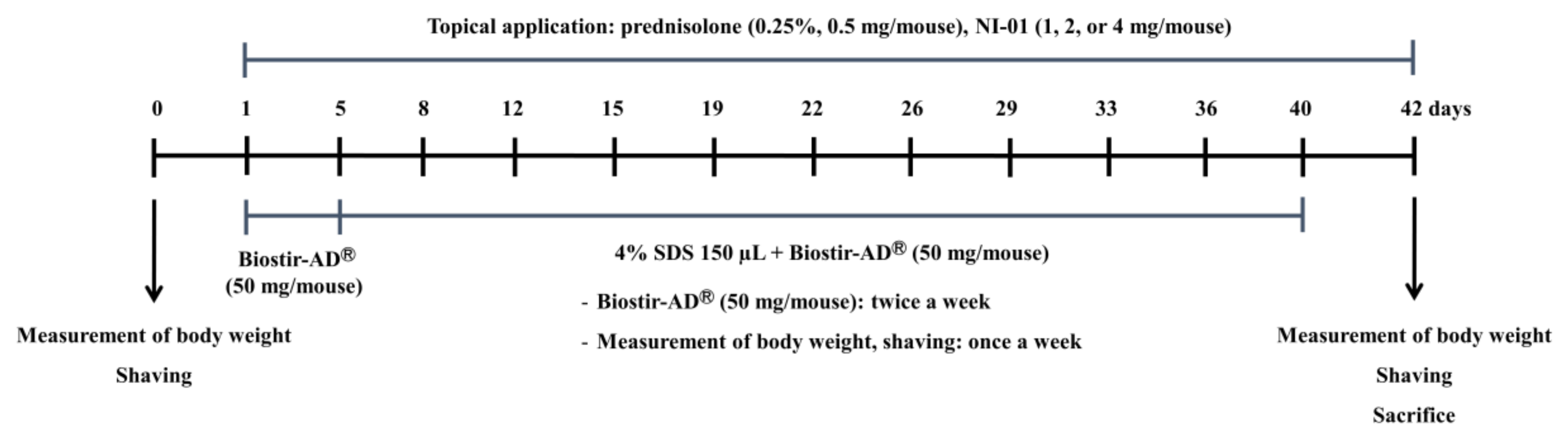
2.7. Animals
2.8. Induction of Atopic Dermatitis and Evaluation of Skin Severity
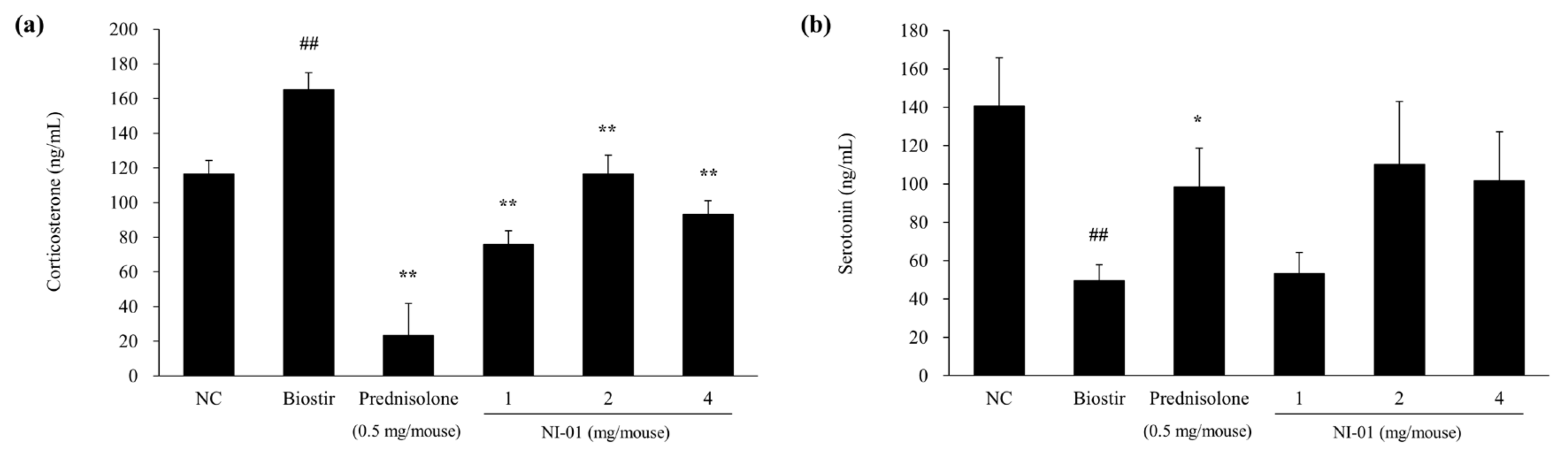
2.9. Measurement of Plasma IgE, Histamine, Corticosterone and Serotonin Levels
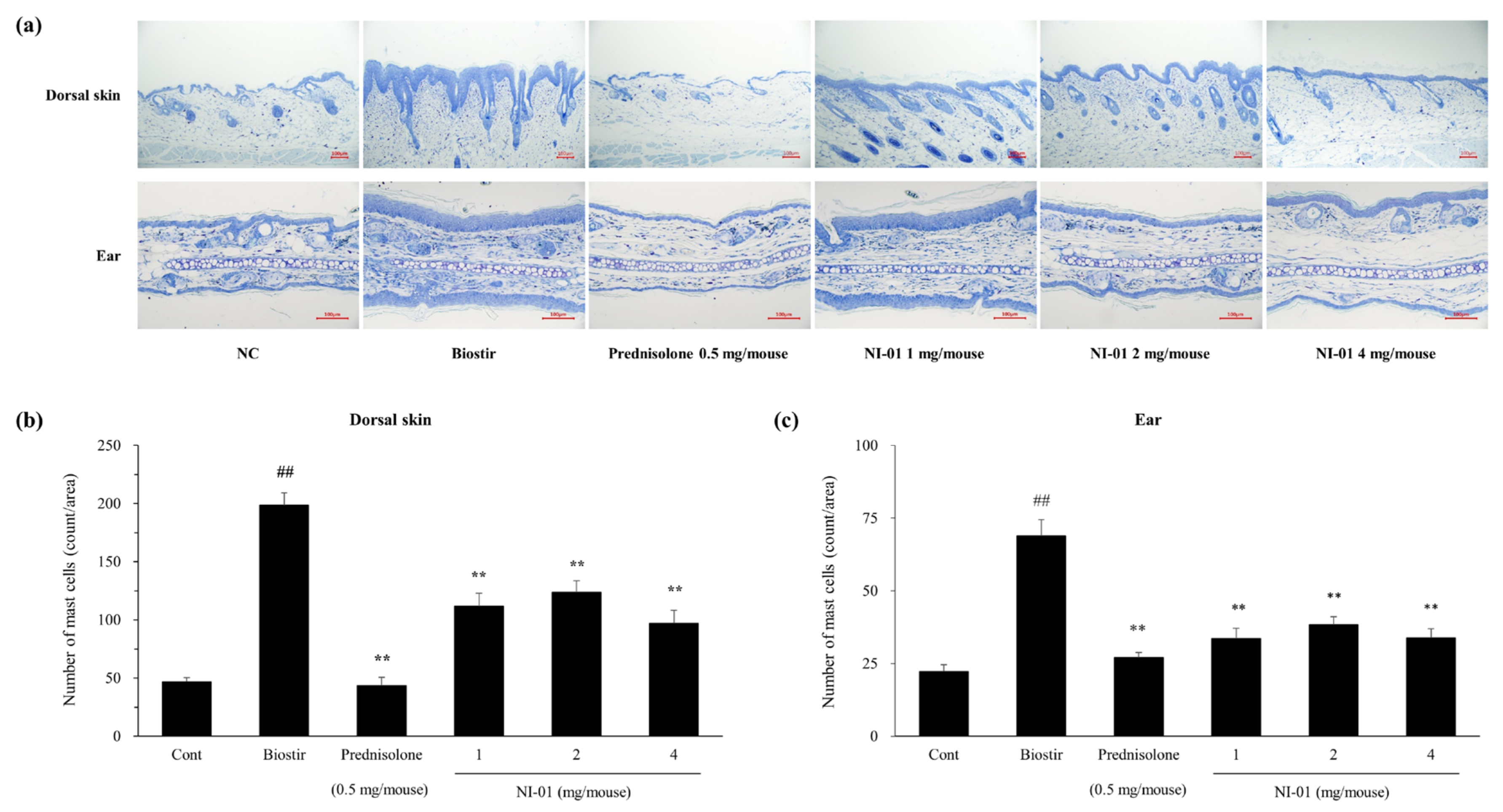
2.10. Histological Analysis
2.11. Immunohistochemistry
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
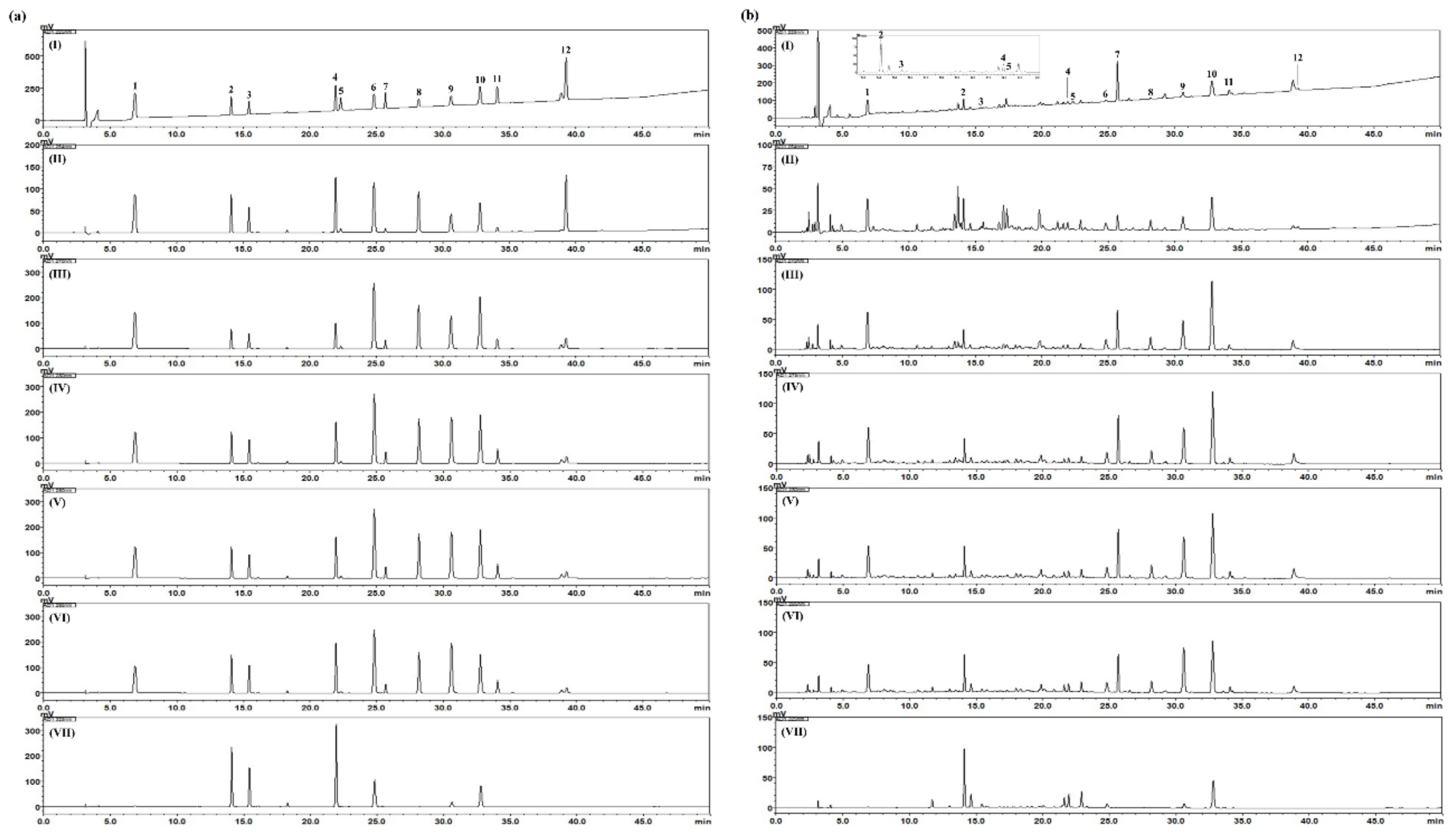
3.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
3.2. Method Validations
3.3. Simultaneous Determination of the 12 Marker Components in the Freeze-Dried NI-01 Sample
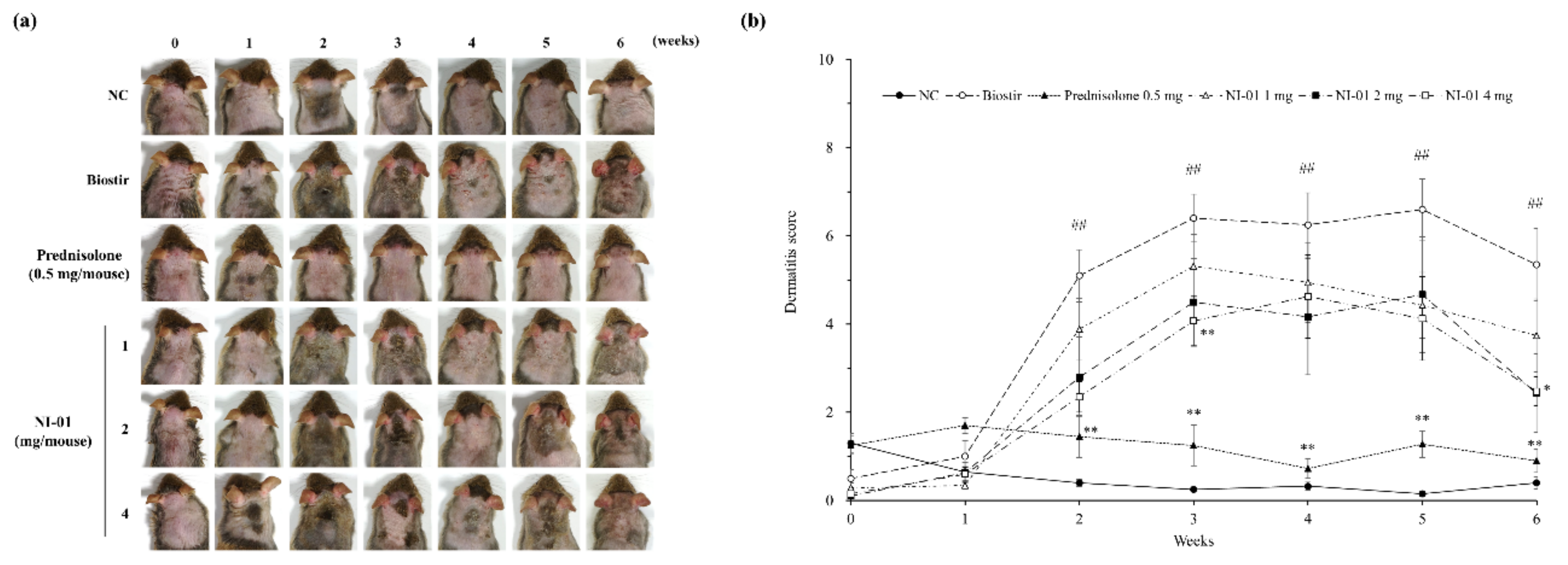
3.4. Effects of NI-01 on Dermatitis Score
3.5. Effect of NI-01 on Histopathological Features and Mast Cell Infiltration
3.6. Effect of NI-01 on CD4+ T cell, IL-4, and ICAM-1 expression
3.7. Effect of NI-01 on the Level of Corticosterone and Serotonin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avena-Woods, C. Overview of atopic dermatitis. Am. J. Manag. Care 2017, 23, S115–S123. [Google Scholar]
- Pastar, Z.; Lipozencic, J.; Ljubojevic, S. Etiopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis—An overview. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2005, 13, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Buske-Kirschbaum, A.; Geiben, A.; Hellhammer, D. Psychobiological aspects of atopic dermatitis: An overview. Psychother. Psychosom. 2001, 70, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.; Soter, N.A. Cellular and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 44, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.K.; Zhong, L.; Santiago, J.L. Association between stress and the HPA axis in the atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestrovic-Stefekov, J.; Novak-Bilic, G.; Kuna, M.; Pap, N.; Lugovic-Mihic, L. Psychological stress in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2018, 26, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rutter, N. Drug absorption through the skin: A mixed blessing. Arch. Dis. Child. 1987, 62, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Undre, N.A.; Moloney, F.J.; Ahmadi, S.; Stevenson, P.; Murphy, G.M. Skin and systemic pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus following topical application of tacrolimus ointment in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papier, A.; Strowd, L.C. Atopic dermatitis: A review of topical nonsteroid therapy. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 212521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Lu, J.M.; Yang, J.J.; Chuang, S.C.; Ujiie, T. Anti-inflammatory and radical scavenge effects of Arctium lappa. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1996, 24, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Shi, J. Pharmacological of Cortex Moutan and core. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1997, 22, 214–216, 254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Hong, S.I.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Lonicera japonica THUNB. extract inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses by suppressing NF-kappaB signaling in BV-2 microglial cells. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.V.; Gan, S.H. Cinnamon: A multifaceted medicinal plant. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 642942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, T.K.; Shin, T.Y.; Kim, S.H. Elsholtzia ciliata inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: Role of calcium, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2011, 236, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szopa, A.; Ekiert, R.; Ekiert, H. Current knowledge of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. (Chinese magnolia vine) as a medicinal plant species: A review on the bioactive components, pharmacological properties, analytical and biotechnological studies. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Yoon, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, G.H.; Kim, H.K. Inhibitory effects of Cinnamomum cassia extract on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by mite antigen in NC/Nga mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH). Guidance for industry. In Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology; ICH: Rockville, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- National Institutes of Health. National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Duan, L.; Dou, L.L.; Liu, L.L.; Yang, H.; Liu, E.H.; Li, P. Quality standardization of herbal medicines using effective compounds combination as labeled constituents. J. Pharm Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, H.; Negishi, I.; Akiyama, H.; Ishikawa, O. Psychological stress can trigger atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice: An inhibitory effect of corticotropin-releasing factor. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, J.; Sengoku, T.; Morita, K.; Kishi, S.; Sato, S.; Ogawa, T.; Tsudzuki, M.; Matsuda, H.; Wada, A.; Esaki, K. Effect of tacrolimus hydrate (FK506) ointment on spontaneous dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsuoka, H.; Maki, N.; Yoshida, S.; Arai, M.; Wang, J.; Oikawa, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Hirota, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Ishii, A. A mouse model of the atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome by repeated application of a crude extract of house-dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae. Allergy 2003, 58, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, H.; Furue, M.; Furukawa, F.; Hide, M.; Ohtsuki, M.; Katayama, I.; Sasaki, R.; Suto, H.; Takehara, K. Committee for guidelines for the management of atopic dermatitis of Japanese dermatological association: Guidelines for management of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2009, 36, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, A.R.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, I.S.; Park, S.Y.; Jeong, S.I.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, K. Douchi (fermented Glycine max Merr.) alleviates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice by regulation of PKC and IL-4. BMC Complement. Altern Med. 2016, 16, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Harvima, I.T. Mast cell-neural interactions contribute to pain and itch. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, A.; Nomura, T.; Rerknimitr, P.; Seidel, J.A.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. The interplay between genetic and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orito, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Ishiura, N.; Yanaba, K.; Matsushita, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Ogawa, F.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 cooperatively contribute to the cutaneous arthus reaction. J. Leukoc Biol. 2007, 81, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, G.; Jung, Y.S.; Park, M.K.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, Y.U. Melatonin inhibits attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder caused by atopic dermatitis-induced psychological stress in an NC/Nga atopic-like mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chida, Y.; Hamer, M.; Steptoe, A. A bidirectional relationship between psychosocial factors and atopic disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2008, 70, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.J.; Essex, M.J. Specificity in the association of anxiety, depression, and atopic disorders in a community sample of adolescents. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joels, M.; Karst, H.; Sarabdjitsingh, R.A. The stressed brain of humans and rodents. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2018, 223, e13066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Peden, D.B. Environmental effects on immune responses in patients with atopy and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, P.J.; Browning, M. What has serotonin to do with depression? World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
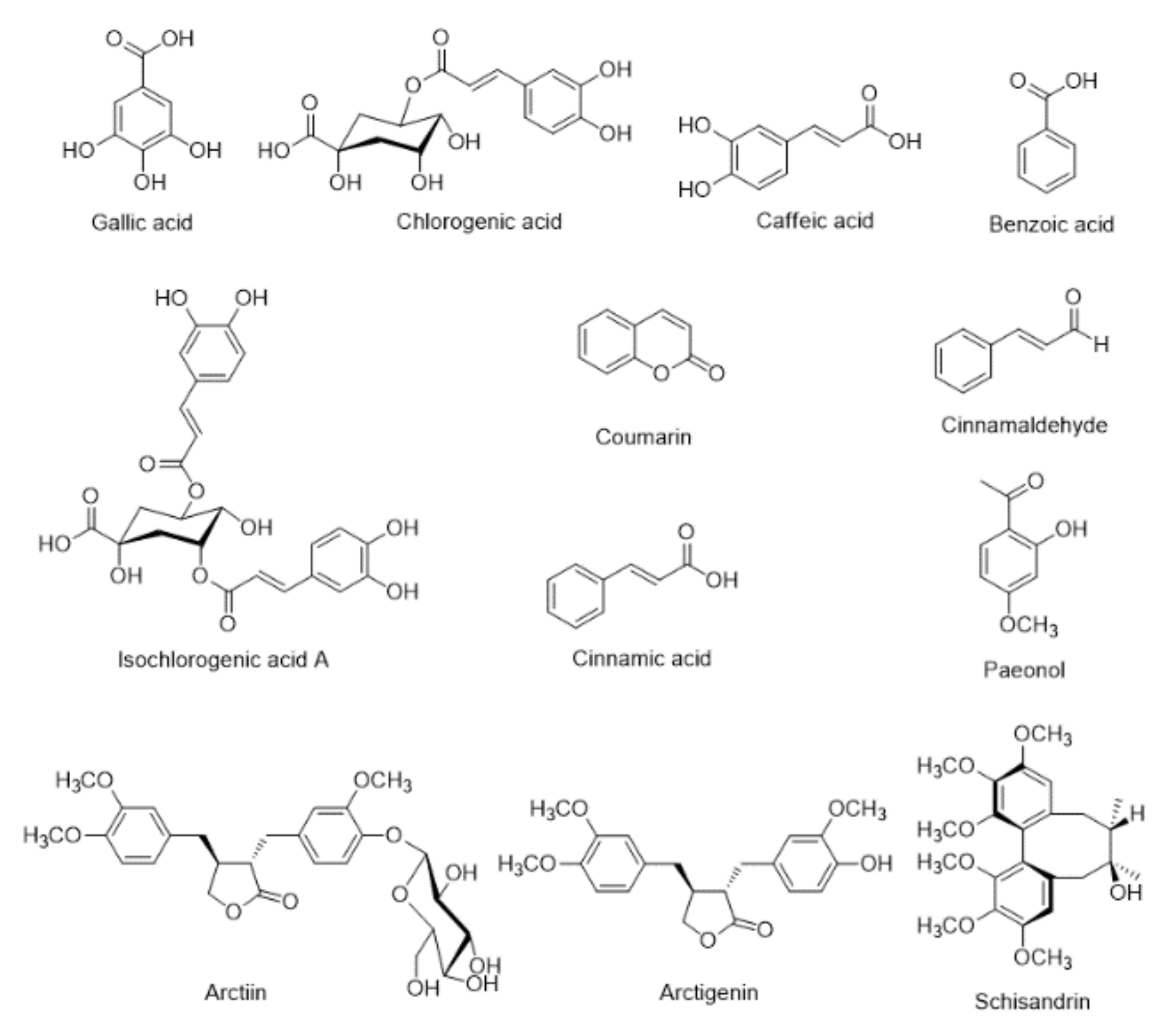


| Herbal Medicine | Scientific Name | Family | Using Parts | Origin | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinnamomi Ramulus | Cinnamomum cassia Presl | Lauraceae | Twigs | Vietnam | 16.67 |
| Lonicerae Flos | Lonicera japonica Thunberg | Caprifoliaceae | Flowers | China | 16.67 |
| Moutan Radicis Cortex | Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews | Paeoniaceae | Root barks | China | 16.67 |
| Schisandrae Fructus | Schisandra chinensis (Thrcz.) Baillon | Schisandraeceae | Fruits | Mungyeong, Korea | 16.67 |
| Arctii Fructus | Arctium lappa Linné | Compositae | Fruits | China | 16.67 |
| Elsholtziae Herba | Elsholtzia ciliate Hylander | Labiatae | Aerial parts | Yeongju, Korea | 16.67 |
| Total (%) | 100 |
| Compound | Linear Range (μg/mL) | Slope | Intercept | r2 | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 0.78–50.00 | 36471.39 | 732.07 | 1.0000 | 0.23 | 0.69 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.78–50.00 | 29040.45 | 8.35 | 1.0000 | 0.18 | 0.53 |
| Caffeic acid | 0.16–10.00 | 62228.23 | 545.65 | 1.0000 | 0.05 | 0.14 |
| Isochlorogenic acid A | 0.31–20.00 | 38643.91 | 65.89 | 1.0000 | 0.08 | 0.24 |
| Benzoic acid | 0.31–20.00 | 41668.71 | −55.39 | 1.0000 | 0.10 | 0.29 |
| Coumarin | 0.31–20.00 | 49231.58 | 214.54 | 1.0000 | 0.07 | 0.22 |
| Arctiin | 1.56–100.00 | 6823.74 | 890.85 | 1.0000 | 0.41 | 1.23 |
| Cinnamic acid | 0.31–20.00 | 82626.47 | 1747.26 | 1.0000 | 0.09 | 0.27 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 0.31–20.00 | 149601.72 | 845.06 | 1.0000 | 0.06 | 0.18 |
| Paeonol | 1.56–100.00 | 58985.35 | 6937.15 | 1.0000 | 0.36 | 1.08 |
| Arctigenin | 0.78–50.00 | 9687.01 | −378.67 | 1.0000 | 0.20 | 0.62 |
| Schisandrin | 0.31–20.00 | 20731.53 | 6609.43 | 0.9999 | 0.09 | 0.26 |
| Compound | Original Conc. (μg/mL) | Spiked Conc. (μg/mL) | Found Conc. (μg/mL) | Recovery (%) | SD | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 16.07 | 3.00 | 19.04 | 99.08 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| 7.50 | 23.62 | 100.60 | 1.29 | 1.29 | ||
| 15.00 | 31.08 | 100.07 | 0.72 | 0.72 | ||
| Chlorogenic acid | 19.73 | 4.00 | 23.65 | 98.15 | 0.14 | 0.15 |
| 10.00 | 29.66 | 99.33 | 0.68 | 0.69 | ||
| 20.00 | 40.76 | 105.17 | 0.81 | 0.77 | ||
| Caffeic acid | 0.66 | 1.00 | 1.66 | 99.30 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| 2.00 | 2.63 | 98.25 | 1.52 | 1.55 | ||
| 4.00 | 4.57 | 97.64 | 0.92 | 0.94 | ||
| Isochlorogenic acid A | 3.98 | 1.00 | 4.98 | 99.69 | 1.77 | 1.78 |
| 2.00 | 5.94 | 97.79 | 1.68 | 1.72 | ||
| 4.00 | 7.95 | 99.20 | 0.70 | 0.71 | ||
| Benzoic acid | 2.83 | 1.00 | 3.83 | 99.38 | 1.19 | 1.19 |
| 2.00 | 4.86 | 101.13 | 0.68 | 0.67 | ||
| 4.00 | 6.97 | 103.38 | 0.88 | 0.85 | ||
| Coumarin | 3.70 | 1.00 | 4.71 | 101.36 | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| 2.00 | 5.66 | 98.18 | 1.44 | 1.46 | ||
| 4.00 | 7.67 | 99.41 | 0.59 | 0.59 | ||
| Arctiin | 75.10 | 15.00 | 89.90 | 98.63 | 1.01 | 1.02 |
| 37.50 | 112.21 | 98.95 | 1.71 | 1.73 | ||
| 75.00 | 148.97 | 98.49 | 1.15 | 1.17 | ||
| Cinnamic acid | 2.20 | 1.00 | 3.23 | 102.45 | 2.03 | 1.99 |
| 2.00 | 4.21 | 100.29 | 1.46 | 1.45 | ||
| 4.00 | 6.30 | 102.30 | 0.71 | 0.70 | ||
| Cinnamaldehyde | 5.11 | 1.00 | 6.11 | 100.15 | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| 2.00 | 7.09 | 99.24 | 1.27 | 1.28 | ||
| 4.00 | 9.07 | 99.09 | 0.59 | 0.60 | ||
| Paeonol | 21.76 | 4.00 | 25.78 | 100.56 | 1.25 | 1.24 |
| 10.00 | 31.65 | 98.85 | 1.00 | 1.02 | ||
| 20.00 | 41.12 | 96.77 | 0.26 | 0.27 | ||
| Arctigenin | 10.11 | 2.00 | 12.11 | 100.04 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| 5.00 | 15.10 | 99.85 | 1.39 | 1.39 | ||
| 10.00 | 20.10 | 99.92 | 0.62 | 0.62 | ||
| Schisandrin | 1.04 | 1.00 | 2.04 | 100.52 | 1.44 | 1.44 |
| 2.00 | 3.00 | 98.07 | 0.19 | 0.20 | ||
| 4.00 | 5.07 | 100.87 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| Compound | Conc. (μg/mL) | Intraday (n = 5) | Interday (n = 5) | Repeatability (n = 6) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Conc. (μg/mL) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) | Observed Conc. (μg/mL) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) of Retention Time | RSD (%) of Peak Area | ||
| Gallic acid | 12.50 | 12.71 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 101.65 | 12.60 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.46 |
| 25.00 | 25.15 | 0.21 | 0.85 | 100.60 | 25.19 | 0.30 | |||
| 50.00 | 50.24 | 0.45 | 0.89 | 100.47 | 50.30 | 0.62 | |||
| Chlorogenic acid | 12.50 | 12.69 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 101.48 | 12.57 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.31 |
| 25.00 | 25.09 | 0.21 | 0.83 | 100.38 | 25.11 | 0.30 | |||
| 50.00 | 50.28 | 0.46 | 0.92 | 100.57 | 50.23 | 0.70 | |||
| Caffeic acid | 2.50 | 2.54 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 101.73 | 2.52 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.46 |
| 5.00 | 5.03 | 0.04 | 0.78 | 100.69 | 5.04 | 0.06 | |||
| 10.00 | 10.06 | 0.11 | 1.09 | 100.59 | 10.07 | 0.13 | |||
| Isochlorogenic acid A | 5.00 | 5.07 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 101.47 | 5.02 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.42 |
| 10.00 | 10.05 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 100.50 | 10.03 | 0.10 | |||
| 20.00 | 20.11 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 100.53 | 20.05 | 0.24 | |||
| Benzoic acid | 5.00 | 5.09 | 0.06 | 1.11 | 101.77 | 5.03 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| 10.00 | 10.06 | 0.12 | 1.19 | 100.64 | 10.04 | 0.12 | |||
| 20.00 | 20.11 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 100.54 | 20.02 | 0.20 | |||
| Coumarin | 5.00 | 5.10 | 0.04 | 0.73 | 101.93 | 5.05 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.40 |
| 10.00 | 10.04 | 0.09 | 0.85 | 100.40 | 10.07 | 0.12 | |||
| 20.00 | 20.12 | 0.21 | 1.05 | 100.62 | 20.09 | 0.22 | |||
| Arctiin | 25.00 | 25.49 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 101.96 | 25.29 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.44 |
| 50.00 | 50.43 | 0.44 | 0.86 | 100.85 | 50.54 | 0.65 | |||
| 100.00 | 100.56 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 100.56 | 100.69 | 1.36 | |||
| Cinnamic acid | 5.00 | 5.08 | 0.03 | 0.61 | 101.70 | 5.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.38 |
| 10.00 | 10.05 | 0.09 | 0.85 | 100.52 | 10.08 | 0.12 | |||
| 20.00 | 20.10 | 0.19 | 0.97 | 100.52 | 20.08 | 0.18 | |||
| Cinnamaldehyde | 5.00 | 5.08 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 101.53 | 5.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.37 |
| 10.00 | 10.01 | 0.08 | 0.80 | 100.09 | 10.06 | 0.11 | |||
| 20.00 | 20.11 | 0.17 | 0.86 | 100.57 | 20.09 | 0.22 | |||
| Paeonol | 25.00 | 25.37 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 101.49 | 25.19 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.40 |
| 50.00 | 50.27 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 100.55 | 50.41 | 0.60 | |||
| 100.00 | 100.52 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 100.52 | 100.36 | 1.10 | |||
| Arctigenin | 12.50 | 12.66 | 0.08 | 0.61 | 101.26 | 12.55 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.41 |
| 25.00 | 25.26 | 0.22 | 0.85 | 101.04 | 25.22 | 0.33 | |||
| 50.00 | 50.26 | 0.53 | 1.05 | 100.53 | 50.29 | 0.62 | |||
| Schisandrin | 5.00 | 5.10 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 101.98 | 5.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.36 |
| 10.00 | 10.07 | 0.10 | 1.01 | 100.72 | 10.12 | 0.13 | |||
| 20.00 | 20.04 | 0.14 | 0.72 | 100.21 | 20.06 | 0.18 | |||
| Compound | Batch No. Concentrations (mg/g) ± SD (× 10−2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Gallic acid | 3.90 ± 1.03 | 3.89 ± 0.84 | 3.89 ± 0.11 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 4.92 ± 0.26 | 4.92 ± 1.09 | 4.93 ± 0.34 |
| Caffeic acid | 0.17 ± 0.09 | 0.17 ± 0.16 | 0.17 ± 0.10 |
| Isochlorogenic acid A | 1.00 ± 0.29 | 1.00 ± 0.12 | 1.00 ± 0.03 |
| Benzoic acid | 0.88 ± 0.76 | 0.88 ± 0.15 | 0.87 ± 0.89 |
| Coumarin | 0.92 ± 0.65 | 0.92 ± 0.09 | 0.92 ± 0.13 |
| Arctiin | 18.95 ± 0.94 | 18.93 ± 0.45 | 18.96 ± 1.13 |
| Cinnamic acid | 0.56 ± 0.15 | 0.56 ± 0.14 | 0.56 ± 0.13 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 1.29 ± 0.28 | 1.29 ± 0.65 | 1.29 ± 0.51 |
| Paeonol | 5.46 ± 0.66 | 5.47 ± 0.75 | 5.46 ± 1.13 |
| Arctigenin | 2.48 ± 6.41 | 2.52 ± 6.15 | 2.49 ± 4.95 |
| Schisandrin | 0.25 ± 0.23 | 0.25 ± 0.40 | 0.25 ± 0.51 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.E.; Ha, H.; Yoo, S.-R.; Jeon, W.-Y.; Lee, N.; Lee, M.-Y.; Choi, S.; Jang, J.-H.; Park, E.; Kim, S.; et al. Topical Application of A New Herbal Complex, NI-01, Ameliorates House Dust Mite-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051240
Jin SE, Ha H, Yoo S-R, Jeon W-Y, Lee N, Lee M-Y, Choi S, Jang J-H, Park E, Kim S, et al. Topical Application of A New Herbal Complex, NI-01, Ameliorates House Dust Mite-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051240
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Seong Eun, Hyekyung Ha, Sae-Rom Yoo, Woo-Young Jeon, Nari Lee, Mee-Young Lee, Susanna Choi, Ji-Hye Jang, Eunsook Park, Sukkyoung Kim, and et al. 2020. "Topical Application of A New Herbal Complex, NI-01, Ameliorates House Dust Mite-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051240
APA StyleJin, S. E., Ha, H., Yoo, S.-R., Jeon, W.-Y., Lee, N., Lee, M.-Y., Choi, S., Jang, J.-H., Park, E., Kim, S., & Seo, C.-S. (2020). Topical Application of A New Herbal Complex, NI-01, Ameliorates House Dust Mite-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice. Nutrients, 12(5), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051240





