Assessment of Two Nutritional Screening Tools in Hospitalized Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
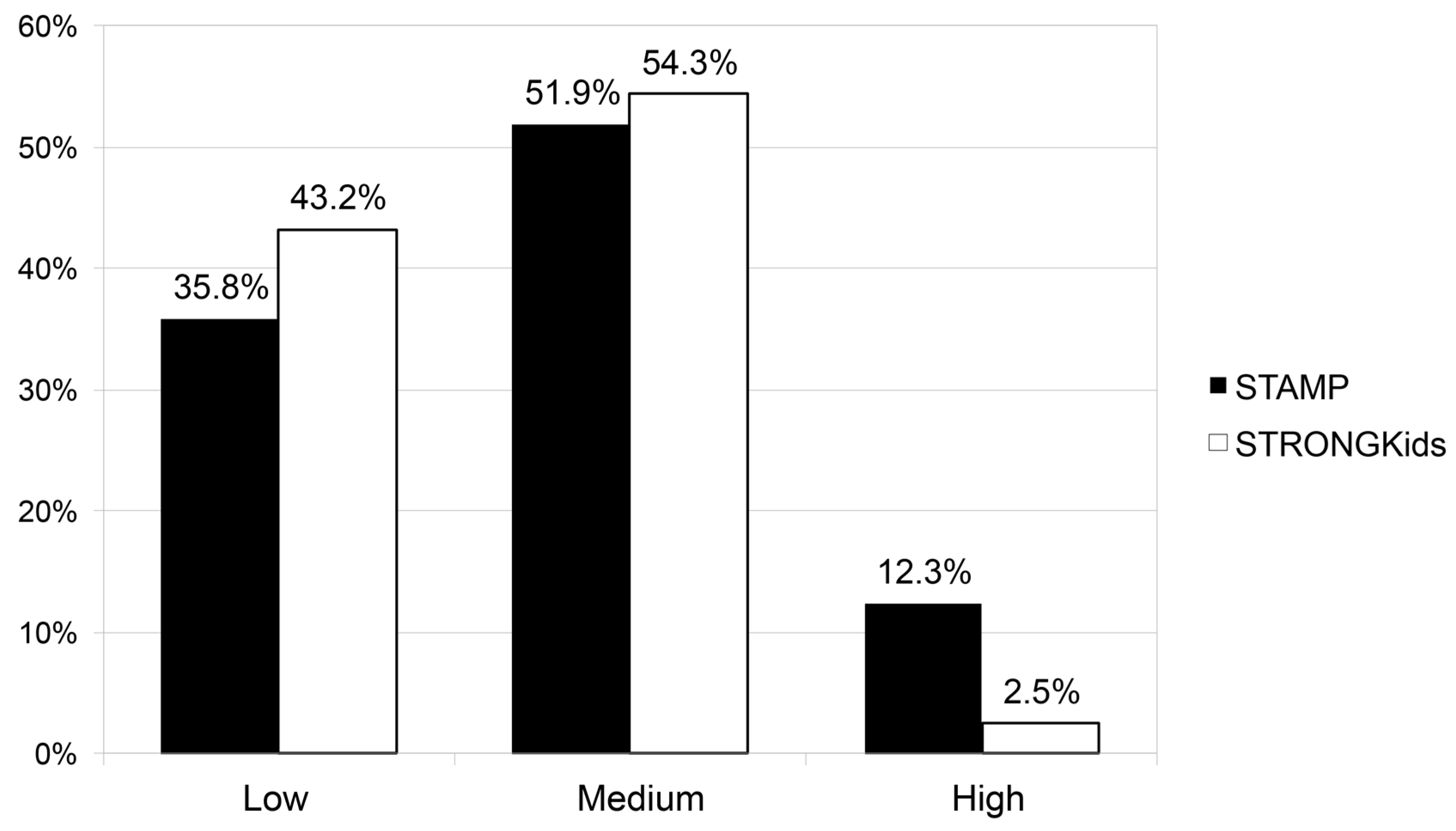
3. Results
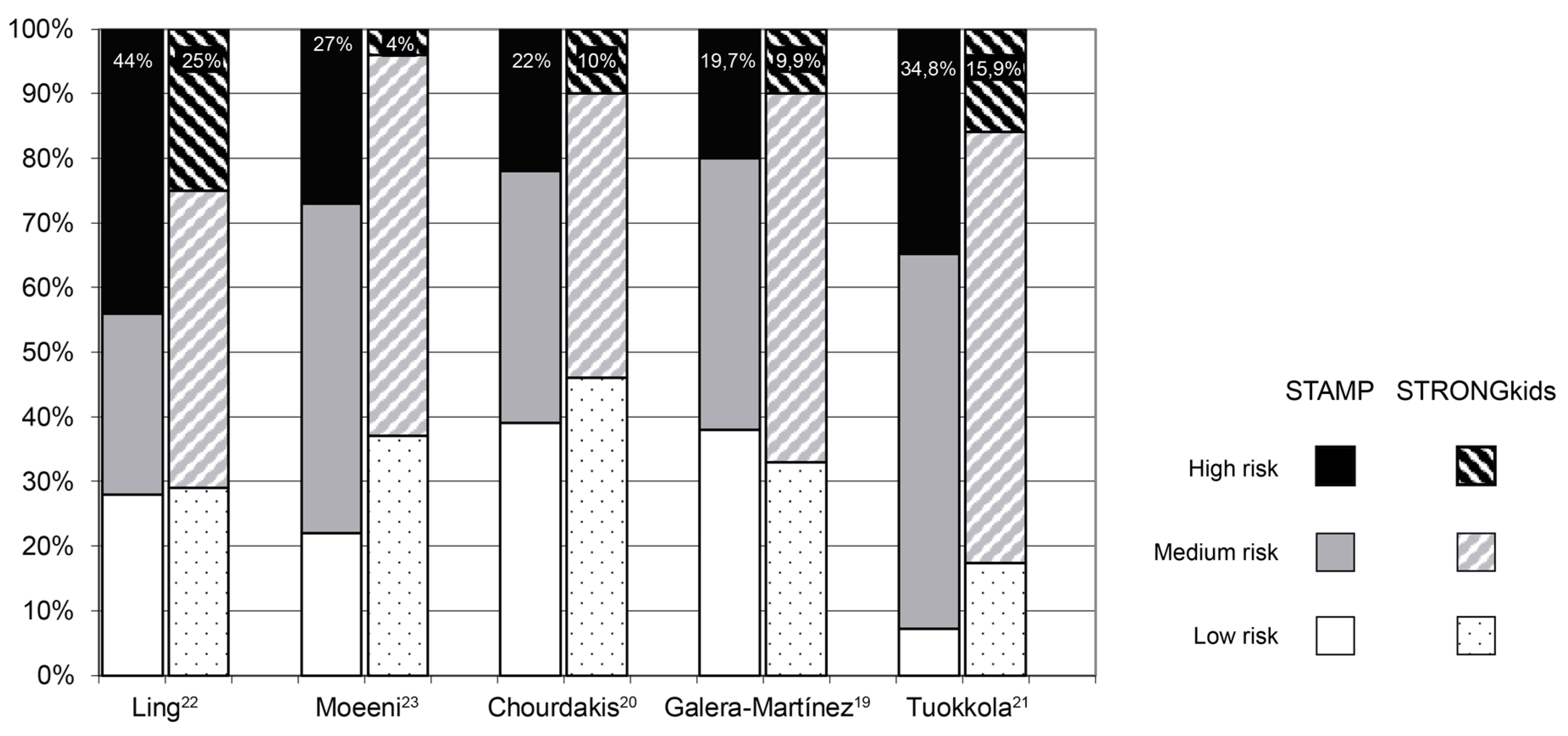
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felder, S.; Lechtenboehmer, C.; Bally, M.; Fehr, R.; Deiss, M.; Faessler, L.; Kutz, A.; Steiner, D.; Rast, A.C.; Laukemann, S.; et al. Association of nutritional risk and adverse medical outcomes across different medical inpatient populations. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, E.; Ferguson, M.; Banks, M.; Batterham, M.; Bauer, J.; Capra, S.; Isenring, E. Malnutrition and poor food intake are associated with prolonged hospital stay, frequent readmissions, and greater in-hospital mortality: Results from the Nutrition Care Day Survey 2010. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2013, 32, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, C.; Weber, M.; Grote, V.; Daskalou, E.; Dell’Era, L.; Flynn, D.; Gerasimidis, K.; Gottrand, F.; Hartman, C.; Hulst, J.; et al. Disease associated malnutrition correlates with length of hospital stay in children. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2015, 34, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secker, D.J.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N. Subjective Global Nutritional Assessment for children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.; Delvin, E.; Marcil, V.; Belanger, V.; Marchand, V.; Boctor, D.; Rashid, M.; Noble, A.; Davidson, B.; Groleau, V.; et al. Prevalence of Malnutrition in Pediatric Hospitals in Developed and in-Transition Countries: The Impact of Hospital Practices. Nutrients 2019, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Villares, J.M.; Varea Calderón, V.; Bousoño García, C.; Lama Moré, R.; Redecillas Ferreiro, S.; Peña Quintana, L. Evaluación del estado nutricional de niños ingresados en el hospital en España; estudio DHOSPE (Desnutrición Hospitalaria en el Paciente Pediátrico en España). Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Council of Europe. Committee of Ministers. Resolution ResAP(2003)3 on Food and Nutritional Care in Hospitals. 2003. Available online: https://search.coe.int/cm/Pages/result_details.aspx?ObjectID=09000016805de855 (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Planas Vilà, M. Declaración de Praga. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 622–623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charney, P. Nutrition Screening vs Nutrition Assessment: How Do They Differ? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Axelsson, I.; Colomb, V.; Goulet, O.; Koletzko, B.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Puntis, J.W.; Rigo, J.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The Need for Nutrition Support Teams in Pediatric Units: A Commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, H.M.; Martineau, J.K.; Moran, A.; Kennedy, H. Nutritional screening—Evaluation and implementation of a simple Nutrition Risk Score. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 1995, 14, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Poisson-Salomon, A.-S.; Colomb, V.; Brusset, M.-C.; Mosser, F.; Berrier, F.; Ricour, C. Simple pediatric nutritional risk score to identify children at risk of malnutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimidis, K.; Keane, O.; Macleod, I.; Flynn, D.M.; Wright, C.M. A four-stage evaluation of the Paediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score in a tertiary paediatric hospital and a district general hospital. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, H.; Dixon, M.; Crabtree, I.; Eaton-Evans, M.J.; McNulty, H. The development and evaluation of the Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Paediatrics (STAMP©) for use by healthcare staff. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 25, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulst, J.M.; Zwart, H.; Hop, W.C.; Joosten, K.F.M. Dutch national survey to test the STRONGkids nutritional risk screening tool in hospitalized children. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2010, 29, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiozoglou-Lampoudi, T.; Daskalou, E.; Lampoudis, D.; Apostolou, A.; Agakidis, C. Computer-Based Malnutrition Risk Calculation May Enhance the Ability to Identify Pediatric Patients at Malnutrition-Related Risk for Unfavorable Outcome. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, K.F.M.; Hulst, J.M. Nutritional screening tools for hospitalized children: Methodological considerations. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2014, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klanjsek, P.; Pajnkihar, M.; Varda, N.M.; Brzan, P.P. Screening and assessment tools for early detection of malnutrition in hospitalised children: A systematic review of validation studies. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Villares, J.M.; Varea Calderón, V.; Bousoño García, C. Malnutrición en el niño ingresado en un hospital. Resultados de una encuesta nacional. Anales Pediatría 2017, 86, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galera-Martínez, R.; Moráis-López, A.; Escartín-Madurga, L.; López-Ruzafa, E.; Ros-Arnal, I.; Ruiz-Bartolomé, H.; Rodríguez-Martínez, G.; Lama-More, R.A. Reproducibility and Inter-rater Reliability of 2 Paediatric Nutritional Screening Tools. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourdakis, M.; Hecht, C.; Gerasimidis, K.; Joosten, K.F.; Karagiozoglou-Lampoudi, T.; Koetse, H.A.; Ksiazyk, J.; Lazea, C.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Malnutrition risk in hospitalized children: Use of 3 screening tools in a large European population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuokkola, J.; Hilpi, J.; Kolho, K.-L.; Orell, H.; Merras-Salmio, L. Nutritional risk screening—A cross-sectional study in a tertiary pediatric hospital. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2019, 38, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, R.E.; Hedges, V.; Sullivan, P.B. Nutritional risk in hospitalised children: An assessment of two instruments. E Spen Eur. E J. Clin. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 6, e153–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moeeni, V.; Walls, T.; Day, A.S. Nutritional status and nutrition risk screening in hospitalized children in New Zealand. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, e419–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huysentruyt, K.; Devreker, T.; Dejonckheere, J.; De Schepper, J.; Vandenplas, Y.; Cools, F. Accuracy of Nutritional Screening Tools in Assessing the Risk of Undernutrition in Hospitalized Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J. Nutritional Screening Tools among Hospitalized Children: From Past and to Present. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2018, 21, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.F.; Viana, K.D.A.L. Nutritional screening in hospitalized pediatric patients: A systematic review. J. Pediatr. 2016, 92, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte Borda, A.D.; Pinzón Espitia, O.L.; Aguilera Otalvaro, P.A. Tamizaje nutricional en paciente pediátrico hospitalizado: Revisión sistemática. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama More, R.A.; Moráis López, A.; Herrero Álvarez, M.; Caraballo Chicano, S.; Galera Martínez, R.; López Ruzafa, E.; Rodríguez Martínez, G.; de la Mano Hernández, A.; Rivero de la Rosa, M. Validación de una herramienta de cribado nutricional para pacientes pediátricos hospitalizados. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar]
| n | 81 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 4.1 (1.3–7.5) |
| Female (%) | 35 (43.2%) |
| BMI z-score | 0.24 (−0.80–1.38) |
| HFA z-score | 0.21 (−0.57–0.92) |
| Length of stay (days) | 3 (2–5) |
| Admission | Follow−Up | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NST | Index | Spearman’s Rho | p | Spearman’s Rho | p |
| STAMP | BMI | −0.044 | 0.698 | 0.022 | 0.844 |
| STRONGkids | BMI | −0.159 | 0.156 | −0.003 | 0.978 |
| STAMP | HFA | −0.213 | 0.056 | −0.220 | 0.049 * |
| STRONGkids | HFA | −0.290 | 0.009 * | −0.285 | 0.010 * |
| Admission | Follow-Up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAMP | STRONGKids | STAMP | STRONGKids | |
| Sensitivity | 100% (70.1–100%) | 100% (70.1–100%) | 100% (61.0–100%) | 100% (61.0–100%) |
| Specificity | 40.3% (29.7–51.8%) | 48.6% (37.4–59.9%) | 38.7% (28.5–50.0%) | 46.7% (35.8–57.8%) |
| PPV | 17.3% (9.4–29.7%) | 19.6% (10.7–33.2%) | 11.5% (5.4–23.0%) | 13.0% (6.1–25.7%) |
| NPV | 100% (88.3–100%) | 100% (90.1–100%) | 100% (88.3–100%) | 100% (90.1–100%) |
| Youden’s J Index | 0.40 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.50 |
| PLR | 1.67 (1.39–2.02) | 1.95 (1.55–2.44) | 1.63 (1.36–1.95) | 1.88 (1.52–2.32) |
| NLR | 0.0 (0–NC) | 0.0 (0–NC) | 0.0 (0–NC) | 0.0 (0–NC) |
| NST | Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAMP | 3 (2–4) | 4 (2–5) | 2.5 (2–3.25) | 0.24 |
| STRONGKids | 3 (2–4) | 4 (2–5) | 2 (2–2) | 0.23 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Solís, D.; Larrea-Tamayo, E.; Menéndez-Arias, C.; Molinos-Norniella, C.; Bueno-Pardo, S.; Jiménez-Treviño, S.; Bousoño-Garcia, C.; Díaz-Martín, J.J. Assessment of Two Nutritional Screening Tools in Hospitalized Children. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051221
Pérez-Solís D, Larrea-Tamayo E, Menéndez-Arias C, Molinos-Norniella C, Bueno-Pardo S, Jiménez-Treviño S, Bousoño-Garcia C, Díaz-Martín JJ. Assessment of Two Nutritional Screening Tools in Hospitalized Children. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051221
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Solís, David, Elene Larrea-Tamayo, Cristina Menéndez-Arias, Cristina Molinos-Norniella, Sara Bueno-Pardo, Santiago Jiménez-Treviño, Carlos Bousoño-Garcia, and Juan J. Díaz-Martín. 2020. "Assessment of Two Nutritional Screening Tools in Hospitalized Children" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051221
APA StylePérez-Solís, D., Larrea-Tamayo, E., Menéndez-Arias, C., Molinos-Norniella, C., Bueno-Pardo, S., Jiménez-Treviño, S., Bousoño-Garcia, C., & Díaz-Martín, J. J. (2020). Assessment of Two Nutritional Screening Tools in Hospitalized Children. Nutrients, 12(5), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051221






