Anti-Obesity Effects of Sargassum thunbergii via Downregulation of Adipogenesis Gene and Upregulation of Thermogenic Genes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Ethanol Extract from Sargassum thunbergii
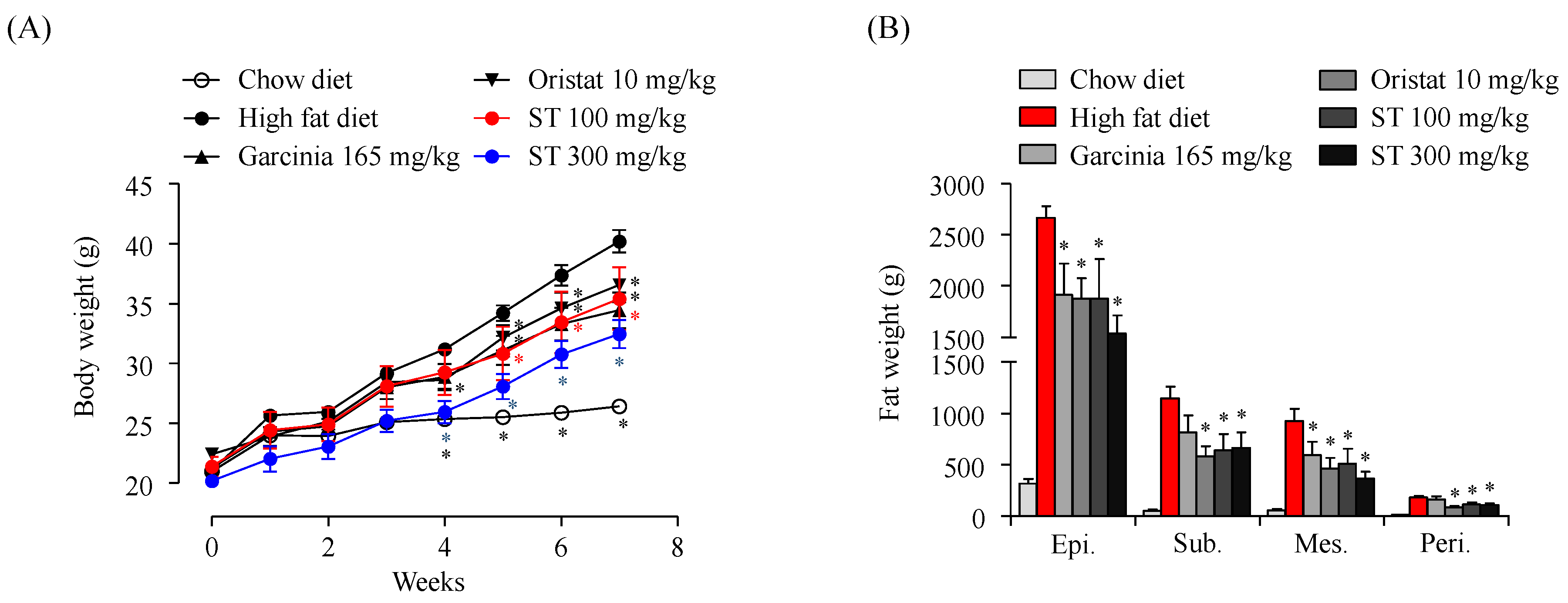
2.2. Animals
2.3. Serum Analysis
2.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Sargassum thunbergii on Serum Biochemical Parameters
3.2. Histological Analysis of Hepatic and Adipose Tissues
3.3. Expression of Adipogenesis- and Thermogenesis-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Wang, L.; Im, S.; Hwang, O.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, M.-C.; Lee, S.-H. Anti-Obesity Effect of Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Isolated from Brown Alga Ishige okamurae in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaodhiar, L.; McCowen, K.C.; Blackburn, G.L. Obesity and its comorbid conditions. Clin. Cornerstone 1999, 2, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S.; Tsigos, C.; Kaltsas, G.; Weickert, M.O. Clinical problems caused by obesity. In Endotext [Internet]; MDText. com, Inc., 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK278973/ (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Kim, G.W.; Lin, J.E.; Blomain, E.S.; Waldman, S.A. Antiobesity pharmacotherapy: New drugs and emerging targets. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 95, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Elkhayat, E.S.; El Dine, R.S. Natural anti-obesity agents. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2014, 52, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, B.M.Y.; Cheung, T.T.; Samaranayake, N.R. Safety of. antiobesity drugs. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2013, 4, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselgrübler, R.; Lanzerstorfer, P.; Röhrl, C.; Stübl, F.; Schurr, J.; Schwarzinger, B.; Schwarzinger, C.; Brameshuber, M.; Wieser, S.; Winkler, S.M. Hypolipidemic effects of herbal extracts by reduction of adipocyte differentiation, intracellular neutral lipid content, lipolysis, fatty acid exchange and lipid droplet motility. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccellino, M.; D’Angelo, S. Anti-Obesity Effects of Polyphenol Intake: Current Status and Future Possibilities. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Lim, Y.; Kim, E.-K. Therapeutic phytogenic compounds for obesity and diabetes. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21505–21537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, O.D.; du Preez, R.; Panchal, S.K.; Brown, L. Tropical foods as functional foods for metabolic syndrome. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 11, 6946–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Seca, A.M.; Pinto, D.C.; Michalak, I.; Trincone, A.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Zam, W.; Martins, N. Current trends on seaweeds: Looking at chemical composition, phytopharmacology, and cosmetic applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.R.; Tiwari, U.; Rajauria, G. Seaweed nutraceuticals and their therapeutic role in disease prevention. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Ros, G.; Amarowicz, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nieto, G. Seaweeds as a Functional Ingredient for a Healthy Diet. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L. Effects of polyphenol intake on metabolic syndrome: Current evidences from human trials. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 5812401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Rodriguez, E.S.; Rangel-Huerta, O.D. Polyphenols in obesity and metabolic syndrome. In Obesity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giriwono, P.E.; Iskandriati, D.; Tan, C.P.; Andarwulan, N. Sargassum seaweed as a source of anti-inflammatory substances and the potential insight of the tropical species: A review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-C.; Lee, H.; Choi, H.-D.; Jeon, Y.-J. Antioxidant properties of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from an enzymatic digest of Sargassum thunbergii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samee, H.; Li, Z.-x.; Lin, H.; Khalid, J.; Guo, Y.-C. Anti-allergic effects of ethanol extracts from brown seaweeds. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2009, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-C.; Ding, Y.; Kim, E.-A.; Choi, Y.K.; De Araujo, T.; Heo, S.-J.; Lee, S.-H. Indole derivatives isolated from brown alga Sargassum thunbergii inhibit adipogenesis through AMPK activation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I. Effect of orlistat alone or in combination with Garcinia cambogia on visceral adiposity index in obese patients. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 5, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, L.O.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Yeap, S.K. Updates on antiobesity effect of garcinia origin (−)-HCA. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2013, 751658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Kong, W.; Zafar, M.I.; Chen, L.-L. Serum triglycerides as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Lee, G.-S.; Cheon, S.-Y.; Cha, Y.-Y.; An, H.-J. The anti-obesity effects of Tongbi-san in a high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model. BMC Complem. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricquier, D.; Bouillaud, F. Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins: From mitochondria to the regulation of energy balance. J. Physiol. 2000, 529, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, T.; Klingenspor, M. Uncoupling protein 1 expression and high-fat diets. Am. J. Physiol. Regul Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R1–R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Goblan, A.S.; Al-Alfi, M.A.; Khan, M.Z. Mechanism linking diabetes mellitus and obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2014, 7, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.A.; Kang, M.-C.; Yang, W.-M.; Hwang, W.M.; Kim, S.S.; Hong, S.H.; Heo, J.-I.; Vijyakumar, A.; de Moura, L.P.; Uner, A. Apolipoprotein J is a hepatokine regulating muscle glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Fernández, S.; Garcés-Rimón, M.; Vera, G.; Astier, J.; Landrier, J.F.; Miguel, M. High fat/high glucose diet induces metabolic syndrome in an experimental rat model. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttar, H.S.; Li, T.; Ravi, N. Prevention of cardiovascular diseases: Role of exercise, dietary interventions, obesity and smoking cessation. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2005, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.F.; Cabezas, M.C. Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H.; Kahn, S.E.; Ferrannini, E.; Goldfine, A.B.; Nathan, D.M.; Schwartz, M.W.; Smith, R.J.; Smith, S.R. Obesity and type 2 diabetes: What can be unified and what needs to be individualized? JCEM 2011, 96, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. JCEM 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.; Abrams, G.A. Metabolic liver disease of obesity and role of adipose tissue in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.A.; Lee, H.G.; Li, X.; Hyun, J.-M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, H.-M.; Lee, J.J.; Kang, M.-C.; Jeon, Y.-J.; et al. Anti-obesity effects of red seaweed, Plocamium telfairiae, in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, K.; Tseng, Y.-H. Brown adipose tissue: Recent insights into development, metabolic function and therapeutic potential. Adipocyte 2012, 1, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Kim, M.; Takahashi, H.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T. Food Intake and Thermogenesis in Adipose Tissue. Korean J. Obes. 2016, 25, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L. Small molecules for fat combustion: Targeting obesity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.-J.; Chang, S.-H.; Li, D.Y.; Villanueva, C.J.; Park, K.W. Induction of thermogenic adipocytes: Molecular targets and thermogenic small molecules. EMM 2017, 49, e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liao, W.; Yin, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Feng, X. Resveratrol-induced brown fat-like phenotype in 3T3-L1 adipocytes partly via mTOR pathway. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, C.-S.; Yu, R. Quercetin upregulates uncoupling protein 1 in white/brown adipose tissues through sympathetic stimulation. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Funayama, K.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin from edible seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida, shows antiobesity effect through UCP1 expression in white adipose tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chow Diet | High-Fat Diet | Gpo (165 mg/kg) | Ori (10 mg/kg) | ST (100 mg/kg) | ST (300 mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin (ng/mL) | 0.86 ± 0.04 * | 2.21 ± 0.62 | 1.76 ± 0.71 | 1.05 ± 0.28 * | 0.96 ± 0.21 * | 1.13 ± 0.42 * |
| Triglyceride (nmol/μL) | 24.37 ± 2.34 * | 30.65 ± 2.19 | 21.55 ± 3.33 * | 25.40 ± 3.63 * | 22.5 ± 2.54 * | 23.28 ± 1.87 * |
| Total cholesterol (μg/μL) | 69.02 ± 2.96 * | 84.77 ± 4.05 | 67.24 ± 7.3 * | 79.13 ± 5.55 | 74.59 ± 5.65 * | 73.76 ± 1.61 * |
| Leptin (pg/mL) | 425.60 ± 0.01 * | 3521.6 ± 0.09 | 2218 ± 0.01 * | 3638 ± 0.09 | 2859.6 ± 1.35 | 2299.6 ± 0.3 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.-C.; Lee, H.-G.; Kim, H.-S.; Song, K.-M.; Chun, Y.-G.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, B.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-Obesity Effects of Sargassum thunbergii via Downregulation of Adipogenesis Gene and Upregulation of Thermogenic Genes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113325
Kang M-C, Lee H-G, Kim H-S, Song K-M, Chun Y-G, Lee MH, Kim B-K, Jeon Y-J. Anti-Obesity Effects of Sargassum thunbergii via Downregulation of Adipogenesis Gene and Upregulation of Thermogenic Genes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113325
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Min-Cheol, Hyo-Geun Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim, Kyung-Mo Song, Yong-Gi Chun, Min Hyeock Lee, Bum-Keun Kim, and You-Jin Jeon. 2020. "Anti-Obesity Effects of Sargassum thunbergii via Downregulation of Adipogenesis Gene and Upregulation of Thermogenic Genes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113325
APA StyleKang, M.-C., Lee, H.-G., Kim, H.-S., Song, K.-M., Chun, Y.-G., Lee, M. H., Kim, B.-K., & Jeon, Y.-J. (2020). Anti-Obesity Effects of Sargassum thunbergii via Downregulation of Adipogenesis Gene and Upregulation of Thermogenic Genes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients, 12(11), 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113325






