Double Burden of Malnutrition among Chinese Women of Reproductive Age and Their Social Determinants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset and Study Sample
2.2. Outcomes of Interest
2.3. Variables
2.3.1. Individual-Level Factors
2.3.2. Community-Level Factors
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Patient and Public Involvement
3. Results
3.1. Malnutrition Prevalence and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Individual and Household Effects
3.3. Community Socioeconomic Factors and Time Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williamson, C.S. Nutrition in pregnancy. Nutr. Bull. 2006, 31, 28–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, F.; Cetin, I.; Verduci, E.; Canzone, G.; Giovannini, M.; Scollo, P.; Corsello, G.; Poli, A. Maternal diet and nutrient requirements in pregnancy and breastfeeding. An Italian consensus document. Nutrients 2016, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLaughlin, S.M.; Walker, S.K.; Roberts, C.T.; Kleemann, D.O.; McMillen, I.C. Periconceptional nutrition and the relationship between maternal body weight changes in the periconceptional period and feto-placental growth in the sheep. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 2005, 565, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Prevalence of Underweight among Adults, BMI <18.5, Crude—Estimates by WHO Region. Available online: https://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.NCDBMILT18CREGv (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Khaskheli, M.-N.; Baloch, S.; Sheeba, A.; Baloch, S.; Khaskheli, F.K. Iron deficiency anaemia is still a major killer of pregnant women. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Micronutrient Deficiencies. Available online: http://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/ida/en/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Miller, J.L. Iron deficiency anemia: A common and curable disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, J.; Thomas, D. Health, nutrition, and economic development. J. Econ. Lit. 1998, 36, 766–817. [Google Scholar]
- Hannum, E.; Liu, J.; Frongillo, E. Poverty, food insecurity and nutritional deprivation in Rural China: Implications for children’s literacy achievement. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2014, 34, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pan, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Prevalence of underweight, overweight, and obesity among reproductive-age women and adolescent girls in Rural China. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mi, J.; Shan, X.-Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Ge, K.-Y. Is China facing an obesity epidemic and the consequences? The trends in obesity and chronic disease in China. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2007, 31, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. Overview of obesity in Mainland China. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 1), 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Malnutrition. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Nykjaer, C.; Alwan, N.A.; Greenwood, D.C.; Simpson, N.A.B.; Hay, A.W.M.; White, K.L.M.; Cade, J.E. Maternal alcohol intake prior to and during pregnancy and risk of adverse birth outcomes: Evidence from a British cohort. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2014, 68, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Tang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S. Disease burden of unintended pregnancy in China. Value Health 2014, 17, A751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stephenson, J.; Heslehurst, N.; Hall, J.; Schoenaker, D.A.J.M.; Hutchinson, J.; Cade, J.E.; Poston, L.; Barrett, G.; Crozier, S.R.; Barker, M.; et al. Before the beginning: Nutrition and lifestyle in the preconception period and its importance for future health. Lancet 2018, 391, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, W.; Genebo, T. Determinants of the Nutritional Status of Mothers and Children in Ethiopia; ORC Macro: Calverton, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- James, W.P.; Ferro-Luzzi, A.; Waterlow, J.C. Definition of chronic energy deficiency in adults. Report of a working party of the International Dietary Energy Consultative Group. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 42, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Hu, D.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of overweight and obesity in older rural Chinese. Intern. Med. J. 2008, 38, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, C.; Cavalli-Sforza, T.; Cutter, J.; Darnton-Hill, I.; Deurenberg, P.; Deurenberg-Yap, M.; Gill, T.; James, P.; Ko, G.; Miu, A.H.; et al. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004, 363, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Smith, J.; Popkin, B.M. Understanding community context and adult health changes in China: Development of an urbanicity scale. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liang, S.; Carlton, E.J.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Remais, J.V. Urbanisation and health in China. Lancet 2012, 379, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Korff, M.; Koepsell, T.; Curry, S.; Diehr, P. Multi-level analysis in epidemiologic research on health behaviors and outcomes. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 135, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobal, J.; Rauschenbach, B.; Frongillo, E.A. Marital status changes and body weight changes: A US longitudinal analysis. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 56, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayga, R.M. Schooling, health knowledge and obesity. Appl. Econ. 2000, 32, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igboanusi, C.J.C.; Joshua, I.A.; Henry, J.; Nmadu, A.G.; Onoja-Alexander, M.O. The prevalence of overweight and obesity and associated factors among Adults in Goni Gora Kaduna State, Northwestern Nigeria. Ann. Afr. Med. Res. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Murakami, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Hashimoto, H. Distinct association between educational attainment and overweight/obesity in unmarried and married women: Evidence from a population-based study in Japan. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umberson, D.; Liu, H.; Powers, D. Marital status, marital transitions, and body weight. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2009, 50, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitsi-Selmi, A.; Bell, R.; Shipley, M.J.; Marmot, M.G. Education modifies the association of wealth with obesity in women in middle-income but not low-income countries: An interaction study using seven national datasets, 2005–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goryakin, Y.; Suhrcke, M. Economic development, urbanization, technological change and overweight: What do we learn from 244 Demographic and Health Surveys? Econ. Hum. Biol. 2014, 14, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, G.; Swinburn, B. An “ecological” approach to the obesity pandemic. BMJ 1997, 315, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakicic, J.M.; Marcus, B.H.; Gallagher, K.I.; Napolitano, M.; Lang, W. Effect of exercise duration and intensity on weight loss in overweight, sedentary women: A randomized trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Poel, E.; O’Donnell, O.; Van Doorslaer, E. Urbanization and the spread of diseases of affluence in China. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2009, 7, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y. Overweight and obesity difference of Chinese population between different urbanization levels. J. Rural. Health 2014, 30, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rao, K.; Kong, L.; Yao, C.; Xiang, H.; Zhai, F.; Ma, G.; Yang, X. Technical working group of China National nutrition and health survey A description on the Chinese national nutrition and health survey in 2002. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2005, 26, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azzoli, C.G.; Baker, S.; Temin, S.; Pao, W.; Aliff, T.; Brahmer, J.; Johnson, D.H.; Laskin, J.L.; Masters, G.; Milton, D.; et al. American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6251–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.S.; Peerson, J.; Love, B.; Achterberg, C.; Murphy, S.P. Food insecurity is positively related to overweight in women. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, B.; Liu, Y. Will rising household incomes solve China’s micronutrient deficiency problems? Econ. Bull. 2007, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Popkin, B.M.; Corvalan, C.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Dynamics of the double burden of malnutrition and the changing nutrition reality. Lancet 2020, 395, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, C.M.; Adair, L.S.; Monteiro, C.; Popkin, B.M. Overweight and underweight coexist within households in Brazil, China and Russia. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2965–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.F.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.Y.; Popkin, B.M. China in the period of transition from scarcity and extensive undernutrition to emerging nutrition-related non-communicable diseases, 1949–1992. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 1), 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bécares, L.; Chandola, T. Patterns and determinants of double-burden of malnutrition among rural children: Evidence from China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Double-Duty Actions for Nutrition: Policy Brief. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/WHO-NMH-NHD-17.2 (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Nugent, R.; Levin, C.; Hale, J.; Hutchinson, B. Economic effects of the double burden of malnutrition. Lancet 2020, 395, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total | Underweight | Normal | Overweight | Obese | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size (n (%)) | 24,606 | 1926 (7.8) | 13,209 (53.7) | 7697(31.3) | 1774 (7.2) | |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 35.2 (8.8) | 30.0 (9.9) | 33.6 (9.3) | 38.3 (7.9) | 40.0 (7.0) | <0.0001 |
| Marriage status (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| Single | 3950 (16.1) | 742 (38.5) | 2579 (19.5) | 560 (7.3) | 69 (3.9) | |
| Married | 20,093 (81.7) | 1146 (59.5) | 10,335 (78.2) | 6965 (90.5) | 1647 (92.8) | |
| Divorced/widowed/separated | 563 (2.3) | 38 (1.96) | 295 (2.2) | 172 (2.2) | 58 (3.3) | |
| Education (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| Illiterate or primary | 3816 (15.5) | 205 (10.6) | 2004 (15.2) | 1314 (17.1) | 293 (16.5) | |
| Primary graduates or junior school | 14,109 (57.3) | 1083 (56.2) | 7412 (56.1) | 4501 (58.5) | 1113 (62.7) | |
| High school or vocational school | 4919 (20.0) | 449 (23.3) | 2770 (21.0) | 1420 (18.5) | 280 (15.8) | |
| University or above | 1762 (7.2) | 189 (9.8) | 1023 (7.7) | 462 (6.0) | 88 (4.94) | |
| Nationality (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| Han | 21,599 (87.8) | 1653 (85.8) | 11,512 (87.2) | 6850 (89.0) | 1584 (89.3) | |
| Others | 3007 (12.2) | 273 (14.2) | 1697 (12.8) | 847 (11.0) | 190 (10.7) | |
| Medical insurance (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| No | 12,985 (52.8) | 1127 (58.5) | 7543 (57.1) | 3630 (47.2) | 685 (38.6) | |
| Yes | 11,621 (47.2) | 799 (41.5) | 5666 (42.9) | 4067 (52.8) | 1089 (61.4) | |
| Household income per capita (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| Lowest | 8310 (33.8) | 753 (39.1) | 4951 (37.5) | 2207 (28.7) | 399 (22.5) | |
| Middle | 9022 (36.7) | 652 (33.9) | 4726 (35.8) | 2965 (38.5) | 679 (38.3) | |
| Highest | 7274 (29.6) | 521 (27.1) | 3532 (26.7) | 2525 (32.8) | 696 (39.2) | |
| Residency (n (%)) | <.0001 | |||||
| Urban | 8185 (33.3) | 690 (35.8) | 4239 (32.1) | 2663 (34.6) | 593 (33.4) | |
| Rural | 16,421 (66.7) | 1236 (64.2) | 8970 (67.9) | 5034 (65.4) | 1181 (66.6) | |
| Region (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| Southwest | 6087 (24.7) | 716 (37.2) | 3546 (26.9) | 1543 (20.1) | 282 (15.9) | |
| Northeast | 4368 (17.8) | 264 (13.7) | 2109 (16.0) | 1541 (20.0) | 454 (25.6) | |
| Central | 8451 (34.4) | 617 (32.0) | 4680 (35.4) | 2618 (34.0) | 536 (30.2) | |
| Coastal | 5700 (23.2) | 329 (17.1) | 2874 (21.8) | 1995 (25.9) | 502 (28.3) | |
| Urban index (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
| Lowest | 8757 (35.6) | 701 (36.4) | 5124 (38.8) | 2468 (32.1) | 464 (26.2) | |
| Middle | 8119 (33.0) | 624 (32.4) | 4128 (31.3) | 2683 (34.9) | 684 (38.6) | |
| Highest | 7730 (31.4) | 601 (31.2) | 3957 (30.0) | 2546 (33.1) | 626 (35.3) | |
| Ever smoked (n (%)) | 0.0013 | |||||
| No | 24,154 (98.2) | 1892 (98.2) | 13,000 (98.4) | 7537 (97.9) | 1725 (97.2) | |
| Yes | 452 (1.8) | 34 (1.8) | 209 (1.6) | 160 (2.1) | 49 (2.8) | |
| Drinking (n (%)) | 0.1498 | |||||
| Never | 22,122 (89.9) | 1755 (91.1) | 11,891 (90.0) | 6883 (89.4) | 1593 (89.8) | |
| Yes | 2484 (10.1) | 171 (8.9) | 1318 (10.0) | 814 (10.6) | 181 (10.2) | |
| Wave (n (%)) | <0.0001 | |||||
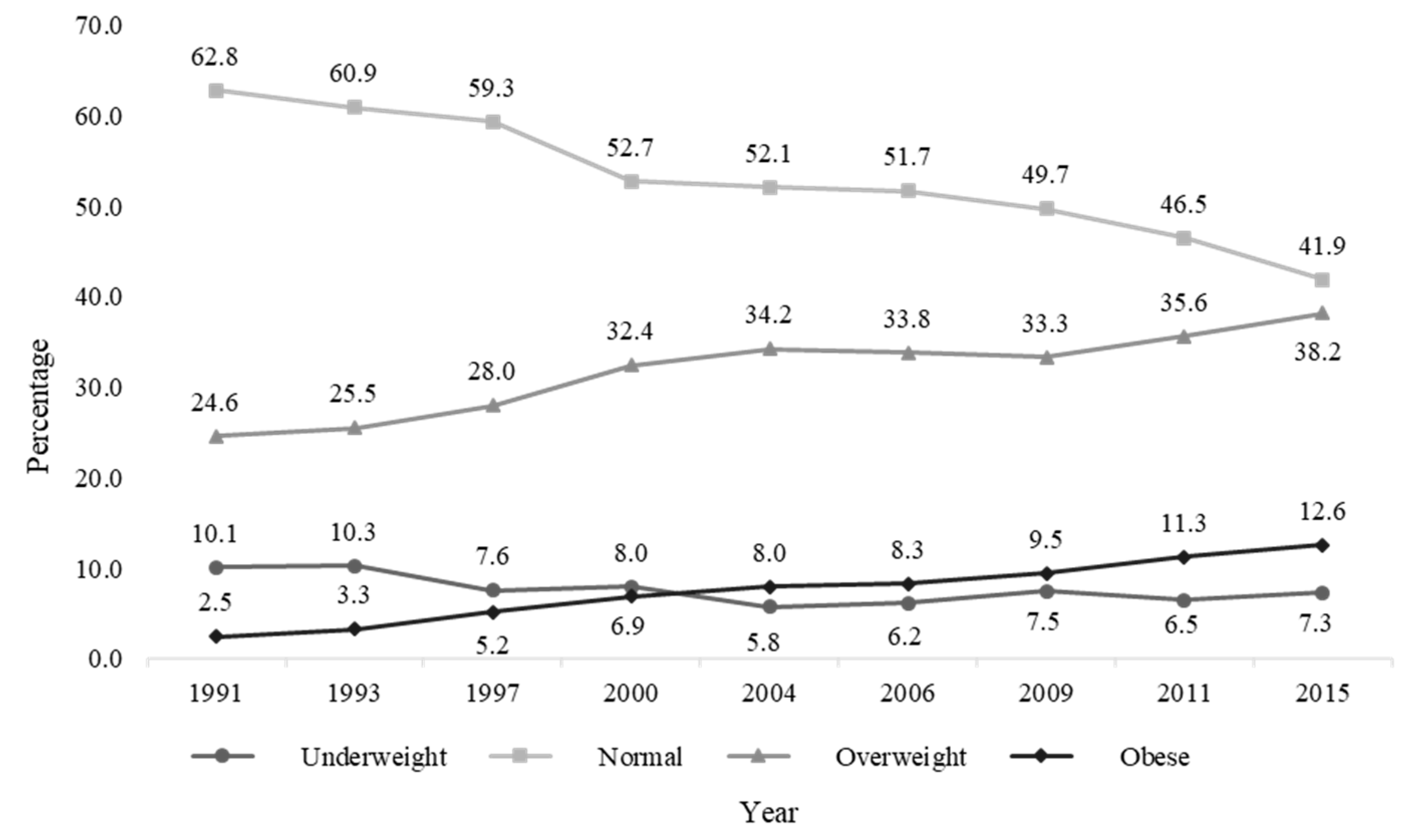
| 1991 | 3298 (13.4) | 334 (17.3) | 2071 (15.7) | 810 (10.5) | 83 (4.7) | |
| 1993 | 3068 (12.5) | 317 (16.5) | 1869 (14.2) | 782 (10.2) | 100 (5.6) | |
| 1997 | 2893 (11.8) | 219 (11.4) | 1714 (13.0) | 809 (10.5) | 151 (8.5) | |
| 2000 | 2939 (11.9) | 235 (12.2) | 1548 (11.7) | 952 (12.4) | 204 (11.5) | |
| 2004 | 2505 (10.2) | 144 (7.5) | 1304 (9.9) | 856 (11.1) | 201 (11.3) | |
| 2006 | 2354 (9.6) | 146 (7.6) | 1217 (9.2) | 796 (10.3) | 195 (11.0) | |
| 2009 | 2324 (9.4) | 174 (9.0) | 1156 (8.8) | 773 (10.0) | 221 (12.5) | |
| 2011 | 3036 (12.3) | 197 (10.2) | 1413 (10.7) | 1082 (14.1) | 344 (19.4) | |
| 2015 | 2189 (8.9) | 160 (8.3) | 917 (6.9) | 837 (10.9) | 275 (15.5) | |
| Variable | BMI Level (Reference: Normal BMI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Overweight | Obesity | ||||
| Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Individual Level | ||||||
| Age (years) | 0.955 (0.947–0.962) | <0.0001 | 1.057 (1.052–1.061) | <0.0001 | 1.074 (1.065–1.083) | <0.0001 |
| Marital status (ref: single) | ||||||
| Married | 0.701 (0.602–0.817) | <0.0001 | 1.238 (1.097–1.398) | 0.0007 | 1.460 (1.108–1.923) | 0.009 |
| Divorced/widowed/separated | 0.828 (0.568–1.208) | 0.34 | 0.991 (0.785–1.250) | 0.92 | 1.656 (1.096–2.504) | 0.02 |
| Education (ref: illiterate or primary) | ||||||
| Primary graduates or junior | 0.947 (0.791–1.133) | 0.53 | 1.024 (0.930–1.127) | 0.58 | 0.863 (0.728–1.023) | 0.09 |
| High school or vocational | 1.056 (0.852–1.309) | 0.57 | 0.755 (0.668–0.854) | <0.0001 | 0.476 (0.380–0.595) | <0.0001 |
| University or above | 1.12 (0.843–1.446) | 0.41 | 0.565 (0.475–0.672) | <0.0001 | 0.278 (0.201–0.385) | <0.0001 |
| Nationality (ref: Han) | ||||||
| Others | 0.906 (0.742–1.107) | 0.33 | 1.050 (0.918–1.200) | 0.46 | 1.039 (0.818–1.321) | 0.75 |
| Medical insurance (ref: no) | ||||||
| Yes | 0.960 (0.829–1.112) | 0.54 | 1.127 (1.033–1.229) | 0.002 | 1.077 (0.920–1.261) | 0.38 |
| Household Income per Capita (Ref: Lowest) | ||||||
| Middle | 0.988 (0.859–1.137) | 0.80 | 1.111 (1.020–1.209) | 0.01 | 1.004 (0.861–1.172) | 0.98 |
| Highest | 1.095 (0.902–1.328) | 0.40 | 1.009 (0.903–1.128) | 0.80 | 0.837 (0.694–1.009) | 0.06 |
| Ever smoked (ref: yes) | ||||||
| Yes | 1.686 (1.144–2.484) | 0.009 | 0.952 (0.760–1.193) | 0.69 | 1.094 (0.772–1.551) | 0.58 |
| Drinking (ref: never) | ||||||
| Yes | 0.901 (0.754–1.076) | 0.27 | 1.011 (0.913–1.120) | 0.82 | 1.070 (0.890–1.287) | 0.53 |
| Community Level and Time Effect | ||||||
| Residency (ref: rural) | ||||||
| Urban | 1.059 (0.885–1.267) | 0.52 | 1.223 (1.072–1.395) | 0.002 | 1.339 (1.027–1.746) | 0.01 |
| Region (ref: southwest) | ||||||
| Central | 0.620 (0.504–0.761) | <0.0001 | 1.334 (1.137–1.566) | 0.0001 | 1.782 (1.277–2.486) | 0.001 |
| Coastal | 0.528 (0.418–0.665) | <0.0001 | 1.598 (1.344–1.900) | <0.0001 | 2.379 (1.669–3.391) | <0.0001 |
| Northeast | 0.642 (0.503–0.819) | 0.0004 | 1.638 (1.362–1.971) | <0.0001 | 2.879 (1.970–4.205) | <0.0001 |
| Urban index (ref: lowest) | ||||||
| Middle | 1.072 (0.920–1.249) | 0.42 | 1.185 (1.075–1.305) | 0.001 | 1.404 (1.17–1.686) | <0.0001 |
| Highest | 1.144 (0.923–1.418) | 0.25 | 1.029 (0.897–1.182) | 0.65 | 1.137 (0.877–1.473) | 0.35 |
| Wave (ref: 1991) | ||||||
| 1993 | 1.058 (0.891–1.257) | 0.40 | 1.011 (0.894–1.143) | 0.84 | 1.196 (0.888–1.613) | 0.34 |
| 1997 | 0.825 (0.673–1.010) | 0.06 | 1.061 (0.929–1.211) | 0.39 | 1.973 (1.472–2.644) | <0.0001 |
| 2000 | 0.999 (0.811–1.231) | 1.00 | 1.364 (1.192–1.561) | <0.0001 | 2.891 (2.169–3.854) | <0.0001 |
| 2004 | 0.842 (0.660–1.074) | 0.18 | 1.293 (1.120–1.493) | 0.000 | 2.995 (2.220–4.041) | <0.0001 |
| 2006 | 0.929 (0.727–1.189) | 0.61 | 1.236 (1.066–1.433) | 0.005 | 3.105 (2.288–4.213) | <0.0001 |
| 2009 | 1.199 (0.926–1.553) | 0.16 | 1.169 (0.994–1.375) | 0.06 | 3.625 (2.627–5.001) | <0.0001 |
| 2011 | 1.101 (0.843–1.437) | 0.46 | 1.443 (1.227–1.696) | <0.0001 | 5.256 (3.820–7.230) | <0.0001 |
| 2015 | 1.319 (0.991–1.756) | 0.07 | 1.815 (1.523–2.164) | <0.0001 | 7.349 (5.247–10.295) | <0.0001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Fawzi, W.; Huang, Y. Double Burden of Malnutrition among Chinese Women of Reproductive Age and Their Social Determinants. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103102
Song J, Zhang J, Fawzi W, Huang Y. Double Burden of Malnutrition among Chinese Women of Reproductive Age and Their Social Determinants. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103102
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jingqi, Ji Zhang, Wafaie Fawzi, and Yangmu Huang. 2020. "Double Burden of Malnutrition among Chinese Women of Reproductive Age and Their Social Determinants" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103102
APA StyleSong, J., Zhang, J., Fawzi, W., & Huang, Y. (2020). Double Burden of Malnutrition among Chinese Women of Reproductive Age and Their Social Determinants. Nutrients, 12(10), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103102






