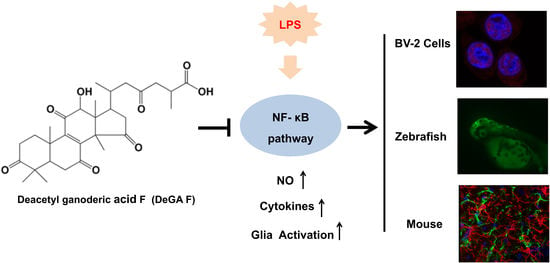
Deacetyl Ganoderic Acid F Inhibits LPS-Induced Neural Inflammation via NF-κB Pathway Both In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Animal Maintenance and Administration
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Nitrite Production Determination
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
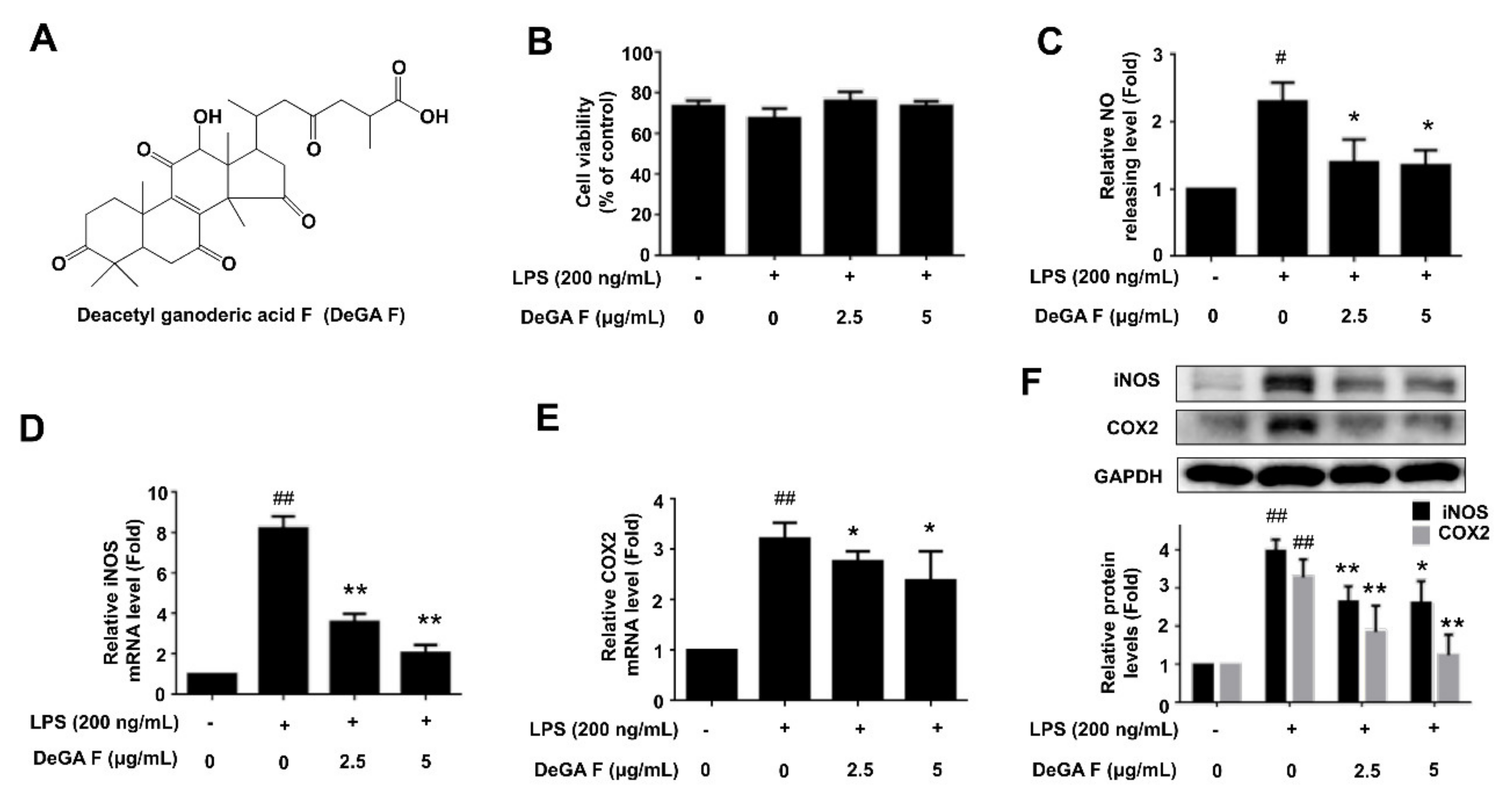
3.1. DeGA F Inhibited NO Production and iNOS Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Cells
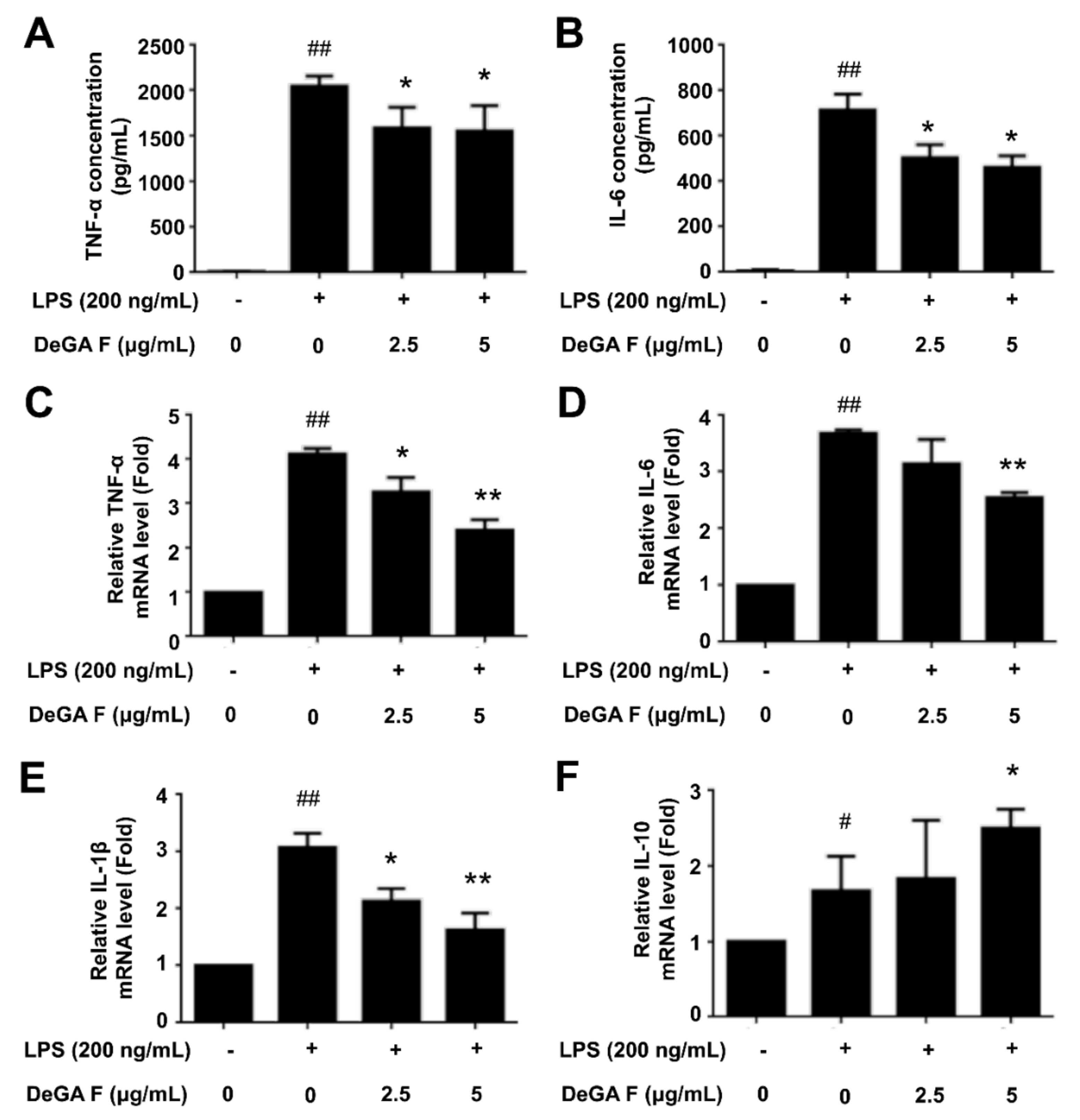
3.2. DeGA F Inhibited LPS-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Release in BV-2 Cells
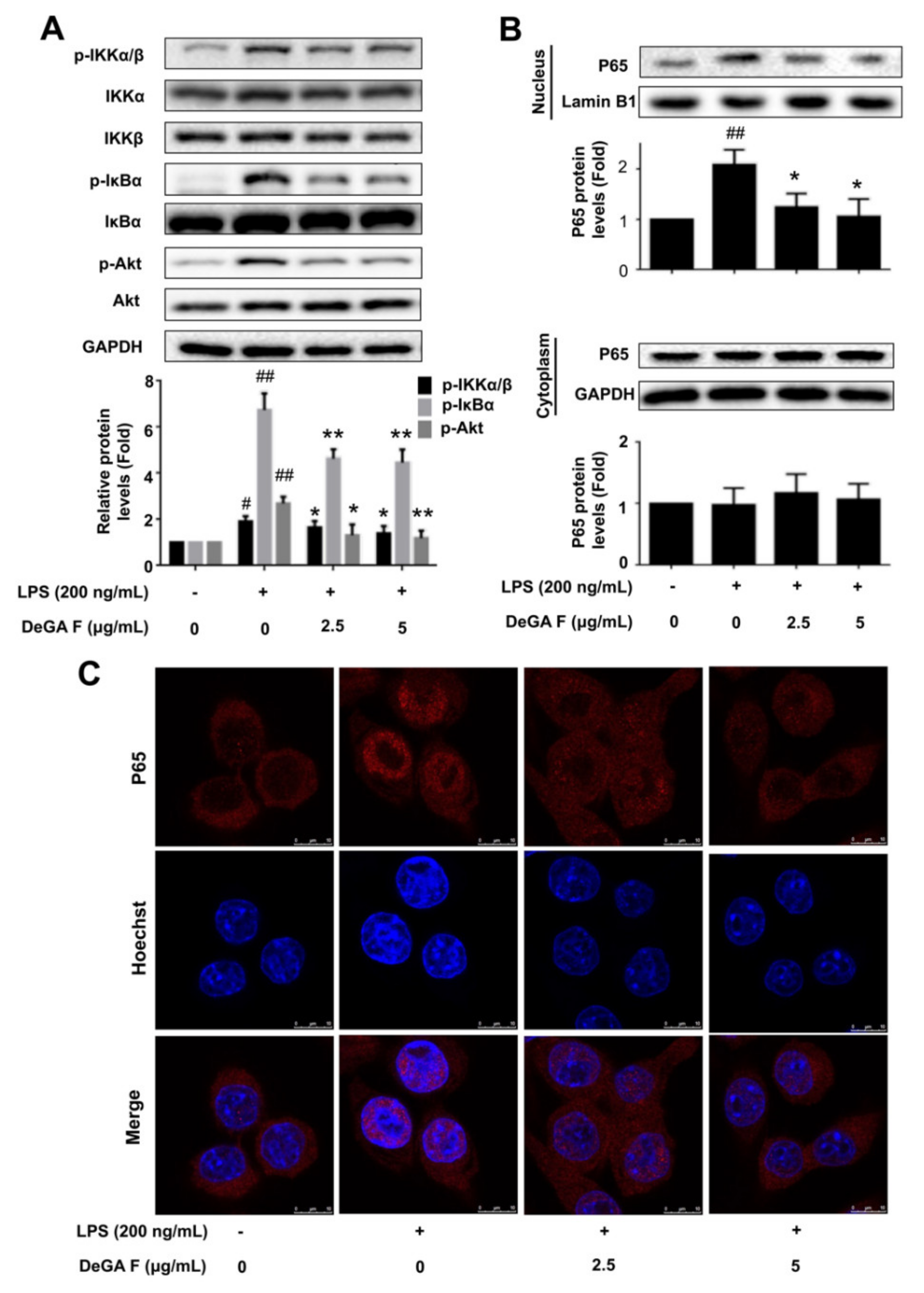
3.3. DeGA F Suppressed LPS-Triggered Inflammatory Response via NF-κB Pathway
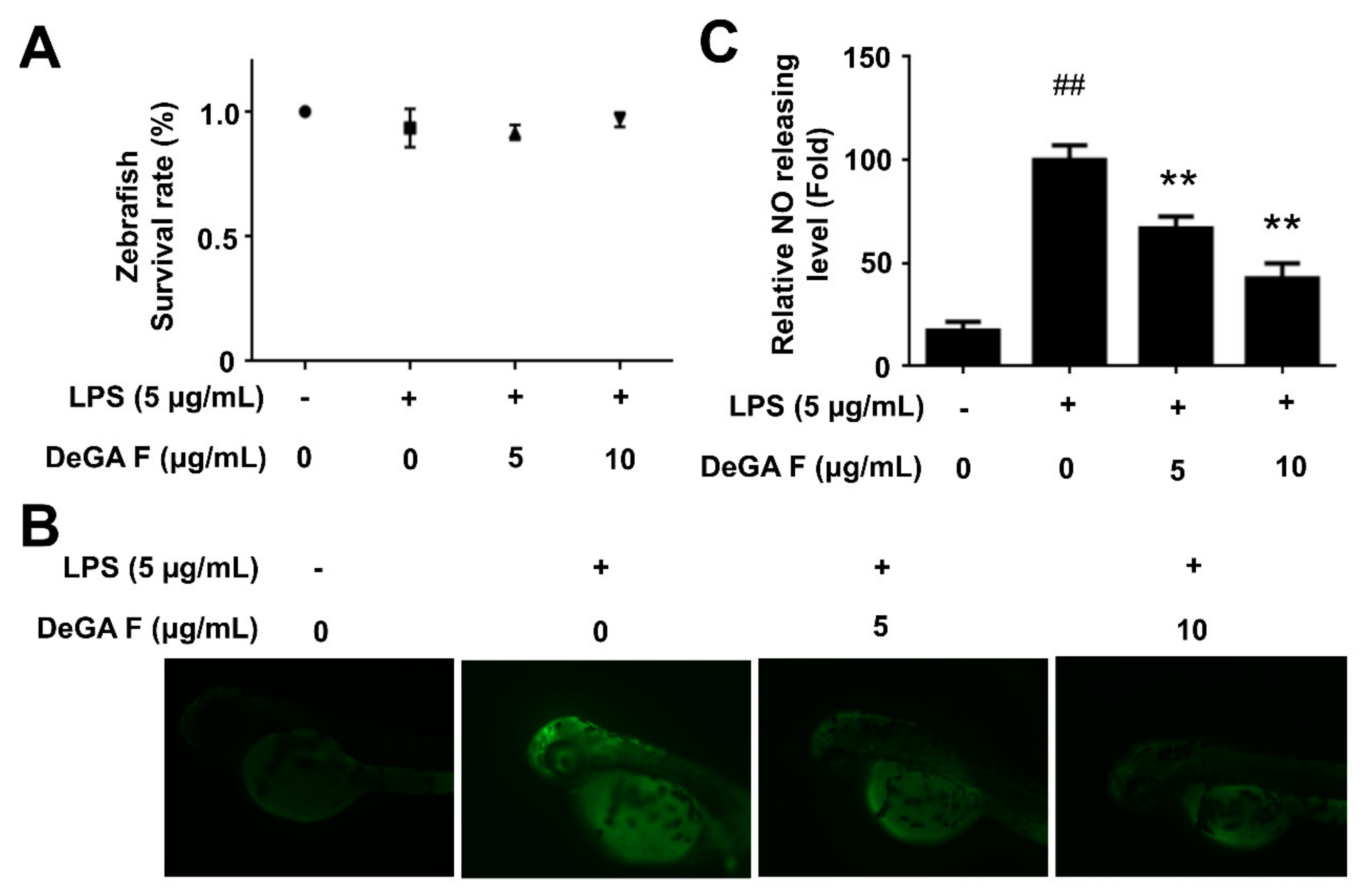
3.4. DeGA F Suppressed NO Production in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish Model
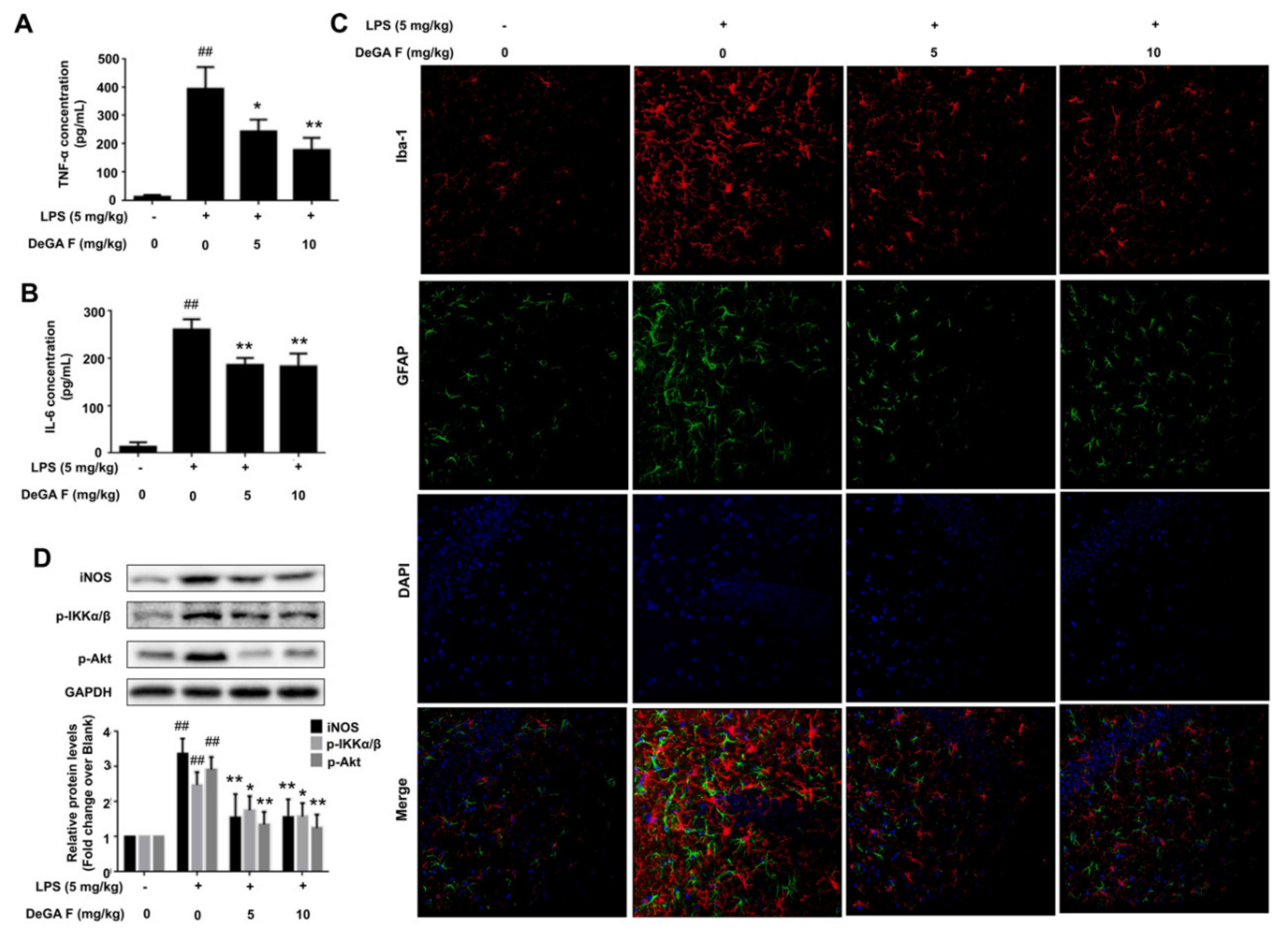
3.5. DeGA F Attenuated LPS-Triggered Inflammatory Response in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.; Lee, W.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, I.K.; Yun, B.S.; Rhee, M.; Cho, J. Src kinase-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of davallialactone from Inonotus xeranticus in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264. 7 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawelec, G.; Goldeck, D.; Derhovanessian, E. Inflammation, ageing and chronic disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 29, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, T.R.; Marsh, S.E.; Stevens, B. Immune Signaling in Neurodegeneration. Immunity 2019, 50, 955–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, B.; Puntambekar, S.S.; Carson, M.J. Microglia and the control of autoreactive T cell responses. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Henn, A.; Lund, S.; Hedtjärn, M.; Schrattenholz, A.; Pörzgen, P.; Leist, M. The suitability of BV2 cells as alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for animal experiments examining brain inflammation. ALTEX Altern. Anim. Exp. 2009, 26, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norden, D.M.; Trojanowski, P.J.; Villanueva, E.; Navarro, E.; Godbout, J.P. Sequential Activation of Microglia and Astrocyte Cytokine Expression Precedes Increased Iba-1 or GFAP Immunoreactivity Following Systemic Immune Challenge. Glia 2016, 64, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Gottfried-Blackmore, A.C.; McEwen, B.S.; Bulloch, K. Microglia derived from aging mice exhibit an altered inflammatory profile. Glia 2007, 55, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, C.T.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Brain Inflammation and Adult Neurogenesis: The Dual Role of Microglia. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cor, D.; Knez, Z.; Hrncic, M.K. Antitumour, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antiacetylcholinesterase Effect of Ganoderma Lucidum Terpenoids and Polysaccharides: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, N.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Zi, J.; Zhang, S.; Dunkin, D.; Busse, P.; Weir, D.; Tversky, J. Ganoderic acid C1 isolated from the anti-asthma formula, ASHMI™ suppresses TNF-α production by mouse macrophages and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from asthma patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 27, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudhgaonkar, S.; Thyagarajan, A.; Sliva, D. Suppression of the inflammatory response by triterpenes isolated from the mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Jia, W.; Pan, Y. Immunomodulation of RAW264. 7 macrophages by GLIS, a proteopolysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boh, B.; Berovic, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhi-Bin, L. Ganoderma lucidum and its pharmaceutically active compounds. Biotechnol. Ann. Rev. 2007, 13, 265–301. [Google Scholar]
- Komoda, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Ishihara, S.; Uchida, M.; Kohda, H.; Yamasaki, K. Structures of new terpenoid constituents of Ganoderma lucidum (Fr.) Karst (Polyporaceae). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 4829–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.X.; McElhaney, J.E.; Walston, J.D.; Xie, D.; Fedarko, N.S.; Kuchel, G.A. ELISA and multiplex technologies for cytokine measurement in inflammation and aging research. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2008, 63, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, C.I.; Jee, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohyd. Polym. 2013, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, L.; Lee, J.H.; Yumnam, S.; Ji, E.; Kim, S.Y. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sulforaphane on LPS-Activated Microglia Potentially through JNK/AP-1/NF-kappa B Inhibition and Nrf2/HO-1 Activation. Cells 2019, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarouchas, T.M.; Wehner, D.; Cavone, L.; Munir, T.; Keatinge, M.; Lambertus, M.; Underhill, A.; Barrett, T.; Kassapis, E.; Ogryzko, N. Dynamic control of proinflammatory cytokines Il-1beta and Tnf-alpha by macrophages in zebrafish spinal cord regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Ryu, S.J.; Lee, B.Y. Caffeine prevents LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells and zebrafish. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 248, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, B.; Bowman, T.V.; Zon, L.; Figueras, A. LPS response and tolerance in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immun. 2009, 26, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.M.; Akerlund, J.; Mittge, E.; Guillemin, K. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase detoxifies lipopolysaccharide and prevents inflammation in zebrafish in response to the gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.A.; Ao, Y.; Sofroniew, M.V. Heterogeneity of reactive astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 565, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerbai, F.; Lana, D.; Nosi, D.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Zecchi, S.; Brothers, H.M.; Wenk, G.L.; Giovannini, M.G. The Neuron-Astrocyte-Microglia Triad in Normal Brain Ageing and in a Model of Neuroinflammation in the Rat Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Larke, L.E.C.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Munch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, S.; Peferoen, L.A.; Vogel, D.Y.; Breur, M.; Valk, P.; Baker, D.; Vannoort, J.M. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases—An update. Immunology 2014, 14, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J.; Nutma, E.; Vandervalk, P.; Amor, S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2018, 154, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniglia, L.; Ramirez, D.; Durand, D.; Saba, J.; Turati, J.; Caruso, C.; Scimonelli, T.N.; Lasaga, M. Neuropeptides and Microglial Activation in Inflammation, Pain, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5048616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlackhansingh, A.F.; Brooks, D.J.; Greenwood, R.J.; Bose, S.K.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Kinnunen, K.M.; Gentleman, S.; Heckemann, R.A.; Gunanayagam, K.; Gelosa, G. Inflammation after Trauma: Microglial Activation and Traumatic Brain Injury. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktan, F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.K.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.G. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-alpha and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Inflammation 2010: New Adventures of an Old Flame. Cell 2010, 140, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Yoon, K.Y.; Lee, O.H.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, B.Y. Oleuropein Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW 264.7 Cell and Zebrafish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappa B signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.F.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, W.Y. Proteomic response of LAP-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages to the anti-inflammatory property of fungal ergosterol. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, H.; Davies, A.M. Regulation of neural process growth, elaboration and structural plasticity by NF-kappa B. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, G.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of β-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin in BV2 microglia are mediated through suppression of the PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway and activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Shi, M. Polysaccharides from Nostoc commune Vaucher activate macrophages via NF-κB and AKT/JNK1/2 pathways to suppress colorectal cancer growth in vivo. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4269–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yuan, C.; Wang, G.; Luo, J.; Ma, H.; Xu, L.; Mu, Y.; Li, Y.; Seeram, N.P.; Huang, X. Urolithins attenuate LPS-induced neuroinflammation in BV2Microglia via MAPK, Akt, and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primer Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F | GGTGAAGGTCGGTGTGAACG |
| R | CTCGCTCCTGGAAGATGGTG | |
| iNOS | F | GGCTGTCAGAGCCTCGTGGCTTTGG |
| R | CCCTTCCGAAGTTTCTGGCAGCAGC | |
| COX2 | F | TTGAAGACCAGGAGTACAGC |
| R | GGTACAGTTCCATGACATCG | |
| TNF-α | F | GGCAGGTCTACTTTGGAGTCATTGC |
| R | ACATTCGAGGCTCCAGTGAATTCGG | |
| IL-6 | F | CCACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGCTT |
| R | CCAGCTTATCTGTTAGGAGA | |
| IL-1β | F | GGCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACTG |
| R | CCATTGAGGTGGAGAGCTTTCAGC | |
| IL-10 | F | ATAACTGCACCCACTTCCCA |
| R | GGGCATCACTTCTACCAGGT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Li, P. Deacetyl Ganoderic Acid F Inhibits LPS-Induced Neural Inflammation via NF-κB Pathway Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients 2020, 12, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010085
Sheng F, Zhang L, Wang S, Yang L, Li P. Deacetyl Ganoderic Acid F Inhibits LPS-Induced Neural Inflammation via NF-κB Pathway Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients. 2020; 12(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Feiya, Lele Zhang, Songsong Wang, Lele Yang, and Peng Li. 2020. "Deacetyl Ganoderic Acid F Inhibits LPS-Induced Neural Inflammation via NF-κB Pathway Both In Vitro and In Vivo" Nutrients 12, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010085
APA StyleSheng, F., Zhang, L., Wang, S., Yang, L., & Li, P. (2020). Deacetyl Ganoderic Acid F Inhibits LPS-Induced Neural Inflammation via NF-κB Pathway Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients, 12(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010085