The Effect of Donor Human Milk Fortification on The Adhesion of Probiotics In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Probiotic Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Collection and Pasteurization of Human Milk
2.3. Human Intestinal Mucus Extracted from Infant Feces
2.4. In Vitro Adhesion Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Adhesion Assay
2.5.2. Viability Assay
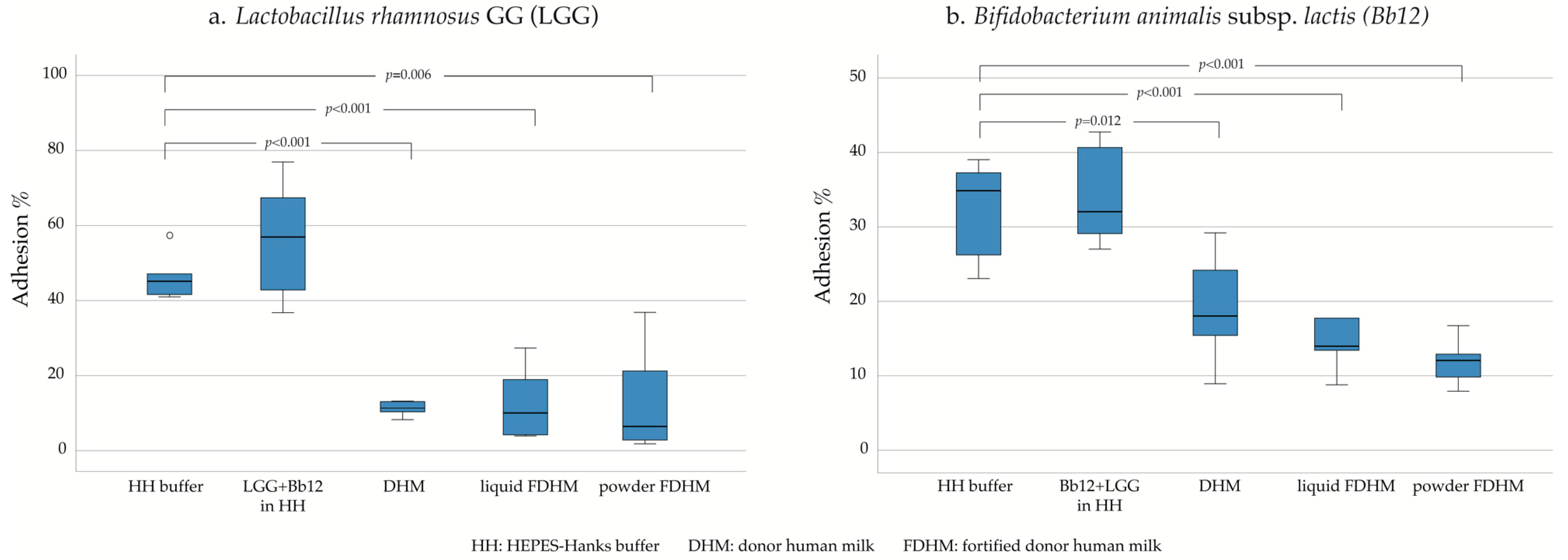
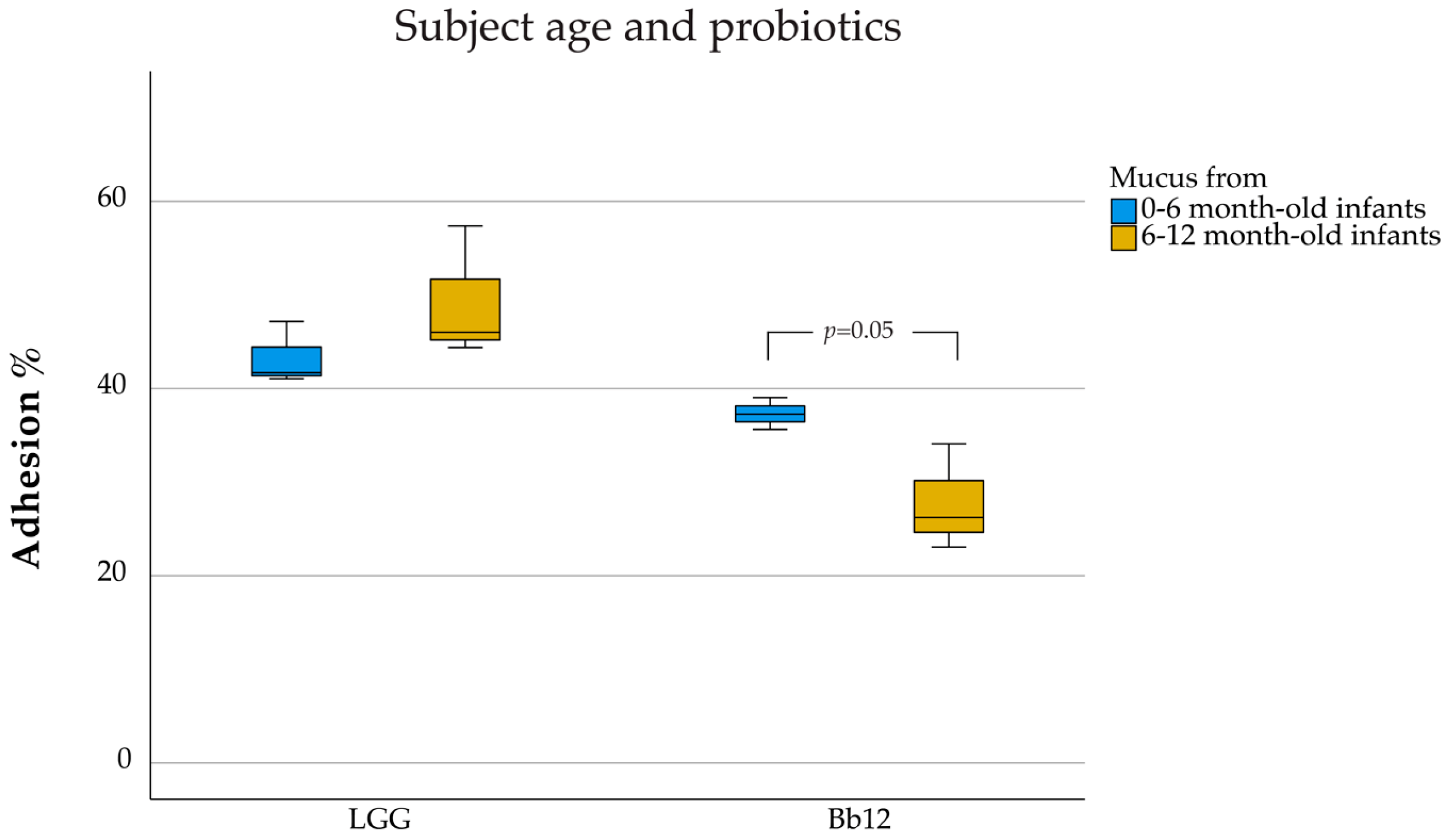
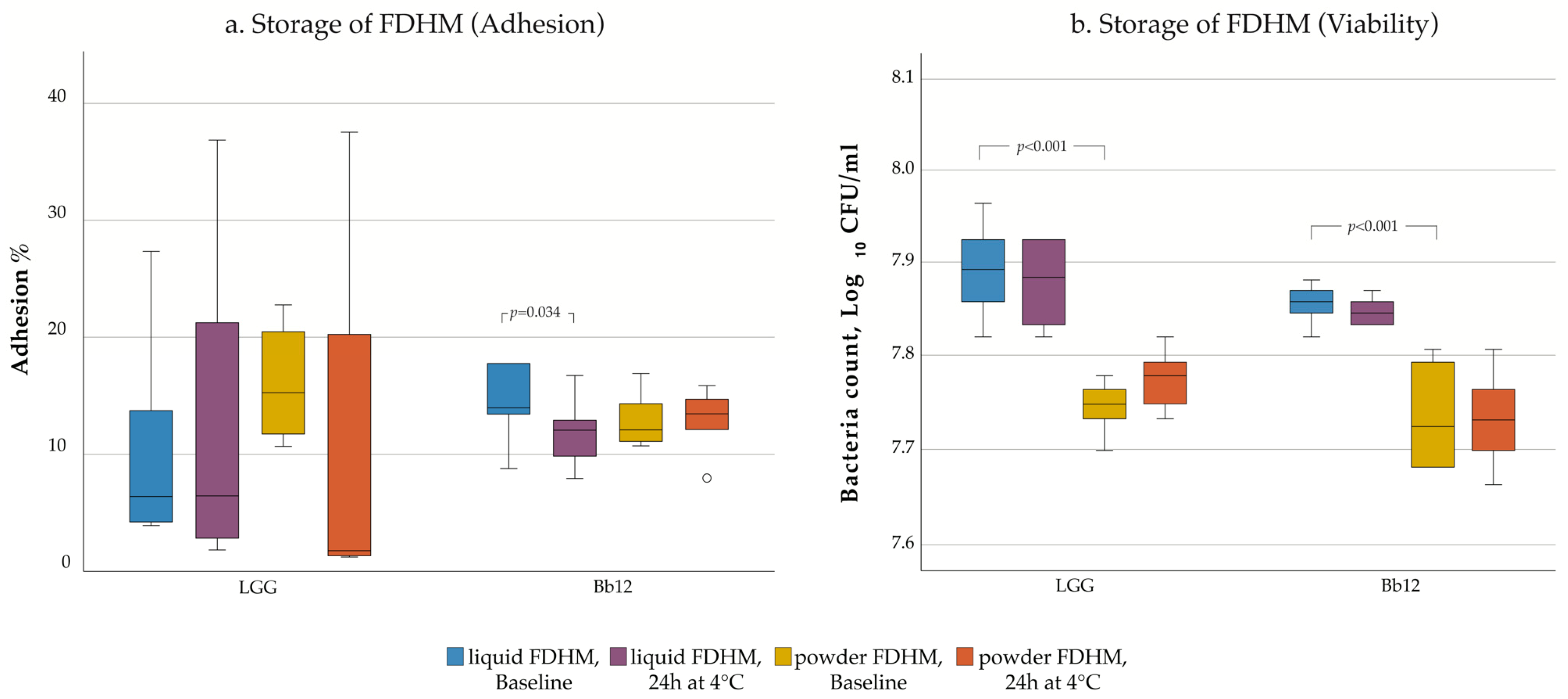
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Strain Dependence of the Adhesion Properties
4.2. Role of DHM on the Adhesion of Probiotics
4.3. Age Dependency of the Adhesion Ability of Probiotics to Intestinal Mucus
4.4. Influence of Storage
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN IGME). Levels & Trends in Child Mortality: Report 2019. In Estimates Developed by the United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation; United Nations Children’s Fund: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, M.C.; Msall, M.E.; Miller, R.J. 17-year outcome of preterm infants with diverse neonatal morbidities: Part 1, impact on physical, neurological, and psychological health status. J. Spec. Pediatr. Nurs. 2012, 17, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K.; Herrmann, K.R. The cost of using donor human milk in the NICU to achieve exclusively human milk feeding through 32 weeks postmenstrual age. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gephart, S.M.; Newnam, K.M. Closing the gap between recommended and actual human milk use for fragile infants: What will it take to overcome disparities? Clin. Perinatol. 2019, 46, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, E.E. Breast-milk fortification. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.V.; Embleton, N.D.; Harding, J.E.; McGuire, W. Multi-nutrient fortification of human milk for preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: Commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, J.; Way, M.; Koorts, P.J.; Davies, M.W. The availability of probiotics and donor human milk is associated with improved survival in very preterm infants. World J. Pediatr. 2018, 14, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Adhesion mechanisms mediated by probiotics and prebiotics and their potential impact on human health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Cernada, M.; Baüerl, C.; Vento, M.; Pérez-Martínez, G. Microbial ecology and host-microbiota interactions during early life stages. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin-Nun, A.; Bromiker, R.; Wilschanski, M.; Kaplan, M.; Rudensky, B.; Caplan, M.; Hammerman, C. Oral probiotics prevent necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight neonates. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirjavainen, P.V.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.J. The ability of probiotic bacteria to bind to human intestinal mucus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 167, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Grönlund, M.-M.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.J. Adhesion of probiotic micro-organisms to intestinal mucus. Int. Dairy J. 1999, 9, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntunen, M.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.J.; Isolauri, E. Adherence of probiotic bacteria to human intestinal mucus in healthy infants and during rotavirus infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbach, S.L.; Goldin, B.R. Lactobacillus Strains and Methods of Selection. U.S. Patent 4,839,281, 13 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ruan, H.; Zhu, D.; He, G. Isolation and characterisation of an oxygen, acid and bile resistant Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Qq08. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Gueimonde, M.; Sanz, Y.; Salminen, S. Adhesion properties and competitive pathogen exclusion ability of bifidobacteria with acquired acid resistance. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankainen, M.; Paulin, L.; Tynkkynen, S.; von Ossowski, I.; Reunanen, J.; Partanen, P.; Satokari, R.; Vesterlund, S.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Lebeer, S.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals pili containing a human-mucus binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17193–17198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybesma, W.; Molenaar, D.; van IJcken, W.; Venema, K.; Kort, R. Genome instability in Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, O.; Svensson, B.; Viborg, A.H.; Stuer-Lauridsen, B.; Jacobsen, S. The extracellular proteome of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 reveals proteins with putative roles in probiotic effects. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Isolauri, E.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Ölkkö, S.T.; Salminen, S.J. The mucus binding of Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 is enhanced in the presence of Lactobacillus GG and Lact. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 30, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, J.; Burgain, J.; Francius, G.; El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Beaussart, A.; Scher, J.; Gaiani, C. Adhesion of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG surface biomolecules to milk proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, D.C.; Ecroyd, H.; Carver, J.A.; Holt, C. Casein structures in the context of unfolded proteins. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 46, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, P. Changes in milk fat globule membrane proteome after pasteurization in human, bovine and caprine species. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trégoat, V.; Montagne, P.; Béné, M.-C.; Faure, G. Changes in the mannan binding lectin (MBL) concentration in human milk during lactation. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2002, 16, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossey, V.; Jeurissen, A.; Bossuyt, X.; Schuermans, A. Effect of pasteurisation on the mannose-binding lectin activity and the concentration of soluble CD14 in human milk. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Larsson, J.M.H.; Hansson, G.C. The two mucus layers of colon are organized by the MUC2 mucin, whereas the outer layer is a legislator of host–microbial interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4659–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Leir, S.-H.; Sutton-Smith, M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Harris, A. N-Glycosylation of the MUC1 mucin in epithelial cells and secretions. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Newburg, D.S. Human milk glycoproteins protect infants against human pathogens. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, M.I.; Imholz, N.C.E.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Balzarini, J.; Damme, E.J.M.V.; Schols, D.; Vanderleyden, J.; Lebeer, S. Lectin-Like Molecules of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Inhibit Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella Biofilm Formation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, S.J.; Haskard, C.A.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.J.; Ahokas, J.T. Binding of aflatoxin B1 to cell wall components of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBouder, E.; Rey-Nores, J.E.; Rushmere, N.K.; Grigorov, M.; Lawn, S.D.; Affolter, M.; Griffin, G.E.; Ferrara, P.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Morgan, B.P.; et al. Soluble forms of Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 capable of modulating TLR2 signaling are present in human plasma and breast milk. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6680–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waard, M.; Mank, E.; van Dijk, K.; Schoonderwoerd, A.; van Goudoever, J.B. Holder-pasteurized human donor milk: How long can it be preserved? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cress, C.; Paxson, C.L., Jr. Breast milk macrophages. Pediatr. Res. 1977, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gibbs, J.H.; Fisher, C.; Bhattacharya, S.; Goddard, P.; Baum, J.D. Drip breast milk: Its composition, collection and pasteurization. Early Hum. Dev. 1977, 1, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkstén, B.; Burman, L.G.; De Château, P.; Fredrikzon, B.; Gothefors, L.; Hernell, O. Collecting and banking human milk: To heat or not to heat? Br. Med. J. 1980, 281, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas García, C.E.; Petrova, M.; Claes, I.J.J.; De Boeck, I.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Dilissen, E.; von Ossowski, I.; Palva, A.; Bullens, D.M.; Vanderleyden, J.; et al. Piliation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Promotes Adhesion, Phagocytosis, and Cytokine Modulation in Macrophages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.; Coppa, G.V.; Giuliani, F.; Coscia, A.; Gabrielli, O.; Sabatino, G.; Sgarrella, M.; Testa, T.; Zampini, L.; Fabris, C. Effects of holder pasteurization on human milk oligosaccharides. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2008, 21, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongaram, T.; Hoeflinger, J.L.; Chow, J.; Miller, M.J. Human milk oligosaccharide consumption by probiotic and human-associated bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7825–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, A.; Barboza, M.; Sonnenburg, E.D.; Pudlo, N.; Martens, E.C.; Desai, P.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Weimer, B.C.; Mills, D.A.; German, J.B.; et al. Bacteroides in the infant gut consume milk oligosaccharides via mucus-utilization pathways. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, J.E.; Yebra, M.J.; Monedero, V. An l-fucose operon in the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is involved in adaptation to gastrointestinal conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3880–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.W.; Simpson, J.B.; Roach, J.; Bruno-Barcena, J.M.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A. Prebiotics for lactose intolerance: Variability in galacto-oligosaccharide utilization by intestinal Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankaanpää, P.E.; Salminen, S.J.; Isolauri, E.; Lee, Y.K. The influence of polyunsaturated fatty acids on probiotic growth and adhesion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 194, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine and the Committee on Nutritional Status during Pregnancy and Lactation. Milk Volume. In Nutrition during Lactation; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Koletzko, B. Human milk lipids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Dorschner, R.A.; Stern, L.J.; Lin, K.H.; Gallo, R.L. Expression and secretion of cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides in murine mammary glands and human milk. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baricelli, J.; Rocafull, M.A.; Vázquez, D.; Bastidas, B.; Báez-Ramirez, E.; Thomas, L.E. β-defensin-2 in breast milk displays a broad antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria. J. Pediatr. 2015, 91, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, T.J.; Ryley, H.C.; Neale, L.M.; Dodge, J.A.; Lewarne, V.M. Effect of storage and heat on antimicrobial proteins in human milk. Arch. Dis. Child. 1978, 53, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, M.E.; Han, V.E.; Harris, D.A.; Baum, J.D. Short-time low-temperature pasteurisation of human milk. Early Hum. Dev. 1982, 7, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viazis, S.; Farkas, B.E.; Allen, J.C. Effects of high-pressure processing on immunoglobulin A and lysozyme activity in human milk. J. Hum. Lact. 2007, 23, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Tölkkö, S.; Salminen, S. The effect of digestive enzymes on the adhesion of probiotic bacteria in vitro. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Braeken, K.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Perea Vélez, M.; Lebeer, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; Hols, P. Flow cytometric testing of green fluorescent protein-tagged Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG for response to defensins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4923–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeer, S.; Claes, I.J.J.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Vanderleyden, J.; Keersmaecker, S.C.J.D. Exopolysaccharides of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG form a protective shield against innate immune factors in the intestine. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-F.; Tian, F.; Cao, R.-M.; Li, J.; Wu, S.-M.; Guo, X.-K.; Chen, T.-X. Antimicrobial activity of human β-defensins against lactic acid bacteria. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2164–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felgentreff, K.; Beisswenger, C.; Griese, M.; Gulder, T.; Bringmann, G.; Bals, R. The antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin interacts with airway mucus. Peptides 2006, 27, 3100–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainulainen, V.; Loimaranta, V.; Pekkala, A.; Edelman, S.; Antikainen, J.; Kylväjä, R.; Laaksonen, M.; Laakkonen, L.; Finne, J.; Korhonen, T.K. Glutamine synthetase and glucose-6-phosphate isomerase are adhesive moonlighting proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus released by epithelial cathelicidin LL-37. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.H.; Camesano, T.A. The Effects of Centrifugation and Filtration as Pre-Treatments in Bacterial Retention Studies. Available online: https://www.jyi.org/2005-june/2005/6/8/the-effects-of-centrifugation-and-filtration-as-pre-treatments-in-bacterial-retention-studies (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Lebeer, S.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Francius, G.; Schoofs, G.; Lambrichts, I.; Dufrêne, Y.; Vanderleyden, J.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.J. Identification of a gene cluster for the biosynthesis of a long, galactose-rich exopolysaccharide in Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and functional analysis of the priming glycosyltransferase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 3554–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleya, S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Solís, G.; Salminen, S.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Gueimonde, M. Characterization and in vitro properties of potentially probiotic Bifidobacterium strains isolated from breast-milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 149, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Isolauri, E.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Salminen, S.J. Adhesion of four Bifidobacterium strains to human intestinal mucus from subjects in different age groups. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 172, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassell, M.L.V.; Miller, M.J. Lactobacillus adhesion to mucus. Nutrients 2011, 3, 613–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtvedt, A.-C.; Carlstedt-Duke, B.; Midtvedt, T. Establishment of a mucin-degrading intestinal microflora during the first two years of human life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1994, 18, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laparra, J.M.; Sanz, Y. Comparison of in vitro models to study bacterial adhesion to the intestinal epithelium. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesterlund, S.; Paltta, J.; Karp, M.; Ouwehand, A.C. Measurement of bacterial adhesion—In vitro evaluation of different methods. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 60, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantziari, A.; Aakko, J.; Kumar, H.; Tölkkö, S.; du Toit, E.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Rautava, S. The impact of storage conditions on the stability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bb12 in human milk. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Alander, M.; von Wright, A.; Vuopio-Varkila, J.; Marteau, P. The survival of and cytokine induction by lactic acid bacteria after passage through a gastrointestinal model. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1999, 10, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mantziari, A.; Tölkkö, S.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.; Rautava, S. The Effect of Donor Human Milk Fortification on The Adhesion of Probiotics In Vitro. Nutrients 2020, 12, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010182
Mantziari A, Tölkkö S, Ouwehand AC, Löyttyniemi E, Isolauri E, Salminen S, Rautava S. The Effect of Donor Human Milk Fortification on The Adhesion of Probiotics In Vitro. Nutrients. 2020; 12(1):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010182
Chicago/Turabian StyleMantziari, Anastasia, Satu Tölkkö, Artur C. Ouwehand, Eliisa Löyttyniemi, Erika Isolauri, Seppo Salminen, and Samuli Rautava. 2020. "The Effect of Donor Human Milk Fortification on The Adhesion of Probiotics In Vitro" Nutrients 12, no. 1: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010182
APA StyleMantziari, A., Tölkkö, S., Ouwehand, A. C., Löyttyniemi, E., Isolauri, E., Salminen, S., & Rautava, S. (2020). The Effect of Donor Human Milk Fortification on The Adhesion of Probiotics In Vitro. Nutrients, 12(1), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010182




