Comparing the Effect of Folic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Delaying Dialysis Initiation in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
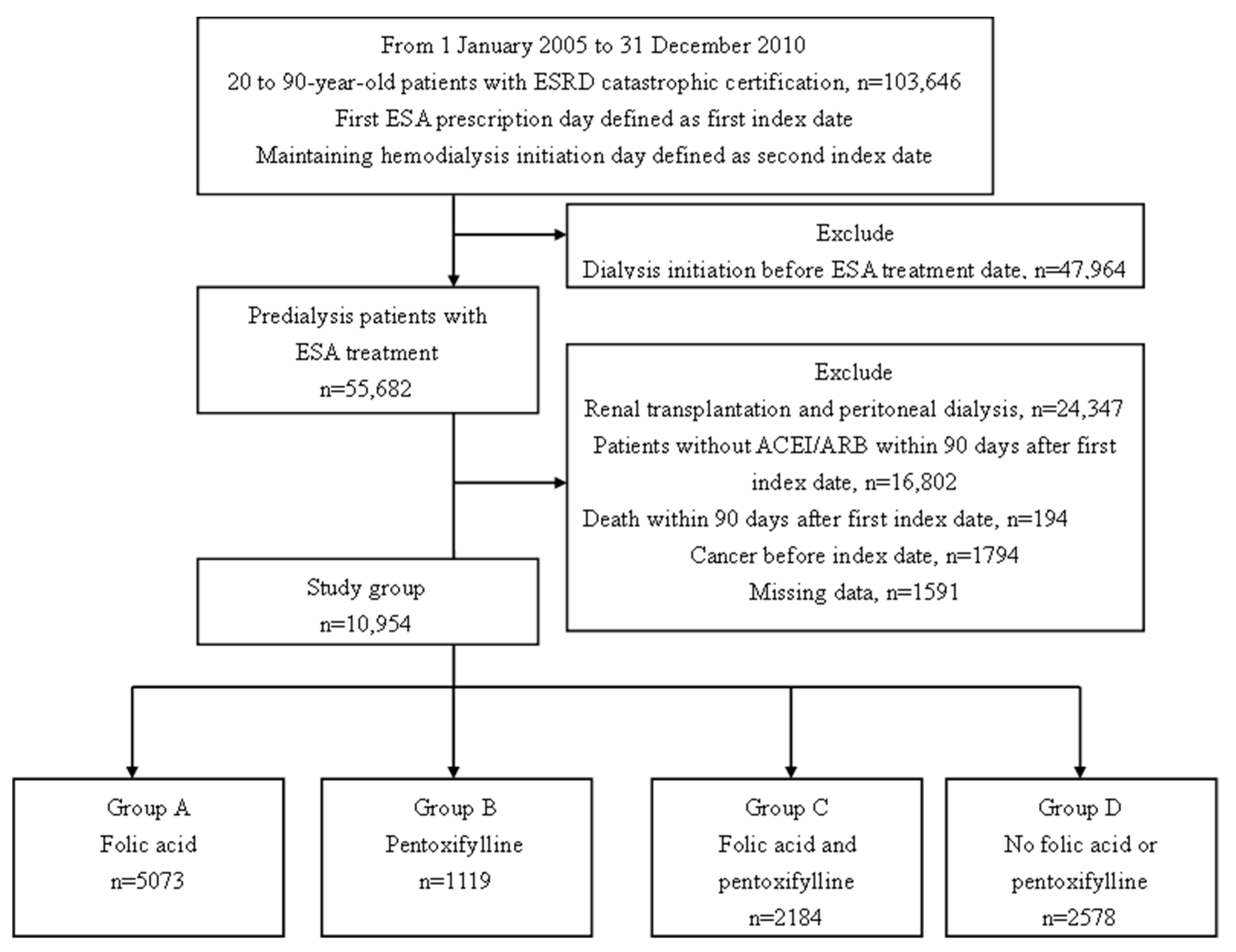
2.2. Study Design and Population
2.3. Statistical Analysis
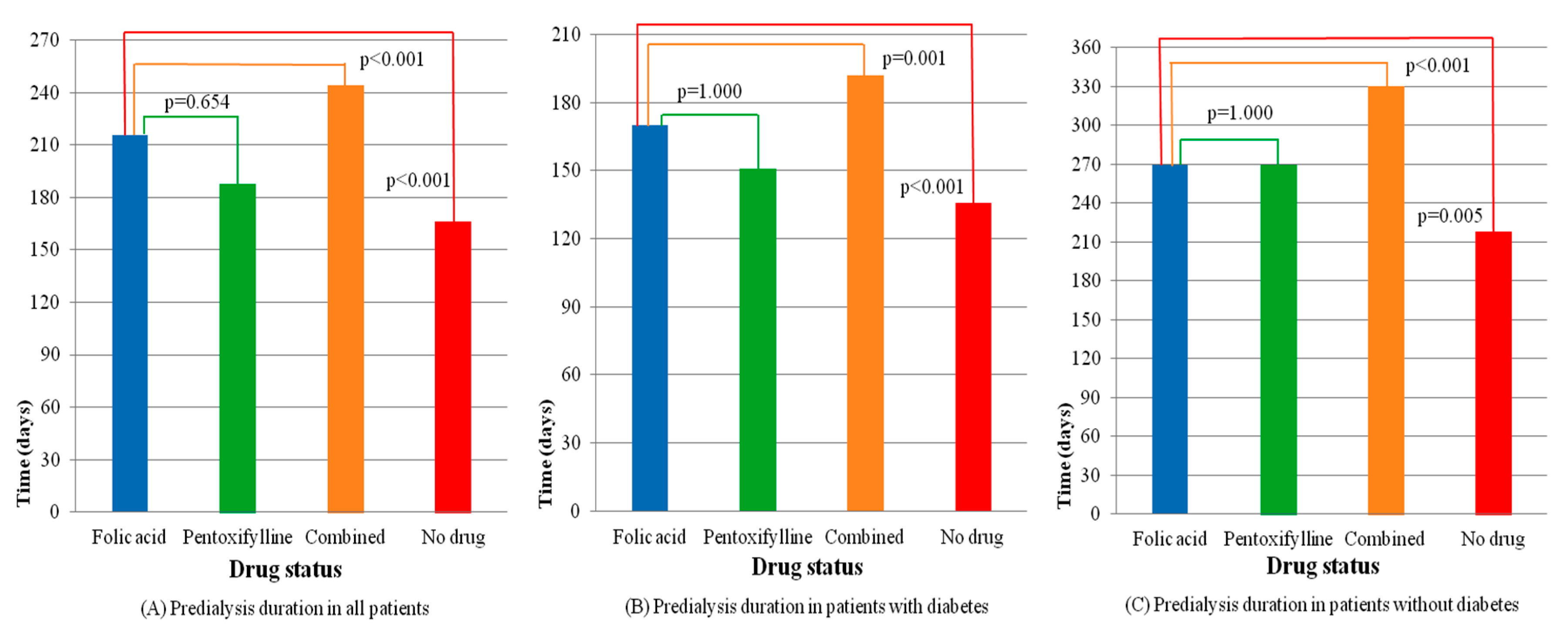
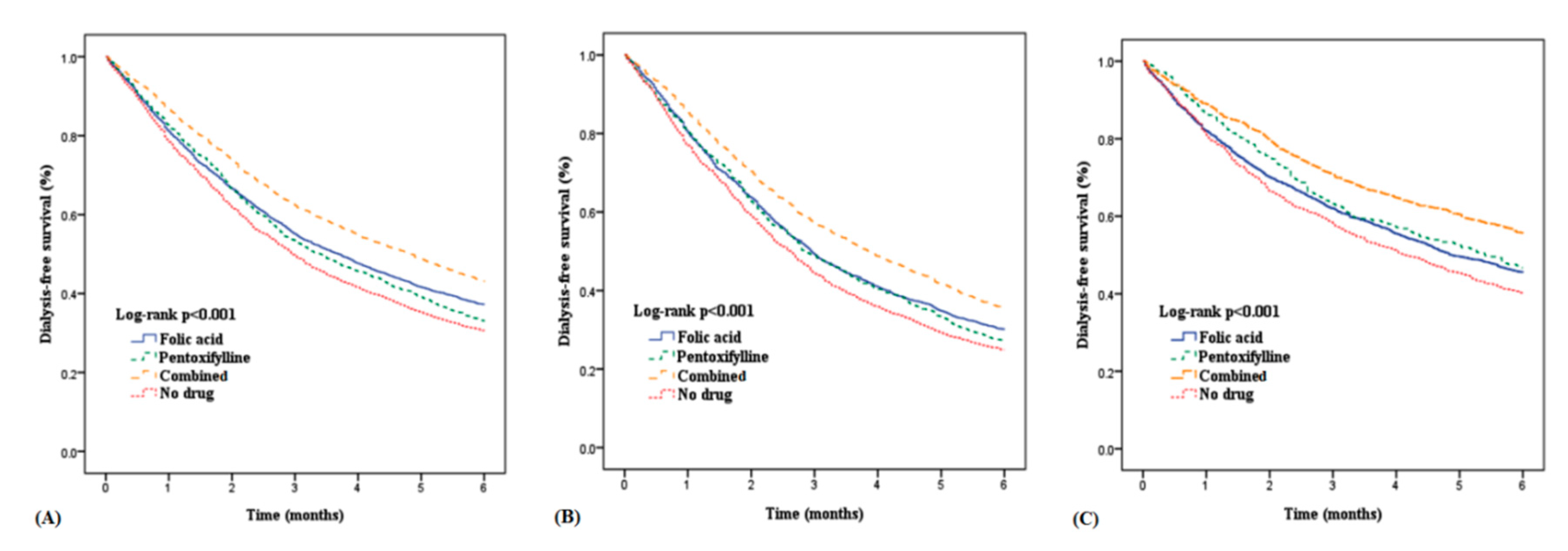
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saran, R.; Li, Y.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Ayanian, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, J.L.; et al. US Renal Data System 2015 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67 (Suppl. 1), S1–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler, T.A. Nutrition, inflammation and chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetti, M.; Ferrario, G.M.; Milani, S.; Serbelloni, P.; La Rosa, L.; Uccellini, M.; Sessa, A. Effects of folic acid treatment on homocysteine levels and vascular disease in hemodialysis patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2003, 9, PI19–PI24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vianna, A.C.; Mocelin, A.J.; Matsuo, T.; Morais-Filho, D.; Largura, A.; Delfino, V.A.; Soares, A.E.; Matni, A.M. Uremic hyperhomocysteinemia: A randomized trial of folate treatment for the prevention of cardiovascular events. Hemodial. Int. 2007, 11, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoungas, S.; McGrath, B.P.; Branley, P.; Kerr, P.G.; Muske, C.; Wolfe, R.; Atkins, R.C.; Nicholls, K.; Fraenkel, M.; Hutchison, B.G.; et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Atherosclerosis and Folic Acid Supplementation Trial (ASFAST) in chronic renal failure: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, A.; Kostense, P.J.; Nijpels, G.; Dekker, J.M.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Donker, A.J.; Stehouwer, C.D. Serum homocysteine levels are associated with the development of (micro)albuminuria: The Hoorn study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, T.; Kiyohara, Y.; Kubo, M.; Tanizaki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Okubo, K.; Nakamura, H.; Hata, J.; Oishi, Y.; Kato, I.; et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia and the development of chronic kidney disease in a general population: The Hisayama study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 44, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, F.; Vollenweider, P.; Marques-Vidal, P.M.; Mooser, V.; Waeber, G.; Paccaud, F.; Bochud, M. Hyperhomocysteinemia is independently associated with albuminuria in the population-based CoLaus study. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, B.; Pruijm, M.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Martin, P.Y.; Burnier, M.; Paccaud, F.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; Bochud, M. Determinants and burden of chronic kidney disease in the population-based CoLaus study: A cross-sectional analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, A.A.; Eliasziw, M.; Cattran, D.C.; Churchill, D.N.; Oliver, M.J.; Fine, A.; Dresser, G.K.; Spence, J.D. Effect of B-vitamin therapy on progression of diabetic nephropathy: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 303, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, R.L.; Hartigan, P.; Kaufman, J.S.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Warren, S.R.; Guarino, P.D.; Gaziano, J.M. Effect of homocysteine lowering on mortality and vascular disease in advanced chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007, 298, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Qin, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, J.; Liang, M.; Wang, B.; Huo, Y.; Hou, F.F. Efficacy of Folic Acid Therapy on the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: The Renal Substudy of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, L.N.; Li, H.X.; Huang, P.; Qu, L.B.; Chen, F.Y. Pentoxifylline plus ACEIs/ARBs for proteinuria and kidney function in chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, C.; Al-Makki, A.; Shepler, B. Can Pentoxifylline be used as Adjunct Therapy to ACE Inhibitors and ARBs in Preserving Kidney Function? J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kuo, K.L.; Hung, S.C.; Liu, J.S.; Chang, Y.K.; Hsu, C.C.; Tarng, D.C. Add-on Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease Treated with Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade—A Nationwide Database Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leporini, C.; Pisano, A.; Russo, E.; D’Arrigo, G.; de Sarro, G.; Coppolino, G.; Bolignano, D. Effect of pentoxifylline on renal outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapter, K.D.I.G.O. 3: Use of ESAs and other agents to treat anemia in CKD. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, P.W.; Ou, S.M.; Chen, Y.T.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, F.M.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, W.C.; Chen, T.J.; Chen, T.W.; Li, S.Y. Acute appendicitis in patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2012, 16, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.M.; Wu, V.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Wang, J.J.; Shiao, C.C.; Chen, L.; Chueh, S.C.; Chueh, E.; Yang, S.Y.; Lai, T.S.; et al. Effects of Statin Use in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Yang, Y.W.; Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Wu, K.D.; Wu, V.C.; Hsieh, T.C. Ketoanalogues supplementation decreases dialysis and mortality risk in patients with anemic advanced chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.C.; Wu, C.J.; Lin, C.J.; Pan, C.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, T.M.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, S.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, L.; et al. Pentoxifylline Decreases Dialysis Risk in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 98, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.W.; Liu, J.S.; Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Chang, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Tarng, D.C. Renoprotective effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with predialysis advanced chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and anemia. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Yang, W.C.; Lin, M.Y.; Mau, L.W.; Chen, H.C.; Taiwan Society of Nephrology. Impact of the clinical conditions at dialysis initiation on mortality in incident haemodialysis patients: A national cohort study in Taiwan. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2010, 25, 2616–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K. Association of low potassium diet and folic acid deficiency in patients with CKD. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, R.L.; Hartigan, P.; Gaziano, J.M.; Fortmann, S.P.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Haroldson, J.A.; Kaufman, J.; Lavori, P.; McCully, K.S.; Robinson, K. Design and statistical issues in the homocysteinemia in kidney and end stage renal disease (HOST) study. Clin. Trials 2004, 1, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högler, W.; Aguiar, M.; Kiely, M.; Tulchinsky, T. Consensus Recommendations for Prevention of Nutritional Rickets: Food Fortification and Micronutrient Supplements for Global Health. AIMS Public Health 2016, 3, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancherla, V.; Wagh, K.; Johnson, Q.; Oakley, G.P., Jr. A 2017 global update on folic acid-preventable spina bifida and anencephaly. Birth Defects Res. 2018, 110, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Cooper, M.E. Diabetic nephropathy: Renoprotective effects of pentoxifylline in the PREDIAN trial. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F.; Mora-Fernandez, C.; Muros de Fuentes, M.; Chahin, J.; Mendez, M.L.; Gallego, E.; Macía, M.; del Castillo, N.; Rivero, A.; Getino, M.A.; et al. Effect of pentoxifylline on renal function and urinary albumin excretion in patients with diabetic kidney disease: The PREDIAN trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concato, J.; Shah, N.; Horwitz, R.I. Randomized, controlled trials, observational studies, and the hierarchy of research designs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, K.; Hartz, A.J. A comparison of observational studies and randomized, controlled trials. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1878–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.C.; Chiu, P.F.; Chou, W.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, J.M.; Chen, T.W.; Ferng, S.H.; Lin, C.L. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary care for chronic kidney disease in Taiwan: A 3-year prospective cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.C.; Chou, W.Y.; Chiu, P.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, W.C.; Chang, J.M.; Chen, T.W.; Ferng, S.H.; et al. Multidisciplinary care improves clinical outcome and reduces medical costs for pre-end-stage renal disease in Taiwan. Nephrology 2014, 19, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Tsai, J.C.; Chen, H.C. Epidemiology, impact and preventive care of chronic kidney disease in Taiwan. Nephrology 2010, 15 (Suppl. 2), 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.Y.; Chang, Y.Y.; Mau, L.W.; Lin, M.Y.; Chiu, H.C.; Tsai, J.C.; Huang, C.J.; Chen, H.C.; Hwang, S.J. Chronic kidney disease care program improves quality of pre-end-stage renal disease care and reduces medical costs. Nephrology 2010, 15, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Group A | Group B | Group C | Group D | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient No. | 5073 | 1119 | 2184 | 2578 | |
| Age, mean ± SD (year) | 60 ± 13 | 61 ± 12 | 61 ± 12 | 60 ± 13 | <0.001 |
| CCIS, mean ± SD | 1.7 ± 1.6 | 2.2 ± 1.6 | 2.0 ± 1.6 | 1.9 ± 1.6 | <0.001 |
| Sex | <0.001 | ||||
| Male | 2476 (48.8) | 667 (59.6) | 1212 (55.5) | 1368 (53.1) | |
| Female | 2597 (51.2) | 452 (40.4) | 972 (44.5) | 1210 (46.9) | |
| SES | 0.060 | ||||
| Low | 1711 (33.7) | 382 (34.1) | 763 (34.9) | 949 (36.8) | |
| Moderate and high | 3362 (66.3) | 737 (65.9) | 1421 (65.1) | 1629 (63.2) | |
| Urbanization | <0.001 | ||||
| Non-urban | 3558 (70.1) | 891 (79.6) | 1625 (74.4) | 1938 (75.2) | |
| Urban | 1515 (29.9) | 228 (20.4) | 559 (25.6) | 640 (24.8) | |
| Geographic region | <0.001 | ||||
| Northern/central | 2981 (58.8) | 838 (74.9) | 1648 (75.5) | 1451 (56.3) | |
| Southern/eastern | 2092 (41.2) | 281 (25.1) | 536 (24.5) | 1127 (43.7) |
| Characteristic | Group A | Group B | Group C | Group D | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient No. | 5073 | 1119 | 2184 | 2578 | |
| Duration (days) | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 216 ± 270 | 188 ± 229 | 244 ± 286 | 166 ± 209 | <0.001 + |
| Median | 111 | 102 | 145 | 89 | <0.001 # |
| 25th pctl–75th pctl | 42–284 | 45–240 | 58–327 | 36–217 |
| Characteristic | Diabetes | No diabetes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | Group B | Group C | Group D | p-Value | Group A | Group B | Group C | Group D | p-Value | |
| Patient No. | 2733 | 774 | 1355 | 1614 | 2340 | 345 | 829 | 964 | ||
| Duration, mean ± SD (days) | 170 ± 217 | 151 ± 181 | 192 ± 229 | 136 ± 171 | <0.001 + | 269 ± 312 | 269 ± 296 | 330 ± 343 | 218 ± 252 | <0.001 + |
| Median (days) | 89 | 86 | 116 | 79 | <0.001 # | 146 | 162 | 220 | 124 | <0.001 # |
| 25th–75th pctl | 39–221 | 40–197 | 50–260 | 33–178 | 47–384 | 61–373 | 74–476 | 42–299 | ||
| Characteristic | Total | Diabetes | No Diabetes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | p-Value | β | SE | p-Value | β | SE | p-Value | |
| Intercept | 180.36 | 8.96 | <0.001 | 150.07 | 9.95 | <0.001 | 158.28 | 16.48 | <0.001 |
| Drug status * | |||||||||
| No drug (ref.) | |||||||||
| Pentoxifylline | 34.47 | 9.08 | <0.001 | 17.40 | 9.02 | 0.054 | 72.48 | 19.04 | <0.001 |
| Folic acid | 41.55 | 6.11 | <0.001 | 33.27 | 6.45 | <0.001 | 47.00 | 11.55 | <0.001 |
| Combined | 84.52 | 7.39 | <0.001 | 57.50 | 7.62 | <0.001 | 125.63 | 14.40 | <0.001 |
| Sex | |||||||||
| Male (ref.) | |||||||||
| Female | 34.81 | 4.85 | <0.001 | 9.81 | 5.15 | 0.057 | 64.76 | 9.05 | <0.001 |
| SES | |||||||||
| Low (ref.) | |||||||||
| Moderate and high | 14.62 | 5.13 | 0.004 | 3.67 | 5.45 | 0.501 | 30.80 | 9.59 | 0.001 |
| Urbanization | |||||||||
| Non-urban (ref.) | |||||||||
| Urban | 7.12 | 5.56 | 0.201 | 7.88 | 5.89 | 0.181 | 7.48 | 10.41 | 0.473 |
| Geographic region | |||||||||
| Northern/central (ref.) | |||||||||
| Southern/eastern | 23.06 | 5.13 | <0.001 | 1.81 | 5.44 | 0.739 | 56.03 | 9.58 | <0.001 |
| CCIS | −27.88 | 1.53 | <0.001 | −10.42 | 1.75 | <0.001 | −25.30 | 4.15 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Juang, S.-Y.; Liao, K.-F.; Chen, Y.-H. Comparing the Effect of Folic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Delaying Dialysis Initiation in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092192
Yang H, Juang S-Y, Liao K-F, Chen Y-H. Comparing the Effect of Folic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Delaying Dialysis Initiation in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2019; 11(9):2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092192
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hsun, Shiun-Yang Juang, Kuan-Fu Liao, and Yi-Hsin Chen. 2019. "Comparing the Effect of Folic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Delaying Dialysis Initiation in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 11, no. 9: 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092192
APA StyleYang, H., Juang, S.-Y., Liao, K.-F., & Chen, Y.-H. (2019). Comparing the Effect of Folic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Delaying Dialysis Initiation in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 11(9), 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092192





