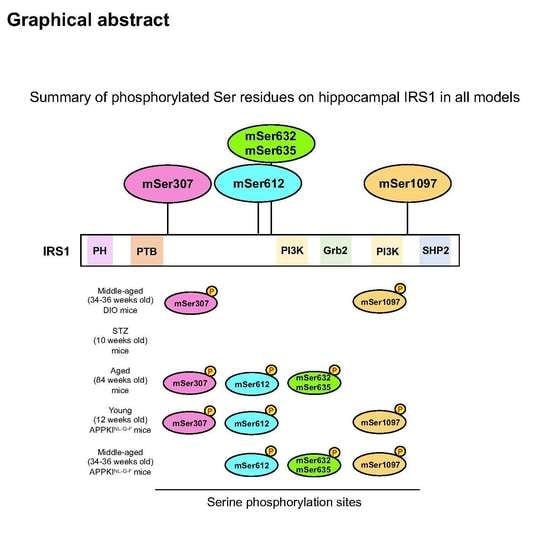
Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Western Blotting
2.3. Water T Maze Test
2.4. Measurement of Metabolic Parameters
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Quantitation of Aβ
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
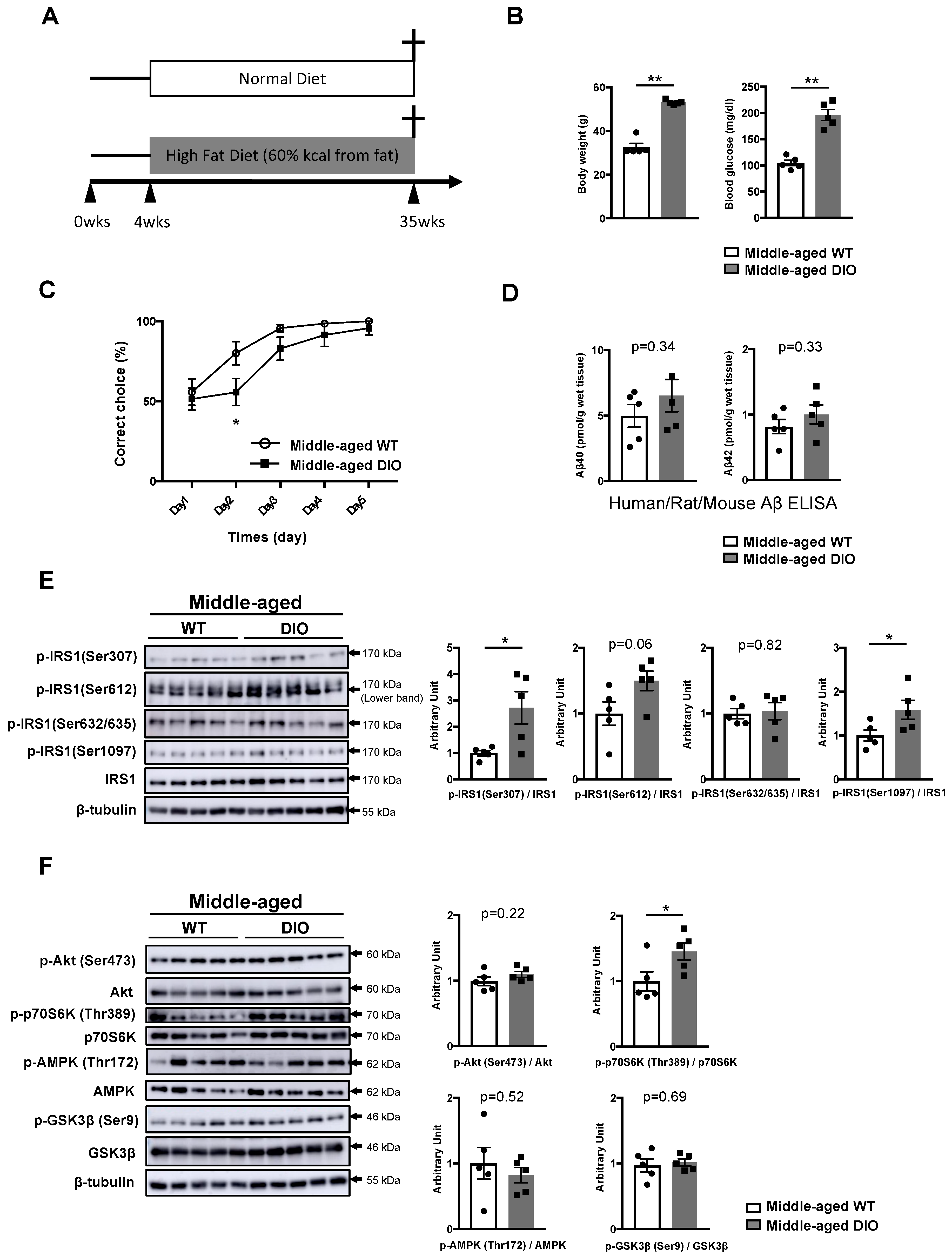
3.1. Activation of Specific Ser Residues on Hippocampal Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS1) Is Associated with T2DM-Induced Memory Impairment
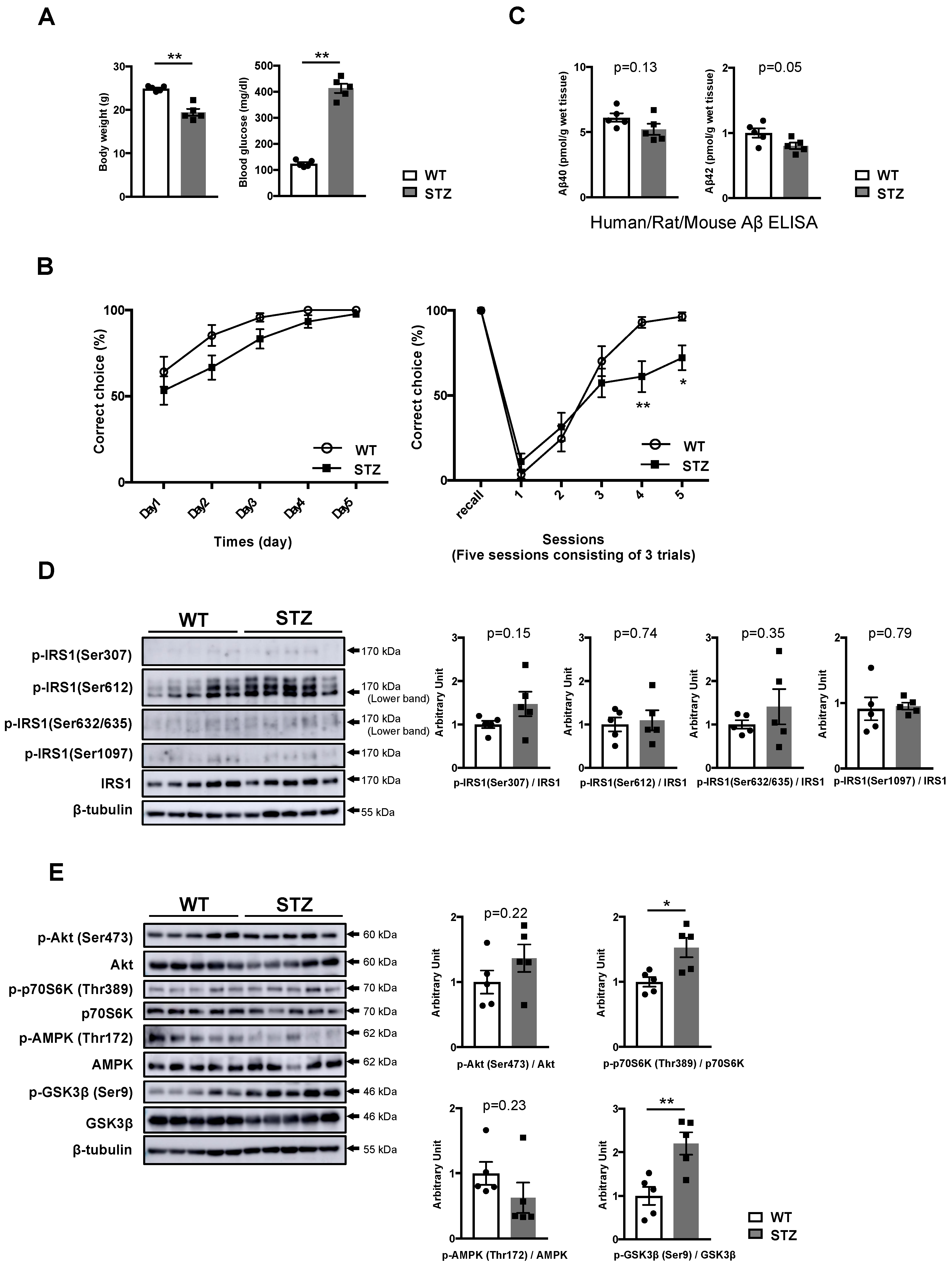
3.2. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)-Induced Memory Deficits Occur Independently of IRS1 Activity
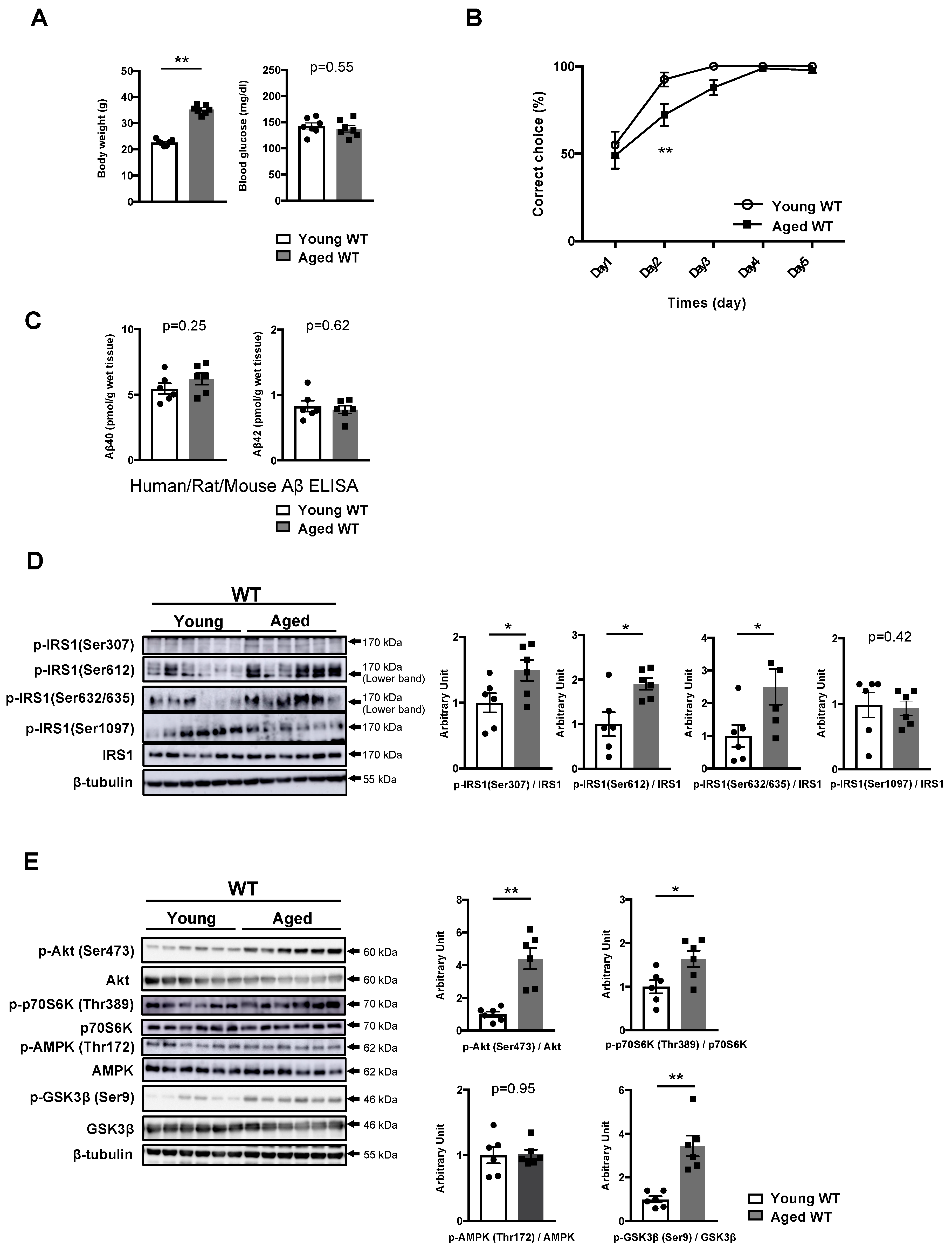
3.3. Phosphorylation of IRS1 at Age-Specific Ser Residues with the Activation of Downstream Kinases Is Linked to Age-Related Memory Deficits
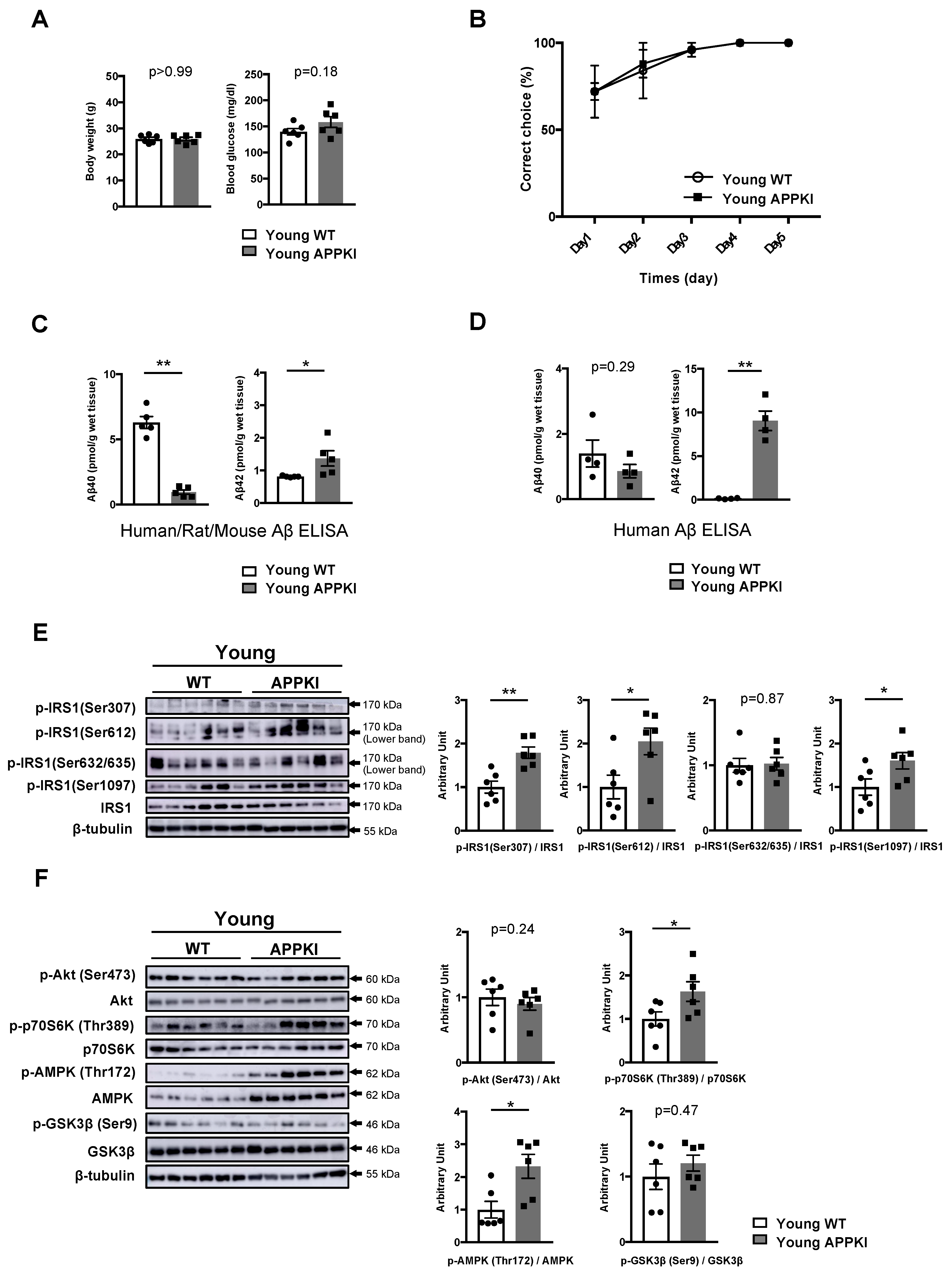
3.4. Increased Phosphorylation of Hippocampal IRS1 at Ser Residues in Young Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Knock-In (APP KINL-G-F) Mice Occurs Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline
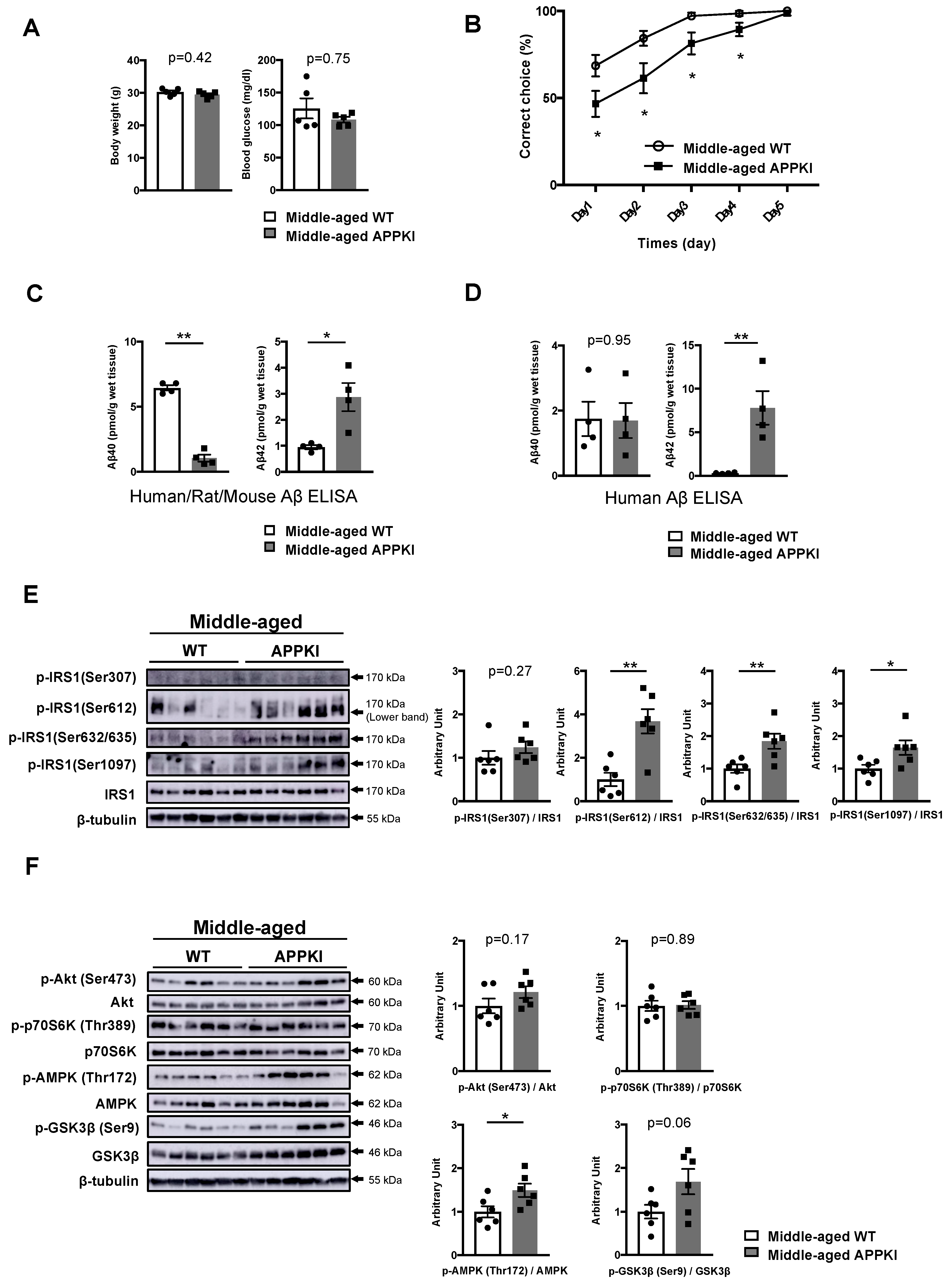
3.5. Memory Decline in Middle-Aged APPKINL-G-F Mice Is Accompanied by the Activation of Specific Ser Sites on IRS1 and Energy Depletion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Taguchi, A.; Park, S.; Kushner, J.A.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; White, M.F. Dysregulation of insulin receptor substrate 2 in beta cells and brain causes obesity and diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Park, S.; Lin, X.; Copps, K.; Yi, X.; White, M.F. Irs1 and Irs2 signaling is essential for hepatic glucose homeostasis and systemic growth. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, A.; Wartschow, L.M.; White, M.F. Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis. Science 2007, 317, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.C.; Cheng, Z.; Copps, K.D.; White, M.F. Insulin receptor substrates Irs1 and Irs2 coordinate skeletal muscle growth and metabolism via the Akt and AMPK pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copps, K.D.; White, M.F. Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2565–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancer, N.J.; Qiu, W.; Cherella, C.; Li, Y.; Copps, K.D.; White, M.F. Insulin and metabolic stress stimulate multisite serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 and inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12467–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.F.; Maron, R.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature 1985, 318, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Dallas-Yang, Q.; Biswas, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.B. Rosiglitazone, an agonist of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), decreases inhibitory serine phosphorylation of IRS1 in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. J. 2004, 377 Pt 2, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morino, K.; Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Frattini, J.; Shatzkes, N.; Neschen, S.; White, M.F.; Bilz, S.; Sono, S.; et al. Reduced mitochondrial density and increased IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 3587–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copps, K.D.; Hancer, N.J.; Opare-Ado, L.; Qiu, W.; Walsh, C.; White, M.F. Irs1 serine 307 promotes insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, F.; Brule, S.; Hee Um, S.; Li, Y.; Masuda, K.; Roden, M.; Sun, X.J.; Krebs, M.; Polakiewicz, R.D.; Thomas, G.; et al. Identification of IRS-1 Ser-1101 as a target of S6K1 in nutrient- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14056–14061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, A.M.; Griffin, R.J.; Timmons, S.; O’Connor, R.; Ravid, R.; O’Neill, C. Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer’s disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, K.; Wang, H.Y.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Bakshi, K.P.; Stucky, A.; Fuino, R.L.; Kawaguchi, K.R.; Samoyedny, A.J.; Wilson, R.S.; et al. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1316–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, M.; Toledo, J.B.; Lee, E.B.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Louneva, N.; Lee, V.M.; Kim, S.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Abnormal serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 is associated with tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomfim, T.R.; Forny-Germano, L.; Sathler, L.B.; Brito-Moreira, J.; Houzel, J.C.; Decker, H.; Silverman, M.A.; Kazi, H.; Melo, H.M.; McClean, P.L.; et al. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease- associated Abeta oligomers. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, M.V.; Clarke, J.R.; Frozza, R.L.; Bomfim, T.R.; Forny-Germano, L.; Batista, A.F.; Sathler, L.B.; Brito-Moreira, J.; Amaral, O.B.; Silva, C.A.; et al. TNF-alpha mediates PKR-dependent memory impairment and brain IRS-1 inhibition induced by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid oligomers in mice and monkeys. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Yang, F.; Rosario, E.R.; Ubeda, O.J.; Beech, W.; Gant, D.J.; Chen, P.P.; Hudspeth, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Beta-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: Suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9078–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Matsuba, Y.; Mihira, N.; Takano, J.; Nilsson, P.; Itohara, S.; Iwata, N.; Saido, T.C. Single App knock-in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanokashira, D.; Kurata, E.; Fukuokaya, W.; Kawabe, K.; Kashiwada, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Nakazato, M.; Taguchi, A. Metformin treatment ameliorates diabetes-associated decline in hippocampal neurogenesis and memory via phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhan, L.; Lu, X.; Sun, X.; Sui, H.; Zheng, L.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, F. Endoplasmic reticulum stress impairs insulin receptor signaling in the brains of obese rats. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0126384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.E.; Lucki, I.; Brookshire, B.R.; Carlson, G.C.; Browne, C.A.; Kazi, H.; Bang, S.; Choi, B.R.; Chen, Y.; McMullen, M.F.; et al. High fat diet produces brain insulin resistance, synaptodendritic abnormalities and altered behavior in mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 67, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Yin, F.; Yao, J.; Brinton, R.D.; Cadenas, E. Lipoic acid restores age-associated impairment of brain energy metabolism through the modulation of Akt/JNK signaling and PGC1alpha transcriptional pathway. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makinodan, M.; Rosen, K.M.; Ito, S.; Corfas, G. A critical period for social experience-dependent oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Science 2012, 337, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.T.; Hull, C.; Chu, Y.; Greene-Colozzi, E.; Sadowski, A.R.; Leech, J.M.; Steinberg, J.; Crawley, J.N.; Regehr, W.G.; Sahin, M. Autistic-like behaviour and cerebellar dysfunction in Purkinje cell Tsc1 mutant mice. Nature 2012, 488, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C.D.; Pistell, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Johnson, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; White, C.L.; Purpera, M.N.; Uranga, R.M.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; et al. High fat diet increases hippocampal oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in aged mice: Implications for decreased Nrf2 signaling. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, H.; Xu, G.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J. Liraglutide improves cognitive impairment via the AMPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in type 2 diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.; Liang, M.; Chen, L.; Xiang, L.; Dong, J.; et al. Alogliptin improves survival and health of mice on a high-fat diet. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, J.F.; Mooradian, A.D.; Morley, J.E. Characteristics of learning and memory in streptozocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes 1990, 39, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Nagaishi, K.; Konari, N.; Saito, Y.; Chikenji, T.; Mizue, Y.; Fujimiya, M. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into damaged neurons and astrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Qin, A.; Chen, Z. The protective effect of formononetin on cognitive impairment in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mo, R.; Wu, N.; Zou, X.; Shi, C.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Fang, K.; Wang, D.; Yang, D.; et al. Berberine ameliorates diabetes-associated cognitive decline through modulation of aberrant inflammation response and insulin signaling pathway in DM rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Mihira, N.; Matsuba, Y.; Sasaguri, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Narasimhan, S.; Zhang, B.; Murayama, S.; Higuchi, M.; Lee, V.M.Y.; et al. Humanization of the entire murine Mapt gene provides a murine model of pathological human tau propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Sonoda, N.; Hayashida, E.; Makimura, H.; Ide, M.; Ikeda, N.; Ohgidani, M.; Kato, T.A.; Seki, Y.; Maeda, Y.; et al. p66Shc signaling mediates diabetes-related cognitive decline. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, R.; Hanyu, H.; Sato, T.; Shimizu, S.; Koyama, S.; Kanetaka, H.; Sakurai, H.; Iwamoto, T. Subgroups of Alzheimer’s disease associated with diabetes mellitus based on brain imaging. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, R.; Hanyu, H.; Shimizu, S.; Kanetaka, H.; Sakurai, H.; Ishii, K. Identification of diabetes-related dementia: Longitudinal perfusion SPECT and amyloid PET studies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 349, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, O.J.; Hunter, T. Turnover of the active fraction of IRS1 involves raptor-mTOR- and S6K1-dependent serine phosphorylation in cell culture models of tuberous sclerosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 6425–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Quon, M.J.; Ye, J. S6K directly phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser-270 to promote insulin resistance in response to TNF-(alpha) signaling through IKK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35375–35382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, S.L.; Pi, L.H.; Shi, X.J.; Ma, L.R.; Chen, Z.; Qu, M.L.; Li, X.; Nie, S.D.; Liao, D.F.; et al. High glucose induces formation of tau hyperphosphorylation via Cav-1-mTOR pathway: A potential molecular mechanism for diabetes-induced cognitive dysfunction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40843–40856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, C.H.; Jung, H.; Kim, E.; Song, H.T.; Lee, J.E. Agmatine ameliorates type 2 diabetes induced-Alzheimer’s disease-like alterations in high-fat diet-fed mice via reactivation of blunted insulin signalling. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113 Pt A, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeilly, A.D.; Williamson, R.; Balfour, D.J.; Stewart, C.A.; Sutherland, C. A high-fat-diet-induced cognitive deficit in rats that is not prevented by improving insulin sensitivity with metformin. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, E.; Vereker, E.; Lynch, M.A. Age-related impairment in LTP is accompanied by enhanced activity of stress-activated protein kinases: Analysis of underlying mechanisms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, S. Alzheimer disease: Insulin resistance and AD—Extending the translational path. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Chern, Y. AMPK-mediated regulation of neuronal metabolism and function in brain diseases. J. Neurogenet. 2015, 29, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zimmermann, H.R.; Ma, T. Therapeutic potential of AMP-activated protein kinase in alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2019, 68, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanokashira, D.; Fukuokaya, W.; Taguchi, A. Involvement of insulin receptor substrates in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Tanokashira, D.; Fukui, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Kuroiwa, C.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.C.; Taguchi, A. Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942
Wang W, Tanokashira D, Fukui Y, Maruyama M, Kuroiwa C, Saito T, Saido TC, Taguchi A. Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Daisuke Tanokashira, Yusuke Fukui, Megumi Maruyama, Chiemi Kuroiwa, Takashi Saito, Takaomi C. Saido, and Akiko Taguchi. 2019. "Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942
APA StyleWang, W., Tanokashira, D., Fukui, Y., Maruyama, M., Kuroiwa, C., Saito, T., Saido, T. C., & Taguchi, A. (2019). Serine Phosphorylation of IRS1 Correlates with Aβ-Unrelated Memory Deficits and Elevation in Aβ Level Prior to the Onset of Memory Decline in AD. Nutrients, 11(8), 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081942