Food Addiction Is Associated with Irrational Beliefs via Trait Anxiety and Emotional Eating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Food Addiction
2.2.2. Irrational Beliefs
2.2.3. Eating Styles
2.2.4. Trait Anxiety
2.2.5. Depression
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Confirmatory Analyses
3.1.1. Correlations
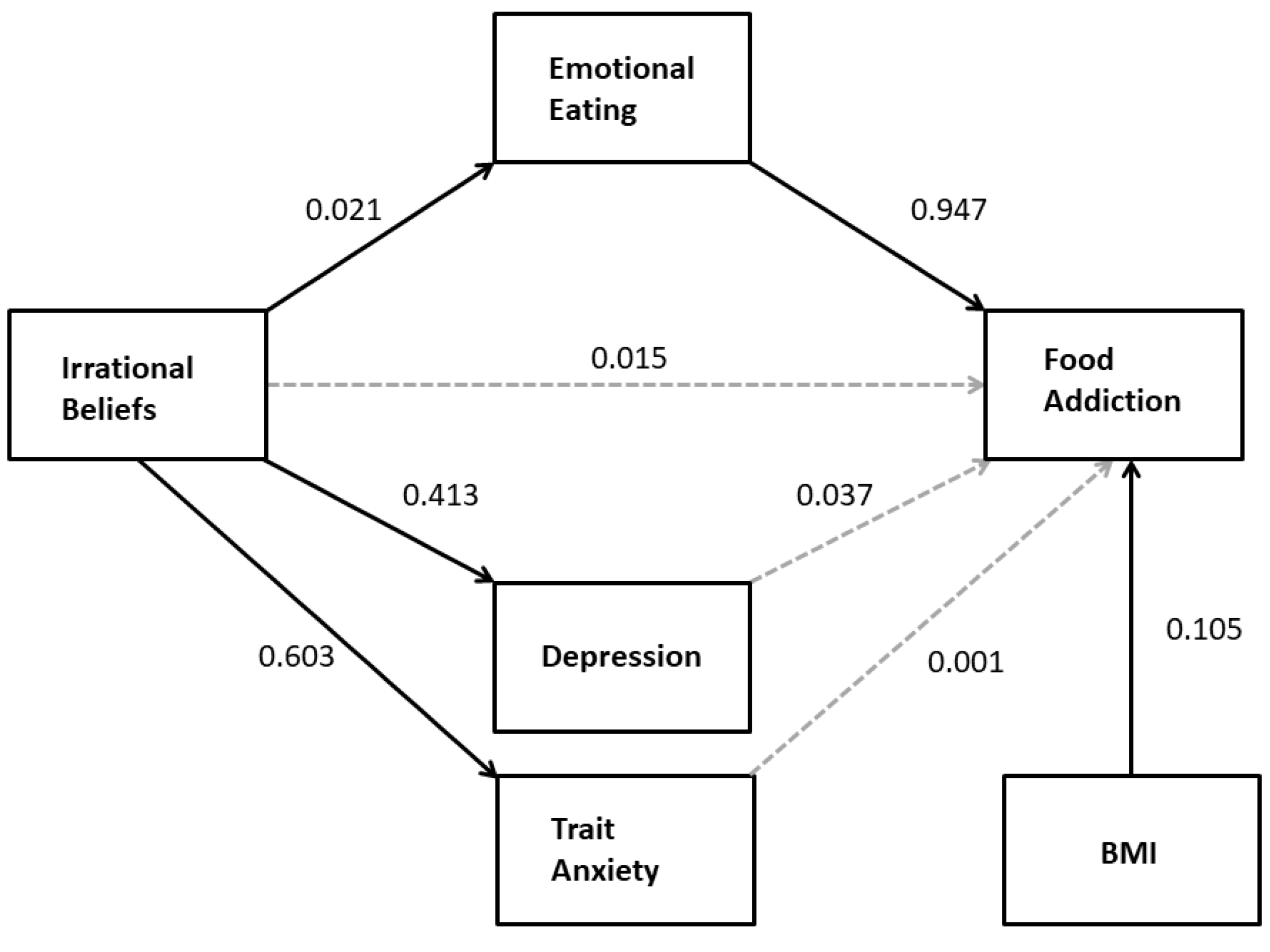
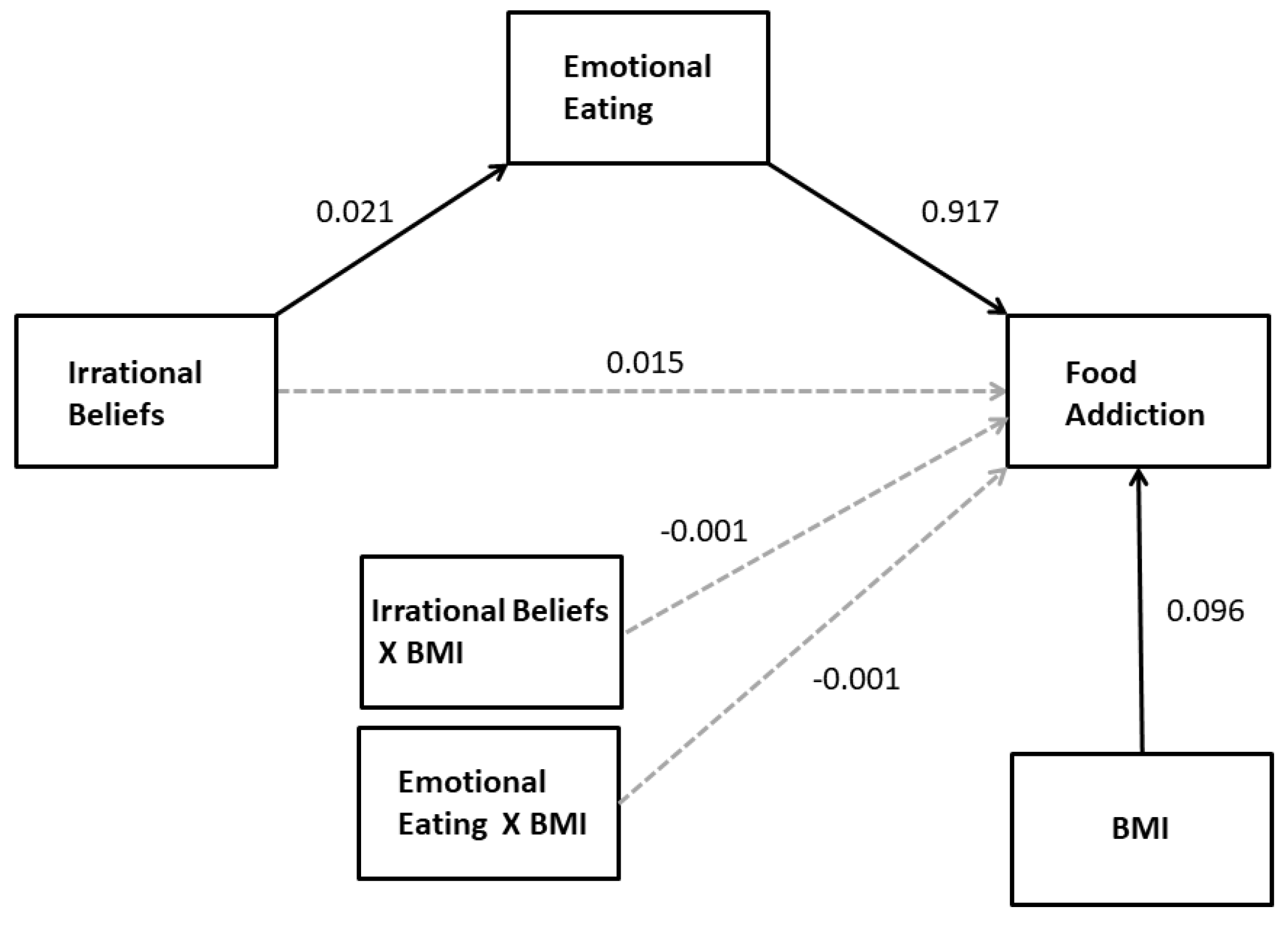
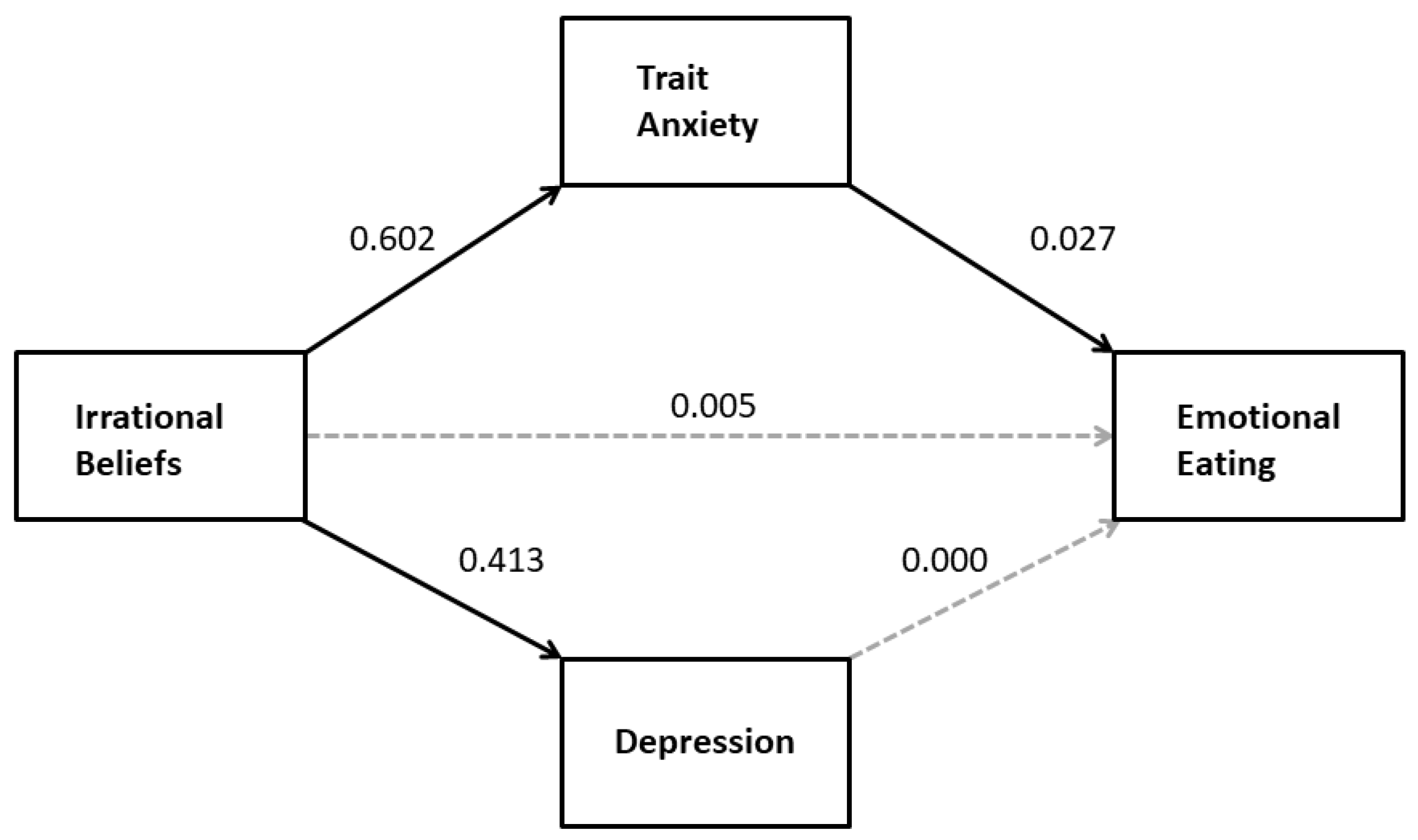
3.1.2. Multiple Regression Mediation Analysis
Multiple Mediation of the Effect of Irrational Beliefs on FA
Moderated Mediation by BMI of the Effect of Irrational Beliefs on FA
Multiple Mediation of the Effect of Irrational Beliefs on Emotional Eating
3.2. Exploratory Analyses: Serial Mediation of the Effect of Irrational Beliefs on FA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Preliminary validation of the Yale food addiction scale. Appetite 2009, 52, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.; Curtis, C.; Levitan, R.D.; Carter, J.C.; Kaplan, A.S.; Kennedy, J.L. Evidence that ‘food addiction’ is a valid phenotype of obesity. Appetite 2011, 57, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; White, M.A.; Masheb, R.M.; Morgan, P.T.; Crosby, R.D.; Grilo, C.M. An examination of the food addiction construct in obese patients with binge eating disorder. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2012, 45, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Boswell, R.G.; White, M.A. The association of “food addiction” with disordered eating and body mass index. Eat. Behav. 2014, 15, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, S.K.; Meule, A. Food addiction and bulimia nervosa: New data based on the Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2016, 24, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, L.J.; Geliebter, A. “Food addiction” is associated with night eating severity. Appetite 2016, 98, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A. How prevalent is “food addiction”? Front. Psychiatry 2011, 2, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedram, P.; Wadden, D.; Amini, P.; Gulliver, W.; Randell, E.; Cahill, F.; Vasdev, S.; Goodridge, A.; Carter, J.C.; Zhai, G.; et al. Food addiction: Its prevalence and significant association with obesity in the general population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebebrand, J.; Albayrak, Ö.; Adan, R.; Antel, J.; Dieguez, C.; de Jong, J.; Leng, G.; Menzies, J.; Mercer, J.G.; Murphy, M.; et al. “Eating addiction”, rather than “food addiction”, better captures addictive-like eating behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, L.J. Is it time to consider the “food use disorder”? Appetite 2017, 115, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.G.; Blundell, J.E.; Finlayson, G. A systematic review of the application and correlates of YFAS-diagnosed ‘food addiction’ in humans: Are eating-related ‘addictions’ a cause for concern or empty concepts? Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A. Back by popular demand: A narrative review on the history of food addiction research. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulte, E.M.; Gearhardt, A.N. Development of the modified Yale food addiction scale version 2.0. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2017, 25, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, A. Reason and Emotion in Psychotherapy; Lyle Stuart: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T. Cognitive Therapy and the Emotional Disorders; International Universities Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, A. The essence of RET—1984. J. Ration. Emot. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 1984, 2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vîslă, A.; Flückiger, C.; Grosse Holtforth, M.; David, D. Irrational beliefs and psychological distress: A meta-analysis. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohsenow, D.J.; Smith, R.E. Irrational beliefs and predictors of negative affective states. Motiv. Emot. 1982, 6, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffenbacher, J.L.; Zwemer, W.A.; Whisman, M.A.; Hill, R.A.; Sloan, R.D. Irrational beliefs and anxiety. Cognit. Ther. Res. 1986, 10, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, E.H.; Poulakis, Z. The relationship among the General Attitude and Belief Scale, other dysfunctional cognition measures, and depressive or bulimic tendencies. J. Ration. Emot. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 1993, 10, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, R.; Edelmann, R.J. Self-esteem, irrational beliefs and coping strategies in relation to eating problems in a non-clinical population. Person. Individ. Differ. 1989, 10, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camatta, C.D.; Nagoshi, C.T. Stress, depression, irrational beliefs, and alcohol use and problems in a college student sample. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.T.; Patock-Peckham, J.A.; Cheong, J.; Nagoshi, C.T. Irrational beliefs and behavioral misregulation in the role of alcohol abuse among college students. J. Ration. Emot. Cogn. Behav. 1998, 16, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, C.T. Perceived control of drinking and other predictors of alcohol use and problems in a college student sample. Addict. Res. 1999, 7, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoff, M.S. Irrational beliefs as predictors of adolescent drug abuse and running away. J. Clin. Psychol. 1987, 43, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.H.; Knudsen, A.K.; Krogh, E.; Pallesen, S.; Molde, H. An overview of cognitive mechanisms in pathological gambling. Nordic Psychol. 2007, 59, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, A.J. Restraint and irrational cognitions. Behav. Res. Ther. 1985, 23, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, A.J. Bulimia and irrational beliefs. Behav. Res. Ther. 1986, 24, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, J.M.; Parkinson, D.L. Irrational beliefs and bulimia symptoms. J. Ration. Emot. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 1989, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomotake, M.; Okura, M.; Taniguchi, T.; Ishimoto, Y. Traits of irrational beliefs related to eating problems in Japanese college women. J. Med. Investig. 2002, 49, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, A.T.; Bothma, M.E. Body dissatisfaction and irrational beliefs. Psychol. Rep. 2001, 88, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, M.; Stark, K. Emotional eating and eating disorder psychopathology. Eat. Disord. 2001, 9, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Strien, T.; Ouwens, M.A. Effects of distress, alexithymia and impulsivity on eating. Eat. Behav. 2007, 8, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallis, D.J.; Hetherington, M.M. Stress and eating: The effects of ego-threat and cognitive demand on food intake in restrained and emotional eaters. Appetite 2004, 43, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.L.; Appelhans, B.M.; Whited, M.C.; Oleski, J.; Pagoto, S.L. Trait anxiety, but not trait anger, predisposes obese individuals to emotional eating. Appetite 2010, 55, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, L.; Braet, C.; Van Vlierberghe, L.; Mels, S. Loss of control over eating in overweight youngsters: The role of anxiety, depression and emotional eating. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2009, 17, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwens, M.A.; van Strien, T.; van Leeuwe, J.F. Possible pathways between depression, emotional and external eating. A structural equation model. Appetite 2009, 53, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, A.; Nolan, L.J.; Higgs, S. Self-perceived food addiction: Prevalence, predictors, and prognosis. Appetite 2017, 114, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parylak, S.L.; Koob, G.F.; Zorrilla, E.P. The dark side of food addiction. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, H.; Kirkby, R.; Wertheim, E.; Birch, P.A. brief assessment of irrational thinking: The Shortened General Attitudes and Belief Scale. Cognit. Ther. Res. 1999, 23, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, K.R.; Harnish, R.J. Role of irrational beliefs in depression and anxiety: A review. Health 2010, 2, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.E.R.; Bergers, G.P.A.; Defares, P.B. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for assessment of restrained, emotional, and external eating behavior. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.R.; Jacobs, G.A. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Consulting Psychologists: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Zung, W.W. A self-rating depression scale. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1965, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, B.J.; Fielding, J.M.; Blashki, T.G. Depression rating scales: A critical review. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1973, 28, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, A. Overcoming Destructive Beliefs, Feelings, and Behaviors: New Directions for Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy; Prometheus Books: Amherst, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Greeno, C.G.; Wing, R.R. Stress-induced eating. Psychol. Bull. 1994, 115, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heatherton, T.F.; Baumeister, R.F. Binge eating as escape from self-awareness. Psychol. Bull. 1991, 110, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A.; Gearhardt, A. Food addiction in the light of DSM-5. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3653–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdier, L.; Orri, M.; Carre, A.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Romo, L.; Dantzer, C.; Berthoz, S. Are emotionally driven and addictive-like eating behaviors the missing links between psychological distress and greater body weight? Appetite 2018, 120, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, D.; Gollust, S.E.; Golberstein, E.; Hefner, J.L. Prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and suicidality among university students. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2007, 77, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiter, R.; Nash, R.; McCrady, M.; Rhoades, D.; Linscomb, M.; Clarahan, M.; Sammut, S. The prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and stress in a sample of college students. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 173, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivin, K.; Eisenberg, D.; Gollust, S.E.; Golberstein, E. Persistence of mental health problems and needs in a college student population. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 117, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearon, B.A.; Utschig, A.C.; Smits, J.A.; Moshier, S.J.; Otto, M.W. The role of anxiety sensitivity and eating expectancy in maladaptive eating behavior. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2013, 37, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, E.M.; Joyner, M.A.; Potenza, M.N.; Grilo, C.M.; Gearhardt, A.N. Current considerations regarding food addiction. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Measure | SGABS | DEBQe | DEBQx | DEBQr | SDS | mYFAS2 | STAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGABS | 0.298 4 | 0.166 1 | 0.242 2 | 0.498 4 | 0.282 3 | 0.601 4 | |
| DEBQe | 0.530 4 | 0.388 4 | 0.338 4 | 0.485 4 | 0.422 4 | ||
| DEBQx | 0.219 2 | 0.039 | 0.409 4 | 0.057 | |||
| DEBQr | 0.182 1 | 0.328 4 | 0.240 2 | ||||
| SDS | 0.342 4 | 0.800 4 | |||||
| mYFAS2 | 0.362 4 | ||||||
| Mean | 59.09 | 2.38 | 3.06 | 2.81 | 40.91 | 1.62 | 43.87 |
| SEM | 0.79 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 1.01 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.79 |
| Measure | SGABS | DEBQe | DEBQx | DEBQr | SDS | mYFAS2 | STAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | −0.020 | 0.082 | 0.037 | 0.161 1 | −0.024 | 0.269 2 | 0.032 |
| Predictor | Mediator: STAI R2 = 0.362, F(1,237) = 148.52, p < 0.0001 | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
| Coeff. | SE | p | Lower | Upper | |
| SGABS | 0.602 | 0.049 | <0.0001 | 0.505 | 0.670 |
| Mediator: SDS R2 = 0.248, F(1,237) = 75.85, p < 0.0001 | |||||
| SGABS | 0.413 | 0.048 | <0.0001 | 0.320 | 0.507 |
| Criterion: DEBQe R2 = 0.182, F(3,235) = 15.98, p < 0.0001 | |||||
| SGABS | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.406 | −0.007 | 0.016 |
| STAI | 0.027 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.044 |
| SDS | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.989 | −0.017 | 0.016 |
| Predictor | Mediator: STAI R2 = 0.363, F(2,236) = 72.58, p < 0.0001 | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
| Coeff. | SE | p | Lower | Upper | |
| SGABS | 0.603 | 0.050 | <0.0001 | 0.504 | 0.702 |
| BMI | 0.109 | 0.171 | 0.525 | −0.227 | 0.445 |
| Mediator: SDS R2 = 0.643, F(3,235) = 180.88, p < 0.0001 | |||||
| SGABS | 0.020 | 0.044 | 0.656 | −0.067 | 0.106 |
| STAI | 0.653 | 0.042 | <0.0001 | 0.570 | 0.735 |
| BMI | −0.100 | 0.083 | 0.229 | −0.263 | 0.063 |
| Mediator: DEBQe R2 = 0.186, F(4,234) = 13.03, p < 0.0001 | |||||
| SGABS | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.387 | −0.007 | 0.017 |
| STAI | 0.026 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.043 |
| SDS | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.933 | −0.016 | 0.017 |
| BMI | 0.013 | 0.120 | 0.299 | −0.011 | 0.036 |
| Criterion: mYFAS2 R2 = 0.334, F(5,233) = 14.51, p < 0.0001 | |||||
| SGABS | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.242 | −0.010 | 0.040 |
| STAI | 0.001 | 0.018 | 0.964 | −0.035 | 0.037 |
| SDS | 0.037 | 0.022 | 0.092 | −0.006 | 0.079 |
| DEBQe | 0.947 | 0.194 | <0.0001 | 0.565 | 1.328 |
| BMI | 0.105 | 0.026 | .0001 | 0.054 | 0.157 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nolan, L.J.; Jenkins, S.M. Food Addiction Is Associated with Irrational Beliefs via Trait Anxiety and Emotional Eating. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081711
Nolan LJ, Jenkins SM. Food Addiction Is Associated with Irrational Beliefs via Trait Anxiety and Emotional Eating. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081711
Chicago/Turabian StyleNolan, Laurence J., and Steve M. Jenkins. 2019. "Food Addiction Is Associated with Irrational Beliefs via Trait Anxiety and Emotional Eating" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081711
APA StyleNolan, L. J., & Jenkins, S. M. (2019). Food Addiction Is Associated with Irrational Beliefs via Trait Anxiety and Emotional Eating. Nutrients, 11(8), 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081711





