Quality of Systematic Reviews of the Foods with Function Claims in Japan: Comparative Before- and After-Evaluation of Verification Reports by the Consumer Affairs Agency
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Scope of This Review
2.2. Criteria for Considering Studies Included in This Review
2.3. Types of Studies
2.4. Types of Participants
2.5. Comparator(s)/Control
2.6. Types of Intervention and Language
2.7. Types of Outcome Measures
2.8. Search Methodology for Identification of Studies
2.8.1. Search Strategies
2.8.2. Hand-Searching and Reference Checking
2.9. Review Methods
2.9.1. Selection of Studies
2.9.2. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
2.9.3. Characteristics of Studies and Data Extraction
2.9.4. Research Protocol Registration
2.9.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
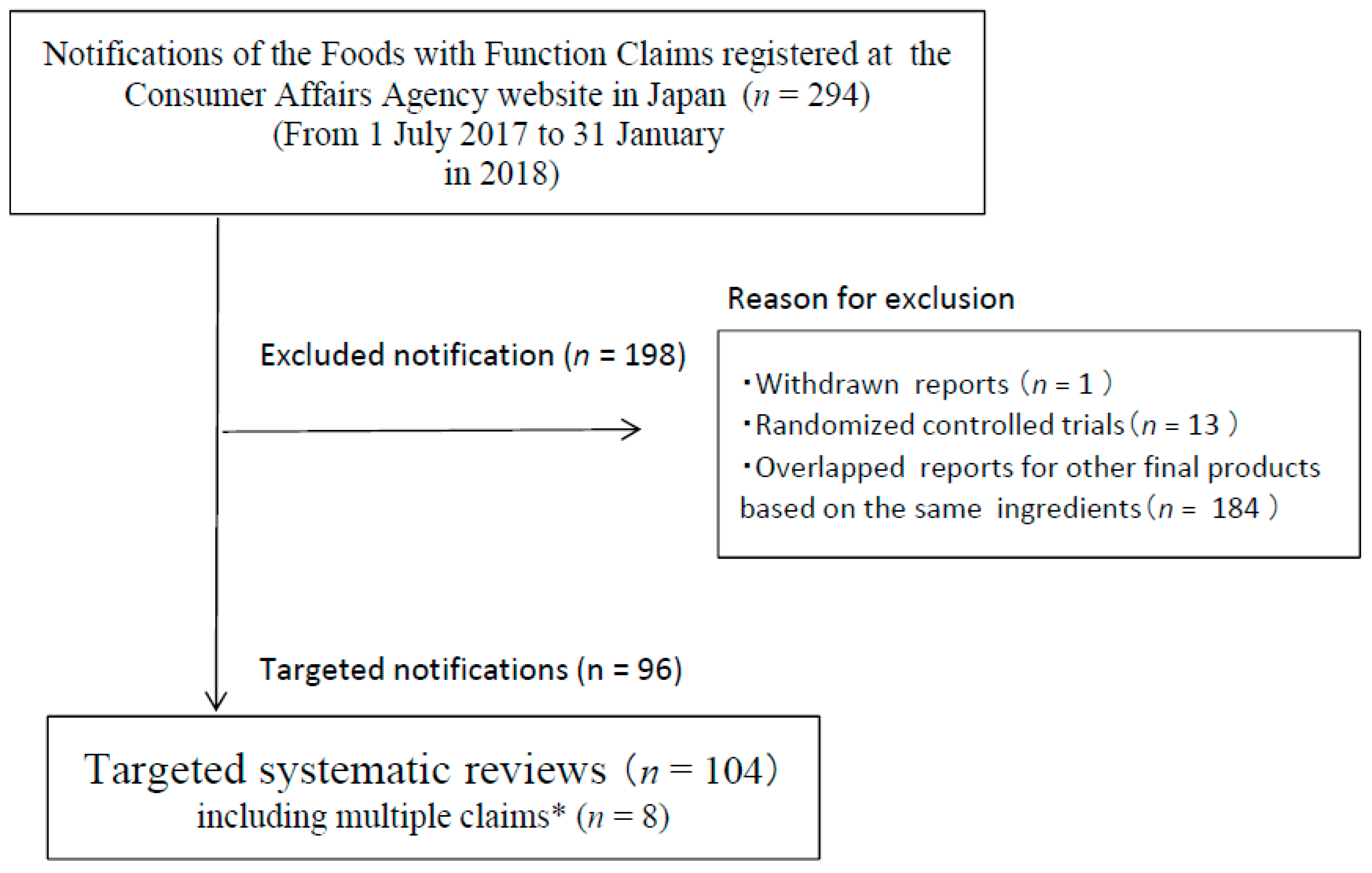
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Quality Assessment of Target SRs
4.2. Validity and Reliability of Quality Assessment by AMSTAR Checklist
4.3. Future Research Challenge to Improve the Quality of SRs of the FFC
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SR | Systematic review |
| CAC | Codex Alimentarius Commission |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| FFC | Foods with Function Claims |
| CAA | Consumer Affairs Agency |
| FOSHU | Foods for Specified Health Uses |
| FNFC | Foods with Nutrient Function Claims |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| MeSH | Medical subject headings |
References
- The CODEX Alimentarius Committee. About Codex Alimentarius. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/about-codex/en/ (accessed on 6 July 2018).
- The CODEX Alimentarius Committee. Guidelines for Use of Nutrition and Health Claims. 1997. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCAC%2BGL%2B23-1997%252FCXG_023e.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2018).
- Consumer Affairs Agency. Government of Japan. Introduction. 2015. Available online: http://www.caa.go.jp/policies/policy/food_labeling/about_foods_with_function_claims/pdf/150810_1.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2018).
- Consumer Affairs Agency. Government of Japan. Guideline. 2015. Available online: http://www.caa.go.jp/policies/policy/food_labeling/foods_with_function_claims/pdf/food_with_function_clains_180328_0001.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- National Information Center on Health Services Research and Health Care Technology. Systematic Reviews Definition. 2017. Available online: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/nichsr/hta101/ta101014.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Page, M.J.; Shamseer, L.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Sampson, M.; Tricco, A.C.; Catalá-López, F.; Li, L.; Reid, E.K.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; et al. Epidemiology and Reporting Characteristics of Systematic Reviews of Biomedical Research: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamser, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocol (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 349, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamioka, H.; Tsutani, K.; Hideki, O.; Yoshizaki, T.; Kitayuguchi, J.; Shimada, M.; Tang, W.; Takano-Ohmuro, H. Quality of systematic reviews of the Foods with Function Claims registered at the Consumer Affairs Agency Web site in Japan: A prospective systematic review. Nutr. Res. 2017, 40, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; A Wells, G.; Boers, M.; Andersson, N.; Hamel, C.; Porter, A.C.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D.; Bouter, L.M. Development of AMSTAR: A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consumer Affairs Agency, Government of Japan. Verification of Scientific Evidence on Effectiveness of the System of “Foods with Function Claim”: Assessment of the Submitted Systematic Literature Reviews (Digest Edition). 2016. Available online: http://www.caa.go.jp/policies/policy/food_labeling/about_foods_with_function_claims/pdf/food_with_function_report_0003.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2018).
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, W65–W94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Jones, A.; Lepage, L. Use of the CONSORT statement and quality of reports of randomized trials: A comparative before-and-after evaluation. JAMA 2001, 285, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopewell, S.; Ravaud, P.; Baron, G.; Boutron, I. Effect of editors’ implementation of CONSORT guidelines on the reporting of abstracts in high impact medical journals: Interrupted time series analysis. BMJ 2012, 344, e4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews. Protocol. 2017. Available online: http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/ (accessed on 21 December 2017).
- Last, J.M. A Dictionary of Epidemiology, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McAuley, L.; Pham, B.; Tugwell, P.; Moher, D. Does the inclusion of grey literature influence the estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta-analyses? Lancet 2000, 356, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, A.; Arroyo, P. Language and country preponderance trends in MEDLINE and its causes. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2005, 93, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Boggio, A. Countries’ biomedical publications and attraction scores: A PubMed-based assessment. F1000Research 2015, 3, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.F.; Briel, M.; D’Amario, A.; Kleijnen, J.; Marusic, A.; Wager, E.; Antes, G.; Von Elm, E.; Lang, B.; Motschall, E.; et al. Defining publication bias: Protocol for a systematic review of highly cited articles and proposal for a new framework. Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Altman, D.G.; Laupacis, A.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Krleža‒Jerić, K.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Mann, H.; Dickersin, K.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. SPIRIT 2013 Statement: Defining standard protocol items for clinical trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals: Updated December 2017. Available online: http://www.icmje.org/icmje-recommendations.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2018).
- Kung, J.; Chiappelli, F.; Cajulis, O.O.; Avezova, R.; Kossan, G.; Chew, L.; Maida, C.A. From systematic reviews to clinical recommendations for evidence-based health care: Validation of revised assessment of multiple systematic reviews (R-AMSTAR) for grading of clinical relevance. Open Dent. J. 2010, 4, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, D.; Buechter, R.B.; Li, L.; Prediger, B.; Eikermann, M. Systematic review found AMSTAR, but not R (revised)-AMSTAR, to have good measurement properties. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 68, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banzi, R.; Cinquini, M.; Gonzalez-Lorenzo, G.; Pecoraro, V.; Capobussi, M.; Minozzi, S. Quality assessment versus risk of bias in systematic reviews: AMSTAR and ROBIS had similar reliability but differed in their construct and applicable. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 99, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanemura, N.; Hamadate, N.; Urushibara, H. Evaluation of randomized controlled trials of foods with functional claims request: The learning outcomes from studies in Japan. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
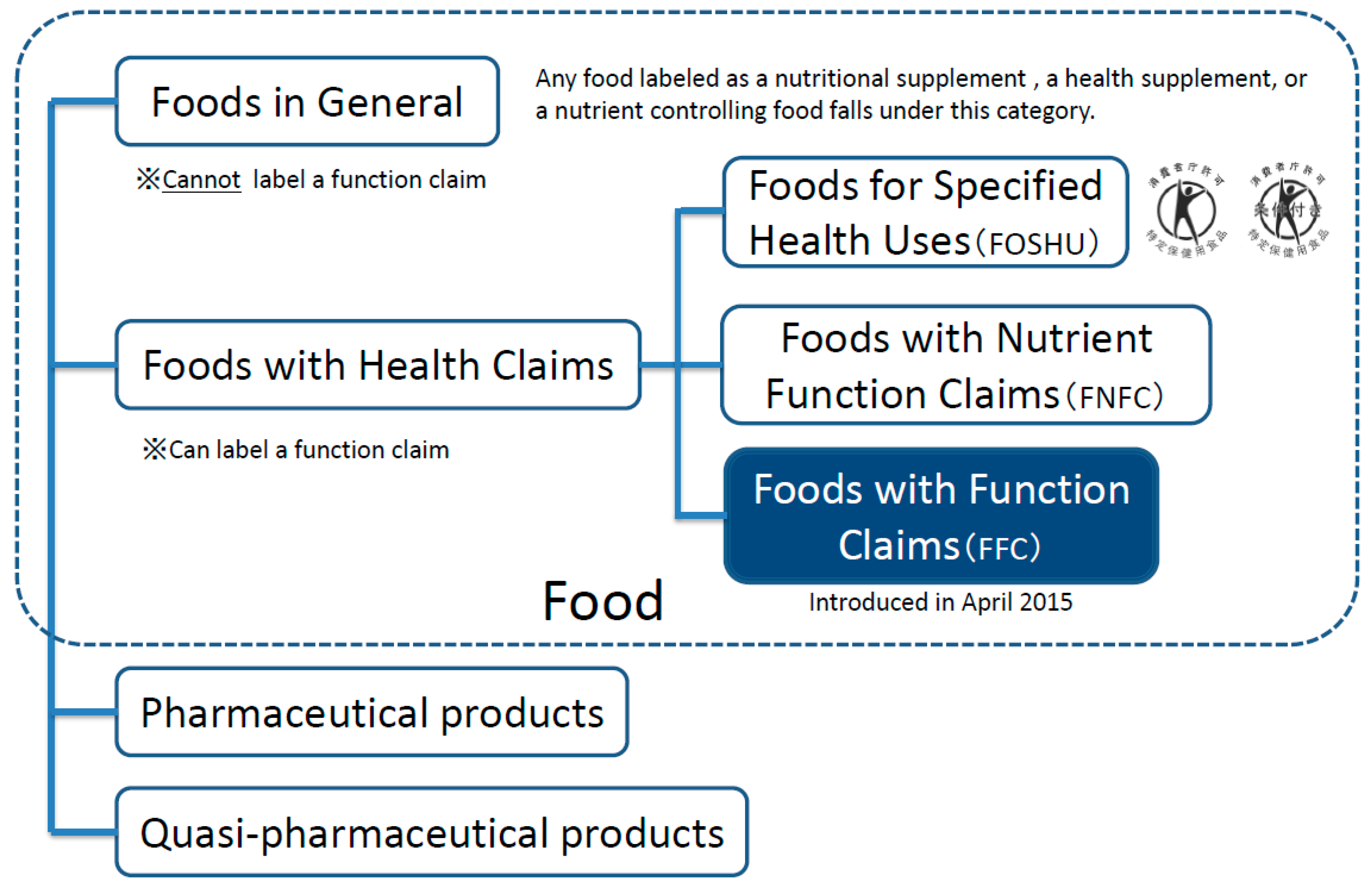
| 1 | Foods with Function Claims are for people not suffering from any disease (excluding minors, pregnant women (and those planning a pregnancy), or lactating women). |
| 2 | All food products including fresh produce are subject to this system.* |
| 3 | Prior to market entry (before at least 60 days), food business operators are required to submit information, such as on food safety and effectiveness and the system in place to collect information on adverse health effects, to the Secretary-General of Consumer Affairs Agency. |
| 4 | Unlike Foods for Specified Health Uses, the government does not evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the submitted product, i.e. notification system. |
| 5 | The submitted all information is disclosed on the website of the Consumer Affairs Agency.** |
| No. * | Product Name | Food Business Operator | Classification of Food 1 Supplement 2 Processed Food 3 Fresh Produce | Functional Substance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C48 | Ayumu Chikara (Fruit Yogurt) | Lion Corporation | 2 | HMB(β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate), Glucosamine hydrochloride |
| C49 | Kangengata CoQ10 150 | FINE JAPAN Co., Ltd. | 1 | Reduced coenzyme Q10 |
| C50 | DESK RAKU | Nihon kefir Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lutein |
| C51 | OFURO TIME cocktail taste salty dog taste | KING BREWING Co., Ltd. | 2 | Indigestible dextrin (dietary fiber) |
| C52 | OFURO TIME cocktail taste cassis orange taste | KING BREWING Co., Ltd. | 2 | Monoglucosyl hesperidin |
| C53 | Karada ni yasashii mizu (lemon taste) | Melodian Co., Ltd. | 2 | Hyaluronic acid Na |
| C54 | Karada ni yasashii mizu (peach taste) | Melodian Co., Ltd. | 2 | Indigestible dextrin (dietary fiber) |
| C55 | Karada ni yasashii mizu (grapefruit taste) | Melodian Co., Ltd. | 2 | Salacinol made from Salacia |
| C59 | The product has not been named in English yet. | Kyoto Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C60 | DHA no kiwami 1000 mg plus | Bizen Chemical Co., Ltd. | 1 | DHA, EPA |
| C61 | SUNKINOU Fish oil | Sunsho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 1 | DHA, EPA |
| C62 | Kotsukotsu Soybean Isoflavone | KYOWA YAKUHIN Co., Ltd. | 1 | Soy isoflavone |
| C63 | DHA no kiwami 1000 mg plus W | Bizen Chemical Co., Ltd. | 1 | DHA, EPA |
| C65 | EGAO GABA Stress Care | EGAO Co., Ltd. | 1 | GABA (γ-Aminobutyric acid) |
| C68 | SUNKINOU Bifidobacteria | Sunsho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 1 | Bifidobacterium longum BB536 |
| C69 | Yumemin | SIMANOYA Co., Ltd. | 1 | L-Theanine |
| C70 | meiji GABA COFFEE | Meiji Co., Ltd. | 2 | GABA |
| C71 | Glucosamine2000 KAIHO | NIHON_YAKUSHIDO Co., Ltd. | 1 | Glucosamine hydrochloride |
| C72 | Ginkgo Extract | Yuuki Medicine manufacture, Inc. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C73 | Soup with Brown rice Chinese soup | SHOKKYO Co., Ltd. | 2 | Indigestible dextrin (dietary fiber) |
| C75 | Ginkgo leaf | Morishita Jintan Co., Ltd. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C78 | Lutein | KYOWA HAKKO BIO Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lutein |
| C80 | Peptide Meinte | FUJI OIL Co., Ltd. | 2 | Seryl tyrosine made from soybean |
| C82 | The product has not been named in English yet. | Mikakuto Co., Ltd. | 2 | GABA |
| C84 | KAGOME tomato juice “kou-lycopene tomato shiyou, syokuen-mutenka” | KAGOME Co., Ltd. | 2 | Lycopene, GABA |
| C85 | Chanson Bilberry Plus | Chanson Cosmetics inc. | 1 | Bilberry extract anthocyanin |
| C86 | MAINICHI KORE 1HON EPA+DHA Fish Sausage 50 | Nippon Suisan Kaisha, Ltd. | 2 | DHA, EPA |
| C90 | Health Fit Cha | Ginza stefany Inc. | 2 | Indigestible dextrin (dietary fiber), Isoflavone made from kudzu (Tectorigenin) |
| C91 | SAGERU | Creare Co., Ltd. | 1 | GABA |
| C95 | The product has not been named in English yet. | Mikakuto Co., Ltd. | 2 | Acetic acid |
| C96 | KOTHARAEX TSUBU | Fuji Sangyo Co., Ltd. | 1 | Neokotalanol |
| C97 | Gussumin GABA no Chikara | Lion Corporation | 2 | GABA |
| C99 | Premier Rich Perfect Asta Hyaluronic acid Powder | Asahi Group Foods, Ltd. | 1 | Hyaluronic acid Na |
| C103 | SUNKINOU Ceramide | Sunsho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 1 | Glucosylceramide made from pineapple |
| C105 | EYE GUARD | NATURALLY HEALTH FOODS Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lutein, Zeaxanthin |
| C109 | Organic Enseki Kale | Enseki Aojiru Co., Ltd. | 2 | GABA (γ-Aminobutyric acid) |
| C110 | Pep-Gyu | YOSHINOYA Co., Ltd. | 2 | Valine-Valine-Tyrosine-Proline made from globin |
| C111 | Daizu peptide Genen shoyu (dashi-iri) | Kikkoman Food Products Company | 2 | Soybean peptide |
| C112 | Clear Lutein | Yazuya Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lutein |
| C114 | Latwell | ASAHI CALPIS WELLNESS Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lactotripeptides (Valine-Proline-Proline/Isoleucine-Proline-Proline) |
| C120 | Suupu you ito kanten | Ina Food Industry Co., Ltd. | 2 | Galactan made from agar (fiber) |
| C121 | Ginkgo biloba leaf Extract Tablet | AFC Co., Ltd. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C123 | Hiaruronsan C-jelly | Earth Corporation | 2 | Hyaluronic acid Na |
| C124 | Beau Clair | HEALTH RESEARCH FOUNDATION | 1 | Lutein, Zeaxanthin |
| C125 | Vegetable lactobacillus TAKUMINO-KIMCHI | Tokai Pickling Co., Ltd. | 2 | L. plantarum TK61406 |
| C126 | HAKKOU TSUBAKICHA containing indigestible dextrin | YAMACHIYA Co., Ltd. | 2 | Indigestible dextrin (dietary fiber) |
| C127 | Kiokuryokusengen | Aishitoto.Co., Ltd | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C130 | Routeri yogurt | OHAYO DAIRY PRODUCTS Co., Ltd. | 2 | L.reuteri DSM 17938 |
| C134 | Bifistock | EVERLIFE Co., Ltd. | 1 | Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 |
| C135 | ICHOBA | MORIKAWA KENKODO Co., Ltd. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C138 | arukumikata | Halmek Corporation | 1 | Undenatured type II collagen |
| C161 | HMB100 | Faveurmarche Co., Ltd. | 1 | 3-Hydroxy 3-MethylButyrate (HMB) |
| C162 | Everyday Dairy yogurt <Low-Fat> | Nippon Dairy Co-operated Co., Ltd. | 2 | Lactobacillus bifidus BB-12 (B. lactis) |
| C166 | Healthy Plus Sarasara Mugicha | ITO EN, LTD. | 2 | Monoglucosyl hesperidin |
| C176 | Suyasuya rerakkusui | Medione | 1 | Hyperoside made from Lafua, Isoqueritrin made from Lafuma |
| C179 | Hitomi Management | QOL Laboratories, Inc. | 1 | Bilberry extract anthocyanin |
| C180 | Lutein Hitomi no Kagayaki | KOHKAN Pharmaceutical Institute Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lutein |
| C181 | Ichimokuryozen W | SOCIA Co., Ltd. | 1 | Lutein |
| C182 | aojiruzanmai akatsuki | TV SHOPPING LABORATORY Co., Ltd. | 1 | L-Theanine |
| C183 | The product has not been named in English yet. | Mizkan Co., Ltd. | 2 | Acetic acid |
| C192 | Nyusankin shokora | LOTTE Co., Ltd. | 2 | Lactobacillus brevis NTT001 |
| C197 | Hiroshima Mikan | Hiroshima Pref. Fruit Growers Cooperative Association | 3 | β-Cryptoxanthins |
| C200 | Body Challenge | Ryusendo Co., Ltd. | 1 | Ellagic acid made from African mango eaves |
| C201 | MUSENMAI GABA KOSHIHIKARI | ZEN-NOH PEARL RICE Co., Ltd. | 2 | γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) |
| C205 | Suntory RURU-CHA | Suntory Beverage & Food Limited | 2 | Inulin |
| C207 | Ginkgo Biloba EX | Amway Japan G.K. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C208 | Mental Balance Chocolate GABA <Bitter>Mobile Type | EZAKI GLICO Co., Ltd. | 2 | γ-Aminobutyric acid |
| C209 | Melax eye | Yawata Corporation | 1 | Lutein |
| C213 | Aminomin N | Pharma Foods International Co., Ltd. | 1 | GABA |
| C216 | Kiokuru | Suppleplus Family Co., Ltd. | 1 | G biloba flavonoid glycoside, G biloba terpene latone |
| C218 | EasyTablet TERMINALIA | EC STUDIO Co., Ltd. | 1 | Gallic acid made from Terminal nari abe lyrica |
| C222 | Supplement Joiner | Shiseido Company, Limited | 1 | Salmon nasal proteoglyan |
| C228 | Moisture + Honey-bush Blend Tea | SHOWA PHARMACEUTICAL Co., Ltd. | 2 | N-Acetylglucosamine |
| C229 | megumi Gasseri SP Strain Yogurt Drink-type Berry Mix 100g | MEGMILK SNOW BRAND Co., Ltd. | 2 | Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055 |
| C230 | Megami | Sun Chlorella Corp. | 1 | Astaxanthin |
| C233 | Medikara supplement | Asahi Group Foods, Ltd. | 1 | Lutein |
| C242 | Kenkou Benifuuki Cha | Yawata Corporation | 2 | Methylated catechin (epigallocatechin-3-O-[3-O-methyl] gallate) |
| C249 | shinn oishiimushimame mushisaradamame | Maruyanagi Foods Inc. | 2 | Soy isoflavone |
| C251 | Glucosamine 2000 | DHC Corporation | 1 | Glucosamine hydrochloride |
| C264 | Kuensan Powder | FINE JAPAN Co., Ltd. | 2 | Citric acid |
| C271 | gaba megumi rice (Special Three percent milled-rice) | Tokyo foods create Co., Ltd. | 3 | GABA (γ-Aminobutyric acid) |
| C272 | Ketsuatsu ga takame no kata no hakkou kuro uuron cha | FINE JAPAN Co., Ltd. | 2 | GABA |
| C273 | CeramiDo? | Facelabo Co., Ltd. | 1 | Glucosylceramide made from rice |
| C275 | Q’SAI lilac-01 lactic acid bacterium | Q’SAI Co., Ltd. | 1 | Bacillus coagulans lilac-01 |
| C276 | Todoku Tsuyosa no Nyusankin 100(Foods with function claims) | ASAHI SOFT DRINKS Co., Ltd. | 2 | L. gasseri CP2305 |
| C282 | Algae DHA Capsule | Nikken Sohonsha Corporation | 1 | DHA made from aurantiochytrium |
| C289 | Omega A.D.E. | Suntory Wellness Limited | 1 | DHA, EPA, ARA |
| C295 | Wasurerumonka | imunos Co., Ltd. | 1 | Phosphatidylserine made from soybean |
| C303 | The product has not been named in English yet. | Takayuki Nishie | 2 | Acetic acid |
| C318 | Mattanthermo | DHC Corporation | 1 | Monoglucosyl hesperidin |
| C321 | Shinjyumai | Kometo Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd. | 2 | GABA |
| C322 | soy isoflavone kodaizumoyashi | Meisui Bijin Factory Co., Ltd. | 3 | Soy isoflavone |
| C331 | The product has not been named in English yet. | Fuji Chemical Industries Co., Ltd. | 2 | Astaxanthin |
| C332 | webber naturals Lutein Plus | factorsgroup Japan LLC | 1 | Lutein |
| C334 | HESPERIDIN & COLLAGEN | EZAKI GLICO Co., Ltd. | 2 | Monoglucosyl hesperidin, Low molecular collagen peptide made from fish |
| C339 | GOMATOUNYUJITATE MINNANOMIKATA DHA | Nippon Suisan Kaisha, Ltd. | 2 | EPA, DHA |
| No. | Items | Before-Verification | After-Verification | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 49 | N = 104 | |||||
| #1 | Was an ‘a priori’ design provided? | 2 | 4% | 89 | 86% | <0.001 |
| #2 | Was there duplicate study selection and data extraction? | 32 | 65% | 43 | 41% | 0.006 |
| #3a | Was a comprehensive literature search performed? | 3.8 ± 1.8 * | (2–15) | 3.8 ± 1.8 * | (2–17) | 1.000 |
| #3b | Did the SR use the MESH terms and related search function to detect comprehensively? | 26 | 53% | 49 | 47% | 0.492 |
| #4 | Was the status of publication used as an inclusion criterion? | 12 | 24% | 3 | 3% | <0.001 |
| #5 | A list of included and excluded studies should be provided. | 49 | 100% | 102 | 98% | 0.329 |
| #6 | Were the characteristics of the included studies provided? | 41 | 84% | 91 | 88% | 0.521 |
| #7 | Was the scientific quality of the included studies assessed and documented? | 36 | 73% | 61 | 59% | 0.076 |
| #8 | Was the scientific quality of the included studies used appropriately in formulating conclusions? | 13 | 27% | 27 | 26% | 0.940 |
| #9 | Were the methods used to combine the findings of studies appropriate? | 5/9** | 56% | 12/13** | 92% | 0.116 |
| #10 | Was the likelihood of publication bias assessed? | 6 | 12% | 13 | 13% | 0.964 |
| #11 | Was the conflict of interest stated? | 38 | 78% | 26 | 25% | <0.001 |
| Evaluation score | pts./11 | 6.2 ± 1.8 | (2–11) | 5.0 ± 1.9 | (1–11) | <0.001 |
| For food industry | |
| #1 | The applicants should conduct research based on AMSTAR 2 checklist. |
| #2 | The applicants should conduct research based on PRISMA checklist and PRISMA-NA (for meta-analysis). |
| #3 | The applicants should examine its quality when using the SR of another company that had already been accepted by the CAA. |
| #4 | The applicants should consult with academia researchers for unclear points in methodology. |
| For academia | |
| #5 | Academic researchers should provide support for food companies and others to implement the SR properly. |
| □ | Study plan (study selection and data extraction, search strategy, and evaluation method of bias risk) |
| □ | Implementation (assessment of publication bias, and formulating conclusion based on methodological rigor quality) |
| □ | Description (conflict of interest) |
| For the Consumer Affairs Agency in Japan | |
| #6 | The authorities should evaluate not only the formal confirmation* in the document but also the quality (certain level or higher) of the SR. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamioka, H.; Tsutani, K.; Origasa, H.; Yoshizaki, T.; Kitayuguchi, J.; Shimada, M.; Wada, Y.; Takano-Ohmuro, H. Quality of Systematic Reviews of the Foods with Function Claims in Japan: Comparative Before- and After-Evaluation of Verification Reports by the Consumer Affairs Agency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071583
Kamioka H, Tsutani K, Origasa H, Yoshizaki T, Kitayuguchi J, Shimada M, Wada Y, Takano-Ohmuro H. Quality of Systematic Reviews of the Foods with Function Claims in Japan: Comparative Before- and After-Evaluation of Verification Reports by the Consumer Affairs Agency. Nutrients. 2019; 11(7):1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071583
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamioka, Hiroharu, Kiichiro Tsutani, Hideki Origasa, Takahiro Yoshizaki, Jun Kitayuguchi, Mikiko Shimada, Yasuyo Wada, and Hiromi Takano-Ohmuro. 2019. "Quality of Systematic Reviews of the Foods with Function Claims in Japan: Comparative Before- and After-Evaluation of Verification Reports by the Consumer Affairs Agency" Nutrients 11, no. 7: 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071583
APA StyleKamioka, H., Tsutani, K., Origasa, H., Yoshizaki, T., Kitayuguchi, J., Shimada, M., Wada, Y., & Takano-Ohmuro, H. (2019). Quality of Systematic Reviews of the Foods with Function Claims in Japan: Comparative Before- and After-Evaluation of Verification Reports by the Consumer Affairs Agency. Nutrients, 11(7), 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071583




